W2 torts - Trespass to the person
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Intentional Torts
Civil wrongs that protect a person’s body, land, and property from unwanted interference.
they are committed with intention.
Types of Intentional Torts
Trespass to the person, trespass to land, trespass to goods (including detinue and conversion).
Trespass vs Negligence
o Trespass focuses on direct interference, while negligence requires proving duty, breach, and causation.
· Trespass Actions
o Historically developed to maintain the King's peace and discourage unlawful retaliation.
· Actionable Per Se = ‘as is’
o Trespass claims do not require proof of harm or damage.
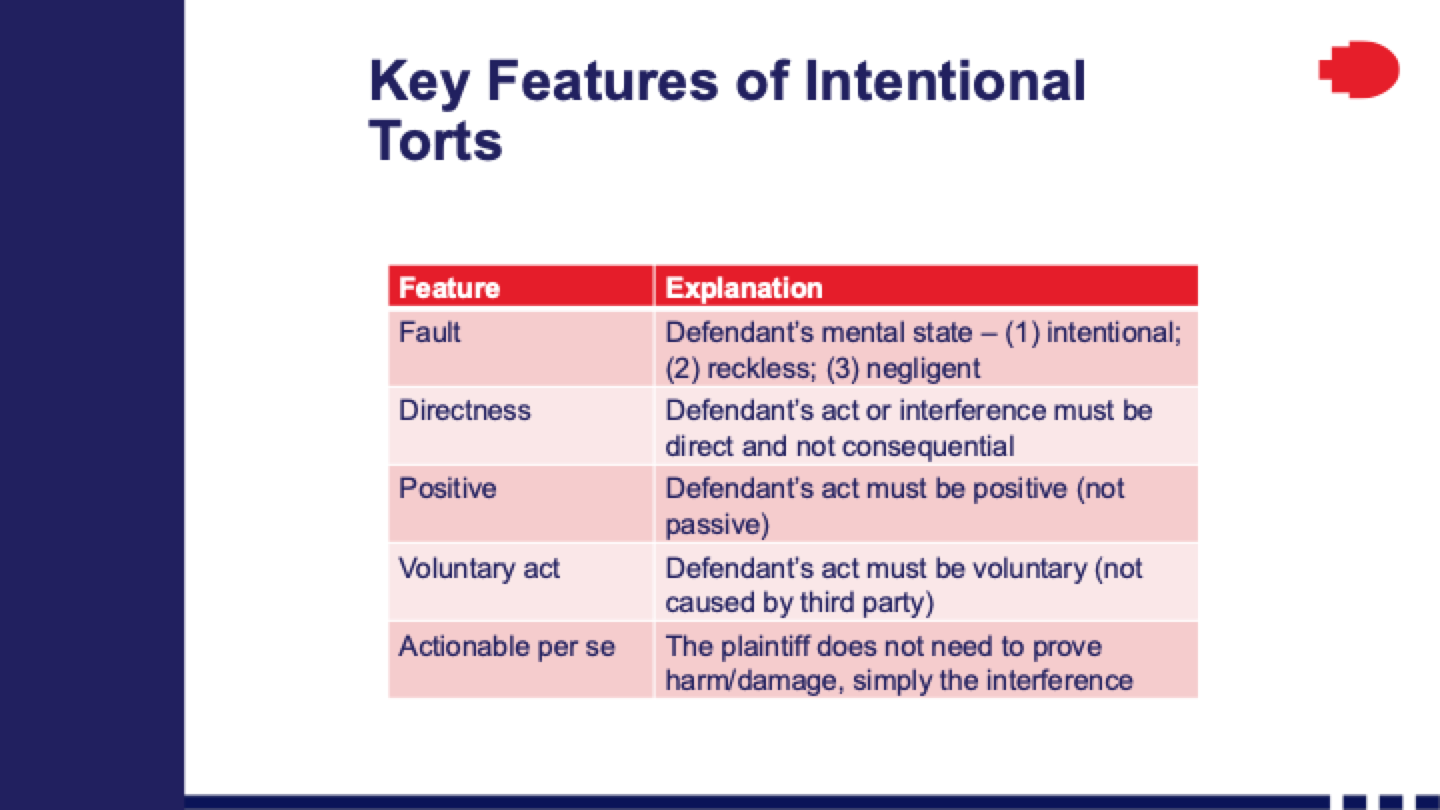
· Elements of Trespass to the Person + Three Torts Under Trespass to the Person
o Direct interference, fault (intentional, reckless, or negligent), and no lawful justification.
o Battery, Assault, and False Imprisonment.
Battery, assault, false imprisonment
Battery
o Unlawful physical contact without consent, either intentional or reckless.
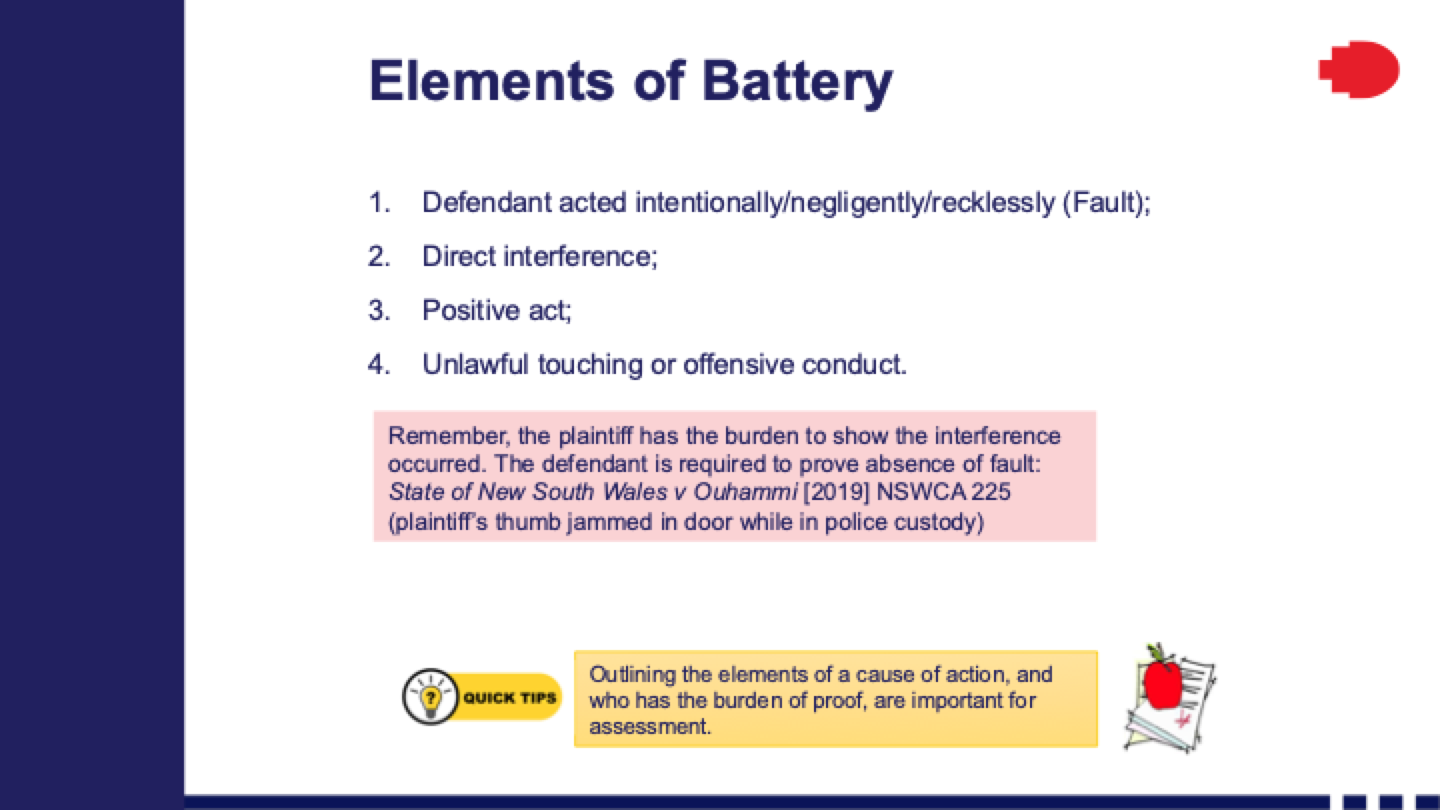
· Elements of Battery
o Intentional act, direct contact, positive act, and unlawful touching.
· Examples of Battery
· Spitting on someone, pulling a chair out from under someone, or unwanted medical procedures.
Assault
· An act causing a person to reasonably apprehend imminent harmful or offensive contact.
· Elements of Assault
· Threat, reasonable apprehension, immediacy, and intention or recklessness.
False Imprisonment
· The total restraint of a person’s liberty without lawful justification.
· Elements of False Imprisonment
· Intentional act, total deprivation of liberty, and no reasonable means of escape.
· Burden of Proof in Trespass Cases
· Plaintiff must prove interference, defendant must prove lack of fault (except for highway accidents).
· Williams v Milotin (1957)
Case that confirmed plaintiffs can sue in either trespass or negligence for direct, unintentional harm




· Venning v Chin (1974)
· Established that plaintiffs in highway cases must prove all elements of trespass, including fault.


significance of Williams a d venting cases

x5 key features of intentional torts (WILL be using this ALOT!!)
tort of battery


element;


element;

element 3';

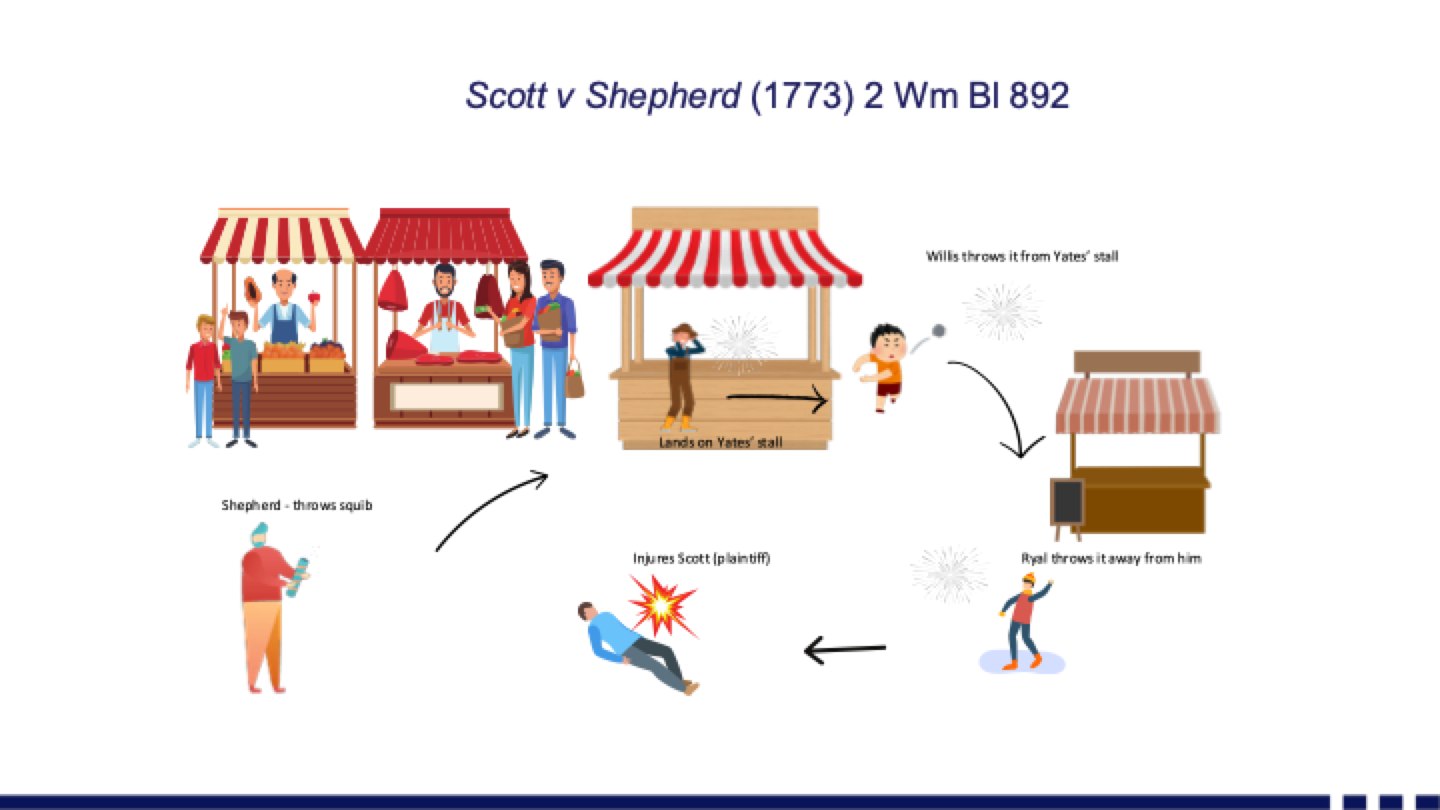
· Scott v Shepherd (1773)


ASSAULT






FALSE IMPRISONMENT



false imprusonment cases



KEY CASE; Myer Stores & Ors v Soo (1991) 2 VR 597



· False Imprisonment Without Physical Barriers
= Situation of you don’t have to be physically locked up in a room or tied to a chair to be falsely imprisonment.
You could be falsely imprisoned because you feel that you have no option but to remain in a particular situation.
Due to authority etc.


