Operations Management: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.5
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is operations management
Operations Management involves the planning, organising, coordinating and controlling of all activities involved in the transformation of inputs into outputs. It plays an important role in the business’s success.
The aim of operations management (operational targets)
Operational targets:
Effectiveness of operations
Consistently producing products in the;
Right qualities
Right specifications
Efficiency of operations
Producing and delivering products in a cost-efficent manner
Sustainability of operations
Meeting the company’s and the government’s sustainability targets and requirements
Job production
A labour-intensive manufacturing method that involves making customized, one-off, and unique goods or services that meet the specific needs of a specific customer.
Each product is completed before the next is started
Advantages of Job Production
Higher customer satisfaction as products are made specifically for them.
Possible higher prices.
High quality due to skilled workers (USP).
Higher employee motivation due to changing requirements.
Low inventory costs: No need to stockpile finished goods (made-to-order).
Direct interaction with customers fosters brand loyalty.
Disadvantages of Job Production
Labour-intensive, so higher labour costs.
Time-consuming and product-specific decisions must be made → less potential for automation.
Fewer economies of scale due to low output over time.
Possible cash flow challenges as each order is unique and will thus have different costs involved
Batch production
Involves producing a set of identical products
Each batch is fully completed before production switches to another batch.
Each batch may have slightly different specifications
Advantages of Batch Production:
More variety within a given product.
More customers are satisfied overall.
Some flexibility to change the product between batches.
Lower unit costs → more economies of scale as more products are made at once.
If there is a high demand, the business can satisfy it, meaning more profit in absolute terms
Mass production
Involves large-scale production of a standardized product using production-line technology, making it heavily automated
Advantages of Mass Production:
Economies of scale (high volume).
High labour efficiency (workers specialize in one job).
Consistent brand image (standardized products).
Lower labour costs (low labour intensity).
Fewer issues due to lack of motivation.
Disadvantages of Mass Production
High initial set-up costs (machinery purchases).
Lower employee motivation (specialization → repetitive tasks).
Difficult to offer different product choices to consumers.
Higher storage costs (high volume of products).
Disadvantages of Mass/Flow Production
High set-up costs (must buy production line machinery).
Lower employee motivation due to repetitive tasks.
More difficult to offer different product choices to consumers.
Higher storage costs due to higher production volume
Higher costs for mass marketing / above the line promotion
Mass customization
Uses technology to produce a variety of models on the same production line.
Combines high production volume (mass production) with flexibility to tailor products to customer demands (e.g., car configuration)
Advantages of Mass Customization
Potentially higher pricing due to higher customization and general uniqueness of each product
Economies of scale through high production volume
Higher customer satisfaction
Disadvantages of Mass Customization
Heavy investment in technology (capital-intensive).
High set-up costs.
Choosing the Most Appropriate Production Method Depends On
The best method depends on:
Demand for the product (size of the market):
High volume → mass production.
Low volume → job/batch production.
Demand for customization vs. standardization.
Financial considerations:
Initial capital expenditure.
Source of finance.
Ongoing production costs.
Marketing considerations:
Pricing and profitability.
Product positioning (quality vs. standardization, USP, personalized product).
Operations considerations:
Loss of operational flexibility.
Economies of scale.
Technical capabilities (R&D and worker skills).
Problems of Changing Production Methods
Demand factors:
Total market volume and consistency of demand.
Financial constraints:
Capital investment and ongoing costs.
Marketing challenges:
Aligning product positioning with new method.
Operational disruptions:
Loss of flexibility, scaling issues, or skill gaps.

5.4 Location
Location
Refers to the geographical position of the business.
Factors that affect the location of a business (Quantitative)
Cost of rent/mortgage.
Labour costs
Government policies,
Distance to market
How far from customers
Distance to inputs.
Availability of government grants and incentives
Factors that affect the location of a business (Qualitative)
External economies of scale
Infrastructure
Potential employees
Near suppliers.
Political and legal factors.
E.g. Maximum working hours.
Brand image
location of competition
Space for expansion
Quality of life in an area
How attractive is the area
Facilities quality
Standard of living
Ways of reorganizing production both nationally & internationally [AO3]
Offshoring
Refers to when a business relocates part or all of its functions and processes to another country
the part of the business might stay internally or go to an external company
Advantages of Offshoring
Lower costs
Labour costs
Import costs
Government tax advantages
Potentially access specialized labour
Leads to higher production quality,
decision-making-factors
Less strict regulation on
Health and safety
Environmental protection.
Employee rights
Can be closer to market where products are sold
Can lead to better market research thus better decision-making
Disadvantages of Offshoring
Culture/language barriers
Can lead to misunderstandings
Or misinterpretation of the task.
Lower quality output
Or lower productivity.
Increased transportation costs.
As finished goods may have to be transported back
Negative brand image
If employees are not treated well (ethically)
If the environment is damaged in the process
Redundancy of home country workers.
As jobs are moved overseas.
Bad PR for the company
Demotivation of remaining workers
Loss of control over quality
Outsourcing
Refers to when a business subcontracts a process, such as packaging or manufacturing, to another business or organization.
The business buys the service from another company rather than doing it internally
(Can be onshore or offshore)
Advantages of Outsourcing
Business can focus on core functions.
Increases efficiency and productivity
Can lead to lower costs
The outsourced business may have specialized equipment that the business would not invest in given operations.
Quick increase in capacity,
without needing internal methods of growth.
Cost advantage
Disadvantages of Outsourcing
Loss of control
The business loses control over the operation methods used for that specific function
Can lead to lower customer satisfaction due to declining quality.
Redundancy after outsourcing
Can lead to negative publicity as the business may be seen as unethical.
Also lead to resistance from existing workforce
The outsourcing supplier may not deliver according to business's needs
Deliver on time so other operations are not held up
Could cause internal diseconomies of scale.
Working conditions of other producer
Negative brand image affect brand image of business which is outsourcing its functions
Unethical practices of producer
Insourcing
Refers to when a business transfers a previously outsourced function back to the organization's own resources
Advantages of Insourcing
Assurance of quality
Methods and standards can be better overseen and changed by the business.
Cheaper than paying the outsourced organization
Disadvantages of Insourcing
May cause short term reduction in cash flow
Purchasing specialist/ required equipment
May distract the business from its core Function
Must recruit and train employees to work in that part of the business
Must oversee quality.
Can negatively impact cash
takes Longer to generate revenue.
5.5 Break-Even Analysis
Governing Equation for Break-Even Analysis
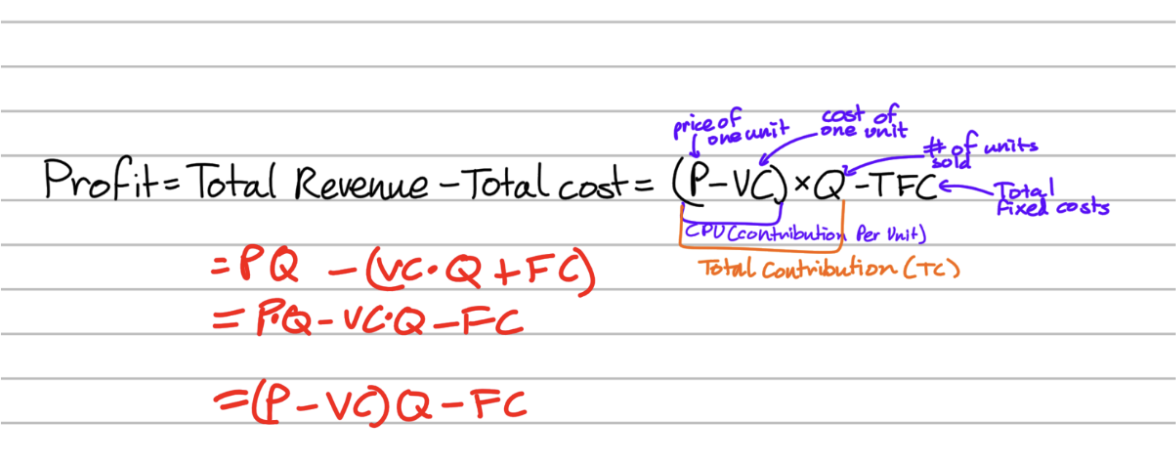
Contribution per unit
CPU (Contribution Per Unit)
The amount of money a business makes from selling each unit of a product after covering variable costs.
CPU = Price - Variable cost
Total Contribution
The total amount of money which contributes to the fixed costs
The total profit after selling all units of production and covering variable costs
TC=CPUxQuantity = (Price-Variable cost)x Quantity
Break-even quantity
The level of output or production at which a business's sales generate just enough revenue to cover all costs
No profit or loss is made at this point.
0 = Total Revenue - Total Costs
Solve for Break-even quantity (BEQ)
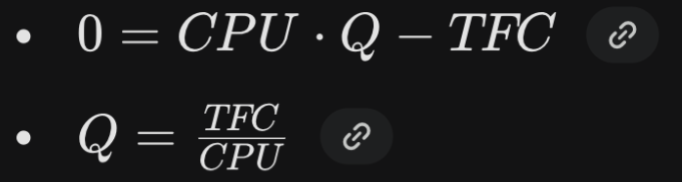
Solve for Break-Even Revenue
Revenue = Price Quantity
Break-even Revenue = Price Break-Even Quantity
Break-Even Point
The point where the total revenue and total costs are equal
Target Profit
The amount of profit that a business aims to earn within a given time period
This is usually given and you will have to solve for
Quantity
Price
Target Profit output (Q)
The quantity of sales required to reach the firm's target profit
Set Q as unknown
Target price
The price of a product per unit in order to reach the firm's target profit
Set price as unknown
Break-even price
A special case of target price where the target profit equals , namely when the business breaks even
Margin of safety
The difference between how much a business sells and its BEQ
Steps for drawing a break-even chart
X axis is "Sales quantity (product)"
Y-axis is "Costs and revenues (currency)"
Step 1: Calculate BEQ & B-E Revenue
Step 2:
Make x-axis range 2x or 1.5x BEQ
Make y-axis range 2x or 1.5x BE Revenue
Step 3: Draw total fixed cost line
Step 4: Add Break-even point on chant (BEQ, BE-Revenue)
Step 5: Draw total Revenue line connecting (0,0) to BEP
Step 6: Draw total cost line from TFC to BEP
Step 7: Title and labels:
Break-even chart for xxx
Axes (see above)
Label BEP, BEQ, BE- Revenue
Step 8: Add arrows & a dotted line for margin of safety.
Effect of price on the profit and margin of safety
Increase in price
Profit = (Price -Variable cost)x Quantity-Fixed cost
Revenue = Price x Quantity
BEQ ↓ CPU ↑ Margin of safety ↑
Margin of Safety increases because the BEP is at a lower quantity
Decrease in price
Opposite of above
Effect of fixed costs on the profit and margin of safety
Increase in fixed costs.
TC = FC + VC
TC shifts upwards (y-int)
CPU stays the same
Profit margin.
GPM stays the same
BEQ ↑ Margin of safely ↓
Effect of Variable cost per unit on profit and margin of safety
Increase in variable cost:
TC = FC + Q x VC
TC will pivot upwards.
CPU ↓
CPU= Price-Variable costs
Profit margin ↓
BEQ ↑
Margin of Sales ↓
Profit ↓
Decrease
Opposite of above
Advantages of Break-Even Analysis
Visual and easy to interpret
Provides guidelines
Will the business make a profit?
How close to a loss is the business
Facilitates Scenario Analysis
profit under different.
at situations
Check
Can be of value in supporting a business's application for a bank loan
Disadvantages of Break-Even Analysis
Costs and prices change frequently
Break even analysis may not be realistic
Costs and Revenues are not usually Straight lines
Total Revenue line does not consider demand
TC: Economies of scale may exist
Assumes all stock is sold