Hemoglobin
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is a ligand?
A molecule that binds to a specific binding site
In hemoglobin, what is the ligand?
Oxygen
What is Ka
The equilibrium constant, the higher the Ka, the more we find proteins bound to a ligand and vice versa.
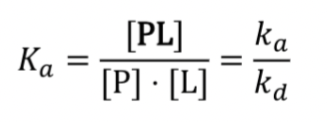
Affinity calculation
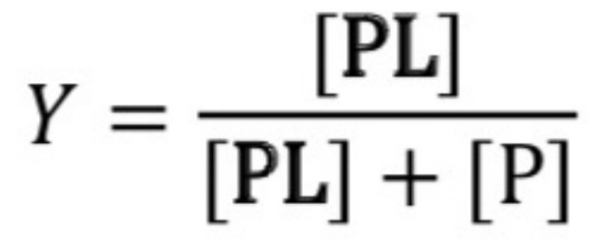
Y=occupied binding sites, therefore, used to calculate the fraction of occupied binding sites.
What is Kd
The dissociation constant, the lower the Kd, the higher the affinity (stronger binding).
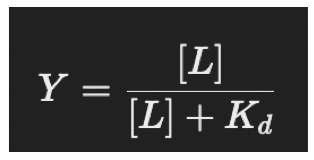
Describes how much of the protein is bound to the ligand at a given concentration.
A ligand binds a protein that is _____
Complementary. Interactions are specific and selectively bind. Some proteins have multiple binding sites for different ligands.
What is lock and key model
Assumes complimentary surfaces are pre-formed
What is induced fit
Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding. Both ligand and protein can change conformation.
How does globin bind oxygen?
Protein side chans lack affinity for O2. Therefore the HEME GROUPS with the iron can capture but can’t release O2. O2 released because it is bound to hemoglobin.
What are the 4 types of globins
Myoglobin, hemoglobin, neuroglobin and cytoglobin
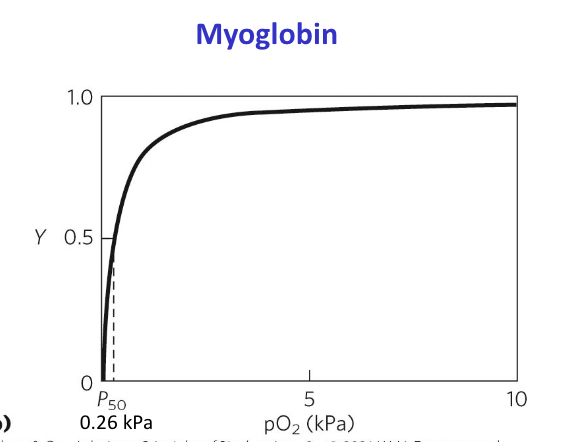
Myoglobin
Monomeric, helps store oxygen, facilitates 02 diffusion in muscle tissues

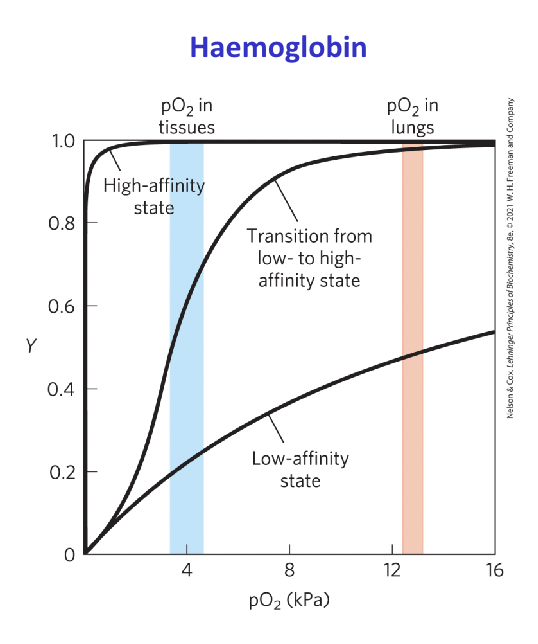
Hemoglobin
Tetrameric, transport oxygen in bloodstream
Neuroglobin
Monomeric, protects the brain from oxygen deprivation
Cytoglobin
Monomeric, regulates nitric oxide levels, which influences bloodflow
Myoglobin 2 bonds:
One bond to oxygen: FE2+ binds O2 but FE3+ does not
One bond to histadine amino acid: holds iron in place and affects how it binds to gases
How does globin prevent CO (Carbon monoxide) binding?
CO is toxic because it sticks to heme better than O2. The histadine bond tilts the gas molecule when it tries to attach to iron, making it harder for CO to bind
Conformational change of hemoglobin
Needs to change affinity to oxygen by changing conformation to both capture and release it.
T (tense) state : more interactions, more stable lower affinity for O2, O2 released
→
R (relaxed) state: fewer interactions, more flexible higher affinity for O2
What is cooperative binding?
The transition between the Tense and Relaxed state for oxygen binding
What is allosteric protein
Binding at one site affects the affinity of another on the same protein. Allosteric regulation is when a molecule binds to a different site and changes the proteins shape and function
Happends on proteins with multiple subunits (e.g. hemoglobin)
Can increase of decrease the proteins activity (activate or deactivate)
Homotropic
Same ligand for binding sites
E.g. Oxygen is a positive homotropic regulator. The binding of one O2 promotes further binding. Positive cooperativity.
Analogy: Imagine a concert, when someone starts clapping more people join in and clap (more oxygen binding)
Heterotropic
Different ligands for each binding site
E.g. 2,3-BPG binding to hemoglobin.
2,3-BPG binds to hemoglobin and reduces its oxygen affinity, helping oxygen release in tissues

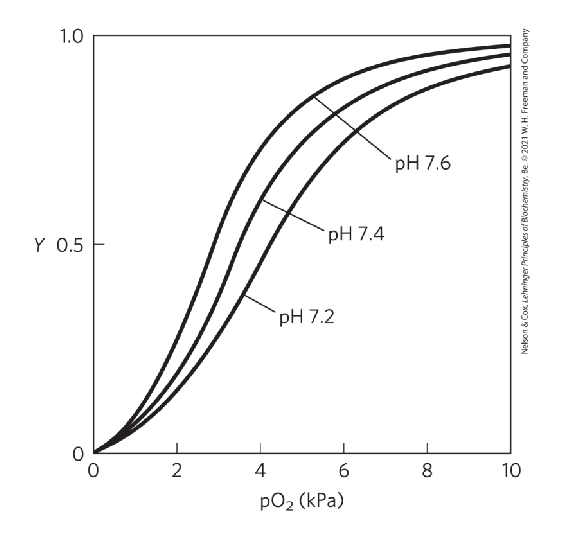
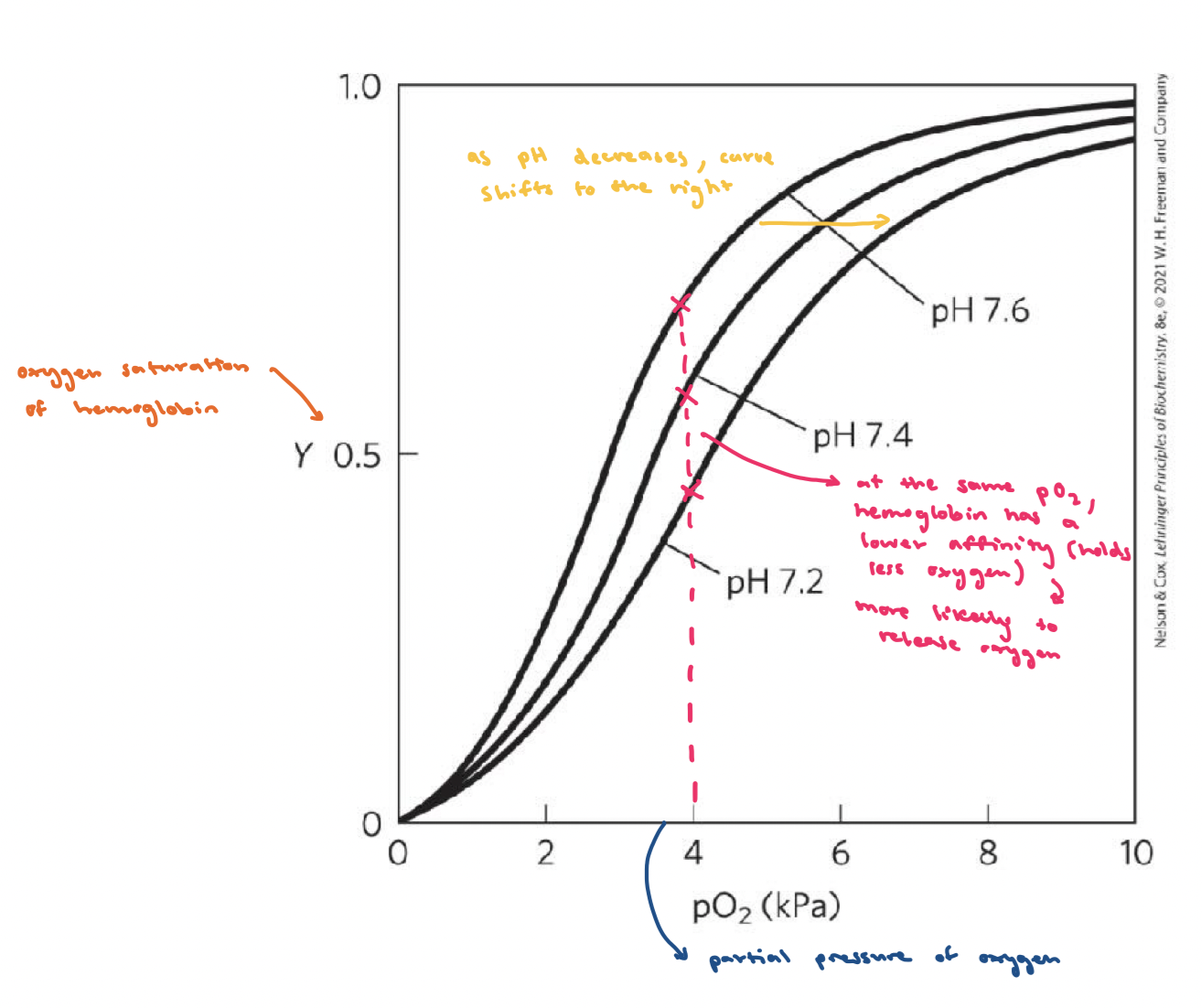
Factors affecting O2 binding to Hb
pO2 (oxygen pressure), pH, CO2 concentration, temperature, BPG levels…