N5 Biology Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What controls glucose levels?
The hormones Insulin and Glucagon
Mitosis
Provides new cells for growth and repair of damaged cells and maintains the diploid chromosome complement
Steps for Mitosis
1. Chromosomes shorten and thicken. Chromosome double.
2. Nuclear membranes break down. Chromosomes line up at the equator.
3. spindle fibres attach each centromere to a pole. The spindle fibres shorten and separate chromatids.
4. Nuclear membranes reform. Cytoplasm divides. Two identical daughter cells are formed.
What is a chromosome?
Lengths of DNA. Humans have 23 pairs.
What is a gene?
A section of a chromosome which codes for a protein.
What is a specialised cell?
Each have a particular structure for a specific job e.g. red blood cell
What are tissues?
A group of specialised cells that works together for a particular function e.g. the blood
What is an organ?
A structure made of a group of tissues working together to preform a function e.g. heart
What is a system?
A group of organs working together
What do stem cells in animals do?
Unspecialised cells which can divide to make more stem cells or become specialised.
What are embryonic stem cells?
Found in embryos at a very early stage
What are tissue stem cells?
Found in the body throughout life
What is specialization in animals?
Leads to the formation of a variety of cells
What is the nervous system made up of?
brain, spinal cord, nerves
What is the CNS?
Brain and spinal cord
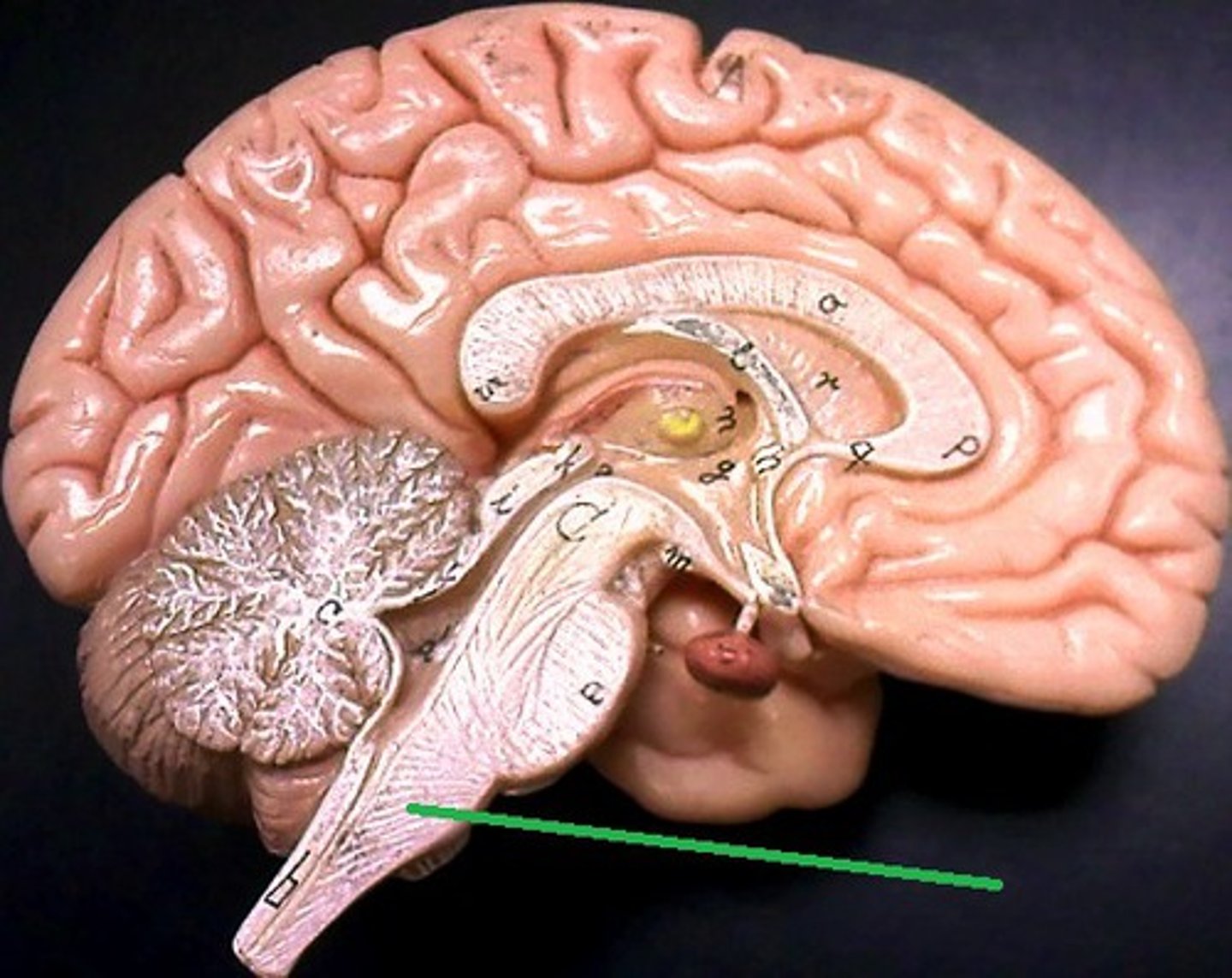
What does the cerebrum do?
Controls memory and conscious thought
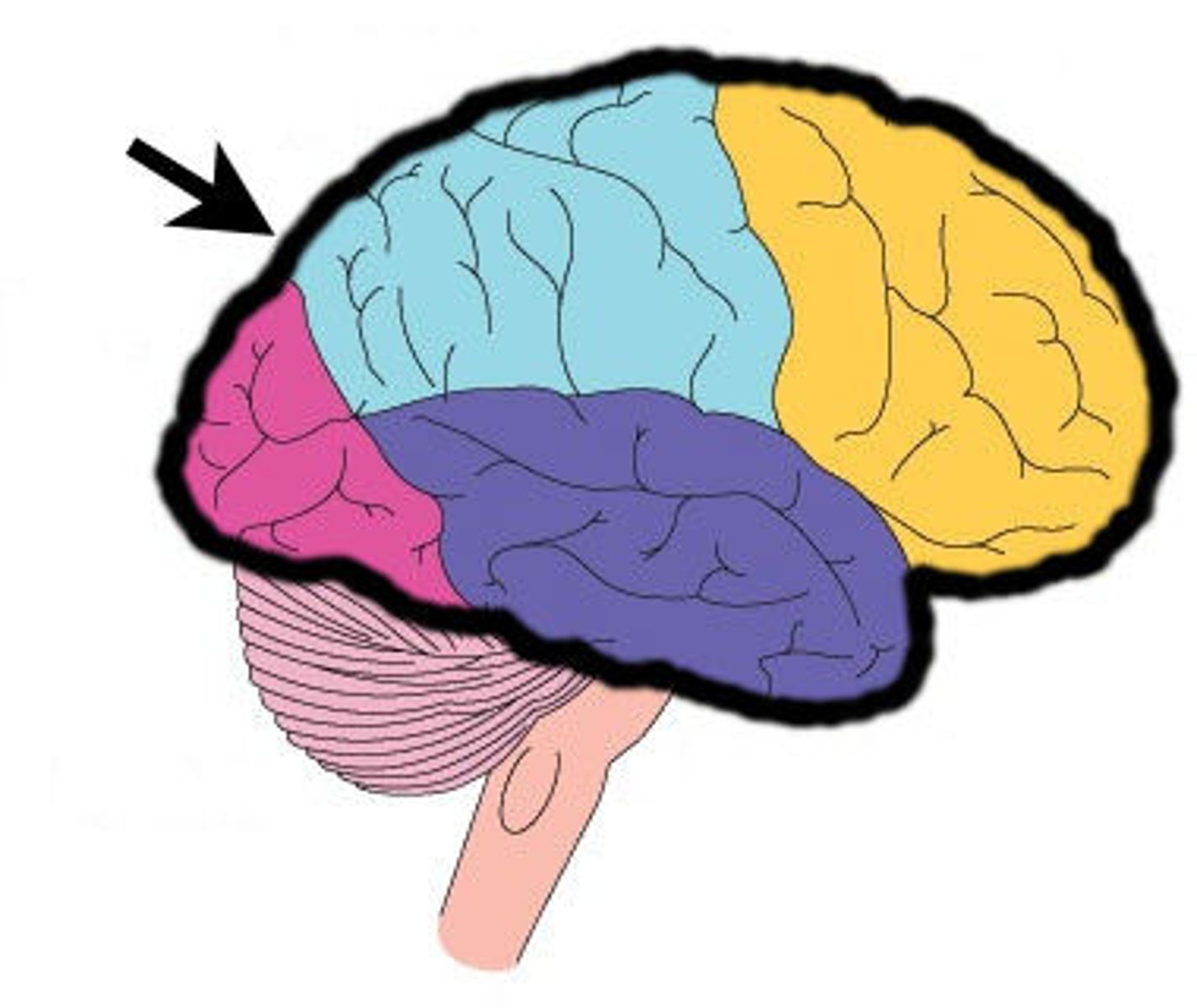
What does the cerebellum do?
controls balance and coordination
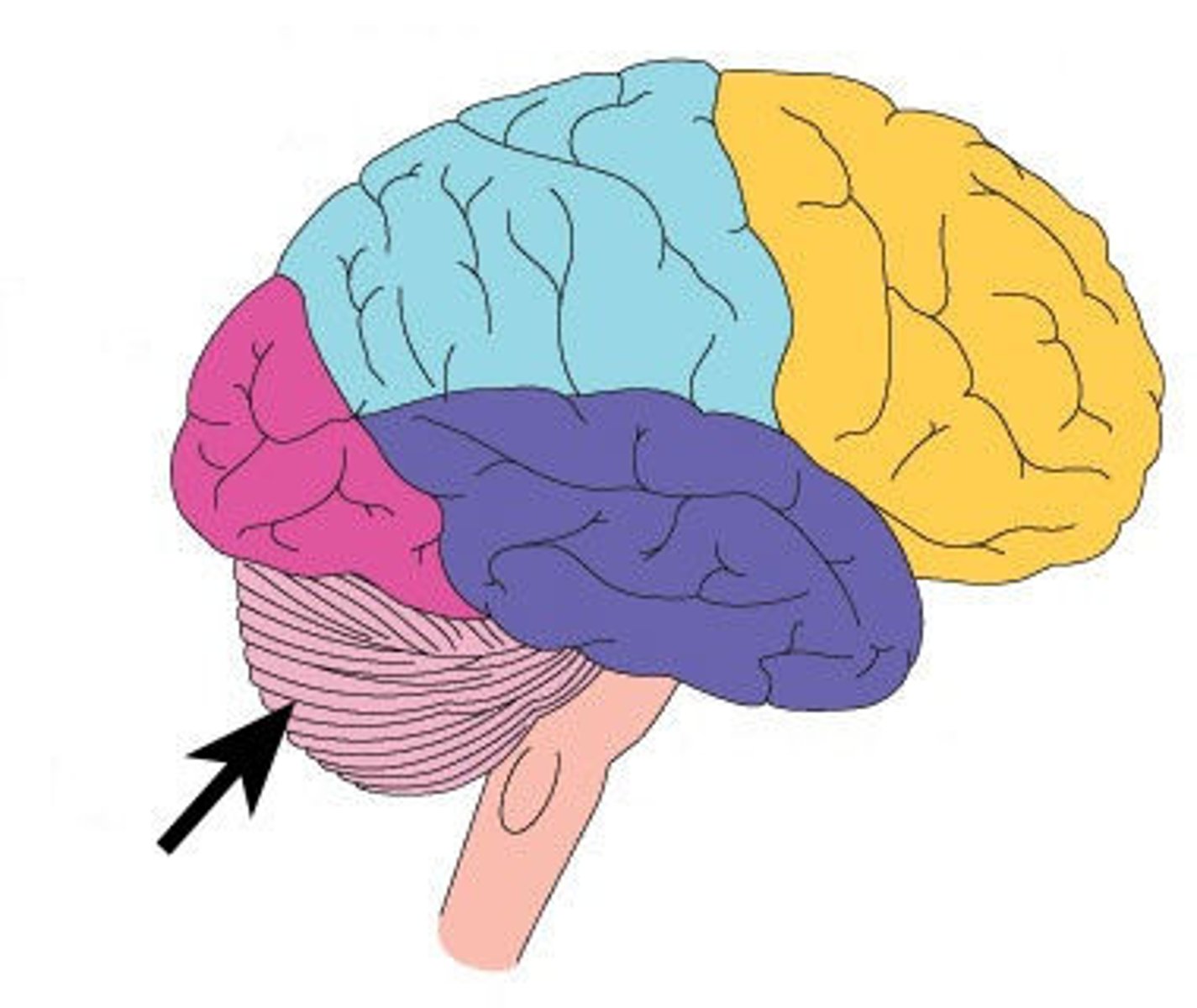
What does the medulla do?
Controls heart rate and breathing rate
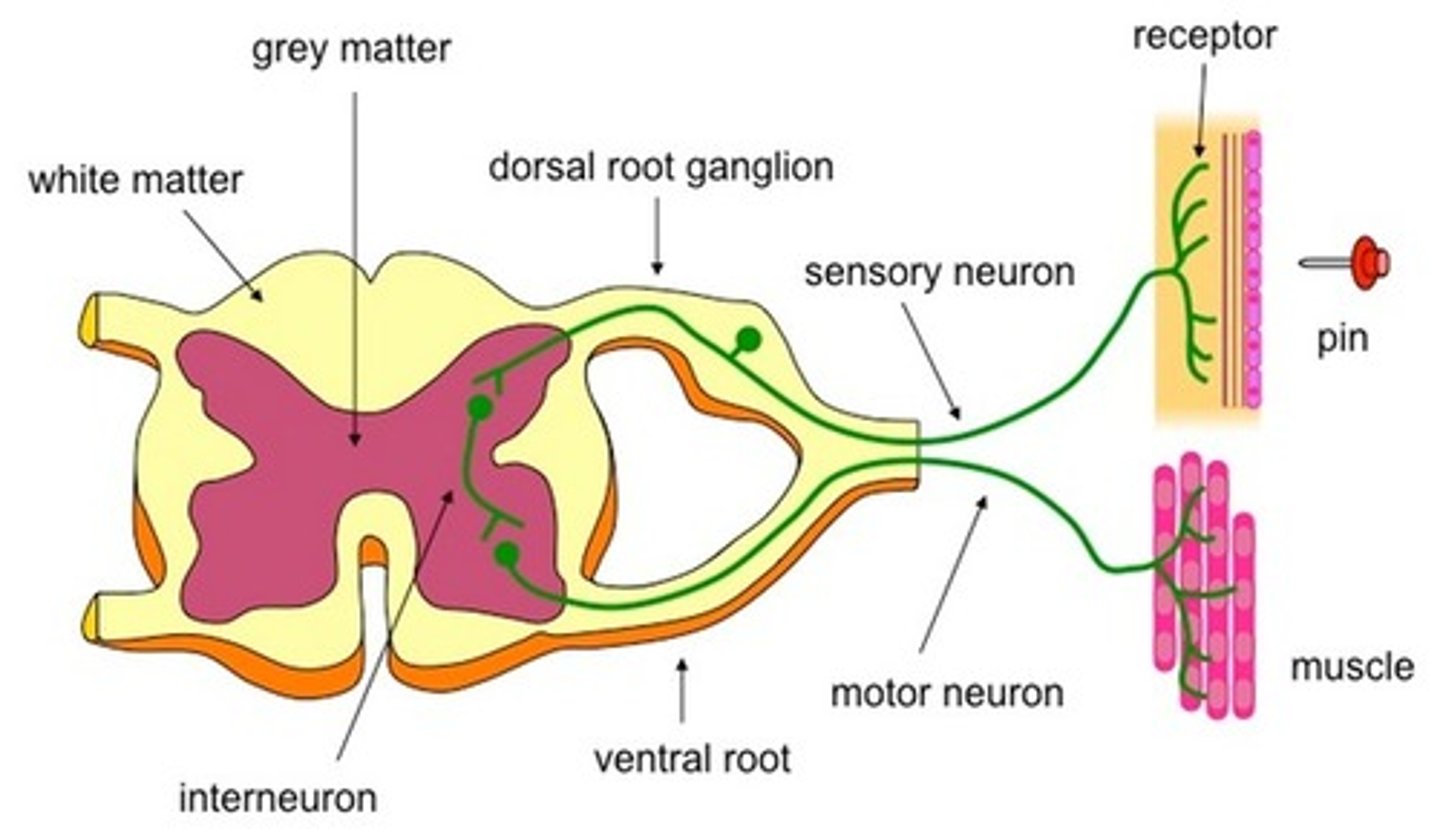
What are sensory neurons?
Pass information to the CNS from a sense organ/receptor
What is an inter neuron?
Pass through information from sensory receptor to the CNS or straight to the Motor Neutron
What are motor neurons?
Enable a response to occur at an effector(muscle or gland)
What is a receptor?
Detect sensory input/stimuli
What carries messages along neurons?
Electrical impulses
What carries messages between neurons?
Chemical messages through synapses
What is a reflex action?
A rapid automatic response to a stimuli which protects the body from harm e.g. blinking, removing hand from hot object
What is the reflex arc?
Sensory Neuron --> Inter Neuron --> Motor Neutron
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers
Where are hormones made?
Endocrine glands
What does a endocrine gland do?
Release hormones into the blood stream e.g. Pancreas, testis, ovaries
What is target tissue?
Has cells with complimentary receptor proteins for specific hormones, so only that tissue will be effected by that hormone
What is glucose needed to make?
ATP
What is glucose stored as?
glycogen
Insulin steps
1. High glucose levels in the blood (after a meal)
2. detected by pancreas and produces more insulin (endocrine gland)
3. Insulin travels in blood to liver. Liver stores glucose to glycogen. (Target tissue)
4. Blood glucose levels go down
Glucagon steps
1. Low glucose levels in blood (after exercise)
2. Pancreas detects and produces more glucagon. (endocrine gland)
3. Glucagon travels in the blood to liver. Liver converts glycogen to glucose. (Target tissue)
4. blood glucose increase.
Sperm
Male gamete in animals
Ova
Female gamete in animals
Diploid
A cell containing two copies of every chromosome
Haploid
A cell containing one copy of every chromosome
Testes
Produces sperm cells
Ovary (animal)
Produces egg cells
Pollen
Male gamete in plants
Ovule
Female gamete in plants
Anther
Produces pollen
Ovary (plant)
Produces ovules
Fertilisation
The fusion of the nuclei of the two haploid gametes
Zygote
Cell produced by fertilisation
Continuous variation
A wide range of values between two extremes e.g height (polygenic inheritance)
Discrete variation
There are distinct groups with no values in between e.g. eye colour (single gene inheritance)
Polygenic inheritance
A trait that is controlled by more than one gene
Variation
Differences between individuals. Can be inherited or due to environmental pressures
Allele
Different types of the same gene
Phenotype
The appearance an organism has
Genotype
The combination of alleles an organism has
Homozygous
Two copies of the same allele in genotype e.g. AA or aa
Heterozygous
Two different alleles in genotype e.g. Aa
Dominant
The allele which always shows in the phenotype
Recessive
The allele which can be hidden in the phenotype
What is the Predicted phenotype ratio?
Often the actual ratio of phenotypes in offspring are different from predicted one because fertilisation is a random process
Roots (plant organ)
Have a large surface area to absorb water and minerals. Water enters root cells by osmosis. Water moves into the cell down a concentration gradient.
Xylem
Carries water and minerals through the plants. Made of dead tissue supported by ring of lignin.
Lignin
Helps the xylem to withstand the pressure changes as water moves through the plant.
Phloem
Transports sugar (glucose) up and down the plant. Made of living cells. Has a companion to provide energy and a sieve plate.
Stomata (leaf)
Holes in the leaf controlled by guard cells which allows CO2 in and oxygen + water out
Guard cells (leaf)
Controls opening/closing of stomata
Veins (leaf)
Made of xylem
Palisade mesophyll
Contains chloroplasts for photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll
Allows gas exchange
Gas transport (in plants)
Gassed enter and exit pants through stomata.
Transpiration process/steps
1. Water in soil
2. Water enters root hair cells by osmosis
3. Transported in xylem vessels
4. Evaporated through stomata
Direction of blood flow
Lungs -> (pulmonary vein -> LA -> LV -> aorta ->) body -> (vena cava -> RA -> RV -> pulmonary artery) -> lungs
Traits of an arteries
Thick and muscular vessel wall. Narrow central channel. High pressure of blood. Blood flow away from heart.
Traits of capillaries
Thinnest Vessel wall. Narrowest central channel. Blood pressure lower than arteries. Blood flow through tissues(from arteries and veins)
Traits of veins
Vessel wall muscular and thinner than arteries. Central channel wider than arteries. Lowest blood pressure. Blood flow toward heart.
What is blood made of and what does it do?
Blood contains plasma, red blood cells and white blood cells. Transports nutrients, oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Traits of Red blood cells
Red blood cells carry oxygen.
Specialised: biconcave in shape, no nucleus, contains haemoglobin; transports oxygen as oxyhaemonglobin
Traits of White blood cells
White blood cells are part of the immune system and are involved in destroying pathogens. Phagocytes and Lymphocytes
Phagocytes
Carry out phagocytosis by engulfing them digesting pathogens.
Lymphocytes
Produces antibodies which destroy pathogens. Each antibody is specific to a particular pathogen.
What's absorbed into the bloodstream?
Oxygen and nutrients (from foods)
Features of surfaces for absorption
1. Large surface area
2. Thin walls
3. Extensive blood supply (capillary networks)
Villi
Found in small intestine. Absorbed nutrients from food. Has a network of capillaries to absorb glucose and amino acids. Has a lacteal to absorb fatty acids and glycerol.
Waste materials
E.g. CO2. Must be removed form cells into the bloodstream.
What is single gene inheritance.
A trait which is controlled by only one gene.
What is absorbed by the lacteal?
Glyercol and fatty acids