(CIE A2 Compsci) Processors
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
the purpose of the control unit
to ensure the correct handling of machine instructions received by the CPU
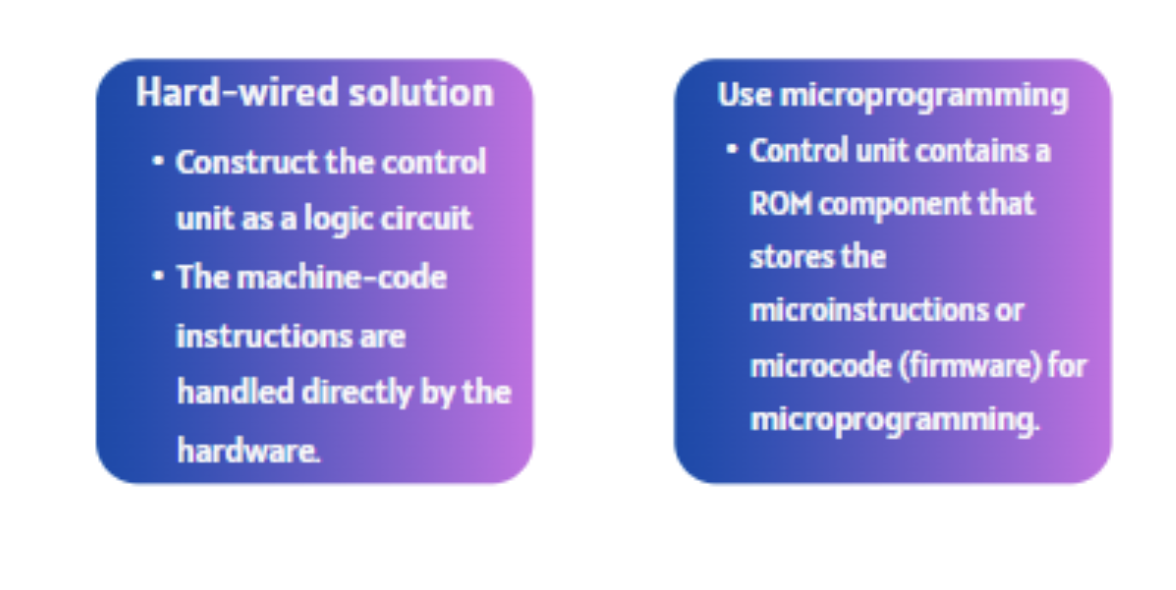
the two ways of constructing a control unit
by either hard-wiring it into a logic circuit (done for RISC) or microprogramming a ROM component storing the firmware into it (done for CISC)
instruction set architecture (ISA)
the processor-unique paradigm describing the instruction sets + instruction formats + addressing modes + accessible registers governing software-hardware interactions in a computer system
CISC (complex instruction set computing)
microprogrammed using more internal instruction formats than RISC to reduce the number of lines of code required through more complex assembly code instructions that need to be processor-converted into sub-instructions for carrying out the required ops
x86 processors
a processor type that uses CISC
RISC (regular instruction set computing)
hardwired using fewer internal instruction formats than CISC which can lead to better processor performance through less complex single-cycle instructions resulting from the pipelining of assembly code instructions
ARM processors
a processor type that uses RISC