Organic molecules (proteins)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Proteins
collagen fiber structure
function is hemoglobin
amino acids as the building blocks
STRUCTURE DETERMINES FUNCTION
If it loses shape then it has denatured and non-functional
build by dehydration synthesis when many amino acids are linked together
Hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions between amino
acids, hydrogen bonding, disulfide bridges all
contribute to the shape a protein will assume its function
CATALYSTS FOR METABOLIC REACTIONS; STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS; MOVEMENT; TRANSPORT; BUFFERS; DEFENSE; CONTROL AND COORDINATION OF ACTIVITIES.
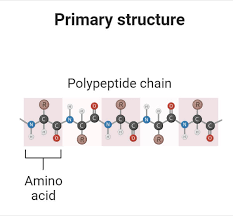
Primary structure
the sequence of amino acids forms the polypeptide chain
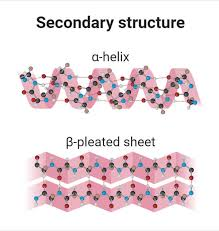
secondary structure
the primary structure chain forms spirals (alpha helix) and sheets (beta sheets)
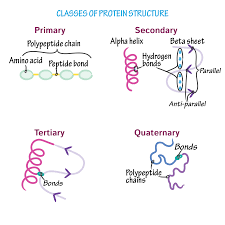
Tertiary structure
folding and coiling due to interactions between R groups and surrounding water
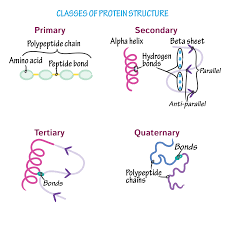
Quaternary structure
association of two or more polypeptide chains with each other
Enzymes
a type of protein that acts as a catalyst to make chemical reactions in the body faster
has specific active sites for specific substrates to bind with for SPECIFIC FUNCTION
lowers activation energy
Nucleic acids
Nucleotide building blocks
has a PHOSPHATE GROUP, SUGAR, NITROGENOUS BASE
Nitrogenous bases are Purines and Pyrimidines
purines = Adenine, Guanine
pyrimidines = cytosine, THYMINE (DNA), Uracil (RNA)
STORAGE AND PROCESSING OF GENETIC INFORMATION
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines
Cytosine
THYMINE (DNA)
URACIL (RNA)
RNA
Ribose
located in cytoplasm
single strand
Cytosine, Uracil
DNA
deoxyribose
located in the nucleus
double strand
cytosine and thymine
adenosine triphosphate
3 phosphate group
energy source
Adenosine Diphosphate
2 phosphate group
energy source
Adenosine monophosphate
1 phosphate group