Market Power Overview
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Market Structures, Profit Maximisation, Perfect Competition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are market structures?
The characteristics of a market affecting firm behaviour and outcomes
What are features of market structures?
Number of buyers/sellers
Size of firms
Type of product → homogenous/differentiated
Barriers to entry and exit
Degree of competition
What are the types of market structures?
Perfect competition
Imperfect competition
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly
What is perfect competition?
Many firms
No market power
Homogenous goods
What is monopolistic competition?
Many firms
Slight market power due to product differentiation
What is a oligopoly?
Few large firms dominate
High interdependence
What is a monopoly?
Single firm dominates
Significant market power
What is market power?
A firm’s ability to influence price and output
How does market power lead to market failure?
Price manipulation
Output restriction
Lack of allocative/productive efficiency
How is market power measured by?
Market share
Concentration ratios
Barriers to entry
High market power → less competition, potential inefficiency
Lower market power → more competition, efficient outcomes
What are the key characteristics of perfect competition?
Many buyers and sellers → price takers
No barriers to entry/exit → easy market access
Perfect knowledge → full information on prices
Homogenous products → no brant loyalty
Firms cannot influence price → P = AR = MR = Demand
Allocative efficiency
Productive efficiency
Dynamic efficiency is unlikely due to lack of abnormal profits
What is allocative efficency?
AR = MC
What is productive efficiency?
MC = AC
What are characteristics of an imperfect competition diagram?
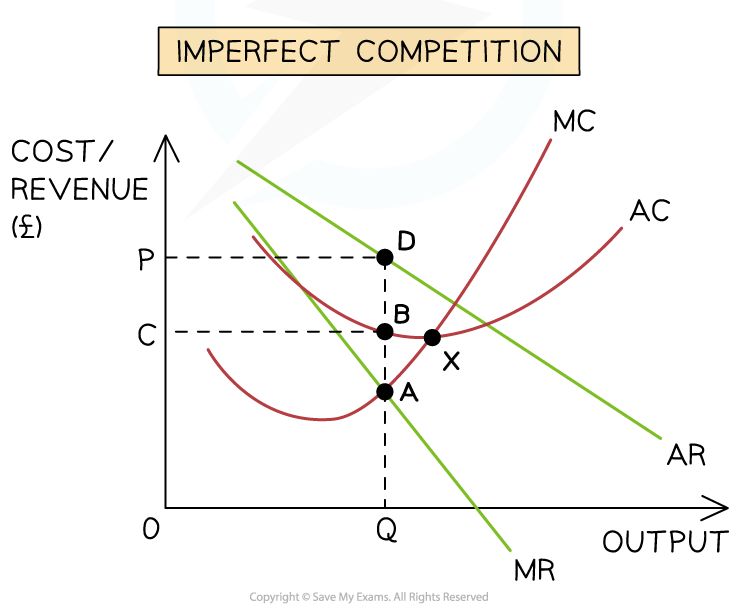
Firm is a price maker → downward sloping demand and revenue curves
Produces at MC = MR (profit maximisation)
Not productively efficient: AC > MC
Not allocatively efficient: AR > MC
Likely dynamically efficient due to reinvested profits and innovation
What are explicit costs?
Direct payments (eg. wages, raw materials)
What are implicit costs?
Opportunity costs (eg. forgone interest from investment)
Entrepreneurs consider implicit costs when deciding whether to reallocate resources
What are total costs (TC)?
Explicit + implicit costs
What is profit?
Total revenue (TR) - Total costs (TC)
What is normal profit?
TR = TC → breakeven
What is abnormal profits?
TR > TC
What is losses?
TR < TC
What is the profit maximisation rule?
Firms aim to maximise profit to benefit stakeholders via dividends or rising share prices
What are dividends?
Distribution of earnings from a company to its stakeholders
When is profit maximised?
MC = MR → no extra profit from producing another unit
MC < MR → produce more, profit increases
When is profit not maximised?
MC > MR → firms stop producing, loss on extra units
Why may firms not always know where MC = MR?
Frequent cost changes (short term)
Consumer disruption from regular price shifts (short term)
Regulatory constraints (long term)
What is the formula for average cost (AC)?
Total costs / output
What is the formula for average revenue?
Total revenue / output
How do you calculate per unit profit?
Average revenue - average costs
How does profit maximisation work in perfect competition?
Firms produce where MC = MR
Short run, firms can make
Abnormal profit: AR > AC
Losses: AR < AC
Long run, firms always make normal profits due to:
No barriers to entry/exit
New firms enter if profits exist → shifts supply right → price falls
Firms exit if losses occur → shifts supply left → price rises
What are some diagram notes for perfect competition?
Short run abnormal profit: AR > AC at MC = MR
Short run losses: AR < AC at MC = MR
Long run equilibrium: AR = AC - P, normal profit only
Supply shifts adjust market price until normal profit is restored
What is the link between efficiency in perfect competition?
Allocative efficiency: P = AR = MC → resources maximally allocated
Productive efficiency: MC = AC → lowest average cost, no resource waste
Long run: perfect competition achieves both efficiencies
What is the profit maximisation point?
MC = MR