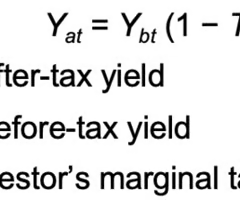FI 301 Test One
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:57 PM on 2/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
Financial market
A market in which financial assets (securities) such as stocks and bonds can be purchased or sold
2
New cards
Funds are transferred when one party purchases financial assets previously held by another party.
Financial market
3
New cards
Role of Financial Markets
Financial markets transfer funds from those who have excess funds to those who need funds.
4
New cards
Surplus units
participants who receive more money than they spend, such as investors
5
New cards
Deficit units
participants who spend more money than they receive, such as borrowers
6
New cards
Securities
represent a claim on the issuers
7
New cards
Deb securities
debt (a.k.a credit or borrowed funds) incurred by the issuer
8
New cards
Equity securities
(a.k.a. stocks) represent equity or ownership in the firm
9
New cards
Accommodating Corporate Finance Needs
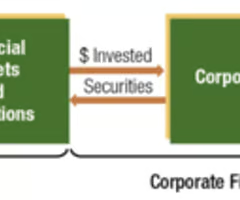
The financial markets serves as the mechanism whereby corporations (acting as deficit units) can obtain funds from investors (acting as surplus units).
10
New cards
Accommodating Investment Needs
Financial institutions serve as intermediaries to connect the investment management activity with the corporate finance activity.
11
New cards
How Financial Markets Facilitate Corporate Finance and Investment Management
12
New cards
Primary markets
facilitate the issuance of new securities
13
New cards
Secondary markets
facilitate the trading of existing securities, which allows for a change in the ownership of the securities
14
New cards
Liquidity
the degree to which securities can easily be liquidated (sold) without loss of value
15
New cards
If securities are illiquid how does that affect investors?
They might can't find a willing buyer for the security in the secondary market and may have to sell the security at a large discount just to attract a buyer
16
New cards
What can securities be classified as?
* Money market securities
* Capital market securities
* Derivative Securities
* Capital market securities
* Derivative Securities
17
New cards
Money Market Securities
Money markets facilitate the sale of short-term debt securities by deficit units to surplus units.
(Debt securities that have a maturity of one year or less.)
(Debt securities that have a maturity of one year or less.)
18
New cards
Capital market securities
facilitate the sale of long-term securities by deficit units to surplus units
19
New cards
Bonds
long-term debt securities issues by the Treasury, government agencies, and corporations to finance their operations (Capital market securities)
20
New cards
Mortgages
Long-term debt obligations created to finance the purchase of real estate (Capital market securities)
21
New cards
Mortgage-backed securities
debt obligations representing claims on a package of mortgages (Capital market securities)
22
New cards
Stocks
Represent partial ownership in the corporations that issued them
(Capital market securities)R
(Capital market securities)R
23
New cards
Derivative securities
financial contracts whose values are derived from the values of underlying assets
24
New cards
Speculation
allow an investor to speculate on movements in the value of underlying assets without having to purchase those assets (Derivative securities)
25
New cards
Risk management
financial institutions and other firms can use derivative securities to adjust the risk of their existing investments in securities (Derivative securities)
26
New cards
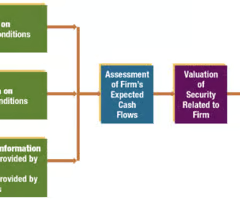
Valuation of securities: impact of information on valuation
* estimate future cash flows by obtaining information that may influence a stock's future cash flows
* use economic or industry information to value a security
* use published opinions about the firm's management to value a security
* use economic or industry information to value a security
* use published opinions about the firm's management to value a security
27
New cards
Use of Information to Make Investment Decisions
28
New cards
Valuation of securities: impact of the internet on valuation
* more timely pricing
* more accurate pricing
* more informative pricing
* more accurate pricing
* more informative pricing
29
New cards
Valuation of securities: impact of behavioral finance on valuation
Various conditions can affect investor psychology
30
New cards
Behavioral finance
the application of psychology to make financial decisions
31
New cards
Uncertainty surrounding valuation of securities
limited information leads to uncertainty in the valuation of securities
32
New cards
Securities Regulations on Financial Disclosure: Required Disclosure
The Securities Act of 1933
\
intended to ensure complete disclosure of relevant financial information on publicly offered securities and to prevent fraudulent practices in selling these securities
\
intended to ensure complete disclosure of relevant financial information on publicly offered securities and to prevent fraudulent practices in selling these securities
33
New cards
Securities Regulations on Financial Disclosure: Required Disclosure
The Securities Exchange Act of 1934
extended the disclosure requirements to secondary market issues
extended the disclosure requirements to secondary market issues
34
New cards
Securities Regulations on Financial Disclosure: Regulatory Response to Financial Reporting Scandals
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
\
required that firms provide more complete and accurate financial information
\
required that firms provide more complete and accurate financial information
35
New cards
International Financial Markets
Financial markets vary across the world in terms of:
* Degree of financial market development
* Volume of funds transferred from surplus to deficit units
* Degree of financial market development
* Volume of funds transferred from surplus to deficit units
36
New cards
International Integration of Financial Markets
under favorable economic conditions this allows governments and corporations easier access to funding from creditors or investors in other countries
37
New cards
Role of Foreign Exchange Market
International financial transactions normally require the exchange of currencies and this facilitates this exchange
38
New cards
Financial institutions are needed to resolve the limitations caused by _________ such as limited information regarding the creditworthiness of borrowers.
market imperfections
39
New cards
Role of Depository Institutions
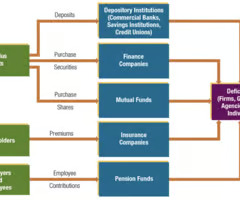
accept deposits from surplus units and provide credit to deficit units through loans and purchases of securities
* offer liquid deposit accounts to surplus units
* provide loans of the size and maturity desired by deficit units
* accept the risk on loans provided
* have more expertise in evaluating creditworthiness
* diversify their loans among numerous deficit units
* offer liquid deposit accounts to surplus units
* provide loans of the size and maturity desired by deficit units
* accept the risk on loans provided
* have more expertise in evaluating creditworthiness
* diversify their loans among numerous deficit units
40
New cards
Role of Depository Institutions: Commercial Banks
* most dominant type of depository institution
* transfer deposit funds to deficit units through loans or purchase of debt securities
* Federal Funds Market: facilities the flow of funds between depository institutions
* transfer deposit funds to deficit units through loans or purchase of debt securities
* Federal Funds Market: facilities the flow of funds between depository institutions
41
New cards
Role of Depository Institutions: Savings Institutions
* a.k.a. thrift institutions and include Savings and Loans (S&Ls) and Savings Banks
* concentrate on residential mortgage loans
* concentrate on residential mortgage loans
42
New cards
Role of Depository Institutions: Credit Unions
* nonprofit organizations
* restrict business to its members with a common bond
* restrict business to its members with a common bond
43
New cards
Role of Non-depository Institutions: Finance companies
obtain funds by issues securities and lend the funds to individuals and small businesses
44
New cards
Role of Non-depository Institutions: Mutual funds
sell shares to surplus units and use the funds received to purchase a portfolio of securities
45
New cards
Role of Non-depository Institutions: Securities firms
provide a wide variety of functions in markets
(Broker, Underwriter, Dealer, Advisory)
(Broker, Underwriter, Dealer, Advisory)
46
New cards
Role of Non-depository Institutions: Insurance companies
provide ______ policies that reduce the financial burden association with death, illness, and damage to property
\
charge premiums and invest in financial markets
\
charge premiums and invest in financial markets
47
New cards
Role of Non-depository Institutions: Pension funds
manage funds until they are withdrawn for retirement
48
New cards
Financial institutions
facilitates the flow of funds from individual surplus units (investors) to deficit units
49
New cards
Comparison of Roles among Financial Institutions
50
New cards
Role of Financial Institutions: Institutional Role as a Monitor of Publicly Traded Firms
Since insurance companies, pension funds, and some mutual funds are major investors in stocks, they can influence the management of publicly traded firms.
\
By serving as activist shareholders, they can help ensure that managers of publicly held corporations make appropriate decisions that are in the best interest of the shareholders.
\
By serving as activist shareholders, they can help ensure that managers of publicly held corporations make appropriate decisions that are in the best interest of the shareholders.
51
New cards
Relative Importance of Financial Institutions
* Households with savings are served by depository institutions.
* Households with deficient funds are served by depository institutions and finance companies.
* Several agencies regulate the various types of financial institutions, and the various regulations may give some financial institutions a comparative advantage over others.
* Households with deficient funds are served by depository institutions and finance companies.
* Several agencies regulate the various types of financial institutions, and the various regulations may give some financial institutions a comparative advantage over others.
52
New cards
Institutional Sources and Uses of Funds: Commercial banks
Source: Deposits from households, businesses, and government agencies
\
Use: Purchases of government and corporate securities; loans to businesses and households
\
Use: Purchases of government and corporate securities; loans to businesses and households
53
New cards
Institutional Sources and Uses of Funds: Savings institutions
Source: Deposits from households, businesses, and government agencies
\
Use: Purchases of government and corporate securities; mortgages and other loans to households; some loans to businesses
\
Use: Purchases of government and corporate securities; mortgages and other loans to households; some loans to businesses
54
New cards
Institutional Sources and Uses of Funds: Credit unions
Source: Deposits from credit union members
\
Use: Loans to credit union members
\
Use: Loans to credit union members
55
New cards
Institutional Sources and Uses of Funds: Finance companies
Source: Securities sold to households and businesses
\
Use: Loans to households and businesses
\
Use: Loans to households and businesses
56
New cards
Institutional Sources and Uses of Funds: Mutual funds
Source: Shares sold to households, businesses, and government agencies
\
Use: Purchases of long-term government and corporate securities
\
Use: Purchases of long-term government and corporate securities
57
New cards
Institutional Sources and Uses of Funds: Money market funds
Source: Shares sold to households, businesses, and government agencies
\
Use: Purchases of short-term government and corporate securities
\
Use: Purchases of short-term government and corporate securities
58
New cards
Institutional Sources and Uses of Funds: Insurance companies
Source: Insurance premiums and earnings from investments
\
Use: Purchases of long-term government and corporate securities
\
Use: Purchases of long-term government and corporate securities
59
New cards
Institutional Sources and Uses of Funds: Pension funds
Source: Employer/employee contributions
\
Use: Purchases of long-term government and corporate securities
\
Use: Purchases of long-term government and corporate securities
60
New cards
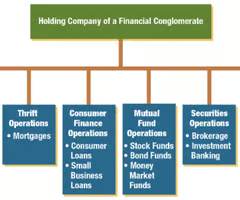
Organizational Structure of Financial Conglomerate
Typical organizational structure of a financial conglomerate
\
Operations of each type of financial service are commonly managed separately, a financial conglomerate offers advantages to customers who prefer to obtain all of their financial services from a single financial institution.
\
Operations of each type of financial service are commonly managed separately, a financial conglomerate offers advantages to customers who prefer to obtain all of their financial services from a single financial institution.
61
New cards
Global Consolidation of Financial Institutions
Many financial institutions have expanded internationally to capitalize on their expertise.
62
New cards
Systemic Risk
the spread of financial problems among financial institutions and across financial markets that could cause a collapse in the financial system
63
New cards
Example of Systemic Risk
During the credit crises of 2008 and 2009, mortgage defaults affected financial institutions in several ways.
* Many financial institutions that originated mortgages shortly before the crisis sold them o other financial institutions.
* Many other financial institutions that invested in mortgage-backed securities received lower payments as mortgage defaults occurred.
* Some financial institutions (esp securities funds) relied heavily on short-term debt to finance their operations and use their holdings of mortgage-backed securities as collateral.
* As mortgage defaults increased, there was an excess of unoccupied housing.
* Most financial institutions that invested heavily in equities experienced large losses on their investments during the credit crisis.
* Many financial institutions that originated mortgages shortly before the crisis sold them o other financial institutions.
* Many other financial institutions that invested in mortgage-backed securities received lower payments as mortgage defaults occurred.
* Some financial institutions (esp securities funds) relied heavily on short-term debt to finance their operations and use their holdings of mortgage-backed securities as collateral.
* As mortgage defaults increased, there was an excess of unoccupied housing.
* Most financial institutions that invested heavily in equities experienced large losses on their investments during the credit crisis.
64
New cards
Loanable Funds Theory
the market interest rate is determined by the factors that control the supply of and demand for loanable funds
Explains:
* Movements in the general level of interest rates in a particular country
* Why interest rates among debt securities of a given country vary
Explains:
* Movements in the general level of interest rates in a particular country
* Why interest rates among debt securities of a given country vary
65
New cards
Household Demand for Loanable Funds
Finances housing expenditures as well as the purchase of automobiles and household items
66
New cards
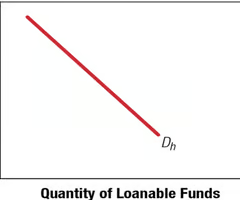
Relationship between Interest Rates and Household(Dh)/Business(Db) Demand for Loanable Funds
Inverse relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds demanded
67
New cards
Business Demand for Loanable Funds
* demand a greater quantity of loanable funds at any given point in time if interest rates are lower
* based on the number of projects that add value to the firm (projects that have positive NPVs)
* based on the number of projects that add value to the firm (projects that have positive NPVs)
68
New cards
Shifts in Demand for Loanable Funds
NPV: net present value of project
INV: initial investment
CFt: cash flow in period *t*
*k*: required rate of return on project
INV: initial investment
CFt: cash flow in period *t*
*k*: required rate of return on project
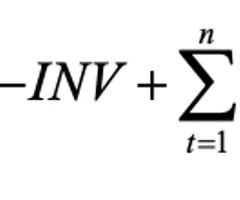
69
New cards
Government Demand for Loanable Funds
* demands loanable funds when planned expenditures are not covered by incoming revenues
* interest inelastic (insensitive to interest rates)...Expenditures and tax policies are independent to interest rates. Expenditures and tax policies are independent of the level of interest rates.
* interest inelastic (insensitive to interest rates)...Expenditures and tax policies are independent to interest rates. Expenditures and tax policies are independent of the level of interest rates.
70
New cards
Impact of Increased Government Deficit on the Government Demand for Loanable Funds
71
New cards
Foreign Demand for Loanable Funds
* country's demand for foreign funds depends on the interest rate differential between the two
* greater the differential, the greater the demand for foreign funds
* Quantity of U.S. loanable funds demanded by foreign governments will be inversely related to U.S. interest rates.
* greater the differential, the greater the demand for foreign funds
* Quantity of U.S. loanable funds demanded by foreign governments will be inversely related to U.S. interest rates.
72
New cards
Impact of Increased Foreign Interest Rates on the Foreign Demand for U.S. Loanable Funds
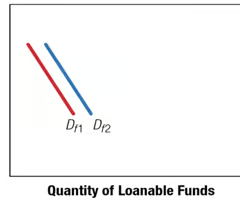
73
New cards
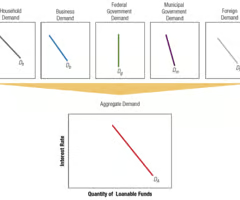
Determination of the Aggregate Demand Curve for Loanable Funds
The sum of the quantities demanded by the separate sectors at any given interest rate.
74
New cards
Supply of Loanable Funds: Households
largest supplier, but some supplied by government units
* more supply at higher interest rates
* supply by buying securities
* more supply at higher interest rates
* supply by buying securities
75
New cards
Supply of Loanable Funds: Effects of the Fed
By affecting the supply of loanable funds, the Fed's monetary policy affects interest rates.
76
New cards
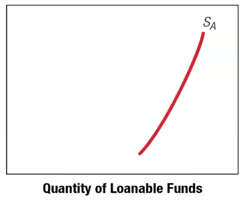
Aggregate Supply Curve for Loanable Funds
The combination of all sector supply schedules along with the supply of funds provided by the Fed's monetary policy.
77
New cards
Equilibrium Interest Rate - Algebraic Presentation
Aggregate Demand for Funds (Da)
Aggregate Demand for Funds (Da)
Da = Dh + Db + Dg + Dm + Df
Dh: household demand for loanable funds
Db: business demand for loanable funds
Dg: federal government demand for loanable funds
Dm: municipal government demand for loanable funds
Df: foreign demand for loanable funds
Dh: household demand for loanable funds
Db: business demand for loanable funds
Dg: federal government demand for loanable funds
Dm: municipal government demand for loanable funds
Df: foreign demand for loanable funds

78
New cards
Equilibrium Interest Rate - Algebraic Presentation
Aggregate Supply for Funds (Sa)
Aggregate Supply for Funds (Sa)
Sa = Sh + Sb + Sg + Sm + Sf
Sh: household supply for loanable funds
Sb: business supply for loanable funds
Sg: federal government supply for loanable funds
Sm: municipal government supply for loanable funds
Sf: foreign supply for loanable funds
Sh: household supply for loanable funds
Sb: business supply for loanable funds
Sg: federal government supply for loanable funds
Sm: municipal government supply for loanable funds
Sf: foreign supply for loanable funds

79
New cards
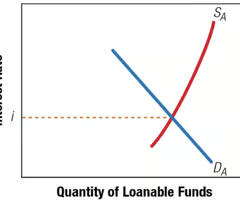
Equilibrium Interest Rate - Graphical Presentation
\
Combining aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves allows comparison of total amount demanded to total amount supplied.
\
At equilibrium interest rate *i*, the supply of loanable funds is equal to the demand for loanable funds.
\
At interest rate above *i*, there is a surplus of loanable funds.
\
At interest rate below *i*, there is a shortage of loanable funds.
Combining aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves allows comparison of total amount demanded to total amount supplied.
\
At equilibrium interest rate *i*, the supply of loanable funds is equal to the demand for loanable funds.
\
At interest rate above *i*, there is a surplus of loanable funds.
\
At interest rate below *i*, there is a shortage of loanable funds.
80
New cards
Impact of economic growth on interest rates
Puts upward pressure on interest rates by shifting demand for loanable funds outward

81
New cards
Impact of Inflation on Interest Rates
Puts upward pressure on interest rates by shifting supply of funds inward and demand for funds outward.

82
New cards
Impact of an Increase in Inflationary Expectations on Interest Rates
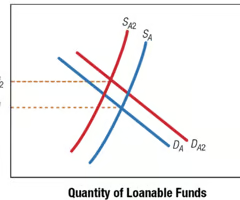
83
New cards
Impact of Monetary Policy on Interest Rates
When the Fed reduces/increases the money supply it reduces/increases the supply of loanable funds, putting upward/downward pressure on interest rates.
84
New cards
Impact of the Budget Deficit on Interest Rates: Crowding-out Effect
Given a certain amount of loanable funds supplied to the market, excessive government demand for funds tends to "crowd out" the private demand for funds as the Treasury issues more and more securities to finance deficits.
85
New cards
Flow of Funds between the Federal Government and the Private Sector
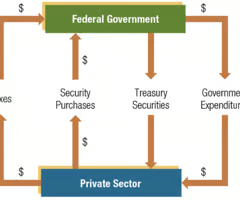
86
New cards
Impact of Foreign Flows of Funds on Interest Rates
Interest rate for a certain currency is determined by the demand for funds in that currency and the supply of funds available in that currency.
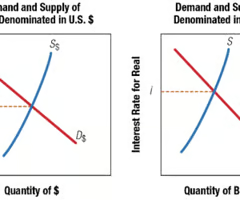
87
New cards
Forecasting Interest Rates: Net Demand (ND)
Da = Dh + Db + Dg + Dm + Df
Dh: household demand for loanable funds
Db: business demand for loanable funds
Dg: federal government demand for loanable funds
Dm: municipal government demand for loanable funds
Df: foreign demand for loanable funds
\
Sa = Sh + Sb + Sg + Sm + Sf
Sh: household supply for loanable funds
Sb: business supply for loanable funds
Sg: federal government supply for loanable funds
Sm: municipal government supply for loanable funds
Sf: foreign supply for loanable funds
Dh: household demand for loanable funds
Db: business demand for loanable funds
Dg: federal government demand for loanable funds
Dm: municipal government demand for loanable funds
Df: foreign demand for loanable funds
\
Sa = Sh + Sb + Sg + Sm + Sf
Sh: household supply for loanable funds
Sb: business supply for loanable funds
Sg: federal government supply for loanable funds
Sm: municipal government supply for loanable funds
Sf: foreign supply for loanable funds
88
New cards
Future Demand for Loanable Funds Depends on future:
* foreign demand for U.S. funds
* household demand for funds
* business demand for funds
* government demand for funds
* household demand for funds
* business demand for funds
* government demand for funds
89
New cards
Future Supply of Loanable Funds depends on:
* future supply by households and others
* future foreign supply of loanable funds in the U.S.
* future foreign supply of loanable funds in the U.S.
90
New cards
Framework for Forecasting Interest Rates
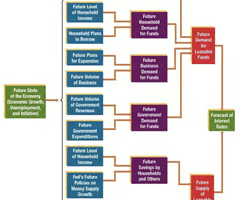
91
New cards
Why Debt Security Yields Vary
Yields on debt securities are affected:
* credit (default) risk
* liquidity
* tax status
* term to maturity
* credit (default) risk
* liquidity
* tax status
* term to maturity
92
New cards
Credit (default) Risk
Investors must consider the -creditworthiness of the security issuer.
* All else being equal, securities with a higher degree of default risk must offer higher yields.
* Especially relevant for longer term securities.
* All else being equal, securities with a higher degree of default risk must offer higher yields.
* Especially relevant for longer term securities.
93
New cards
Use of Rating Agencies to Assess Credit Risk
Rating Agencies: Investors can personally assess the creditworthiness of corporations that issue bonds, but they may prefer to rely on bond ratings provided by rating agencies.
94
New cards
Rating Classifications by Rating Agencies
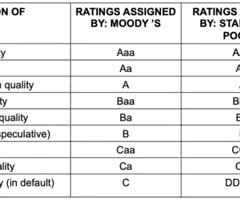
95
New cards
Credit Ratings and Risk Premiums over Time
Rating agencies can change bond ratings over time in response to changes in the issuing firm's financial condition.
96
New cards
Accuracy of Credit Ratings
The ratings issues by the agencies are opinions, not guarantees. Bonds that are assigned a low credit rating experience default more frequently than bonds assigned a high credit rating, which suggests that the rating can be a useful indicator of credit risk. Credit rating agencies do not always detect firms' financial problems.
97
New cards
Oversight of Credit Rating Agencies
The Financial Reform Act of 2010 established an Office of Credit Ratings within the Securities and Exchange Commission in order to regulate credit rating agencies. Rating agencies must establish internal controls.
98
New cards
The lower a security's _______ the higher the yield preferred by an investor.
Liquidity
Debt securities with a short-term maturity or an active secondary. market have greater liquidity.
Debt securities with a short-term maturity or an active secondary. market have greater liquidity.
99
New cards
Tax Status
* Investors are more concerned with after-tax income.
* Taxable securities must offer a higher before-tax yield.
* Taxable securities must offer a higher before-tax yield.
100
New cards
Formula for Expected Yields After-Tax