The Pharynx and Swallowing
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the muscles of the pharynx and the process of swallowing.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Pharynx
Muscular tube attached to the base of the skull (temporal, sphenoid, and occipital bones) made mostly of skeletal muscle.
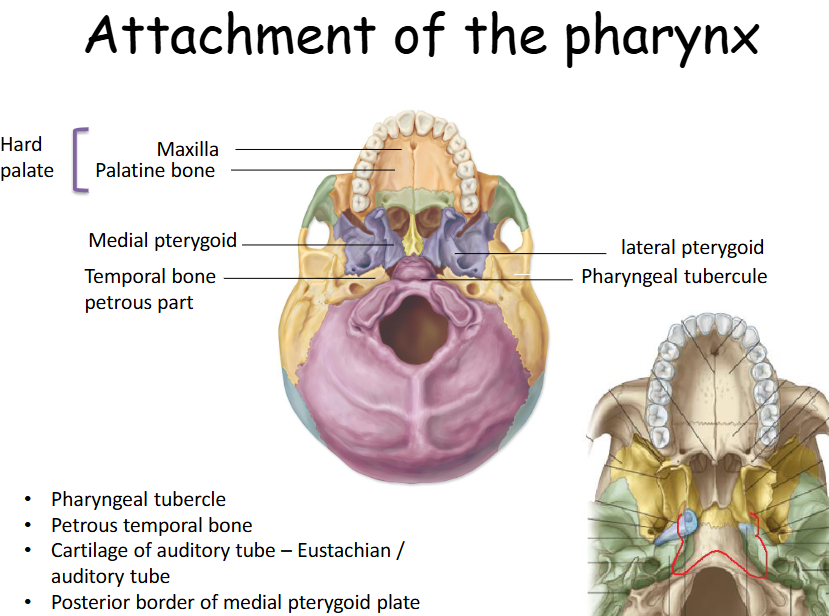
Attachments of the Pharynx
Pterygomandibular raphe, Lesser and greater horns of the hyoid, Posterior border of thyroid cartilage, Side of cricoid cartilage, Medial plate of pterygoid, Pterygoid hamulae, Stylohyoid ligament, Oblique line, Cricothyroid muscle, Cricoid cartilage
Two Main Muscle Groups of the Pharynx
Constrictor and Longitudinal muscles.
Innervation of the Pharynx
Cranial nerves IX and X.
Action of the Pharynx Muscles
Narrows the pharyngeal cavity
Function of Constrictor Muscles
Moves a bolus of food from the pharynx into the esophagus.
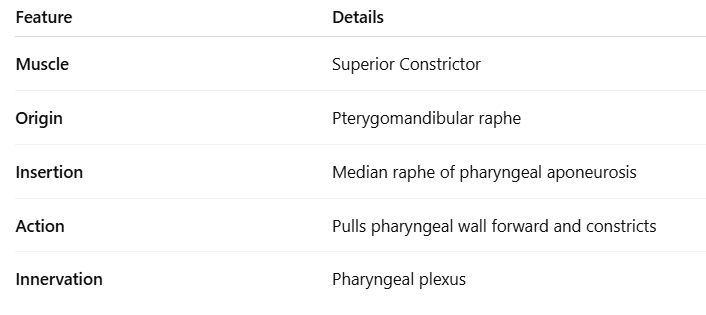
Origin of Superior Constrictor
Pterygomandibular raphe.
Insertion of Superior Constrictor
Median Raphe of pharyngeal apornerosis.
Action of Superior Constrictor
Pulls pharyngeal wall forward and constricts
Origin of Middle Constrictor
Horns of the hyoid and stylohyoid ligament.
Insertion of Middle Constrictor
Median pharyngeal raphe.
Action of Middle Constrictor
Narrows diameter of pharynx.
Origin of Inferior Constrictor
Thyroid and Cricoid cartilage.
Insertion of Inferior Constrictor
Pharyngeal raphe and Orifice of the oesophagus.
Action of Inferior Constrictor
Constricts superior orifice of oesophagus.
Parts of Inferior Constrictor
Cricopharyngeus and Thyropharyngeus.
Longitudinal Muscles of the Pharynx
Palatopharyngeus, Salpingopharyngeus, Stylopharyngeous
Function of Longitudinal Muscles
Elevate the pharyngeal wall up and over a bolus of food as it moves into the oesophagus.
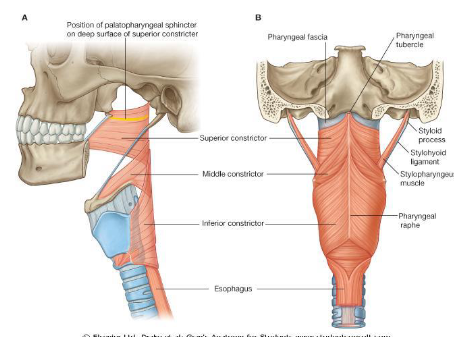
Structures passing through gap superior to superior constrictor muscle
Levator veli palatini, pharynotympani tube and ascending palatine artery
Structures passing through gap inferior to superior constrictor and above the middle constrictor
Hypoglossal nerve
Structures passing through gap superior to the inferior constrictor and inferior to the middle constrictor
Internal laryngeal vessels
Structures passing through gap below the inferior constrictor muscle
Recurrent laryngeal nerve and vessels
Blood Supply to Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
External Carotid Arteries and branches of the thyrocervical trunk.
Blood vessels for the Thyroid Gland
Superior thyroid artery and Inferior thyroid vessel
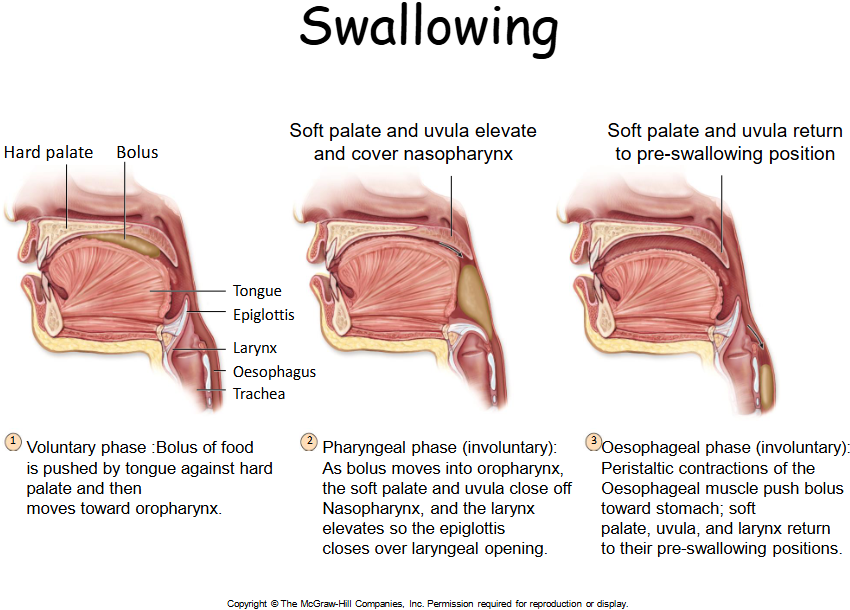
Three Stages of Swallowing
Buccal phase, Pharyngeal stage, Esophageal stage.
Dysphagia
Difficulty in swallowing
What bones does the pharynx attach too?
The pharynx is a muscular tube which takes its attachments from the base of the skull, namely the:
• temporal bones
• sphenoid and
• occipital bone
What are the 2 main muscle groups that the pharynx splits into?
• Constrictor muscles
• Longitudinal muscles
What are the constrictor muscles?
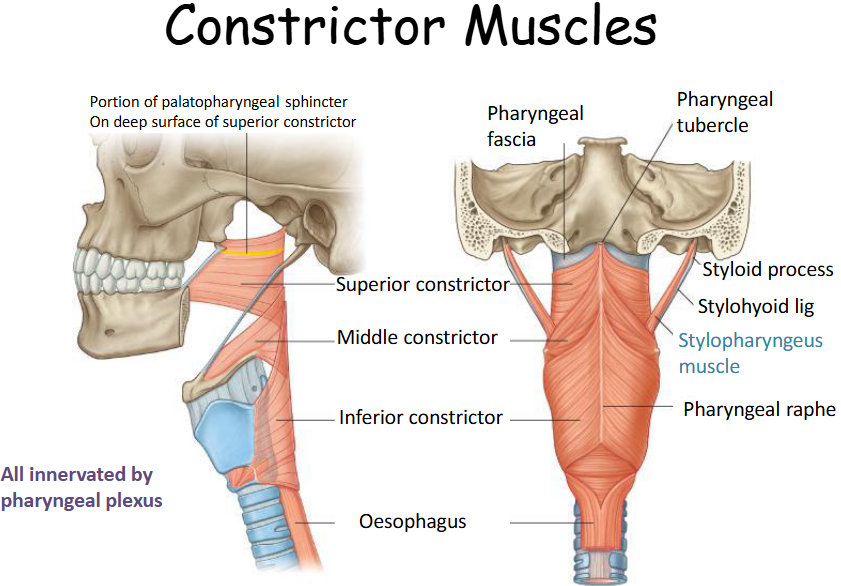
What are the inferior constrictor muscles?
What are the superior constrictor muscles?
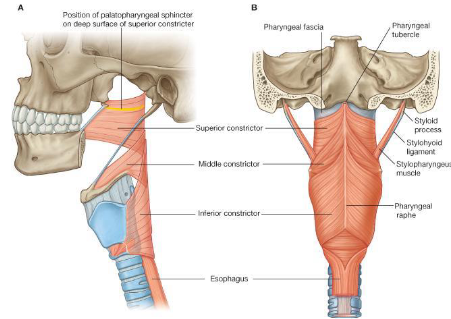
What are the middle constrictor muscles?
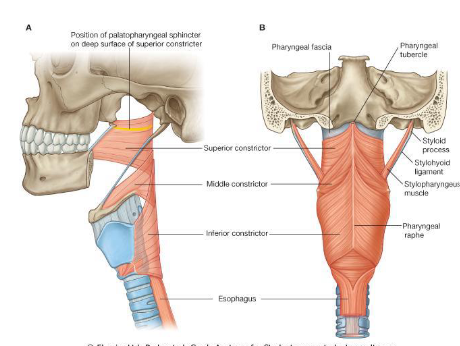
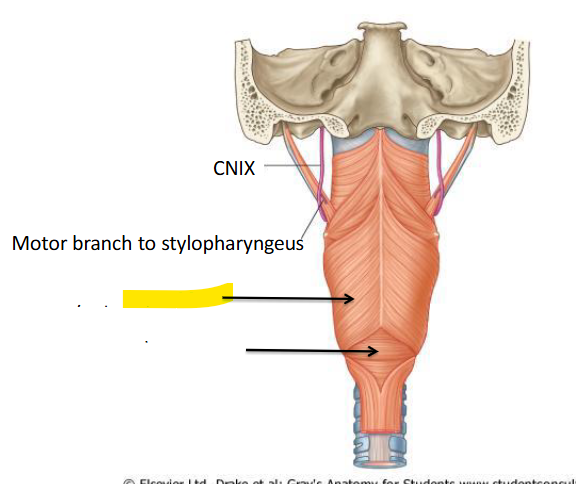
What is this?
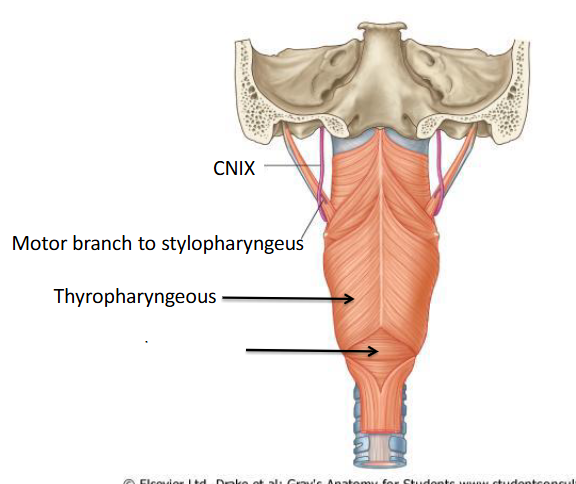
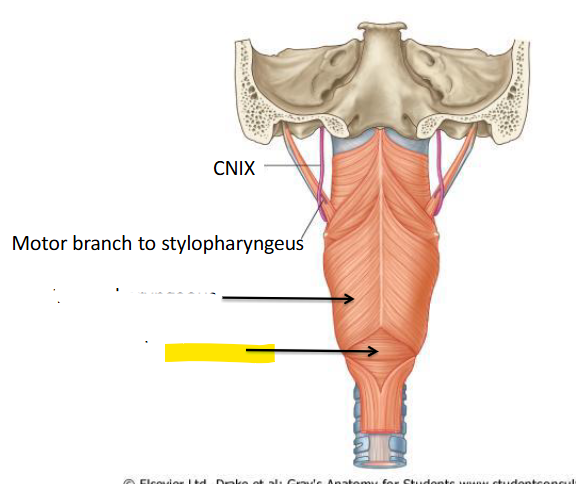
What is this?
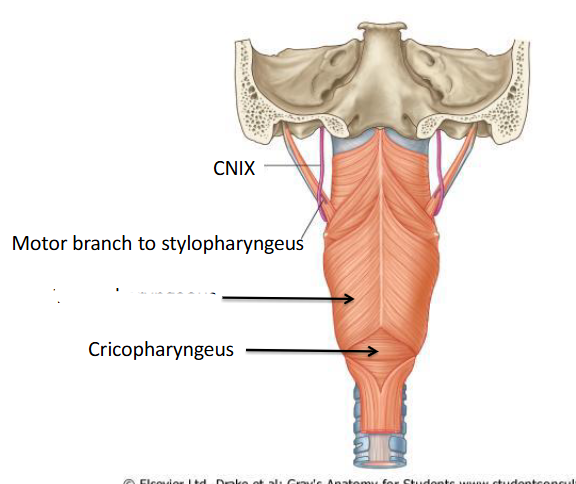
What are the Constrictor muscles and Longitudinal muscles innervated by?
They are supplied by the pharyngeal plexus which consists of cranial nerves IX and X (same as the muscles of the soft palate)
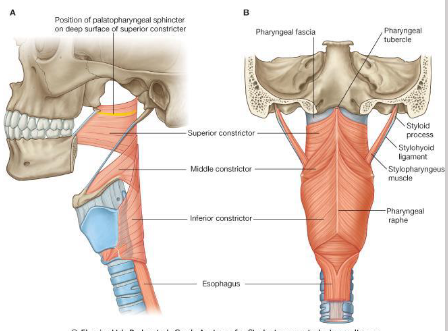
What is the origin, insertion, innervation and action of the superior constrictor?
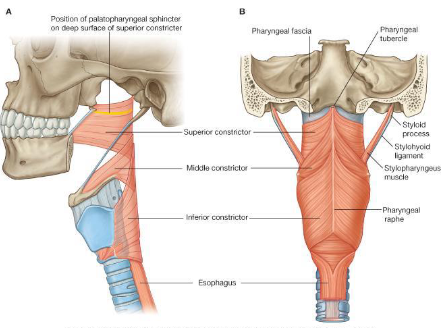
What is the origin, insertion, innervation and action of the middle constrictor?
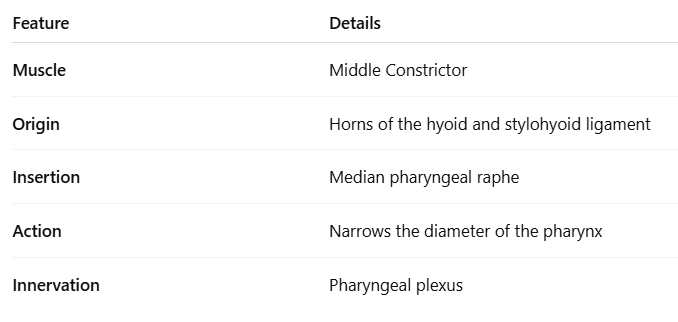
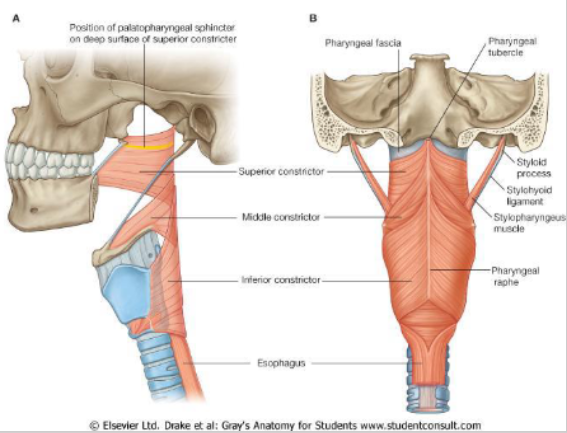
What is the origin, insertion, innervation and action of the inferior constrictor?
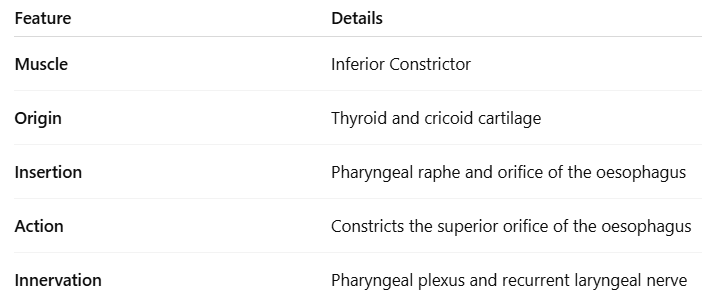
What are the 2 parts of the inferior constrictor
• Cricopharyngeus
• Thyropharyngeus
Where does the cricopharyngeus attach?
• Cricopharyngeus which attaches to the cricoid cartilage (transverse fibres). Comes from the cricoid cartilage to the pharynx.
Where does the thyropharyngeus attach onto?
• Thyropharyngeus which attached to the thyroid cartilage (superior). Comes from the thyroid cartilage to the pharynx.
What are the 3 longitundinal muscles?
Palatopharyngeus
Salpingopharyngeus
Stylopharyngeous
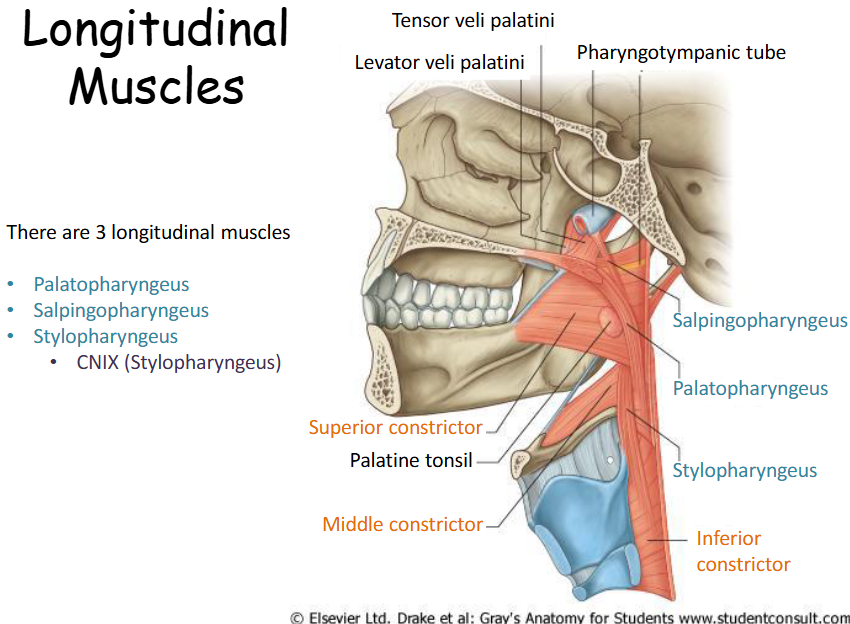
Where is the palatopharyngeus?
Palatopharyngeus – from the palatine aproneurosis and runs posteriorly and inferiorly and blends with the deep pharyngeal wall (also a muscle of the soft palate).
Where is the salpingopharyngeus?
Salpingopharyngeus – from the cartilaginous part of the pharyngotympanic tube (salpinx = tube) and blends with the deep pharyngeal wall (small muscle). During swallowing the eustachian tube opens to equilibrate
Where is the stylopharyngeus
Stylopharyngeous – from the styloid process of the temporal bone, descends between the superior and middle constrictor muscles where is fans out and blends with the deep pharyngeal wall.
Where do the longitudinal muscles attach and what do they do?
All three descend and attach into the pharyngeal wall.
The longitudinal muscles elevate the pharyngeal wall up and over a bolus of food as it moves into the oesophagus
What is the pharyngeal wall?
The pharyngeal wall is a muscular structure that forms the lateral and posterior walls of the pharynx, playing a crucial role in swallowing and directing food towards the esophagus.
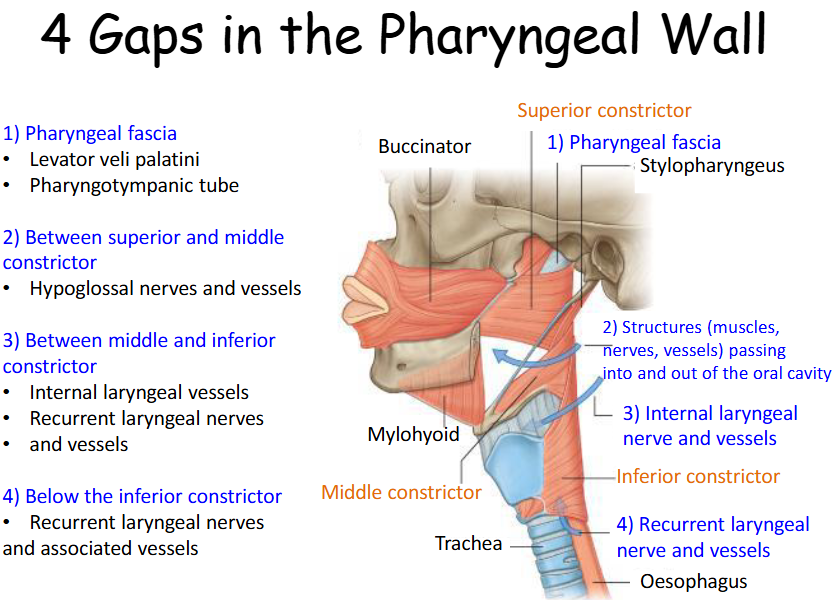
Look at this diagram of the 4 gaps in the pharyngeal wall
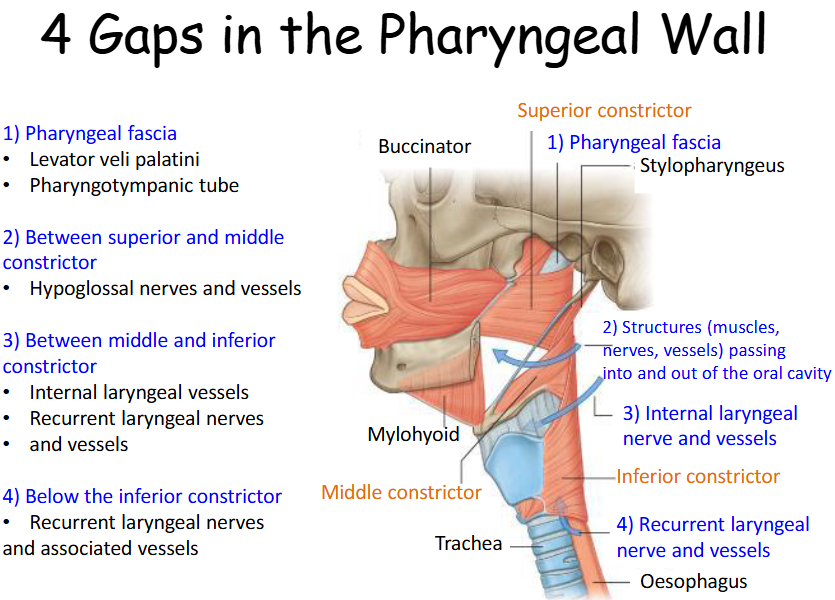
What are the 4 gaps in the pharyngeal wall?
1) Pharyngeal fascia
2) Between superior and middle constrictor
3) Between middle and inferior constrictor
4) Below the inferior constrictor
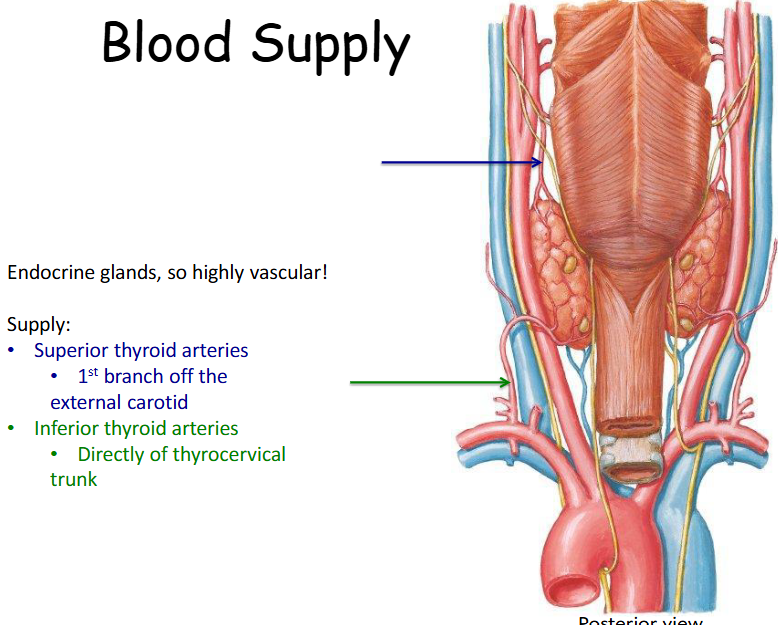
Where does majority of the blood supply come from for the thyroid and parathyroid gland
The majority of this blood supply comes form the External Carotid Arteries and branches of the thyrocervical trunk (branches of the subclavian artery)
Look at this diagram of the blood supply
What are the 3 stages of swallowing?
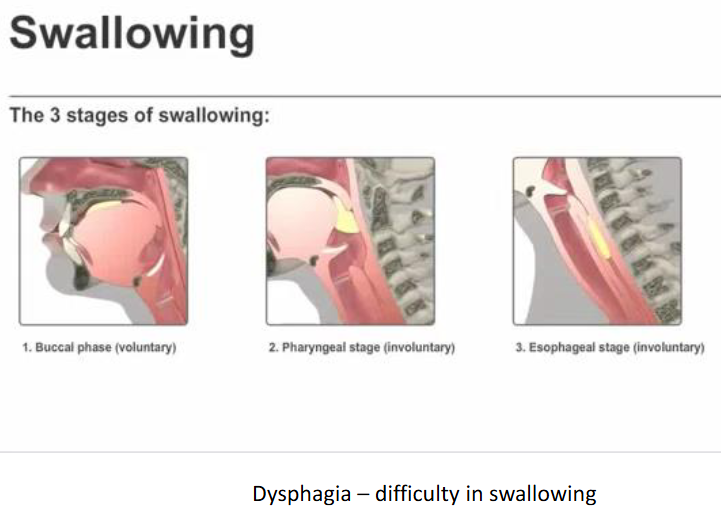
Describe the process of swallowing
Swallowing is a complex process that involves three stages: the oral stage, where food is voluntarily pushed to the back of the mouth; the pharyngeal stage, which is involuntary and moves food down through the pharynx; and the esophageal stage, where food travels through the esophagus to the stomach.