2) Heart and Fetal Circulation
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Cardiovascular System - Major Components
– Heart
– Blood vessels
– Blood
Cardiovascular System - Major Function
– Transportation
• Nutrients and Oxygen
• Waste Products
• Hormones
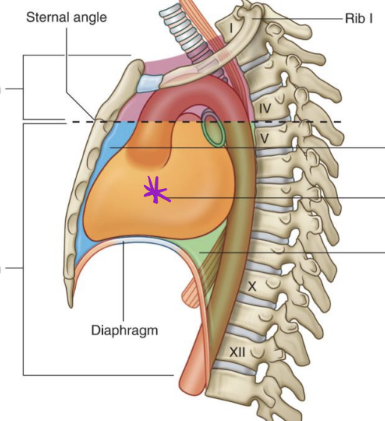
Location of the heart in body
Middle mediastinum
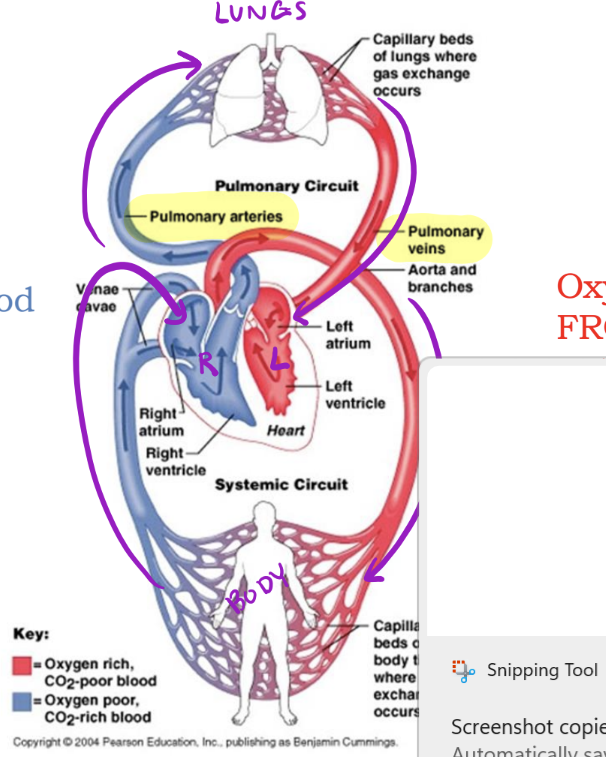
Heart - 2 Circuits
Pulmonary & Systemic
Hint for identifying pulmonary circuit
pulm = lu
Pulmonary Circuit
_____ side of heart pumps blood to lungs, then it goes back to _____side of heart
Right, left
Hint for Identifying Systemic Circuit
System = Body
Systemic Circuit
_____ side of heart pumps blood to the body, then it goes back to _____side of heart
Left, right
Why does blood need to go to the lungs?
To become oxygenated
What parts of the body does this blood go to?
Everywhere
Pathway of Blood Through the Mature Heart
Right Side
Deoxygenated blood FROM body enters right side of heart & gets pumped TO lungs
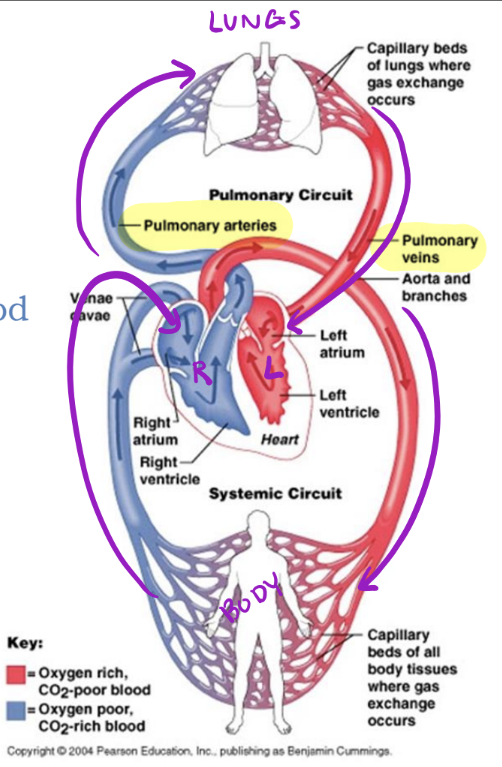
Pathway of Blood Through the Mature Heart
Left Side
Oxygenated blood FROM lungs enters left side of heart & gets pumped TO body
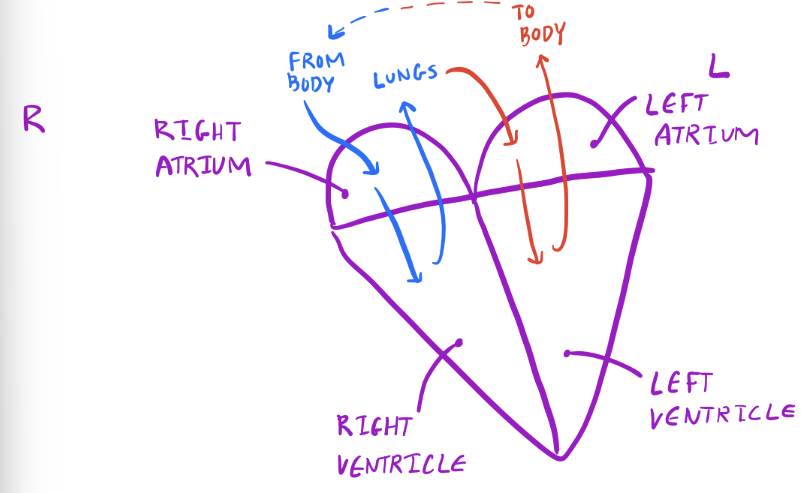
Chambers of the Heart
Vein =
Take blood towards heart
Bump into atria
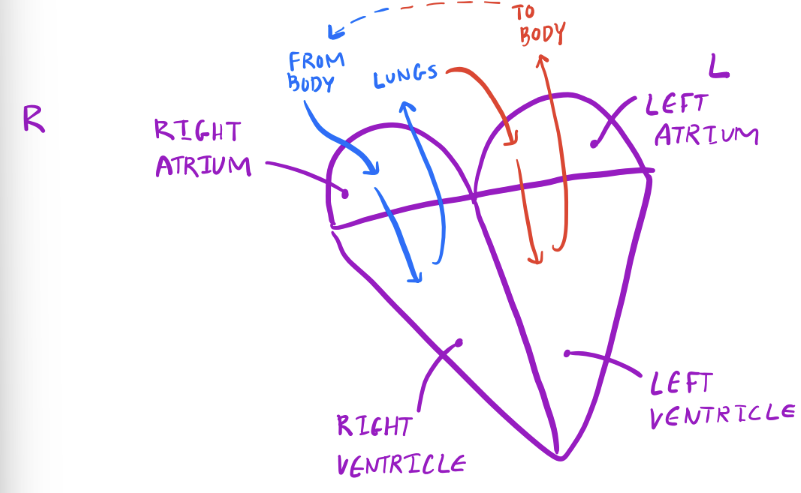
Chambers of the Heart
Artery =
Take blood away from heart
Leave via ventricles
Great Vessels of the Heart
Superior vena cava (SVC)
Inferior vena cava (IVC)
Pulmonary veins
Pulmonary trunk & arteries
Aorta
Great Vessels of the Heart: Veins
Superior vena cava (SVC)
Inferior vena cava (IVC)
Pulmonary veins
Great Vessels of the Heart: Arteries
Pulmonary trunk & arteries
Aorta
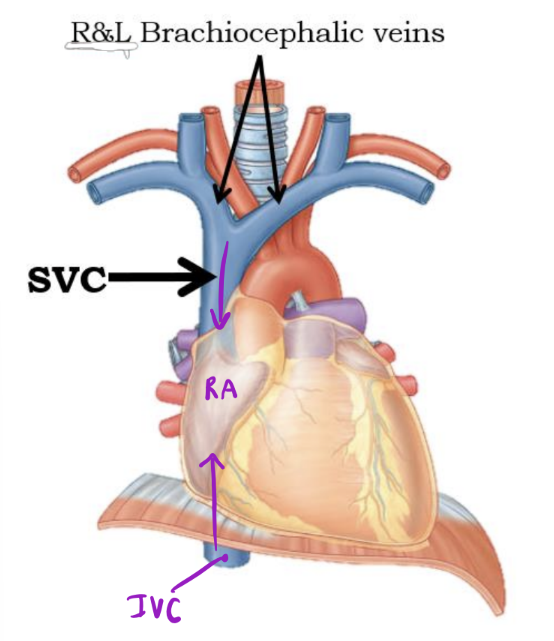
SVC
Returns blood from thoracic wall, upper limb, head and neck
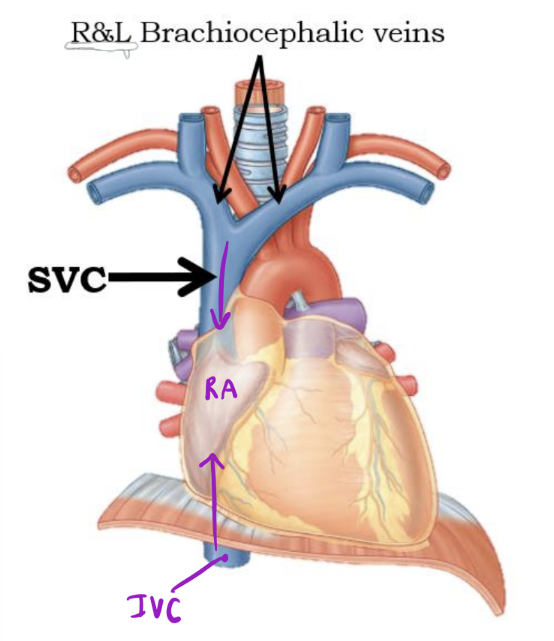
IVC
Returns blood from the abdomen, pelvis, and lower limb
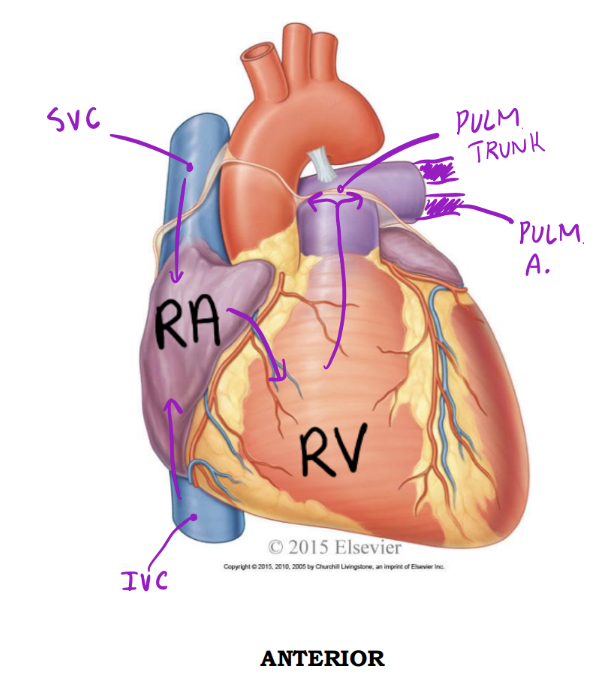
Entering & Exiting the Right Side
Right Atrium of heart - Anterior
Receives deoxygenated blood from:
1. Superior vena cava
2. Inferior vena cava
3. Coronary sinus*
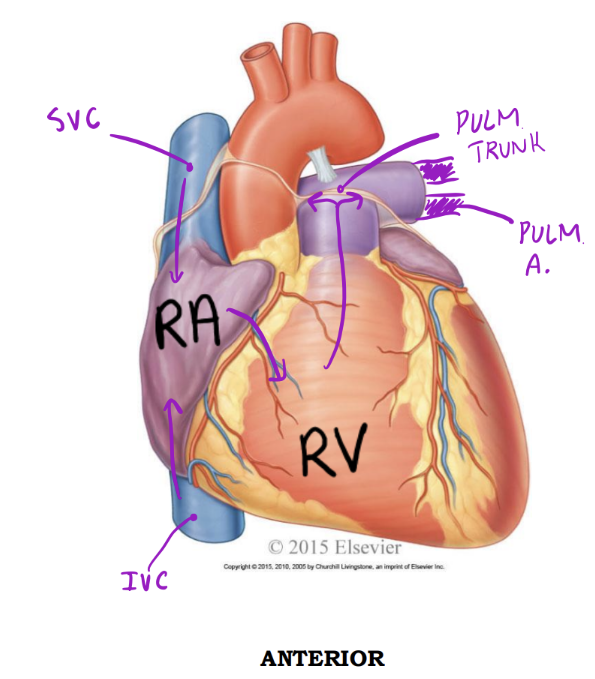
Entering & Exiting the Right Side
Right ventricle - Anterior
Discharges deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary circuit via the:
1. Pulmonary trunk; splits into pulmonary arteries*
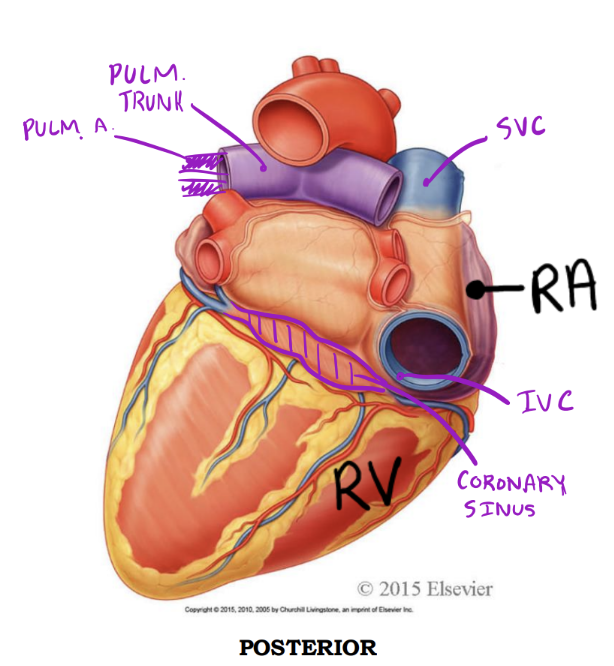
Entering & Exiting the Right Side
Right atrium - Posterior
Receives deoxygenated blood from:
1. Superior vena cava
2. Inferior vena cava
3. Coronary sinus
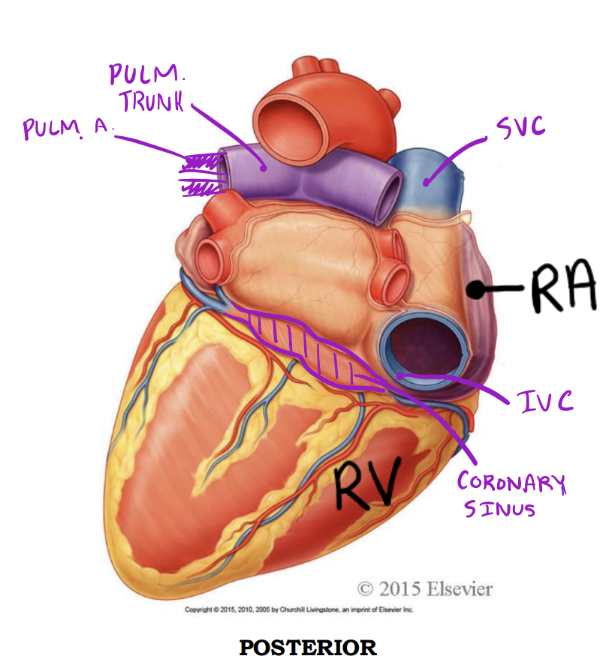
Entering & Exiting the Right Side
Right ventricle - Posterior
Discharges deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary circuit via the:
1. Pulmonary trunk; bifurcates into right and left pulmonary arteries
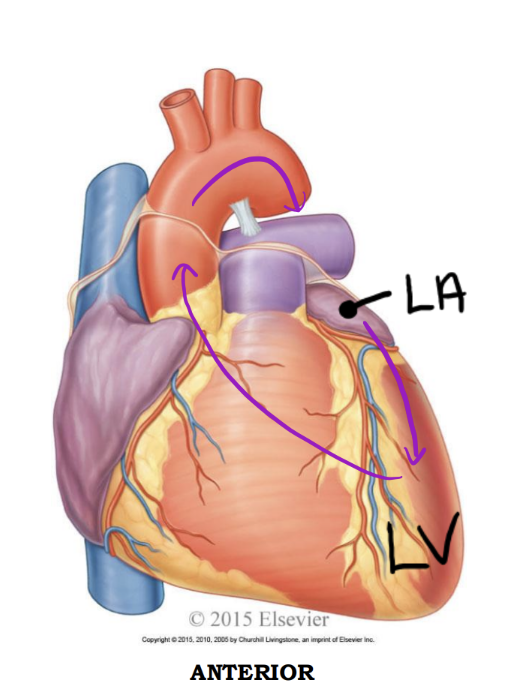
Entering & Exiting the Left Side
Left atrium - Anterior
Receives oxygenated blood from
1. Four pulmonary veins*
1. 2 Right pulmonary v.
2. 2 Left pulmonary v.
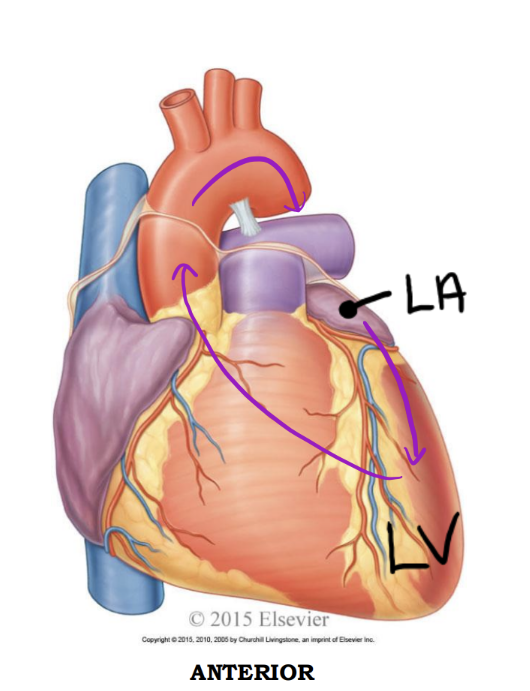
Entering & Exiting the Left Side
Left ventricle - Anterior
Discharges oxygenated blood into the systemic circuit via the:
1. Aorta; ascending aorta, arch of aorta, descending aorta
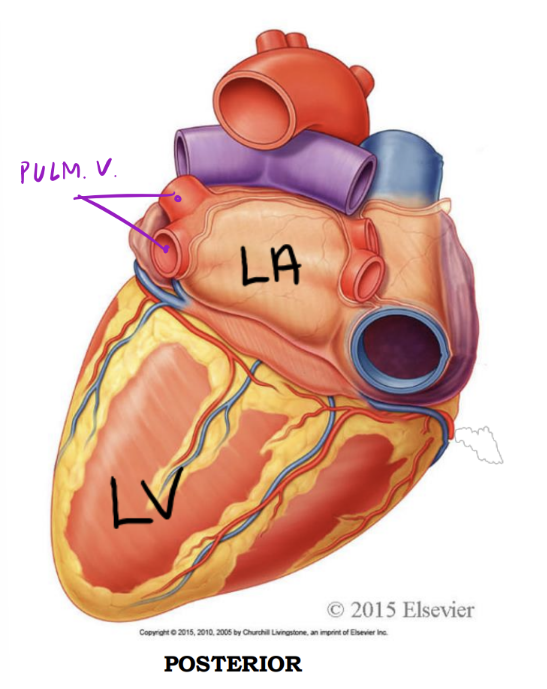
Entering & Exiting the Left Side
Left atrium - Posterior
Receives oxygenated blood from
1. Four pulmonary veins
1. 2 Right pulmonary v.
2. 2 Left pulmonary v.
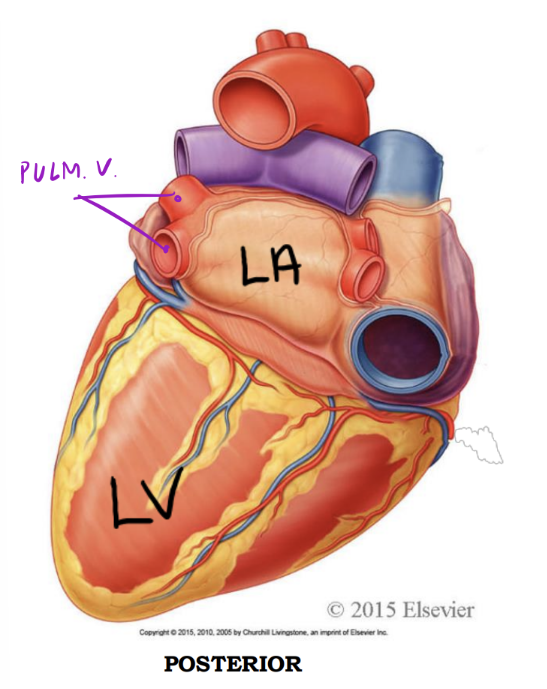
Entering & Exiting the Left Side
Left ventricle - Posterior
Discharges oxygenated blood into the systemic circuit via the:
1. Aorta; ascending aorta, arch of aorta, descending aorta
Oxygenated blood travels in:
Arteries and Veins
Arteries away from heart
Veins towards heart
The RIGHT side of the heart receives ___________ blood from the body, and pumps it to the lungs.
deoxygenated
The RIGHT side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the _____, and pumps it to the lungs.
body
The RIGHT side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body, and pumps it to the _____.
lungs
The LEFT side of the heart receives ___________ blood from the lungs, and pumps it to the body.
oxygenated
The LEFT side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the _____ , and pumps it to the body.
lungs
The LEFT side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs, and pumps it to the _____.
body
How do we prevent backflow in chambers?
Valves
Valves of the heart: Atrioventricular Valves
Between atria & ventricles
Valves of the heart: Semilunar Valves
Between ventricles & outflow arteries
Atrioventricular valves prevent backflow into _____
atria
Semilunar valves prevent backflow into _____
ventricles
Atrioventricular Valves: Tricuspid Valve
*Tri=3
“Try (tri) before you buy (bi)”
Between right atrium and right ventricle
Atrioventricular Valves: Bicuspid or Mitral Valve
*Bi =2
“Try (tri) before you buy (bi)”
Between left atrium and left ventricle
Atrioventricular Valves: Tricuspid Valve
Left or Right?
Right
Atrioventricular Valves: Bicuspid or Mitral Valve
Left or Right?
Left
Semilunar Valves: Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
Left or Right? Where?
Right → lungs
Semilunar Valves: Aortic Semilunar Valve
Left or Right? Where
Left → aorta
Semilunar Valves: Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
Between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
Semilunar Valves: Aortic Semilunar Valve
Between left ventricle and aorta
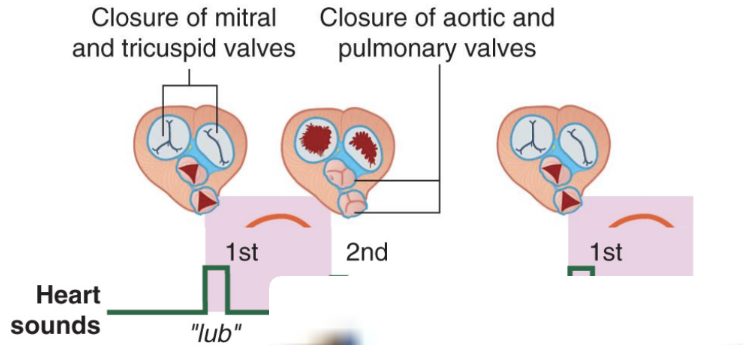
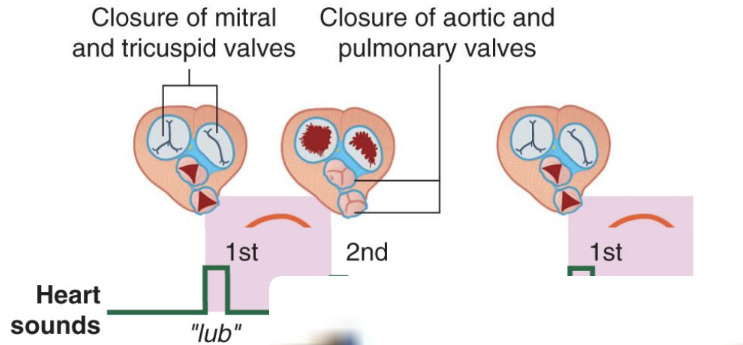
Heart Contraction & Sounds
Systole
Ventricles contract to pump blood out of the heart
– Tricuspid & bicuspid valves close (don’t want back-flow)
– Together, these are S1 (“lub”)
Heart Contraction & Sounds
Diastole
Ventricles relax so blood can fill them again
– Tricuspid & bicuspid valves open, and the pulmonary and aortic
semilunar valves close (don’t want back-flow from outflow vessels)
– This is S2 (“dub”)
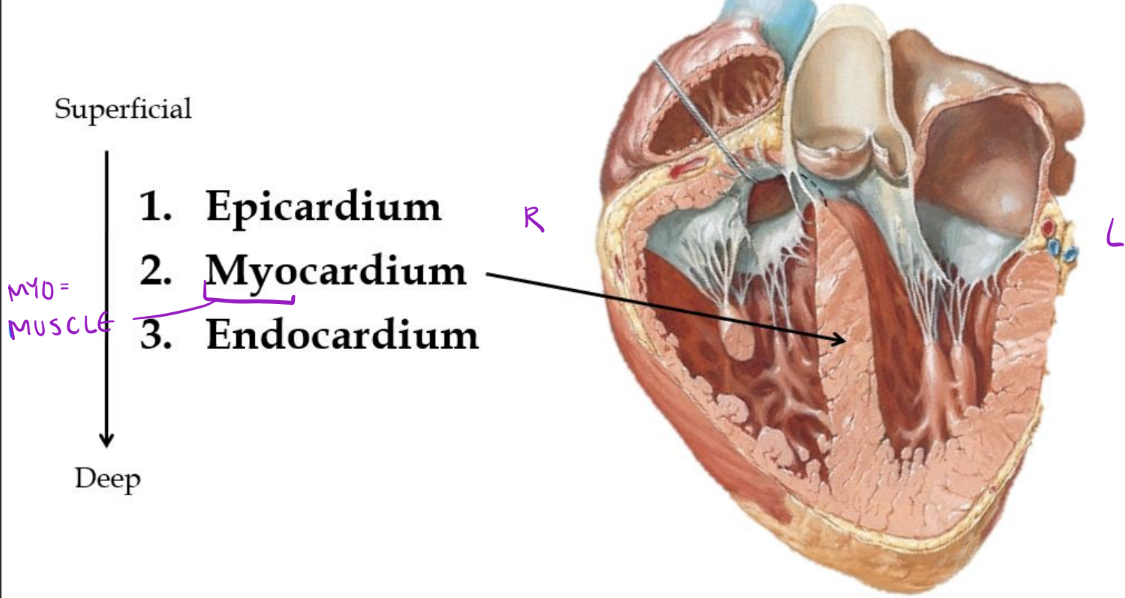
Layers of the Heart
Arterial Coronary Circulation: Maximal blood flow to the _____ occurs when the heart is relaxed (diastole)
myocardium
Arterial Coronary Circulation: There is very little blood flow through the _____ when the heart is contracting (systole):
• Contraction of myocardium compresses coronary arteries
• Entrances into the coronary circulation are partially blocked by the cusps of the open aortic semilunar valve
coronary circulation
Arterial Coronary Circulation: There is very little blood flow through the coronary circulation when the heart is contracting (systole):
• Contraction of myocardium _____ coronary arteries
• Entrances into the coronary circulation are partially blocked by the cusps of the open aortic semilunar valve
compresses
Arterial Coronary Circulation: There is very little blood flow through the coronary circulation when the heart is contracting (systole):
• Contraction of myocardium compresses coronary arteries
• Entrances into the coronary circulation _____ the cusps of the open aortic semilunar valve
are partially blocked by
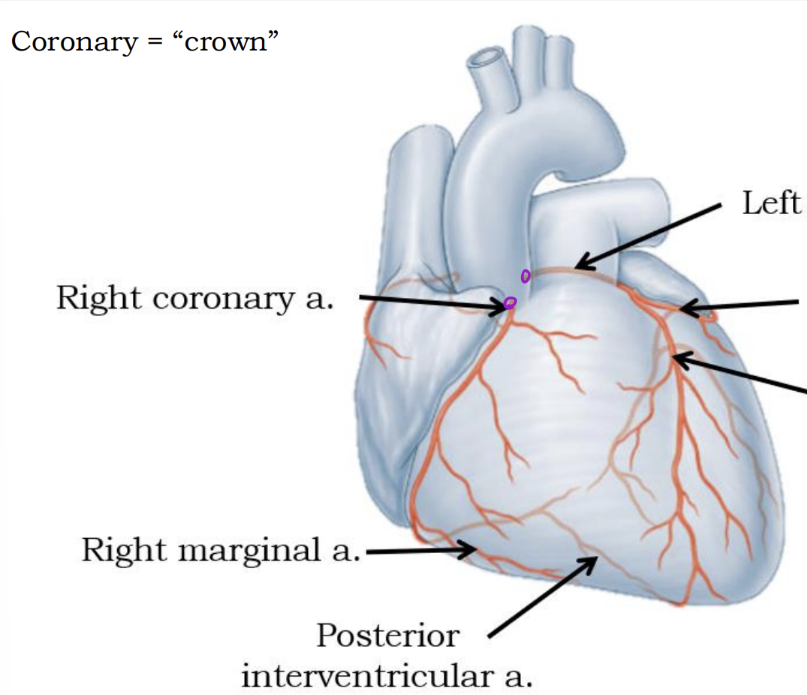
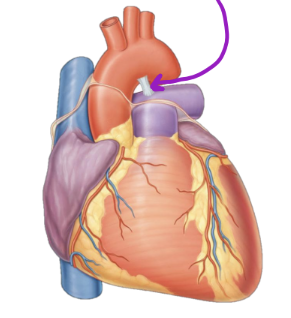
Anterior interventricular artery (Lower arrow on right side
Coronary a. disease
Plaque build up
*Coronary = “crown”
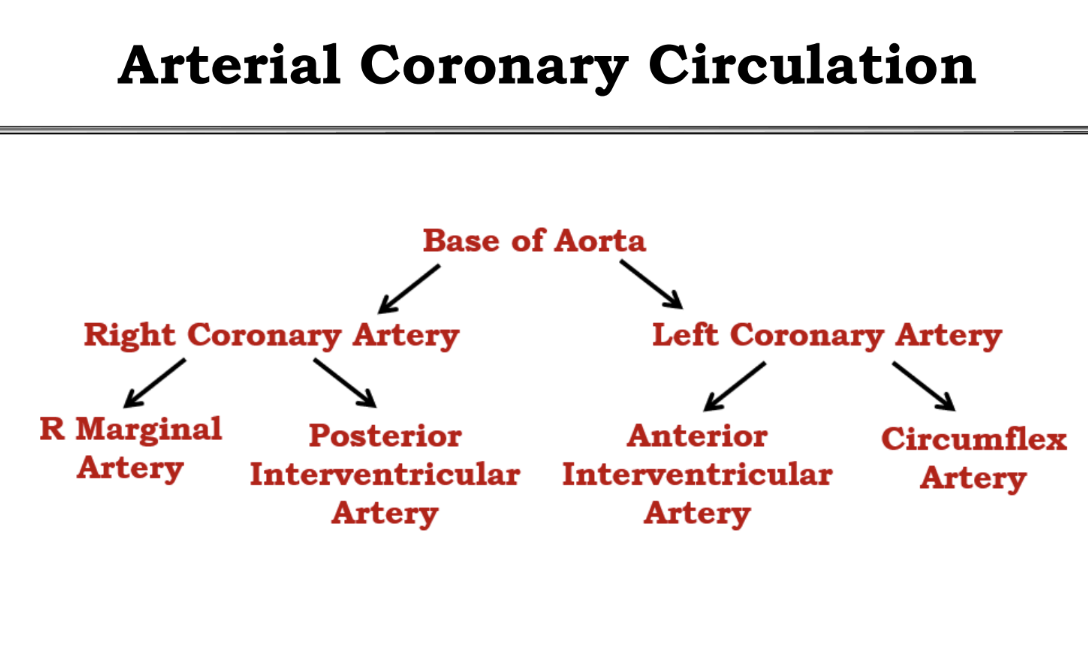
Memorize the Arterial Coronary Circulation
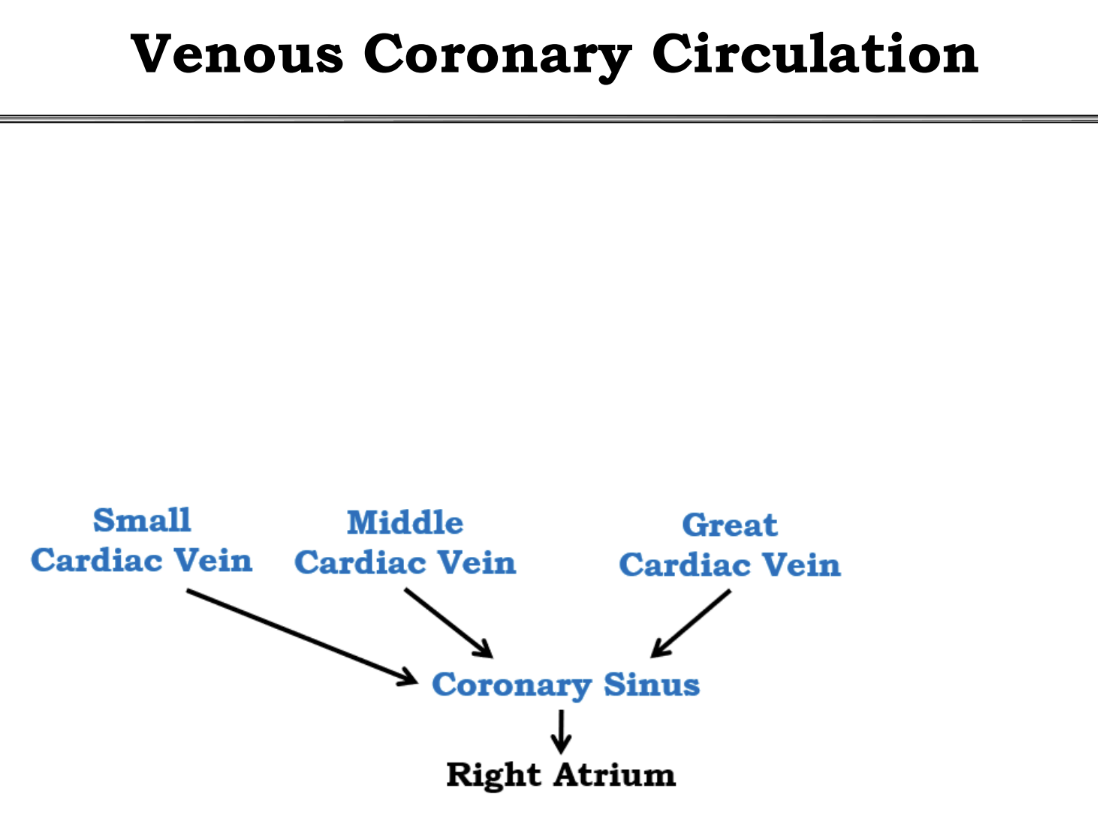
Memorize the Venous Coronary Circulation
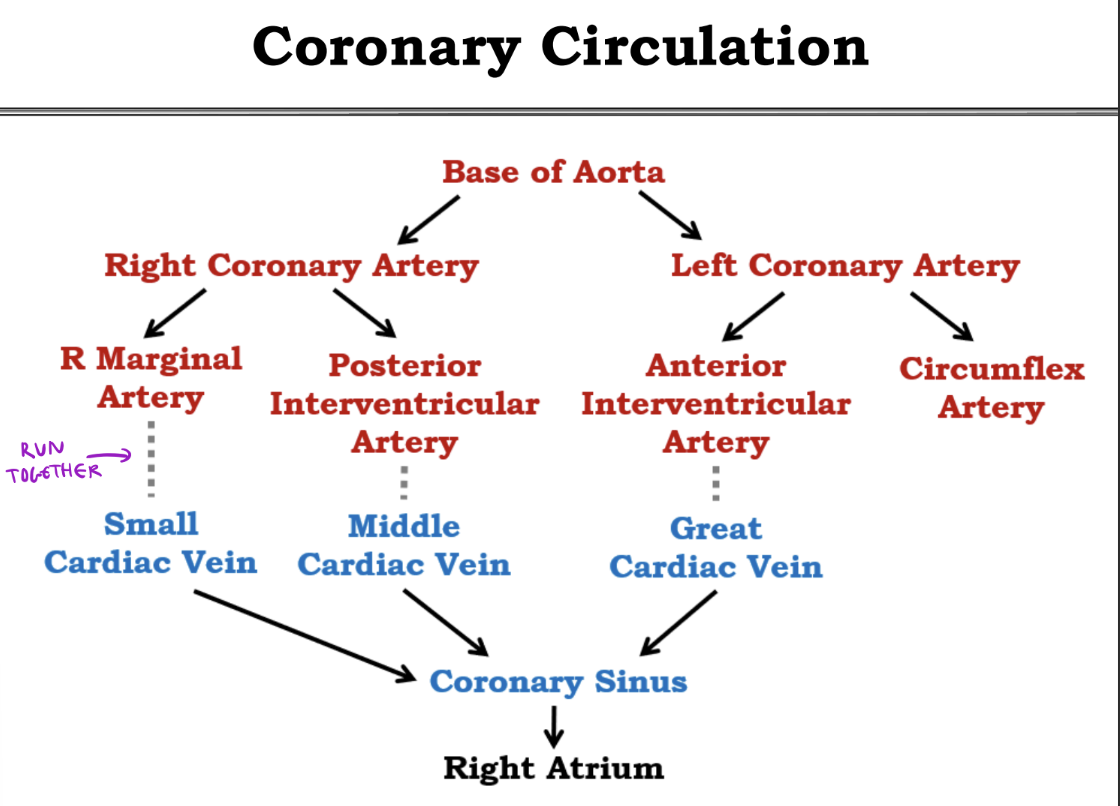
Memorize all coronary Circulation
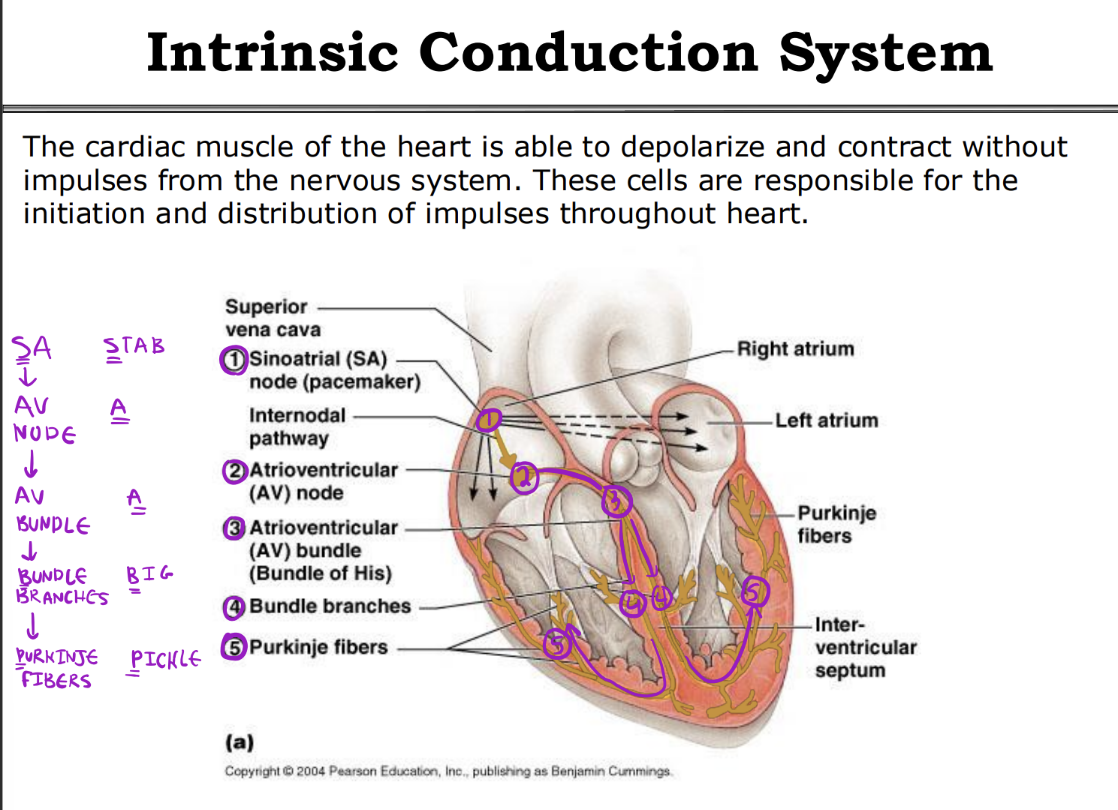
Memorize Intrinsic Conduction System
Intrinsic Conduction System
The rate of the intrinsic cardiac muscle contraction set by these pacemaker cells is altered by the sympathetic (_____________) and by the parasympathetic (_____________) divisions of the autonomic nervous system.
accelerates the heartbeat, decelerates the heartbeat
Parasympathetic - Intrinsic Conduction System
*Parasympathetic = Rest + Digest
Lowers heart rate
Sympathetic - Intrinsic Conduction System
*Sympathetic = Fight or Flight
Increases heart rate
Fetal vs. Post-natal Circulation
Fetus has _____ lungs
Fetus has non-functioning lungs
Fetal vs. Post-natal Circulation
Fetus _____ provide its own nutrients
can not
Fetal vs. Post-natal Circulation
Fetus can not remove its own _____
waste
Fetus has non-functioning lungs
Fetus can not provide its own nutrients
Fetus can not remove its own waste
What must fetus use to compensate for these deficiencies?
Use the mother’s circulation
Fetal Circulation – Placenta
The placenta develops in the uterus alongside the fetus to allow _____ to communicate.
maternal and fetal blood
Fetal Circulation – Placenta
The placenta develops in the uterus alongside the fetus to allow maternal and fetal blood to communicate.
• This communication occurs via ______
umbilical vessels in the umbilical cord
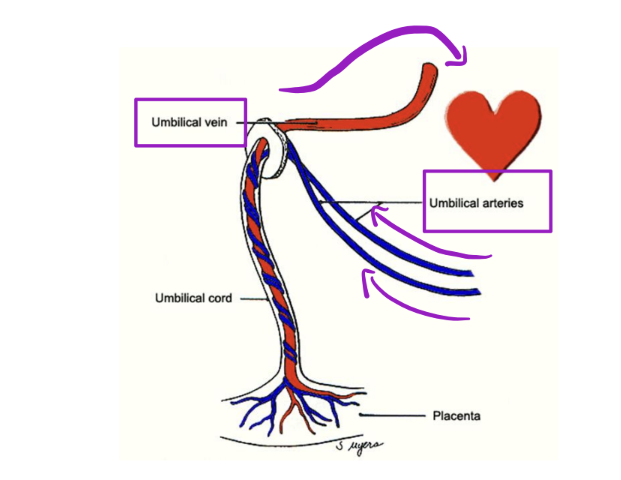
Fetal Circulation – Placenta
The placenta develops in the uterus alongside the fetus to allow maternal and fetal blood to communicate.
• This communication occurs via umbilical vessels in the umbilical cord
• 1 umbilical vein (towards!)
• Bringing oxygen and nutrients TO the fetal heart. Why is this
oxygenated?
From mothers circulation
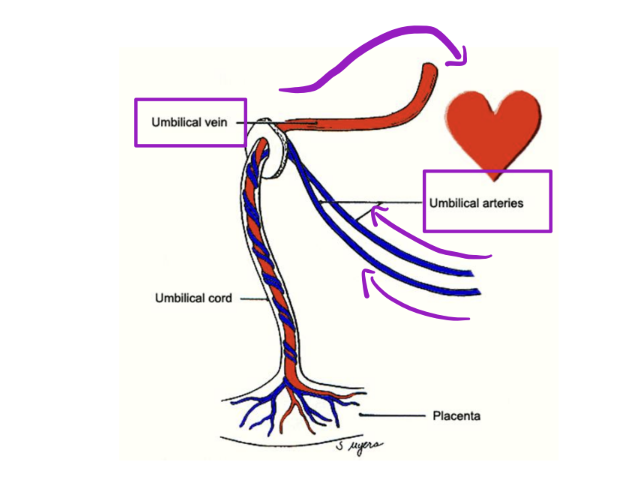
Fetal Circulation – Placenta
The placenta develops in the uterus alongside the fetus to allow maternal and fetal blood to communicate.
• This communication occurs via umbilical vessels in the umbilical cord
• 1 umbilical vein (towards!)
• Bringing oxygen and nutrients TO the fetal heart. Why is this
oxygenated?
• 2 umbilical arteries (away!)
• Take deoxygenated blood _____ the fetal hear
AWAY from
Fetal Circulation:
_____ passes through primitive liver and carries oxygenated blood to the IVC
Umbilical vein
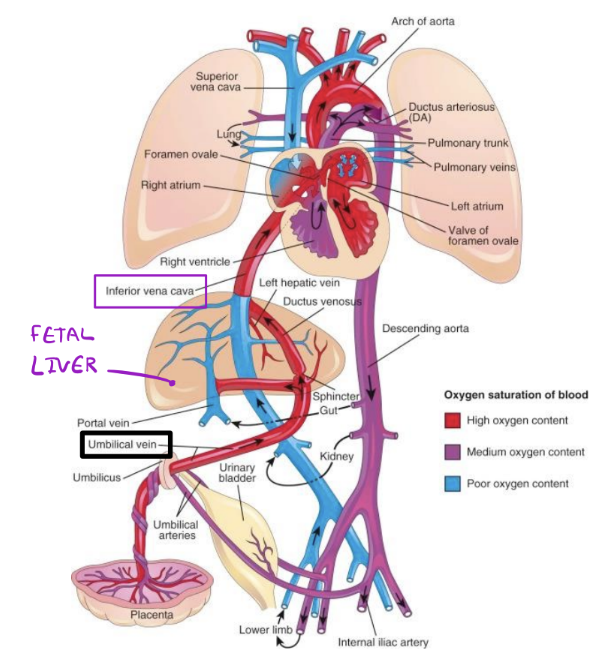
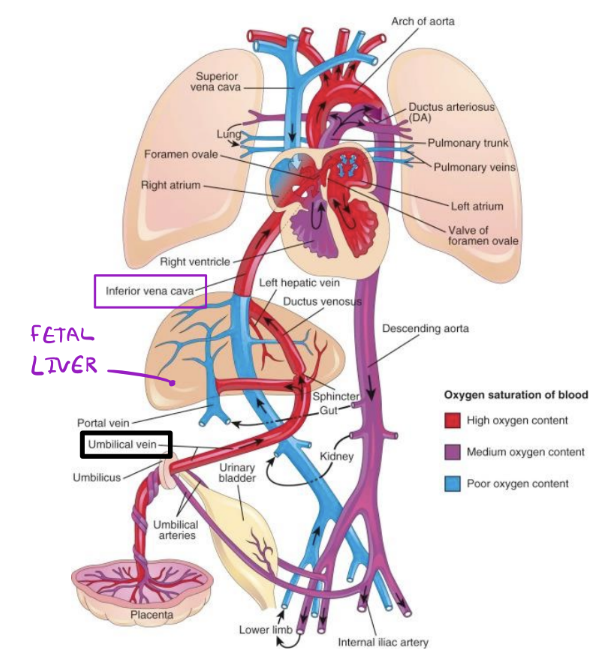
Umbilical vein regresses to form the _____, which is found within the inferior edge of the falciform ligament
ligamentum teres (round ligament of the liver)
Fetal Circulation
The _____ is a hole that shunts blood from the right atrium to the left atrium to bypass the lungs
foramen ovale
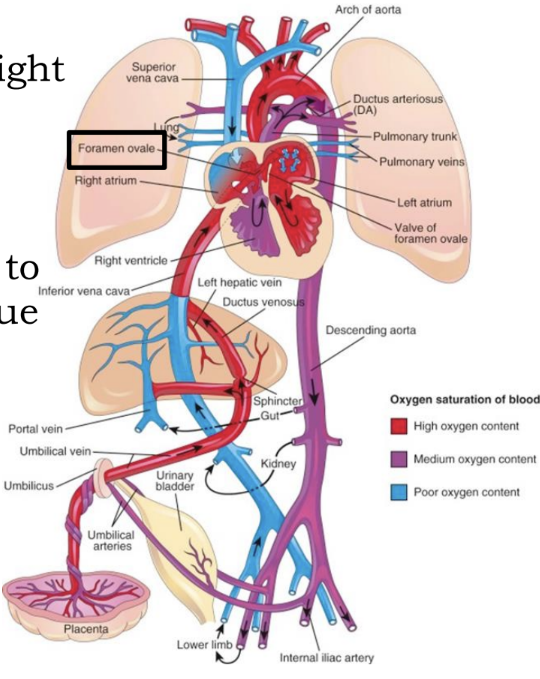
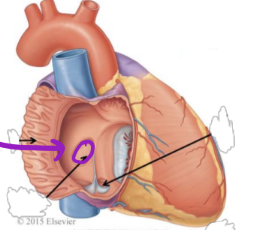
Fetal Circulation - Foramen Ovale
Small amount of blood flows to _____ to nourish the tissue
the lungs
Closure after birth forms the _____
fossa ovalis
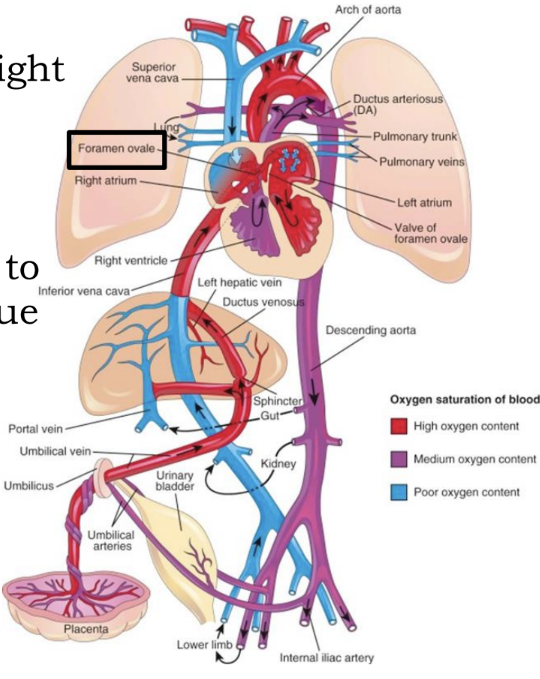
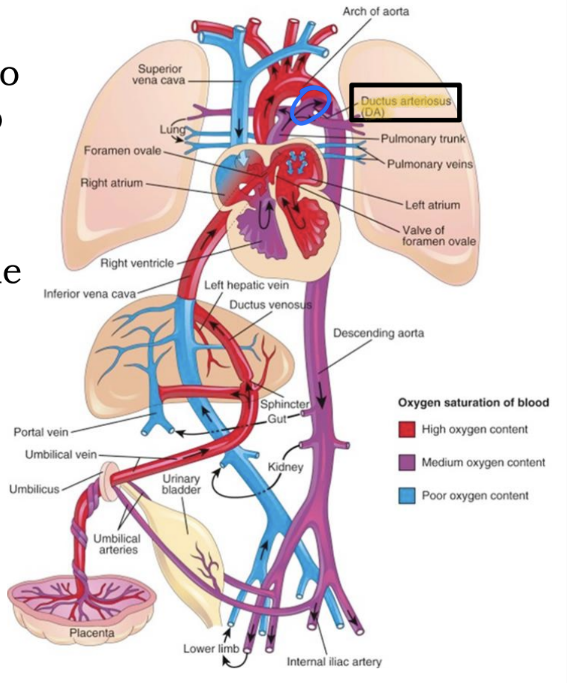
Fetal Circulation
The _____ shunts blood that made it to the left pulmonary artery to the aorta
ductus arteriosus
Fetal Circulation - ductus arteriosus
Closure after birth forms the _____
ligamentum arteriosum
Derivatives Summarized:
Umbilical vein —>
Ligamentum teres
Foramen ovale —>
Fossa ovalis
Foramen ovale —>
Ligamentum arteriosum

Next steps