Geography GCSE Paper 1 (copy)
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
3.1.1.1 ~natural hazards~
HAZARD RISK
The probability or chance that a natural hazard may take place.
3.1.1.1 ~natural hazards~
NATURAL HAZARD
A natural event (for example an earthquake, volcanic eruption, tropical storm, flood) that threatens people or has the potential to cause damage, destruction and death.

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
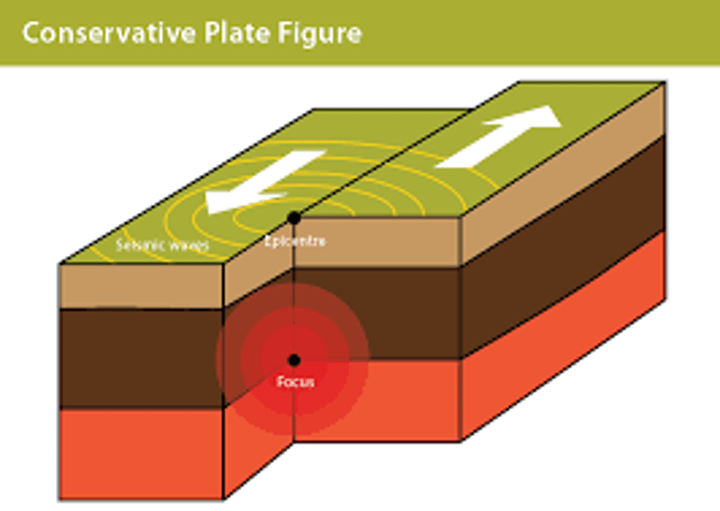
CONSERVATIVE PLATE MARGIN
Tectonic plate margin where two tectonic plates slide past each other.
3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
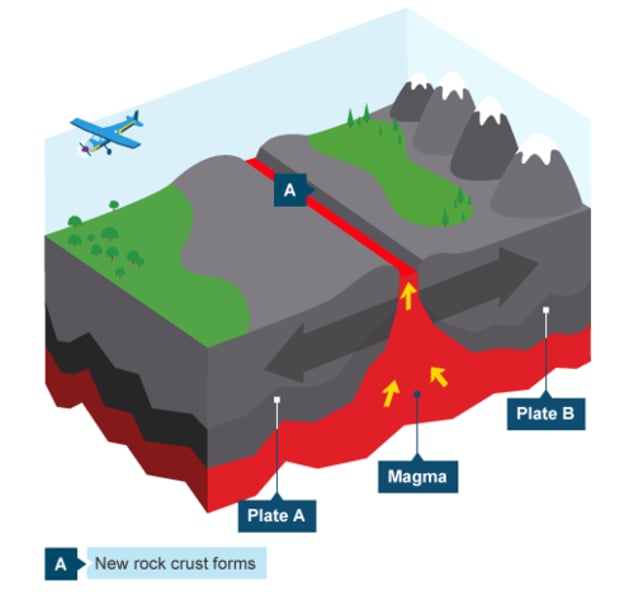
CONSTRUCTIVE PLATE MARGIN
Tectonic plate margin where rising magma adds new material to plates that are diverging or moving apart.
3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
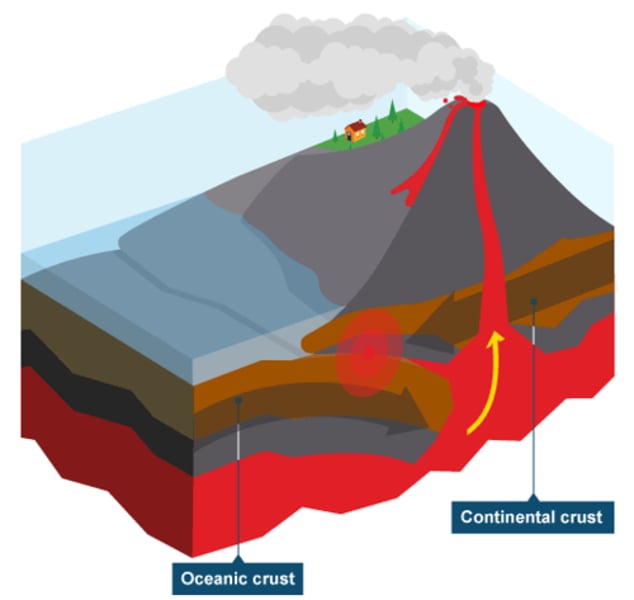
DESTRUCTIVE PLATE MARGIN
Tectonic plate margin where two plates are converging or coming together and oceanic plate is subducted. It can be associated with violent earthquakes and explosive volcanoes.
3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
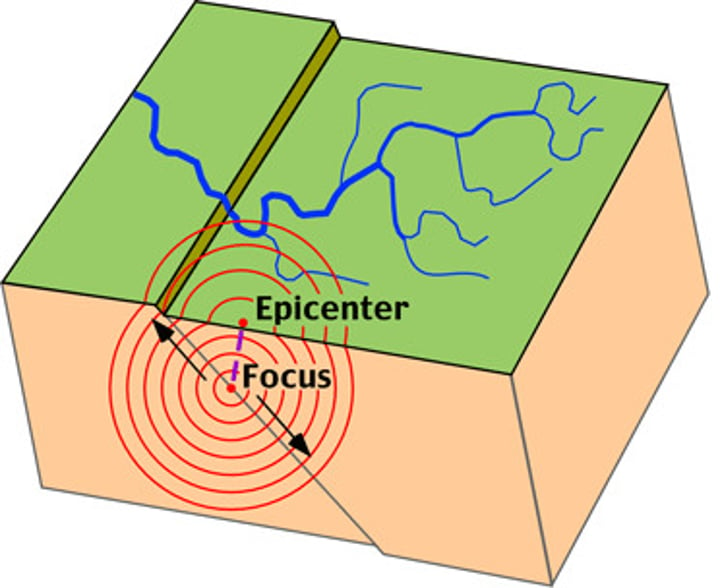
EARTHQUAKE
A sudden or violent movement within the Earth's crust followed by a series of shocks.
3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
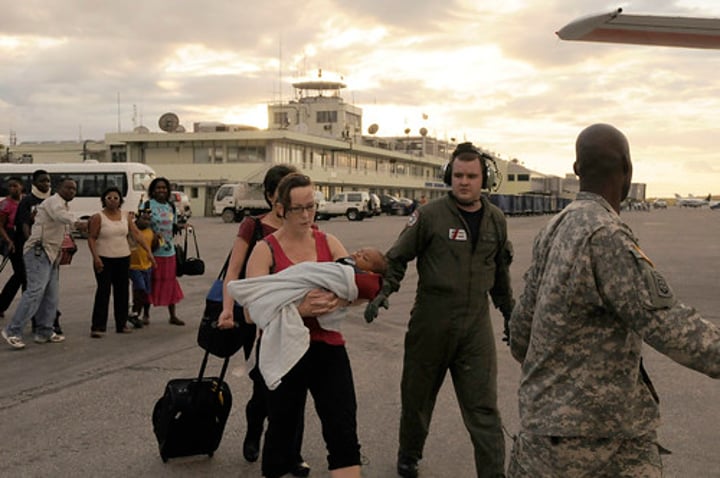
IMMEDIATE RESPONSES
The reaction of people as the disaster happens and in the immediate aftermath.

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
LONG-TERM RESPONSES
Later reactions that occur in the weeks, months and years after the event.

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
MONITORING
Recording physical changes, such as earthquake tremors around a volcano, to help forecast when and where a natural hazard might strike.

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
PLATE MARGIN
The margin or boundary between two tectonic plates.
3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
PLANNING
Actions taken to enable communities to respond to, and recover from, natural disasters, through measures such as emergency evacuation plans, information management, communications and warning systems

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
PREDICTION
Attempts to forecast when and where a natural hazard will strike, based on current knowledge. This can be done to some extent for volcanic eruptions (and tropical storms), but less reliably for earthquakes.

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
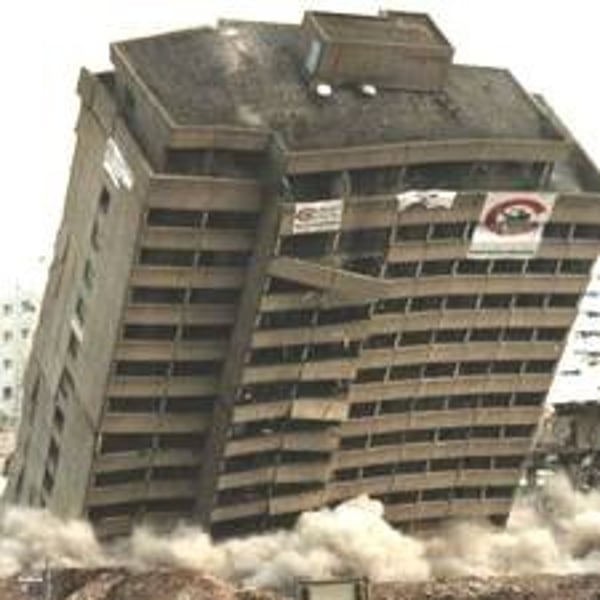
PRIMARY EFFECTS
The initial impact of a natural event on people and property, caused directly by it, for instance the ground buildings collapsing following an earthquake.

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards
PROTECTION
Actions taken before a hazard strikes to reduce its impact, such as educating people or improving building design.

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
SECONDARY EFFECTS
The after-effects that occur as indirect impacts of a natural event, sometimes on a longer timescale, for instance fires due to ruptured gas mains resulting from the ground shaking.
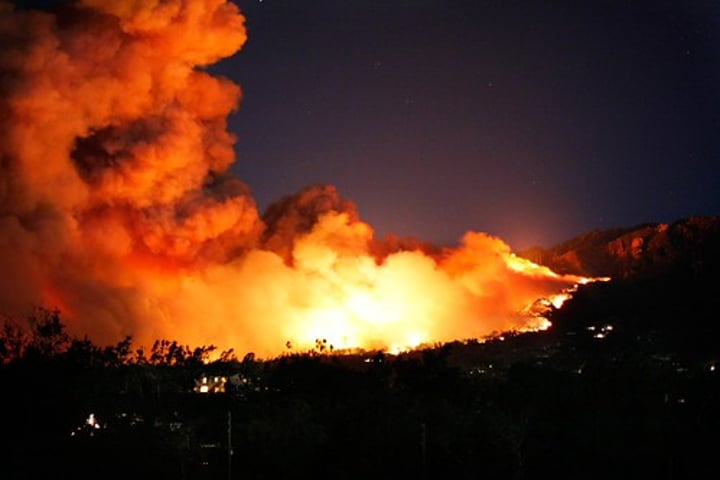

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
TECTONIC HAZARD
A natural hazard caused by movement of tectonic plates (including volcanoes and earthquakes).
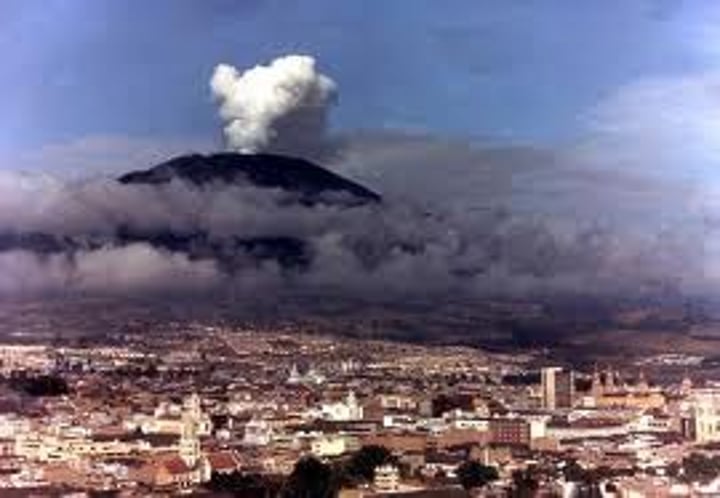

3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
TECTONIC PLATE
A rigid segment of the Earth's crust which can 'float' across the heavier, semimolten rock below. Continental plates are less dense, but thicker than oceanic plates.
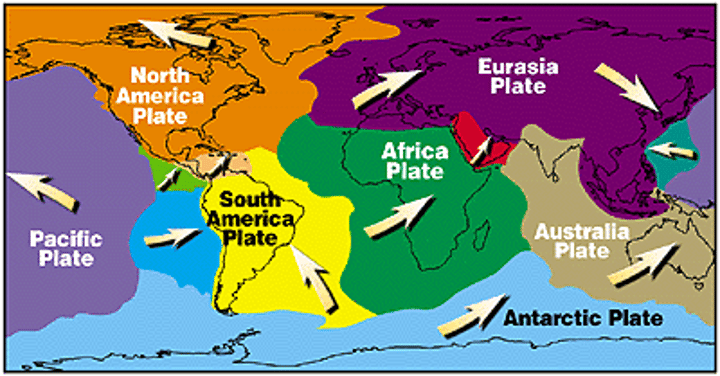
3.1.1.2 ~tectonic hazards~
VOLCANO
An opening in the Earth's crust from which lava, ash and gases erupt.

3.1.1.3 ~weather hazards~
ECONOMIC IMPACT
The effect of an event on the wealth of an area or community.

3.1.1.3 ~weather hazards~
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
Th effect of an event on the landscape and ecology of the surrounding area.

3.1.1.3 ~weather hazards~
EXTREME WEATHER
This is when a weather event is significantly different from the average or usual weather pattern, and is especially severe or unseasonal. This may take place over one day or a period of time. A severe snow blizzard or heat wave are two examples of extreme weather in the UK.

3.1.1.3 ~weather hazards~
GLOBAL ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION
The worldwide system of winds, which transports heat from tropical to polar latitudes. In each hemisphere, air also circulates through the entire depth of the troposphere which extends up to 15 km.
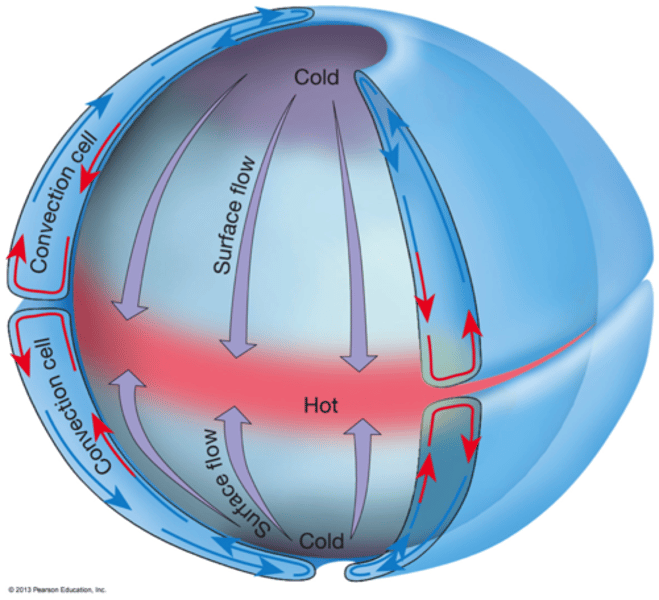
3.1.1.3 ~weather hazards~
MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
Techniques of controlling, responding to, or dealing with an event.

3.1.1.3 ~weather hazards~
SOCIAL IMPACT
The effect of an event on the lives of people or community.

3.1.1.3 ~weather hazards~
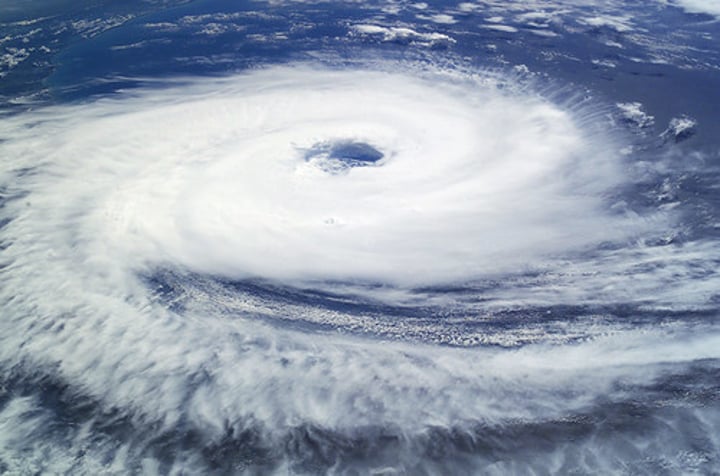
TROPICAL STORM (hurricane, cyclone, typhoon)
An area of low pressure with winds moving in a spiral around the calm central point called the eye of the storm. Winds are powerful and rainfall is heavy.

3.1.1.4 ~climate change~
ADAPTATION
Actions taken to adjust to natural events such as climate change, to reduce potential damage, limit the impacts, take advantage of opportunities, or cope with the consequences.

3.1.1.4 ~climate change~
CLIMATE CHANGE
A long-term change in the earth's climate, especially a change due to an increase in the average atmospheric temperature.

3.1.1.4 ~climate change~
MITIGATION
Action taken to reduce or eliminate the long-term risk to human life and property from natural hazards, such as building earthquake-proof buildings or making international agreements about carbon reduction targets.

3.1.1.4 ~climate change~
ORBITAL CHANGES
Changes in the pathway of the Earth around the Sun.
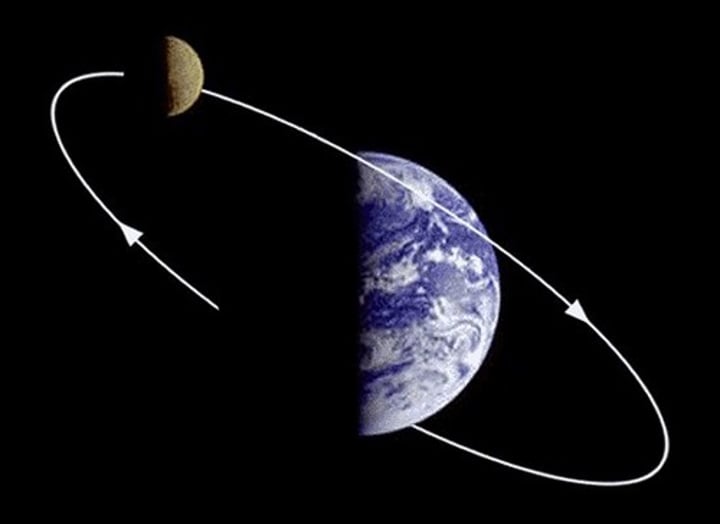
3.1.1.4 ~climate change~
QUATERNARY PERIOD
The period of geological time from about 2.6 million years ago to the present. It is characterized by the appearance and development of humans and includes the Pleistocene and Holocene Epochs.
3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
ABIOTIC
Relating to non-living things.

3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
BIOTIC
Relating to living things.

3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
CONSUMER
A creature that eats herbivores and/or plant matter.

3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
DECOMPOSER
An organism such as a bacterium or fungus, that breaks down dead tissue, which is then recycled to the environment.

3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
ECOSYSTEM
A community of plants and animals that interact with each other and their physical environment.

3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
FOOD CHAIN
The connections between different organisms (plants and animals) that rely on one another as their source of food.
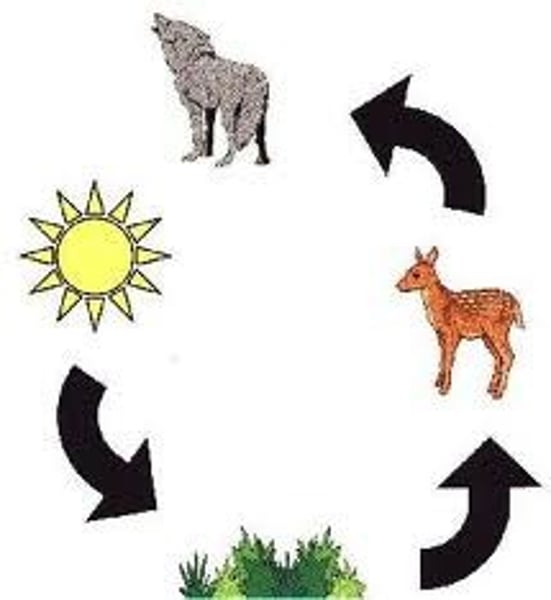
3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
FOOD WEB
A complex hierarchy of plants and animals relying on each other for food.
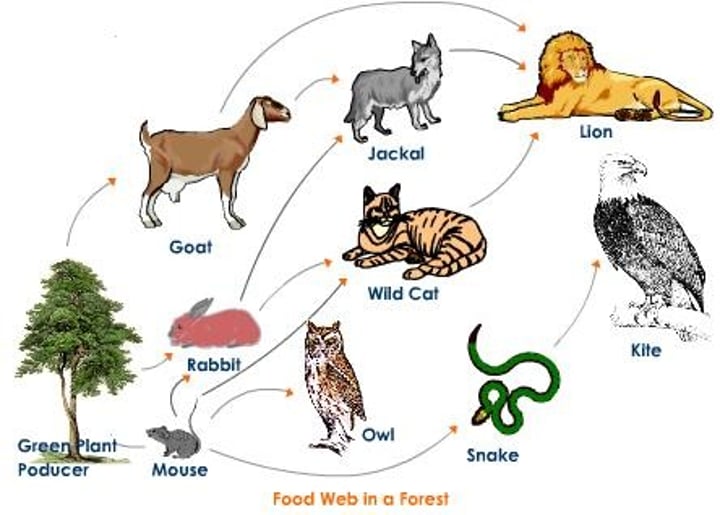
3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
NUTRIENT CYCLING
A set of processes whereby organisms extract minerals necessary for growth from soil or water, before passing them on through the food chain - and ultimately back to the soil and water.
3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
GLOBAL ECOSYSTEM
Very large ecological areas on the earth's surface (or biomes), with fauna and flora (animals and plants) adapting to their environment. Examples include tropical rainforest and hot desert.

3.1.2.1 ~ecosystems~
PRODUCER
An organism or plant that is able to absorb energy from the sun through photosynthesis.

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
BIODIVERSITY
The variety of life in the world or a particular habitat.

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
COMMERCIAL FARMING
Farming to sell produce for a profit to retailers or food processing companies.

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
DEBT REDUCTION
Countries are relieved of some of their debt in return for protecting their rainforests.

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
DEFORESTATION
The chopping down and removal of trees to clear an area of forest.
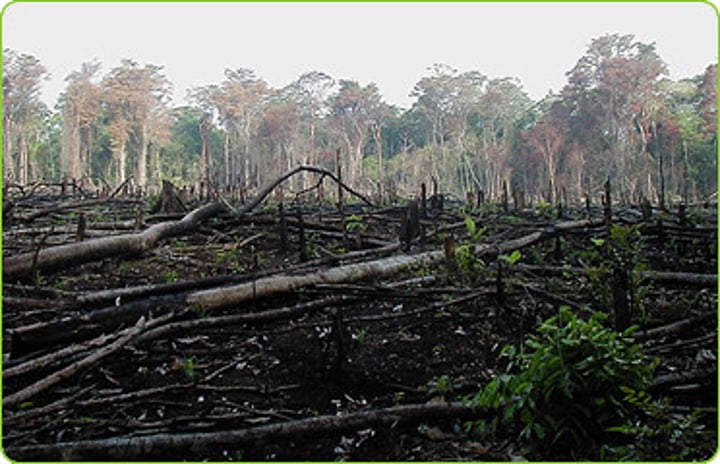

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
ECOTOURISM
Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the wellbeing of the local people, and may involve education. It is usually carried out in small groups and has minimal impact on the local ecosystem.

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
LOGGING
The business of cutting down trees and transporting the logs to sawmills
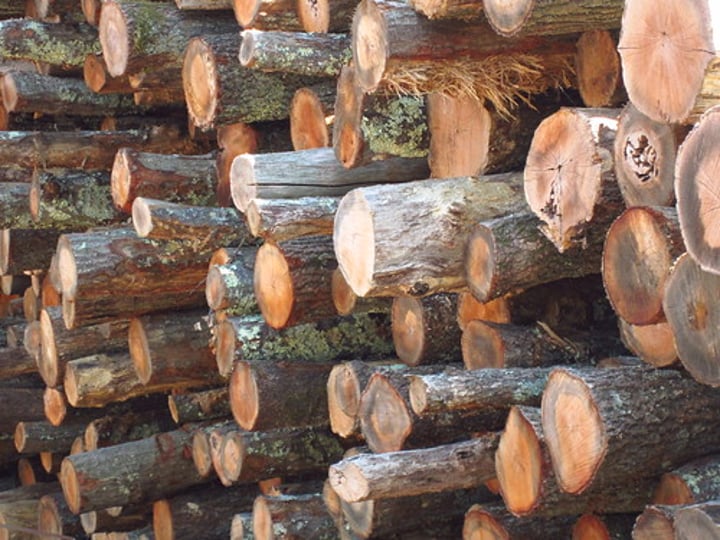

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
MINERAL EXTRACTION
The removal of solid mineral resources from the earth. These resources include ores, which contain commercially valuable amounts of metals, such as iron and aluminum; precious stones, such as diamonds; building stones, such as granite; and solid fuels, such as coal and oil shale

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
SELECTIVE LOGGING
The cutting out of trees which are mature or inferior, to encourage the growth of the remaining trees in a forest or wood.

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
SOIL EROSION
Removal of topsoil faster than it can be replaced, due to natural (water and wind action), animal, and human activity. Topsoil is the top layer of soil and is the most fertile because it contains the most organic, nutrient-rich materials.

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
SUBSISTENCE FARMING
A type of agriculture producing food and materials for the benefit only of the farmer and his family.

3.1.2.2 ~tropical rainforests~
SUSTAINABILITY
Actions and forms of progress that meet the needs of the present without reducing the ability of future generations to meet their needs.

3.1.2.3 ~hot deserts~
APPROPRIATE TECHNOLOGY
(Also called Intermediate technology) Technology that is suited to the needs, skills, knowledge and wealth of local people in the environment in which they live. It usually combines simple ideas with cheap and readily available materials, especially for use in poorer countries, and is environmentally friendly.
3.1.2.3 ~hot deserts~
DESERTIFICATION
The process by which land becomes drier and degraded, as a result of climate change or human activities, or both.

3.1.2.3 ~hot deserts~
HOT DESERTS
Parts of the world that have high average temperatures and very low precipitation.

3.1.2.3 ~hot deserts~
OVER-CULTIVATION
Exhausting the soil by over-cropping the land.

3.1.2.3 ~hot deserts~
OVERGRAZING
Grazing too many livestock for too long on the land, so it is unable to recover its vegetation.

3.1.2.4 ~cold environments~
FRAGILE ENVIRONMENT
An environment that is both easily disturbed and difficult to restore if disturbed. Plant communities in fragile areas have evolved in highly specialised ways to deal with challenging conditions. As a result, they cannot tolerate environmental changes.

3.1.2.4 ~cold environments~
INFRASTRUCTURE
The basic equipment and structures (such as roads, utilities, water supply and sewage) that are needed for a country or region to function properly.

3.1.2.4 ~cold environments~
PERMAFROST
Permanently frozen ground, found in polar and tundra regions.

3.1.2.4 ~cold environments~
POLAR
The regions of Earth surrounding the North and South Poles. These regions are dominated by Earth's polar ice caps, the northern resting on the Arctic Ocean and the southern on the continent of Antarctica.

3.1.2.4 ~cold environments~
TUNDRA
The flat, treeless Arctic regions of Europe, Asia and North America, where the ground is permanently frozen. Lichen, moss, grasses and dwarf shrubs can grow here.

3.1.2.4 ~cold environments~
WILDERNESS AREA
A natural environment that has not been significantly modified by human activity. Wilderness areas are the most intact, undisturbed areas left on Earth - places that humans do not control and have not developed.

3.1.3.1 ~UK physical landscapes~
LANDSCAPE
An extensive area of land regarded as being visually and physically distinct.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
ABRASION (or corrasion)
The wearing away of cliffs by sediment flung by breaking waves.
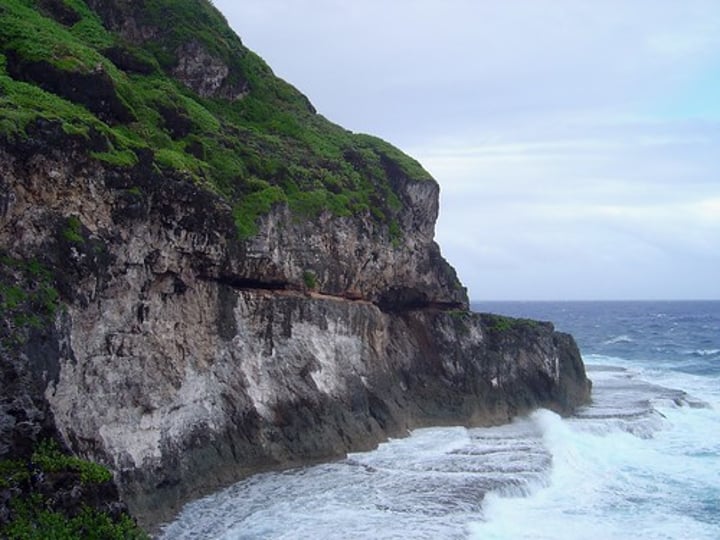

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
ARCH
A wave-eroded passage through a small headland. This begins as a cave formed in the headland, which is gradually widened and deepened until it cuts through.
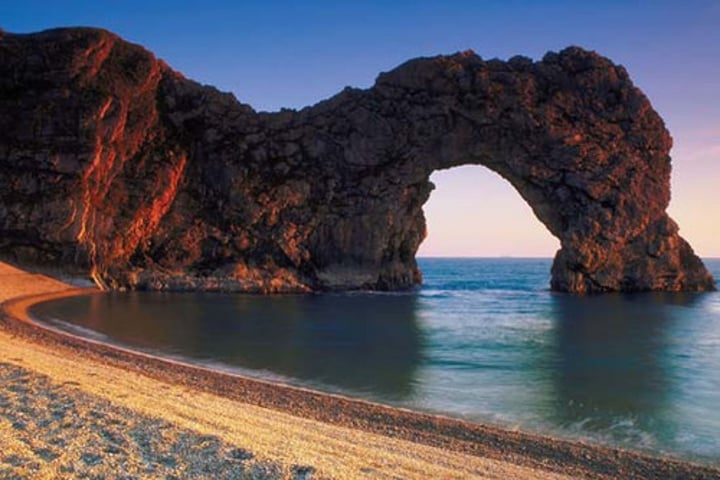

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
ATTRITION
Erosion caused when rocks and boulders transported by waves bump into each other and break up into smaller pieces.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
BAY BAR
Where a spit grows across a bay, a bay bar can eventually enclose the bay to create a lagoon. Bars can also form offshore due to the action of breaking waves.
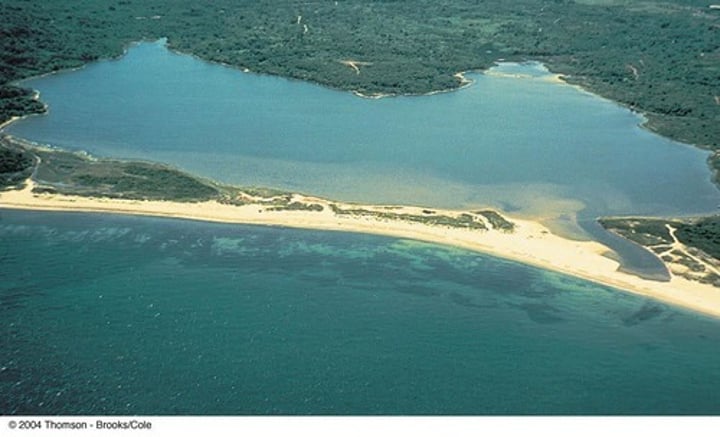

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
BEACH
The zone of deposited material that extends from the low water line to the limit of storm waves. The beach or shore can be divided in the foreshore and the backshore.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
BEACH NOURISHMENT
The addition of new material to a beach artificially, through the dumping of large amounts of sand or shingle.
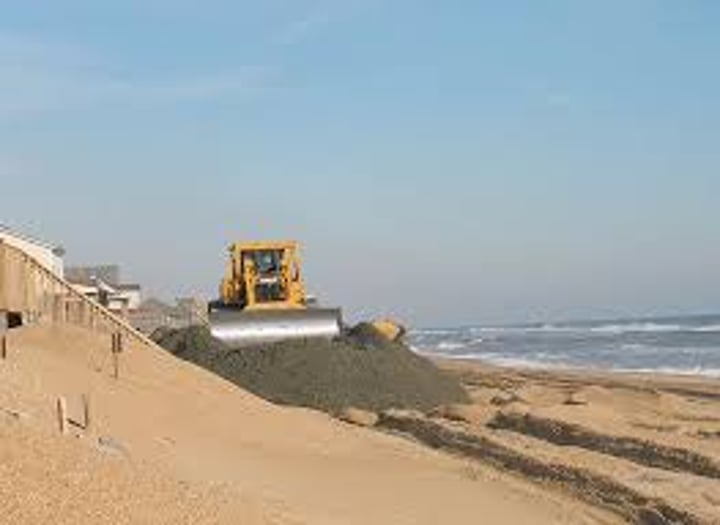

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
BEACH REPROFILING
Changing the profile or shape of the beach. It usually refers to the direct transfer of material from the lower to the upper beach or, occasionally, the transfer of sand down the dune face from crest to toe.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
CAVE
A large hole in the cliff caused by waves forcing their way into cracks in the cliff face.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
CHEMICAL WEATHERING
The decomposition (or rotting) of rock caused by a chemical change within that rock; sea water can cause chemical weathering of cliffs.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
CLIFF
A steep high rock face formed by weathering and erosion along the coastline.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
DEPOSITION
Occurs when material being transported by the sea is dropped due to the sea losing energy.
3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
DUNE REGENERATION
Action taken to build up dunes and increase vegetation to strengthen the dunes and prevent excessive coastal retreat. This includes the re-planting of marram grass to stabilise the dunes, as well as planting trees and providing boardwalks.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
EROSION
The wearing away and removal of material by a moving force, such as a breaking wave.
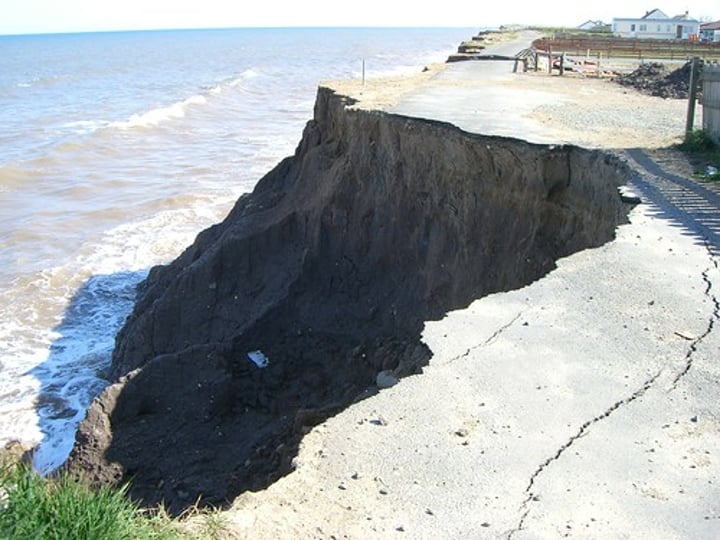

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
GABION
Steel wire mesh filled with boulders used in coastal defences.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
GROYNE
A wooden barrier built out into the sea to stop the longshore drift of sand and shingle, and so cause the beach to grow. It is used to build beaches to protect against cliff erosion and provide an important tourist amenity. However, by trapping sediment it deprives another area, down-drift, of new beach material.
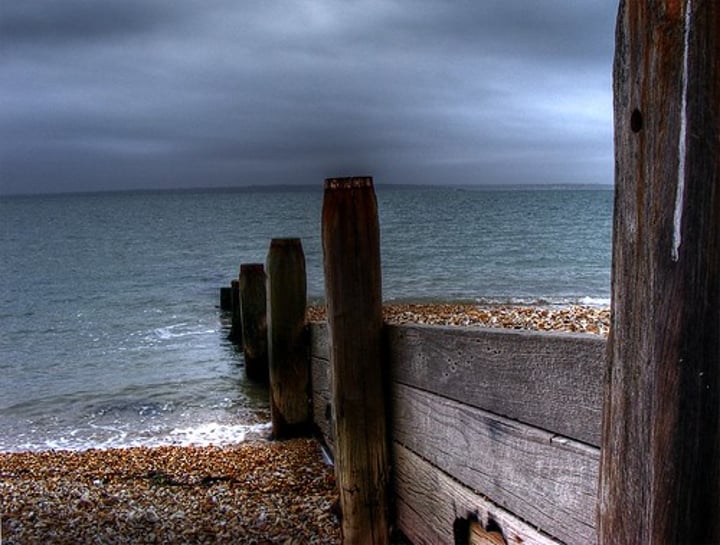

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
HARD ENGINEERING
The use of concrete and large artificial structures by civil engineers to defend land against natural erosion processes.
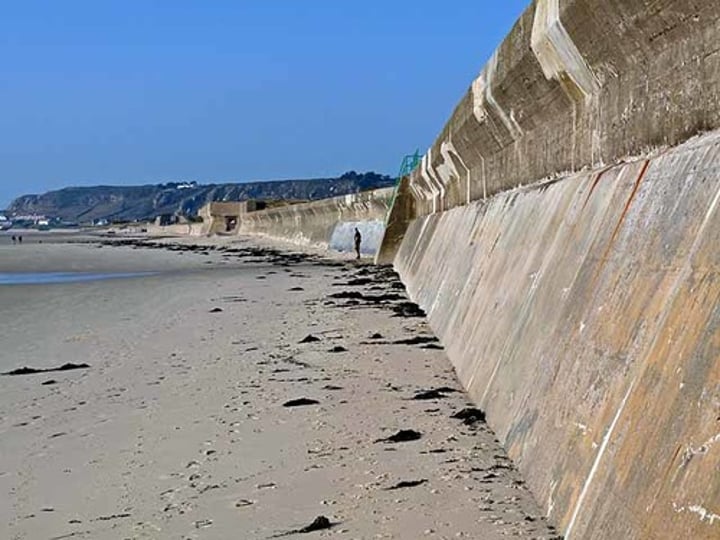

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
HEADLANDS AND BAYS
A rocky coastal promontory made of rock that is resistant to erosion; headlands lie between bays of less resistant rock where the land has been eroded back by the sea.
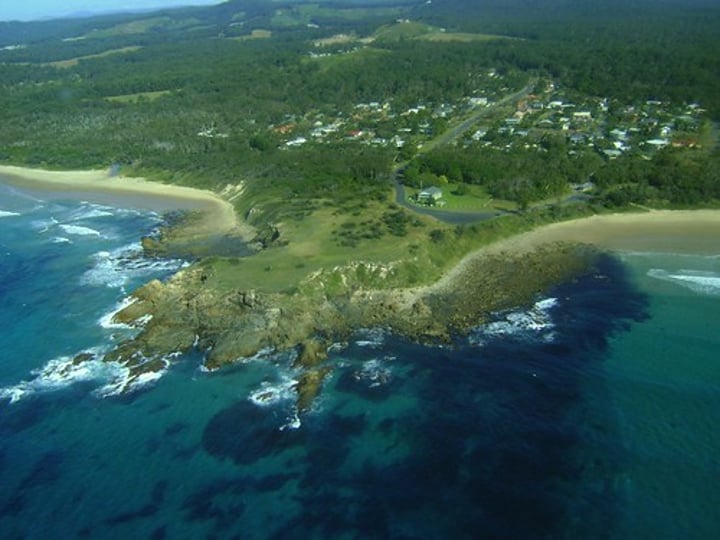

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
HYDRAULIC POWER
The process by which breaking waves compress pockets of air in cracks in a cliff. The pressure may cause the crack to widen, breaking off rock
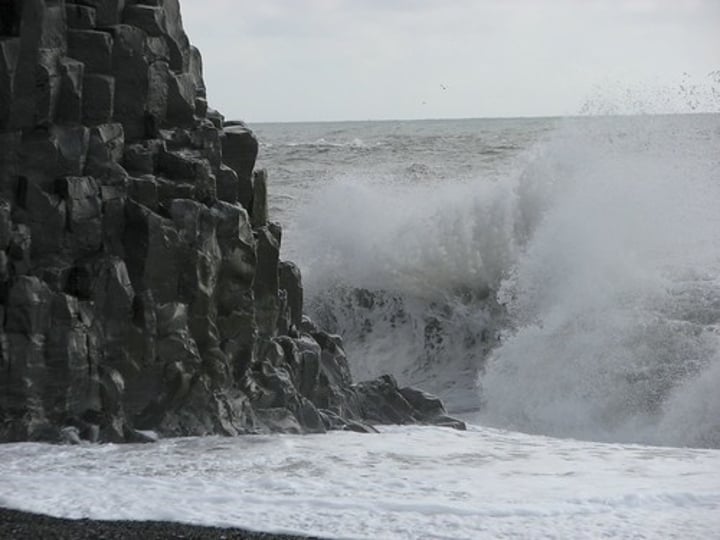

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
LONGSHORE DRIFT
The zigzag movement of sediment along a shore caused by waves going up the beach at an oblique angle(wash) and returning at right angles(backwash). This results in the gradual movement of beach materials along the coast.
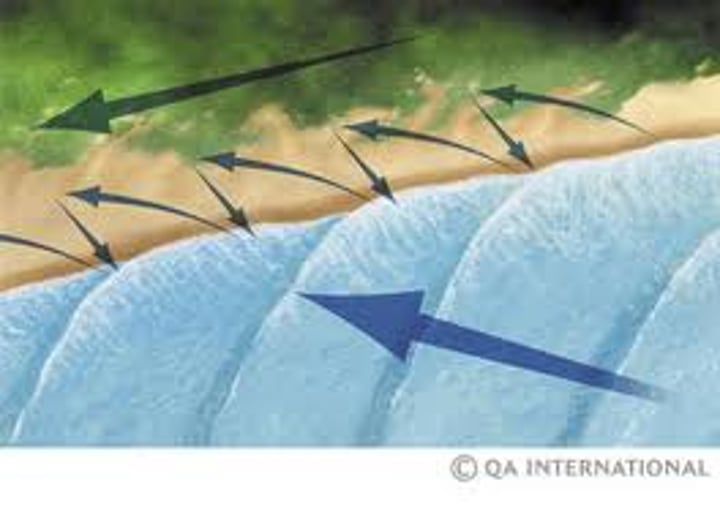
3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
MANAGED RETREAT
Allowing cliff erosion to occur as nature taking its course: erosion in some areas, deposition in others. Benefits include less money spent and the creation of natural environments. It may involve setting back or realigning the shoreline and allowing the sea to flood areas that were previously protected by embankments and seawalls.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
MASS MOVEMENT
The downhill movement of weathered material under the force of gravity. The speed can vary considerably.
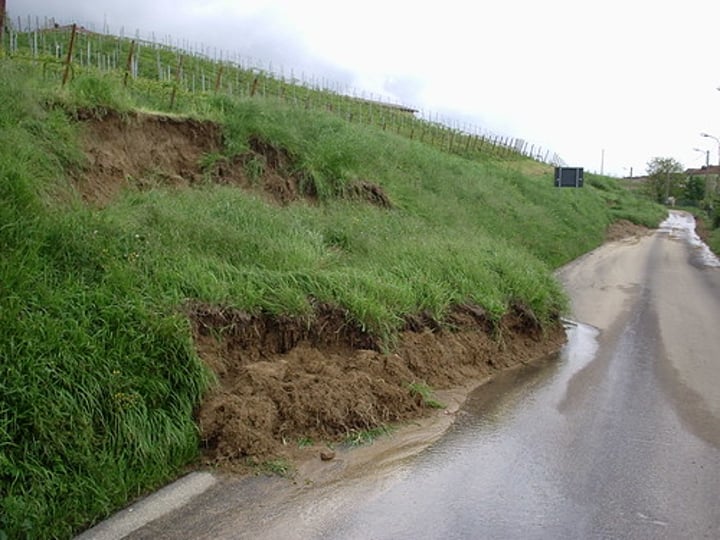

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
MECHANICAL WEATHERING
Weathering processes that cause physical disintegration or break up of exposed rock without any change in the chemical composition of the rock, for instance freeze thaw.
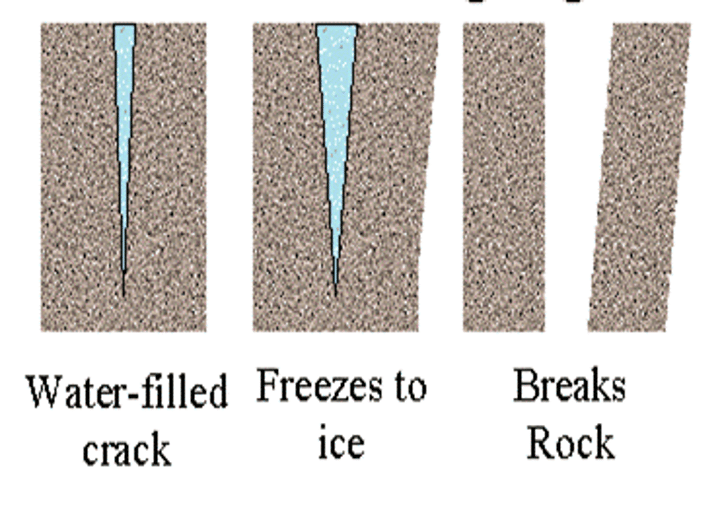
3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
ROCK ARMOUR
Large boulders dumped on the beach as part of the coastal defences.
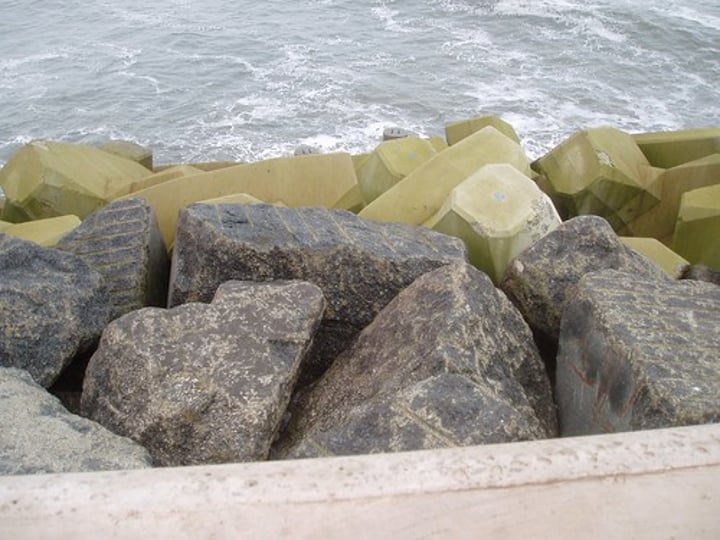

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
SAND DUNE
Coastal sand hill above the high tide mark, shaped by wind action, covered with grasses and shrubs.
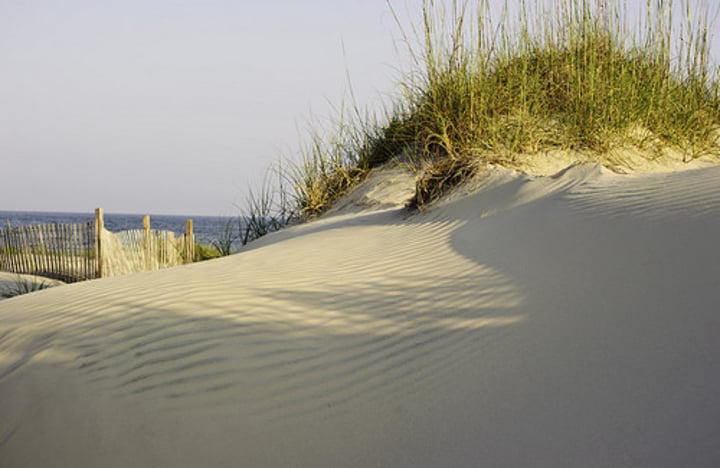

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
SEA WALL
A concrete wall which aims to prevent erosion of the coast by providing a barrier which reflects wave energy.
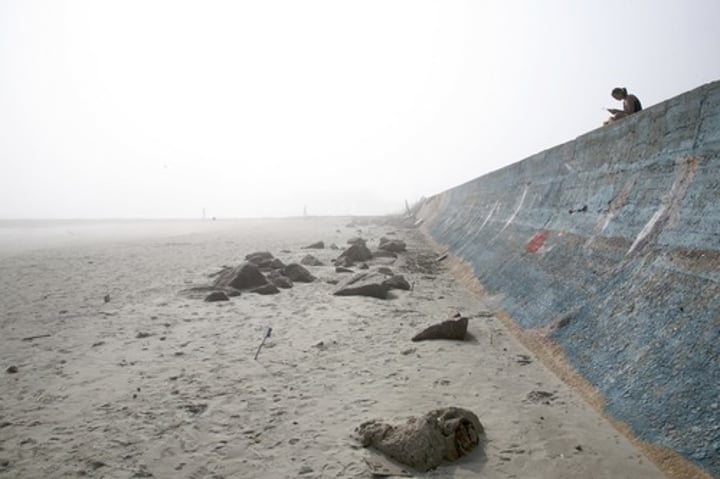

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
SLIDING
Occurs after periods of heavy rain when loose surface material becomes saturated and the extra weight causes the material to become unstable and move rapidly downhill, sometimes in an almost fluid state.
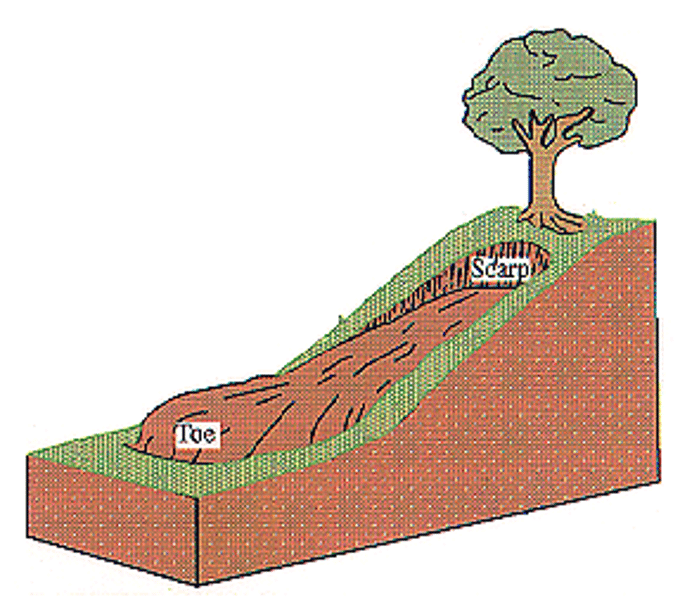
3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
SLUMPING
Rapid mass movement which involves a whole segment of the cliff moving down-slope along a saturated shear-plane or line of weakness.
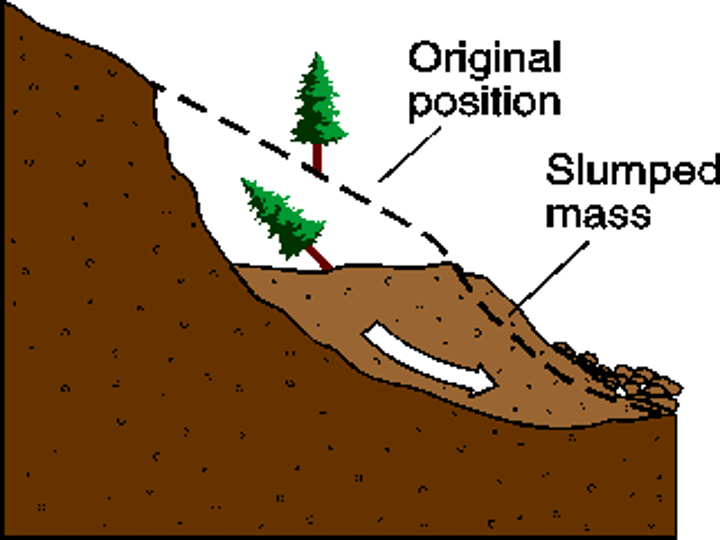
3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
SOFT ENGINEERING
Managing erosion by working with natural processes to help restore beaches and coastal ecosystems.
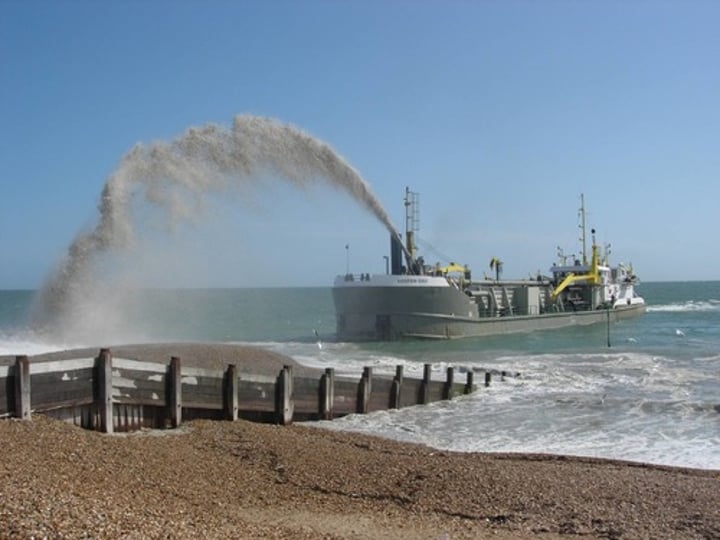

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
SPIT
A depositional landform formed when a finger of sediment extends from the shore out to sea, often at a river mouth. It usually has a curved end because of opposing winds and currents.
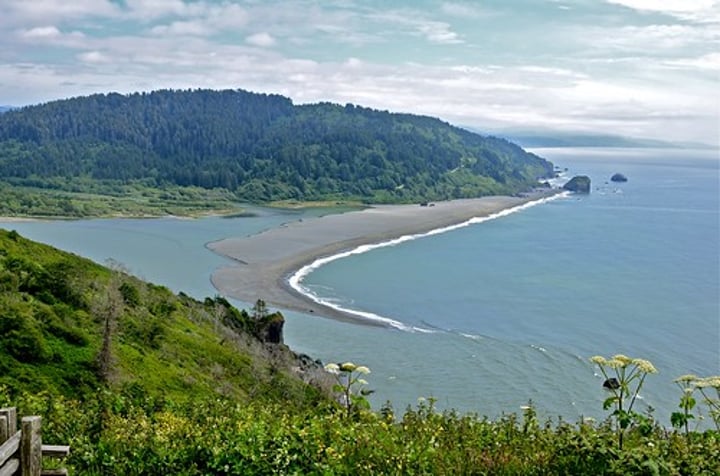

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
*STACK
An isolated pillar of rock left when the top of an arch has collapsed. Over time further erosion reduces the stack to a smaller, lower stump.
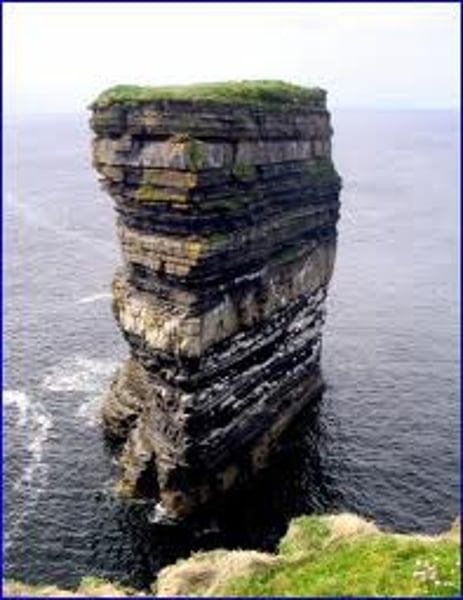

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
TRANSPORTATION
The movement of eroded material.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
WAVE CUT PLATFORM
A rocky, level shelf at or around sea level representing the base of old, retreated cliffs.

3.1.3.2 ~coastal landscapes in the UK~
WAVES
Ripples in the sea caused by the transfer of energy from the wind blowing over the surface of the sea. The largest waves are formed when winds are very strong, blow for lengthy periods and cross large expanses of water.
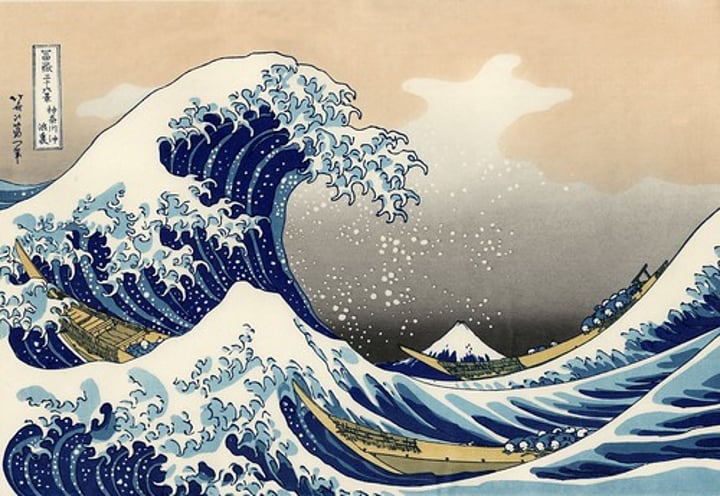

3.1.3.3 ~river landscapes in the UK~
ABRASION
Rocks carried along by the river wear down the river bed and banks.
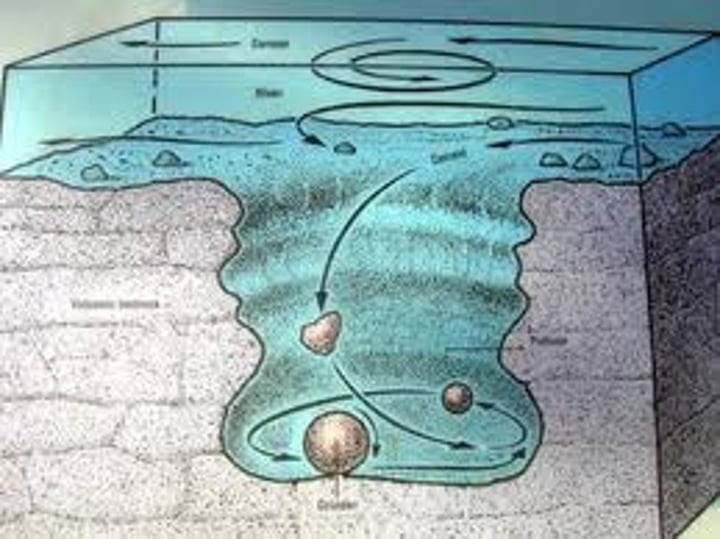
3.1.3.3 ~river landscapes in the UK~
ATTRITION
Rocks being carried by the river smash together and break into smaller, smoother and rounder particles.
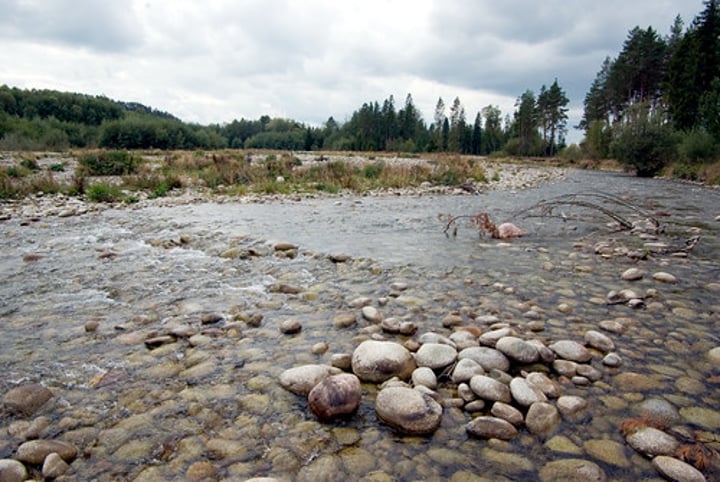

3.1.3.3 ~river landscapes in the UK~
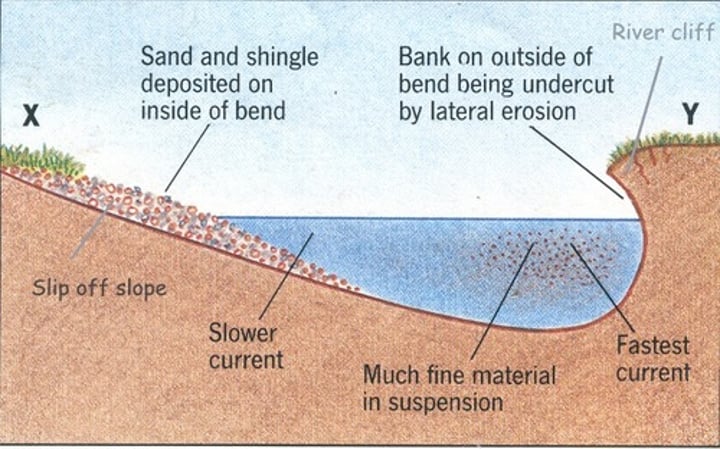
CROSS PROFILE
The side to side cross-section of a river channel and/or valley.
3.1.3.3 ~river landscapes in the UK~
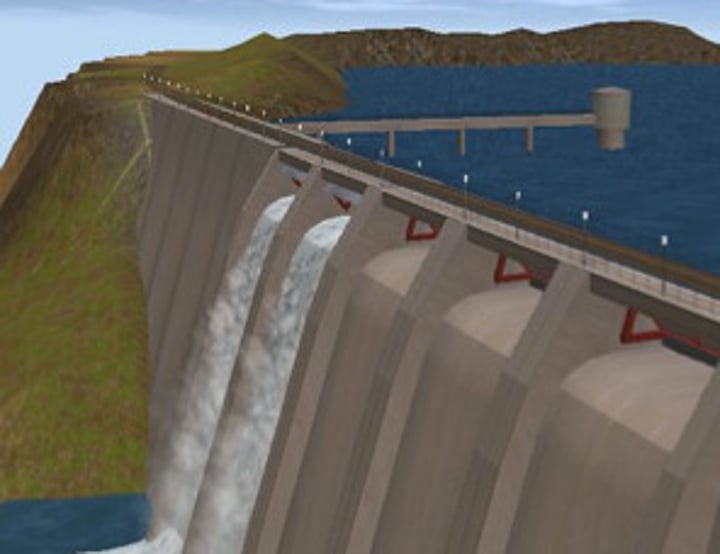
DAM AND RESERVOIR
A barrier(made on earth, concrete or stone) built across a valley to interrupt river flow and create a man‐made lake(reservoir) which stores water and controls the discharge of the river.
