blood vessels
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the three main types of blood vessels and their functions?
Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart
Capillaries: Exchange nutrients and gases with tissue cells
Veins: Carry blood toward the heart
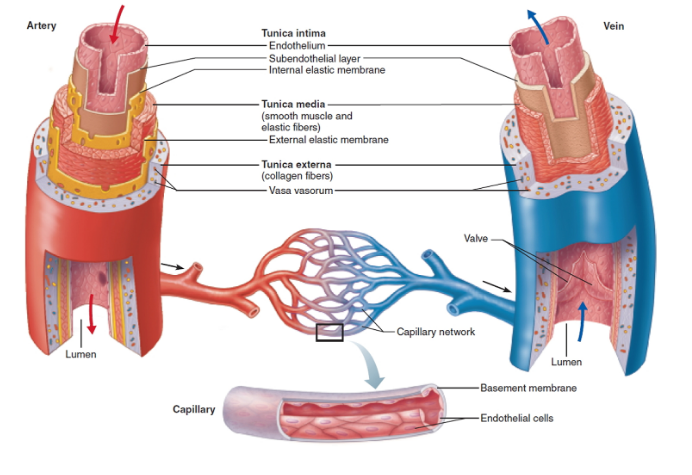
What are the structural layers of blood vessels?
All vessels have a lumen (central blood-filled space)
All except capillaries have 3 layers:
Tunica intima
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Capillaries consist of only endothelium (simple squamous) and a sparse basal lamina
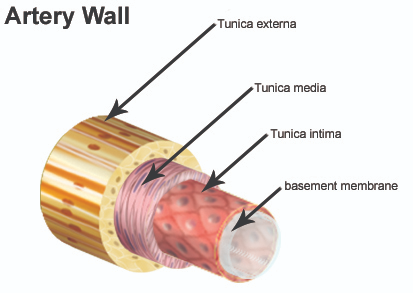
Tunica intima
Innermost layer that is in “intimate” contact with blood
Made of endothelium (simple squamous epithelium)
Has a subendothelial layer (CT basement membrane) in vessels >1 mm
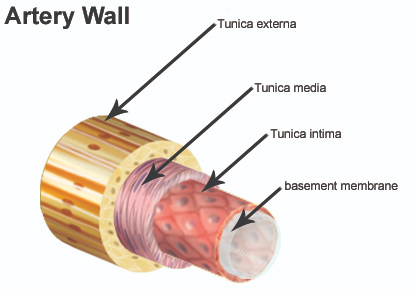
Tunica Media
Middle layer made of smooth muscle and elastin
Controlled by sympathetic vasomotor nerves
Regulates:
Vasoconstriction (↓ lumen diameter)
Vasodilation (↑ lumen diameter)
Thickest layer, helps maintain blood flow and pressure
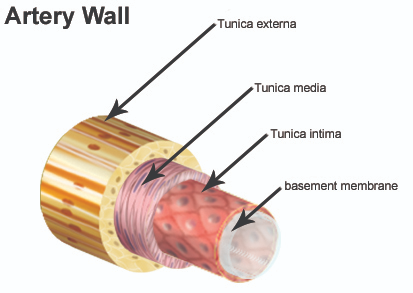
Tunica Externa
Outermost layer of a blood vessel wall
Made of loose collagen fibers for protection and anchoring
Contains nerve fibers and lymphatic vessels
Large veins may have elastic fibers in this layer
vasa vasorum—tiny vessels that nourish the outer wall of large blood vessels
When vascular smooth muscle contracts, what happens to the diameter of the blood vessel? What is this called?
The diameter decreases, and this is called vasoconstriction.
Arteries
Carry blood away from heart
Divided into three groups based on size and function
• Elastic arteries
• Muscular arteries
• Arterioles

Elastic Arteries
Large arteries (like the aorta) with thick walls and elastin; they act as pressure reservoirs to maintain blood flow between heartbeats.

Muscular Arteries
Deliver blood to organs
Most common type of artery
Thick tunica media with lots of smooth muscle
Less elastic tissue, but active in vasoconstriction

Arterioles
Smallest arteries
Larger ones have all 3 tunics; smaller ones mostly smooth muscle and endothelium
Regulate blood flow into capillary beds via vasodilation and vasoconstriction
Lead directly to capillary beds

Capillaries
Function: Exchange gases, nutrients, wastes, and hormones with interstitial fluid
Structure: Endothelial cells joined by tight junctions with intercellular clefts for fluid/solute passage
Types: Continuous, fenestrated, sinusoidal
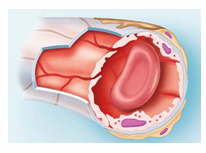
Continuous Capillaries
skin, muscles, lungs, and CNS
In the brain, they form the blood-brain barrier with tight junctions and no intercellular clefts
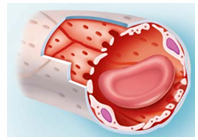
Fenestrated Capillaries
Found in kidneys, intestines, and endocrine glands
Have fenestrations (pores) in endothelial cells
Allow increased permeability
Pores often covered by a thin glycoprotein diaphragm
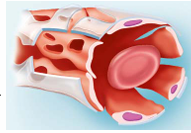
Sinusoidal Capillaries
large lumens, large clefts
Found in liver, bone marrow, spleen, and adrenal medulla
slow blood flow
Contain macrophages
Name the type of artery that matches each description
A. Major role in dampening the pulsatile pressure of the
heart contractions
B. Vasodilation or constriction determines blood flow to
individual capillary beds
C. Have the thickest tunica media relative to their lumen size
A → Elastic artery
B → Arteriole
C → Muscular artery
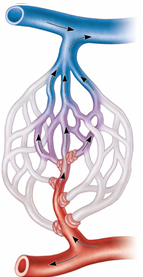
Capillary Beds
Vascular shunt – a direct path from arteriole to venule (metarteriole → thoroughfare channel), bypassing true capillaries
Precapillary sphincter – smooth muscle cuff that controls blood flow into true capillaries; regulated by local chemicals, not nerves
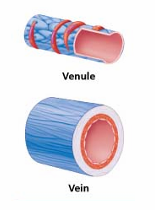
Types of veins
Carry blood toward the heart
Formation begins when capillary beds unite downstream
• Two groups
Venules
Veins
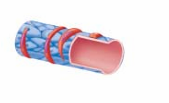
Venules
Formed when capillaries unite
Made of endothelium and a few pericytes
Very porous—allow fluid and WBC movement
Larger venules may have 1–2 layers of smooth muscle
a very small vein, especially one collecting blood from the capillaries.
Veins
Formed when venules merge
Have all three tunics, but with thinner walls and larger lumens than arteries
Thin tunica media, thick tunica externa
Contain collagen fibers and elastic networks
Act as blood reservoirs due to large lumen and thin walls
Venous valves
•Prevent backflow of blood
•Most abundant in veins of limbs
Venous sinuses
•Flattened veins with extremely thin walls
•Composed only of endothelium
•Examples: coronary sinus of the heart and dural sinuses of the brain
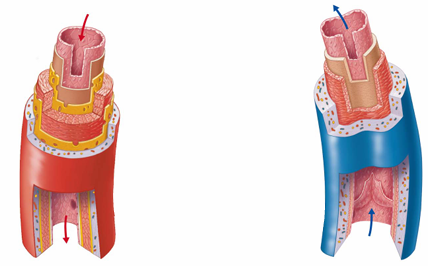
What are the key differences between arteries and veins?
Arteries:
Carry blood away from the heart
Thick walls, especially tunica media
Smaller lumen
High pressure
No valves (except in the heart)
Veins:
Carry blood toward the heart
Thinner walls, especially tunica media
Larger lumen
Low pressure
Have valves to prevent backflow
What is the function of venous valves? What layer of the vessel are these valves composed of?
Function: Prevent the backflow of blood, especially in limbs
Layer: Made from folds of the tunica intima