Cell macromolecules
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:57 PM on 1/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
1
New cards
Condensation reactions
Endergonic reactions which form polymers from their monomeric constituents and generate water as a waste product
2
New cards
300 Da
Avg mr of nucleotide
3
New cards
110Da
Avg mr of amino acid
4
New cards
180 Da
Mr of glucose
5
New cards
Spontaneous reaction
A reaction that can occur without an input of energy, they have a negative change in free energy (deltaG)
6
New cards
Monosaccharide
Monomer of polysaccharides, with general formula (CH₂O)ₙ. Smallest being trioses.
7
New cards
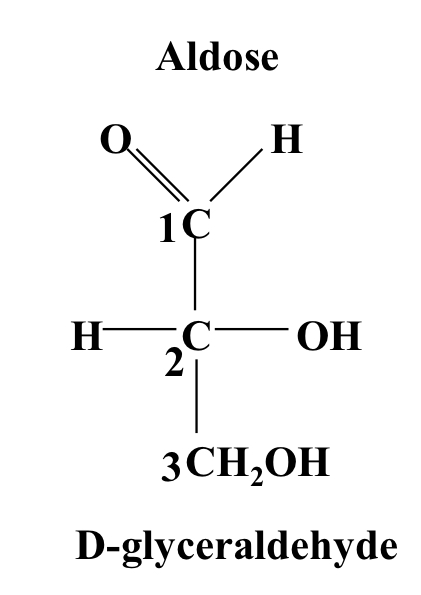
Glyceraldehyde
An aldotriose with 3 carbons and ending in a CH₂OH group. Has a chiral central carbon.
8
New cards
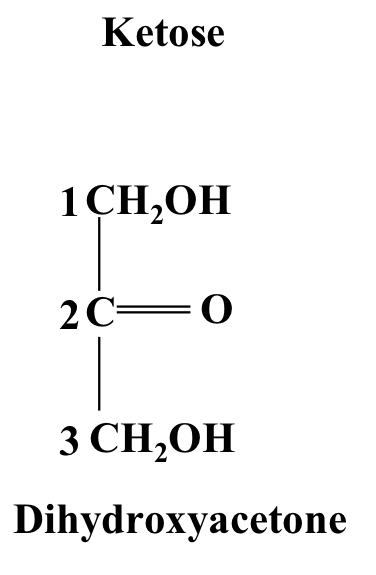
Dihydroxyacetone
A ketotriose ending in a CH₂OH group, non-chiral
9
New cards
Chiral
A molecule which has two forms that are mirror images and non-superimposable.
10
New cards
D (right) or L (left)
Descriptions of the two forms of chiral molecule depending on the direction in which plane polarised light is rotated to. D=right, L=left. Cannot be determined by structure, so structure are compared against d/l glyceraldehyde. Most natural sugars are D-configuration.
11
New cards
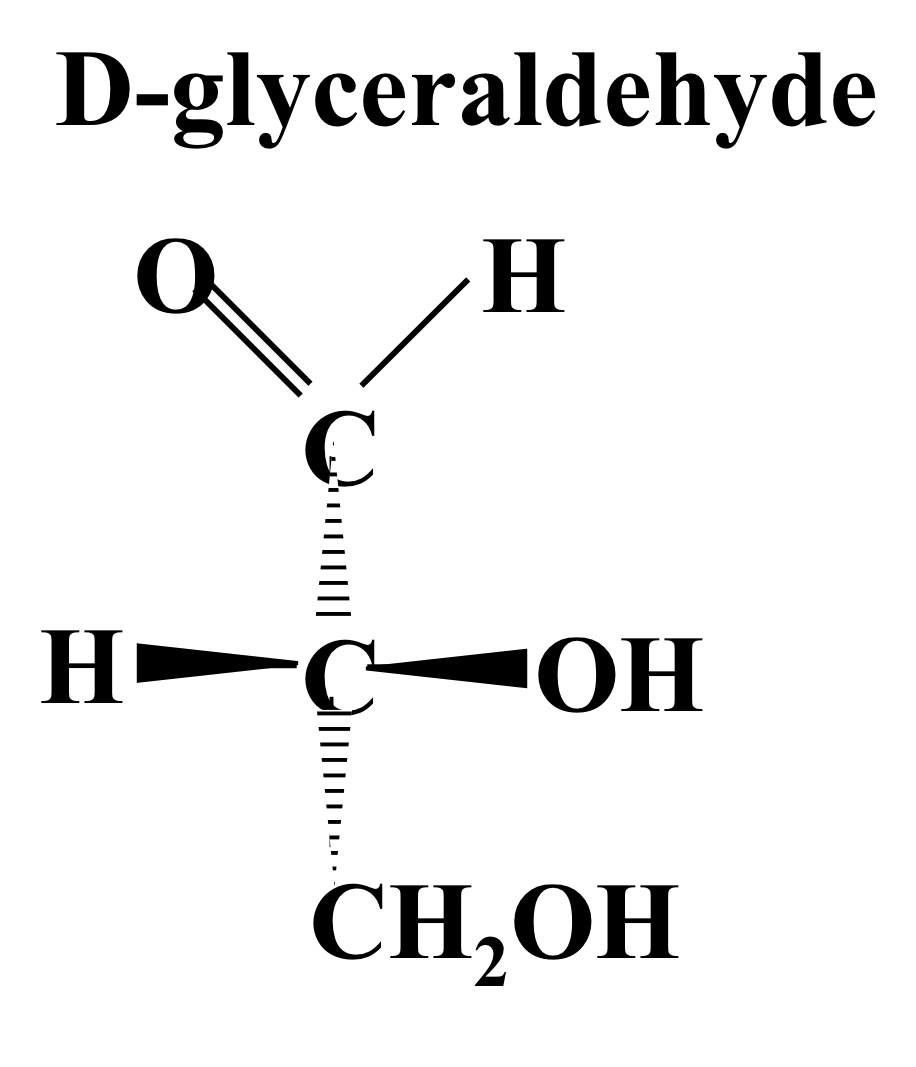
D-glyceraldehyde
OH and H group both protrude out of the page, OH on the **right** and H on the left.
12
New cards
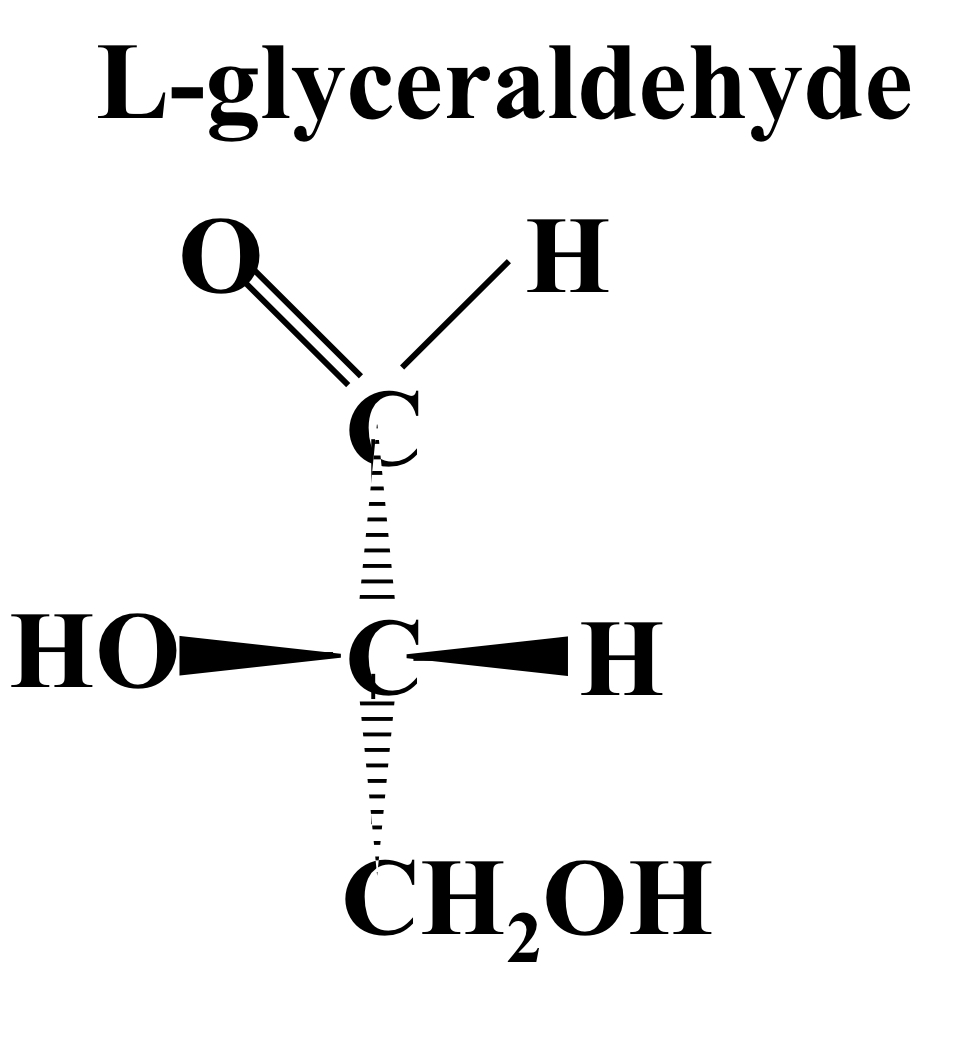
L-glyceraldehyde
OH and H both protrude from the page, OH on the left and H on the right.
13
New cards
Example- D-glucose
D-glucose is an extended glyceraldehyde, so is an aldohexose with most similarity to D-glyceraldehyde.
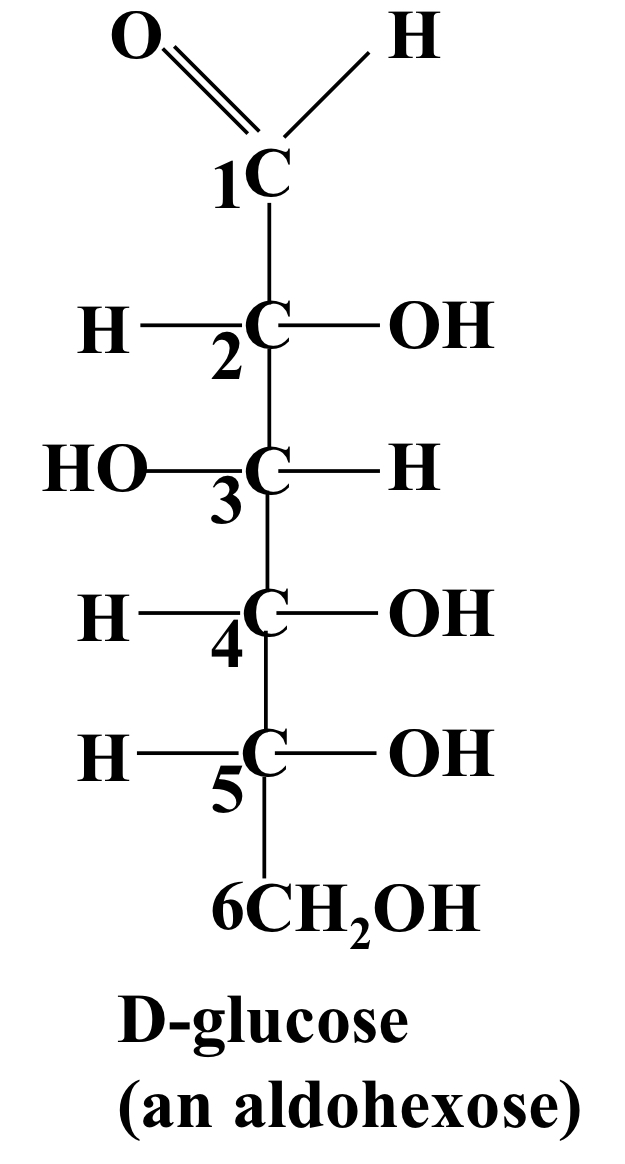
14
New cards
Enantiomers
Chiral mirror images of a molecule.
15
New cards
Stereoisomers
Compounds that have the same molecular formulae but differ in the configuration of atoms in space.
16
New cards
Epimers
Sugars that differ in only a single chiral centre. E.g. D-glucose and D-galactose
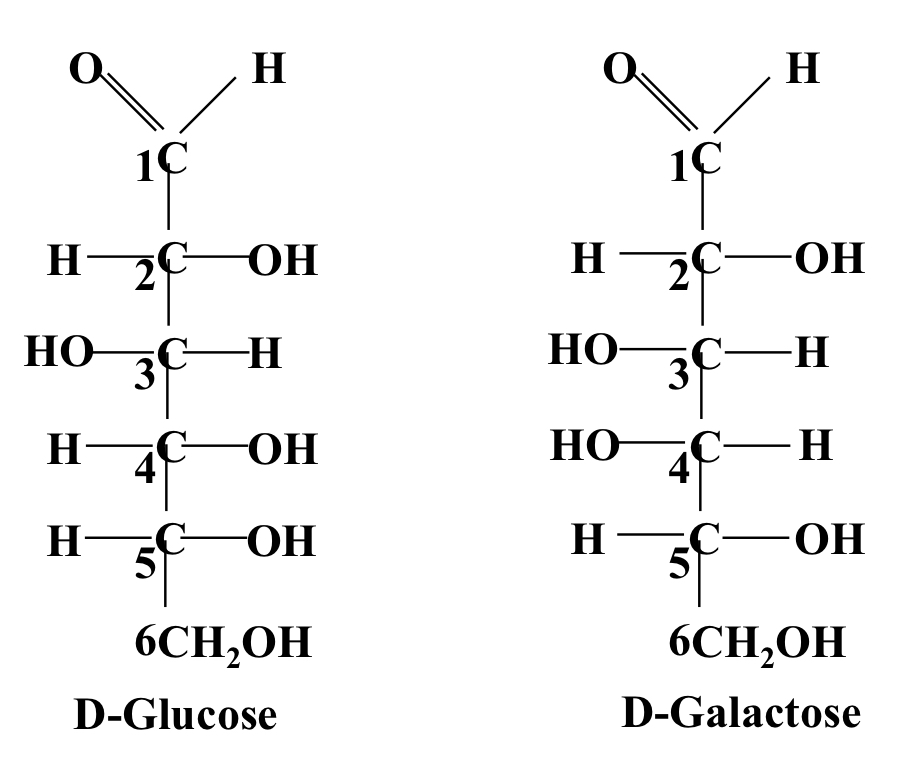
17
New cards
Intramolecular cyclisation
Reaction of glucose where the rotation of the bond between C4 and C5, allows the hydroxyl group on C5 to react with the aldehyde on C1 to form a 6-membered ring structure. The PYRANOSE ring.
18
New cards
Pyranose ring
Structure of glucose in which it becomes a 6-membered ring. E.g. α-D-glucopyranose or β-D-galactopyranose
19
New cards
Anomeric carbon
Carbon derived form a carbonyl carbon which becomes a chrial centre
20
New cards
Furanose ring
Structure of fructose in which it becomes a 5-membered ring. E.g. β-D-fructofuranase
21
New cards
α-D-glucopyranose
On C1, OH is **below** H
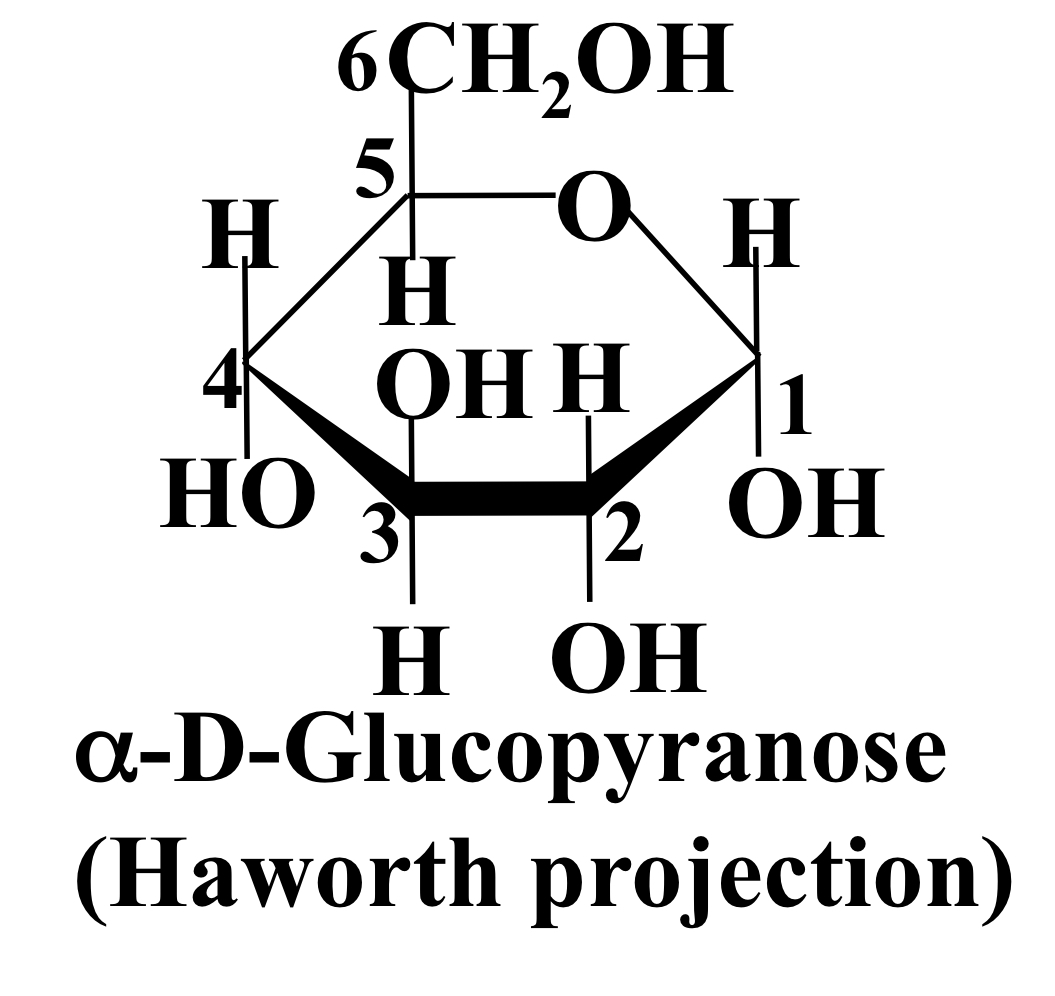
22
New cards
β-D-glucopyranose
On C1, OH is above H with continuing alternating pattern around the carbon ring.
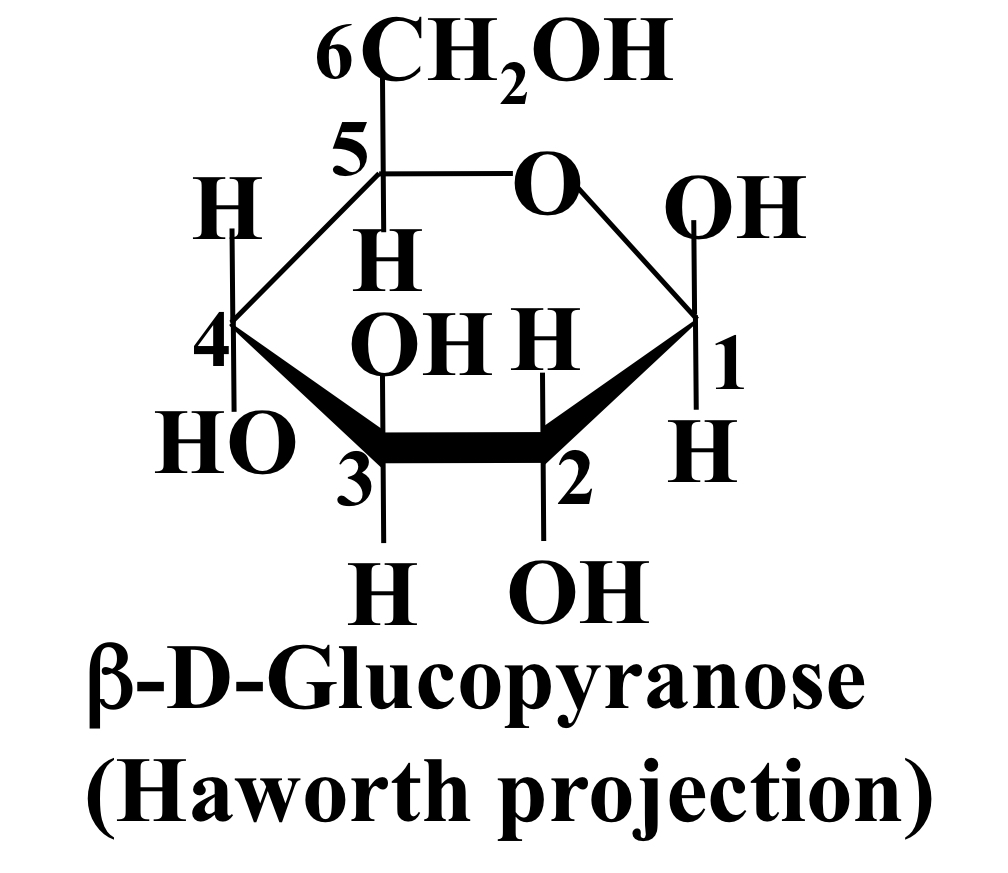
23
New cards
Chair vs boat form
Tetrahedral bond arrangement around each carbon means the ring is not flat (like benzene) but is puckered, and exists in either a chair or boat form. The chair reform is more stable as there is less oxygen interactions.
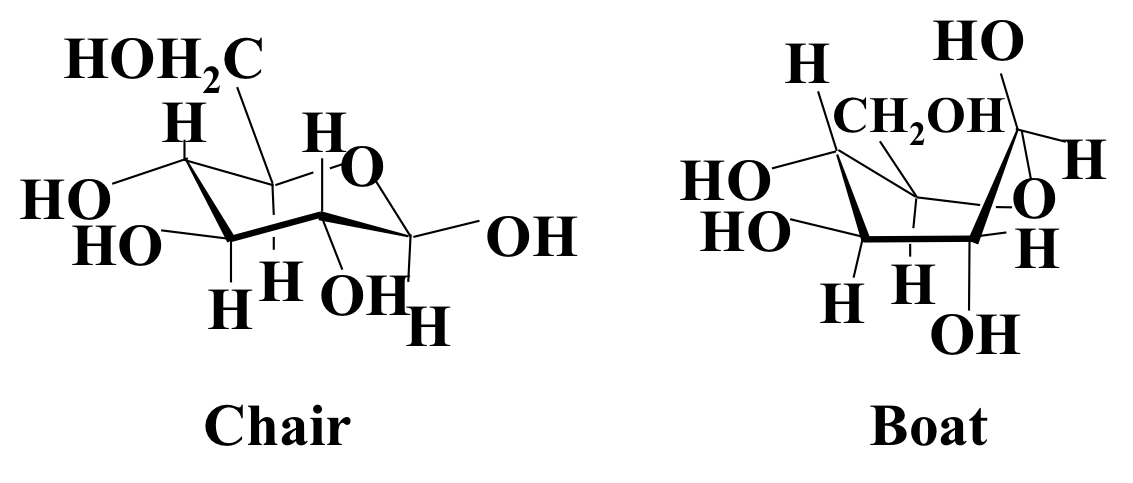
24
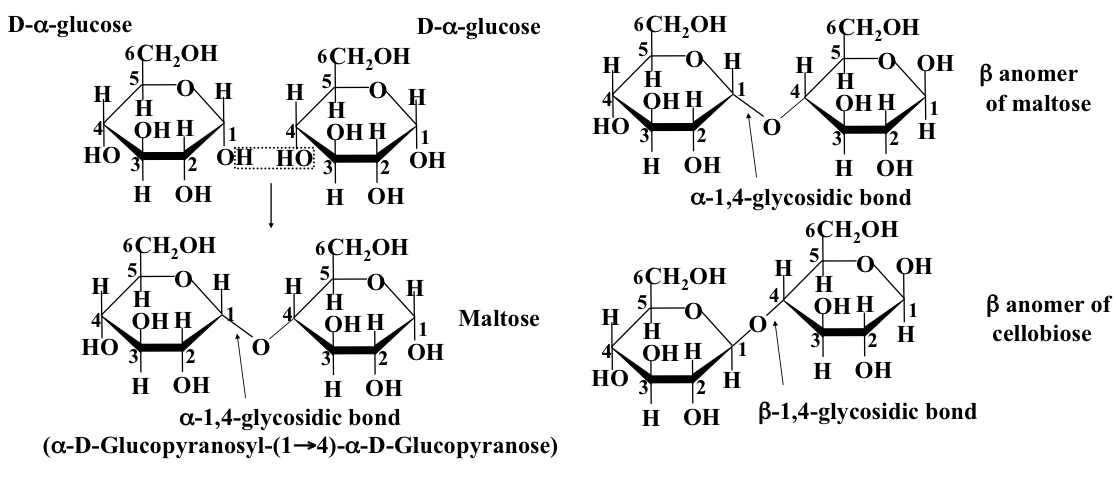
New cards
Disaccharide
Structure formed when two monosacchrrides are linked together by glycosidic bonds in a condensation reaction between the anomeric carbon on one sugar and a hydroxyl group on the other. (E.g. 1-6, or 1-4)
25
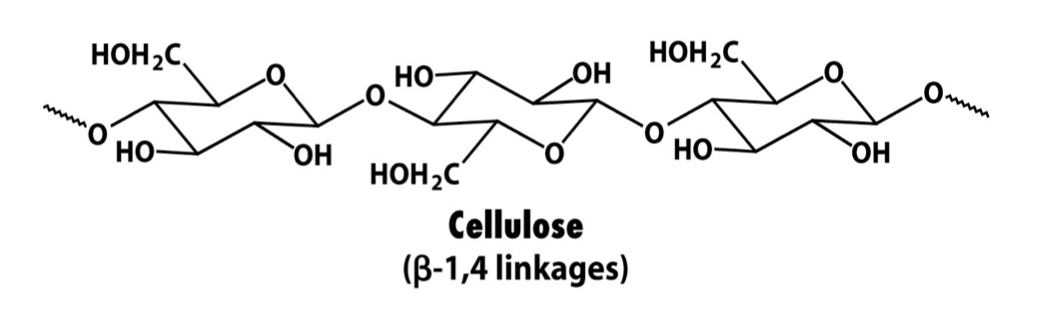
New cards
Cellulose
Polymer formed by polymerisation of β-D-glucose via 1-4 glycosidic linkages. (Disaccharide is cellobiose). Major component of plant cell walls and one of the msot common biopolymers on earth. Adjacent chains hydrogen bond to one another for rigidity.
26
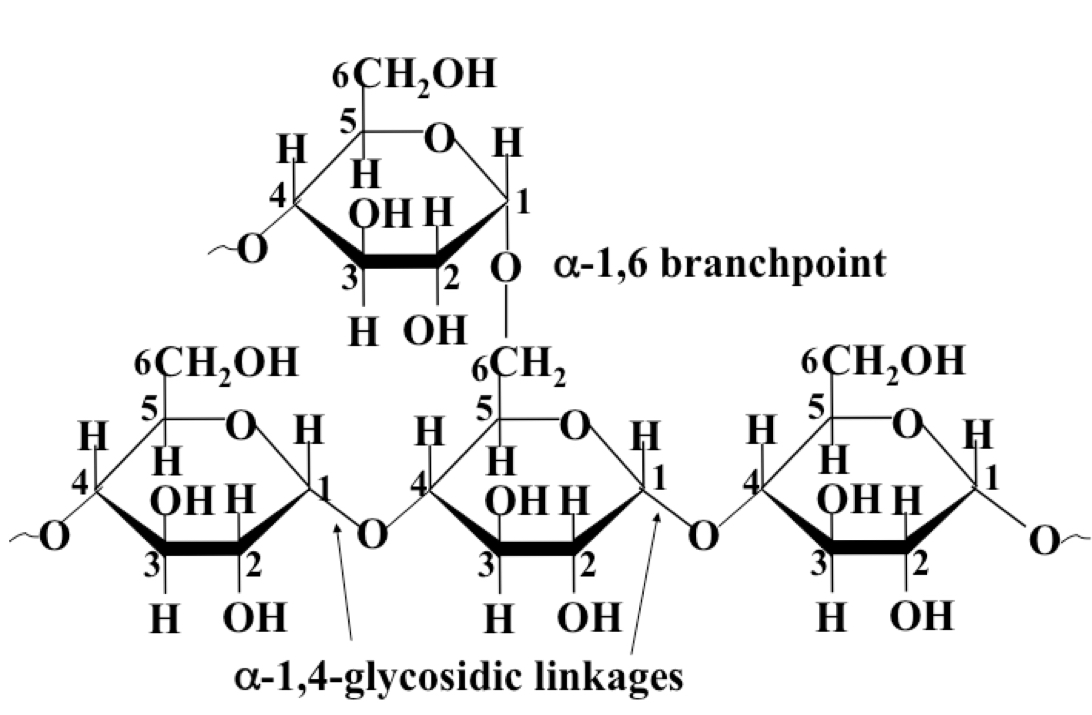
New cards
Glycogen
Polymer formed by polymerisation of α-D-glucose via primarily 1-4, but also 1-6 glycosidic bonds (at branching points) at approx every 10 monomers. Responsible for energy storage in animals.
27
New cards
Starch
Polymer formed by polymerisation of α-D-glucose via 1-4 glycosidic bonds, has far less branching points (either none or one every 30 monomers. Responsible for energy storage in plants.
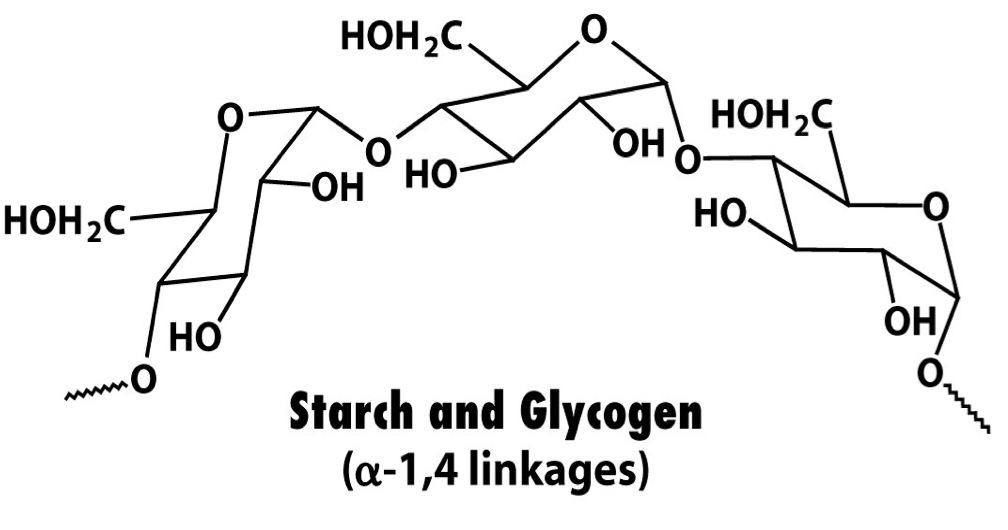
28
New cards
Reducing sugars
Sugars with a reactive carbonyl group, that can react with oxidising agents. Sucrose is **not** a reducing sugar.
29
New cards
Directionality
Can be assigned to polysaccharide chains based on their reducing and non-reducing end. Branched polysaccharides have multiple non-reducing ends but only one reducing end.
30
New cards
Chitin
β-1,4 polymer of N-acetyl glucosamine. Found in the cell walls of fungi and the exoskeleton of anthropods like insacts.
31
New cards
Glycoprotein
A composite protein/carbohydrate molecule, generally secreted from the cell or inserted into the plasma membrane. Made via addition of an oligosaccharide followed by further carbohydrate chains.
32
New cards
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Long-chain copolymers of D-glucuronic or L-iduronic acid with N-acetyl-D-glucosamine or N-acetyl-D-galactosamine. High negative charge density repels adjacent cartilage molecules, acting to resist compression under load. E.g. hyaluronic acid
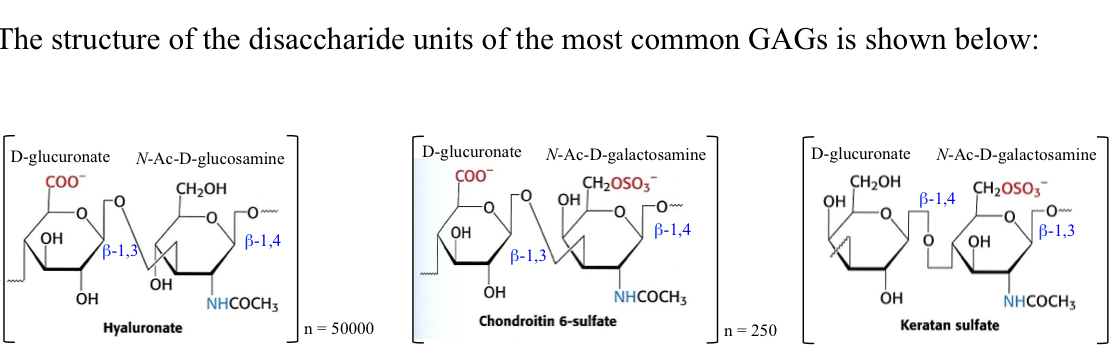
33
New cards
Hyaluronic acid
β-1,4 linked polymer of a β-1,3-linked D-glucoronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine dimer, up to 50,000 monomers and forms extremely viscous solutions which act as the primary component of synovial fluid in skeletal joints.
34
New cards
Nucleic acid
Major class of macromolecules made of nucleotides. Which are made of a base, pentose sugar and inorganic phosphate.
35
New cards
Purine bases
Adenine and guanine. 2-ringed bases
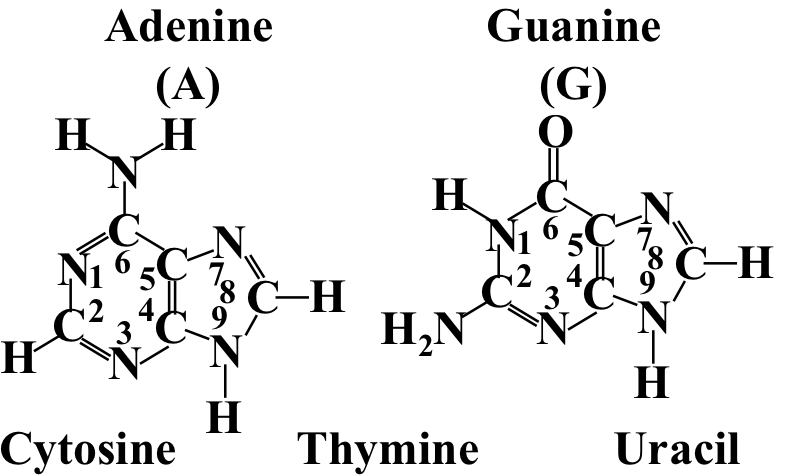
36
New cards
Pyramidine bases. 1-ringed bases
Cytosine, thymine and uracil
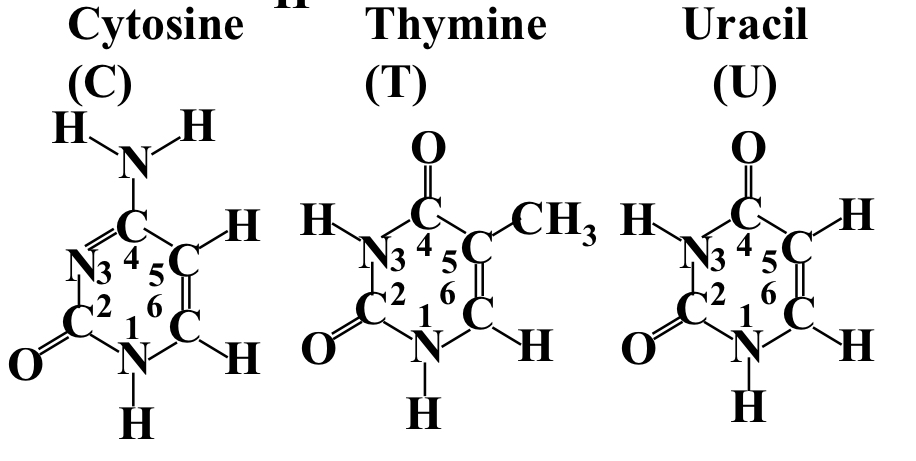
37
New cards
Nucleoside
Same structure as a nucleotide, the base is connected to C1 of the ribose via a β-N-glycosidic bond, but no phosphate is present. Can be ribonucleosides or deoxyribonucleosides.
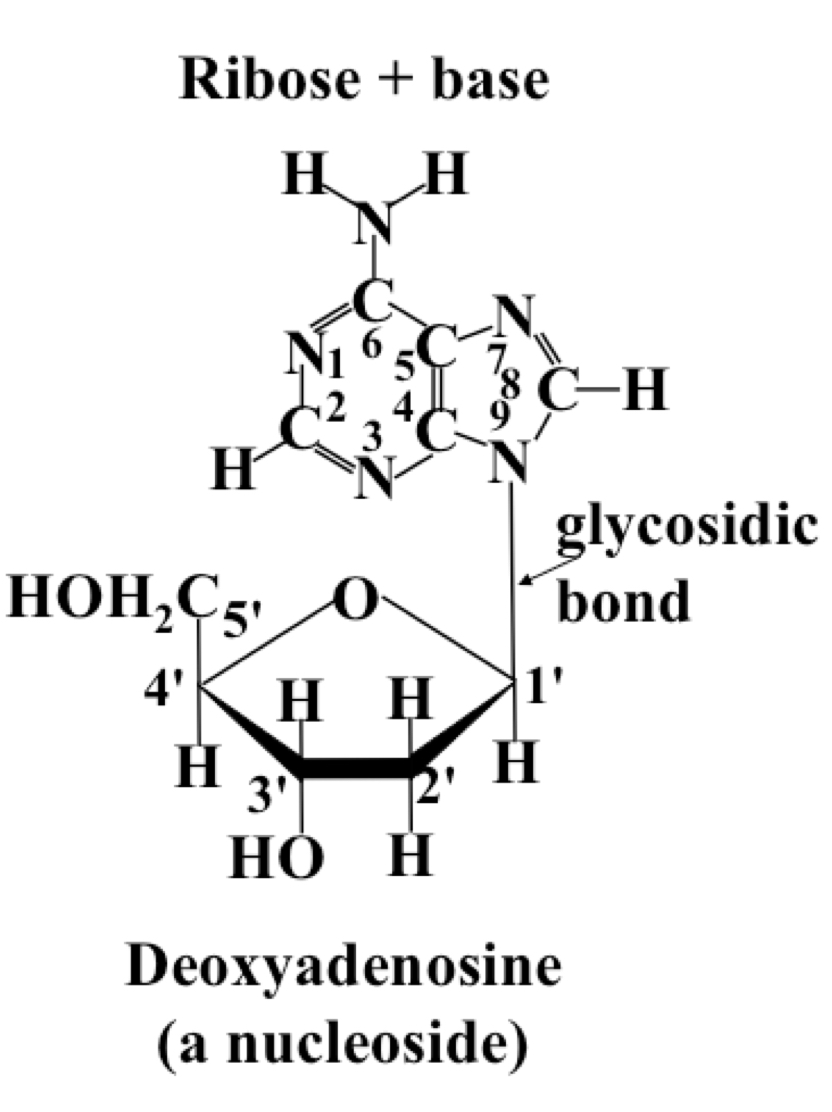
38
New cards
Nucleotide
Nucleoside with the addition of a phosphoryl group to the 5’ hydroxyl group by a phosphate ester bond. (Can be up to 3 phosphate groups in a row)
39
New cards
3’-5’ phosphodiester linkage
The bond between sugar residues of nucleotides which forms a nucleic acid
40
New cards
Directionality of nucleic acids
5’-end is the end with a free phosphoryl group, 3’-end is the end with a free hydroxyl group. Sequences are written from 5’ to 3’ generally.
41
New cards
Extra methyl group
Difference between thymine (has extra) and uracil
42
New cards
Hydrogen bonding
Occurs when a hydrogen atom that is covalently bound to an electronegative atom (donor) is close enough to another electronegative atom (acceptor). The hydrogen is shared between the two atoms due to small opposing charges. (Strongest when atoms are in a straight line)
43
New cards
Hydrogen acceptors
Carbonyl groups of guanine, thymine and uracil.
44
New cards
Hydrogen donors
Amino groups of adenine and cytosine.
45
New cards
Base pairing
C and G bond to form 3 hydrogen bonds. A and T/U bond to form 2 hydrogen bonds.
46
New cards
DNA double helix
Structure formed when two DNA molecules with opposite directionality (antiparralel) are in close proximity, they spontaneously associate via base pairing to form a right-handed double helix.
47
New cards
10 base pairs
1 complete double helix turn
48
New cards
Cooperative non-covalent interactions
Bonding that occurs between the upper and lower surfaces of each base pair, causing twisting.
49
New cards
Major.minor grooves
Have a major role in sequence-specific DNA recognition
50
New cards
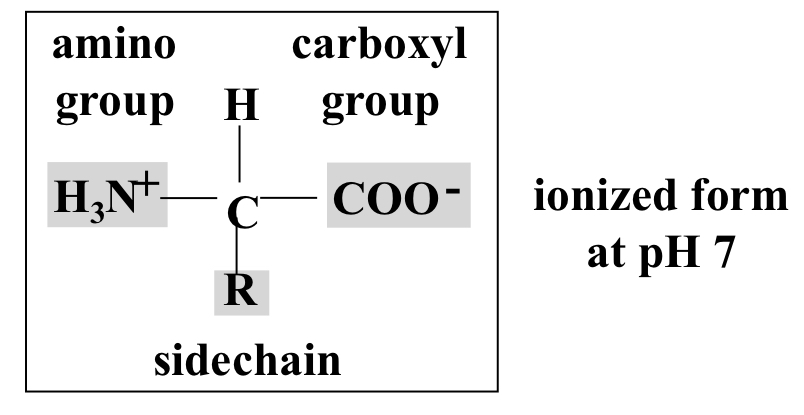
Amino acids
Monomer of protein with identical backbone but differing R groups/side chains
51
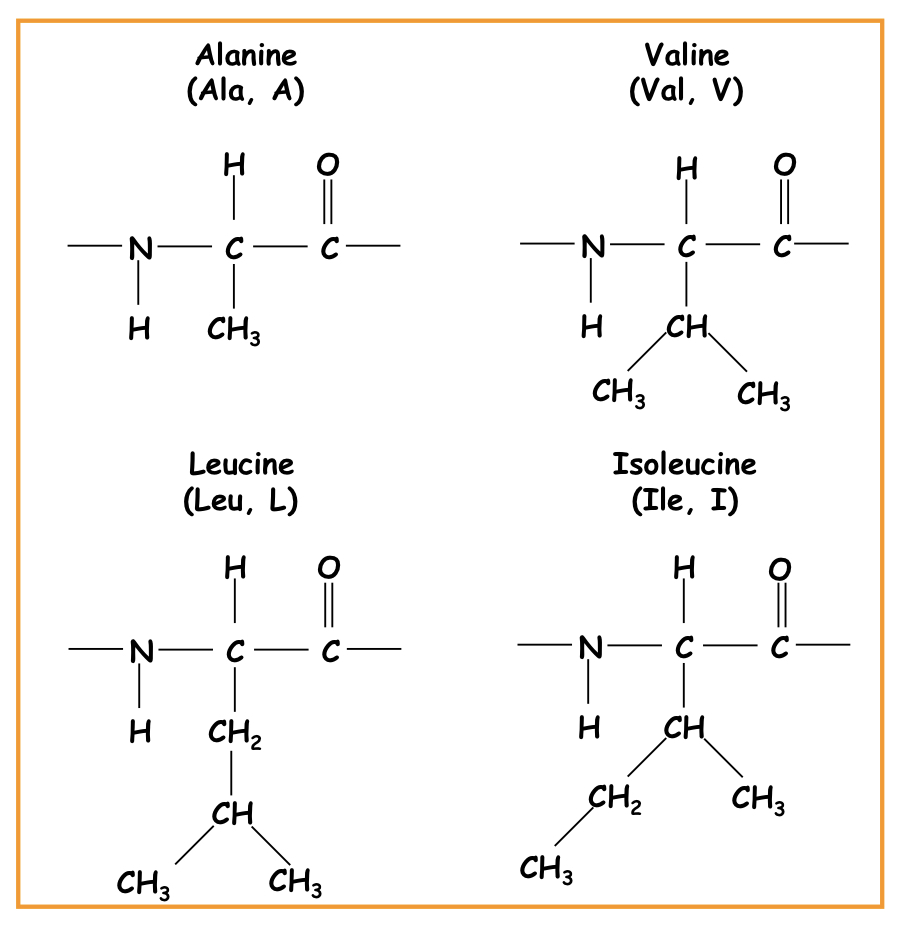
New cards
Non-polar sidechains
Alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine
52
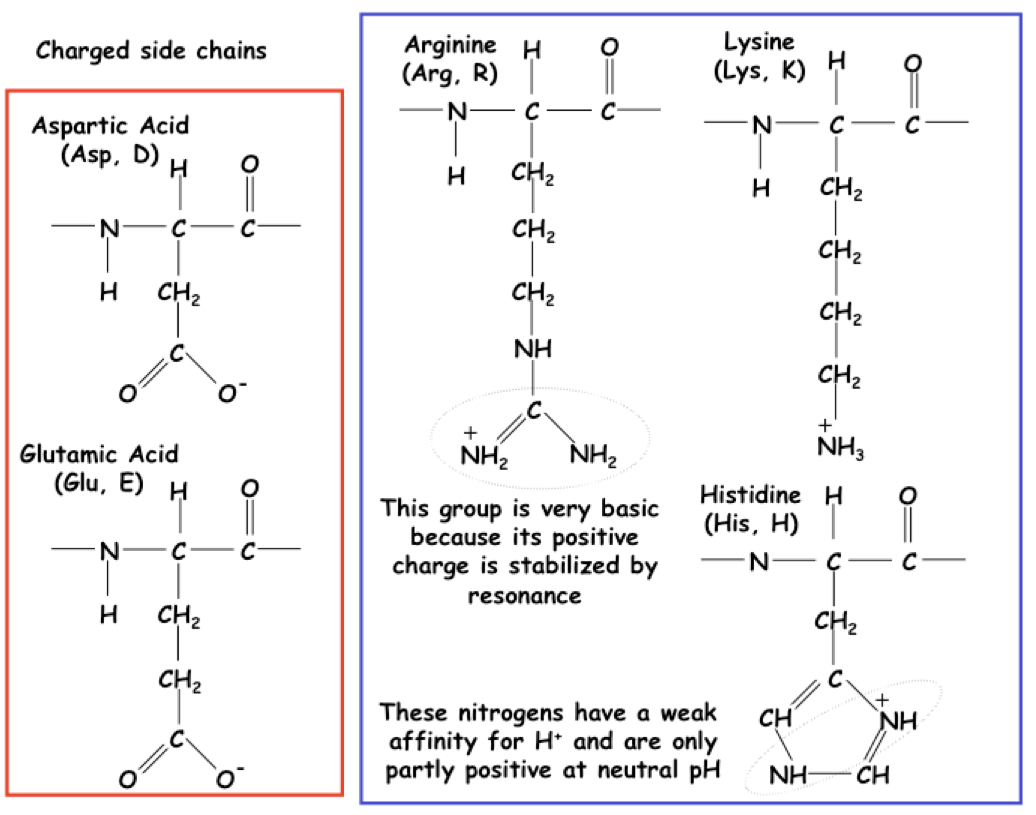
New cards
Charged side chain
Aspartic acid and glutamic acid (negative), arginine and lysine (positive)
53
New cards
Imino acid
Proline
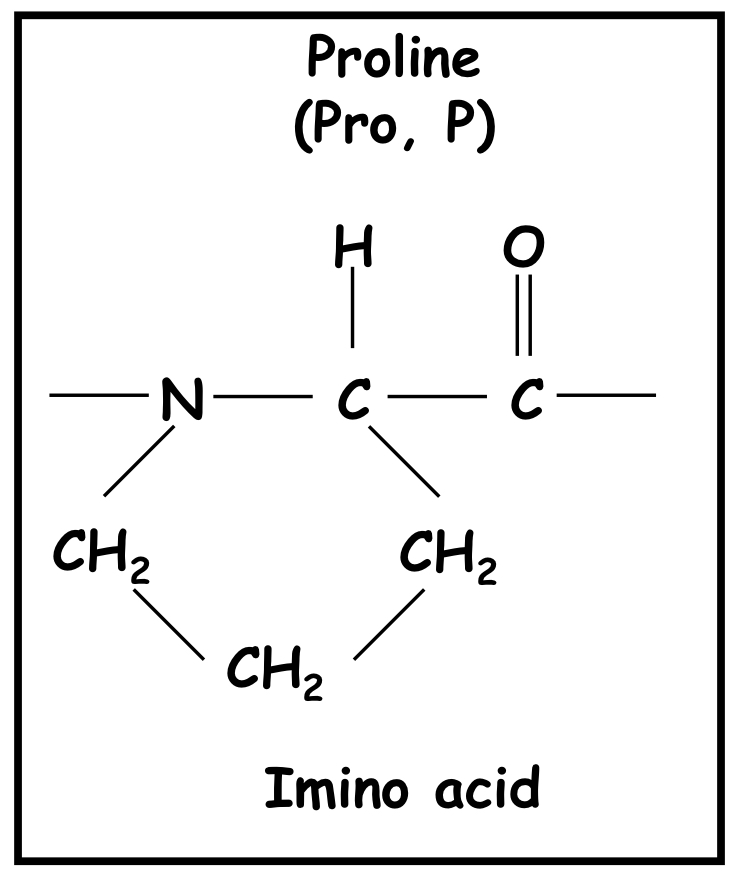
54
New cards
Sulfur-containing side chain
Cysteine and methionine
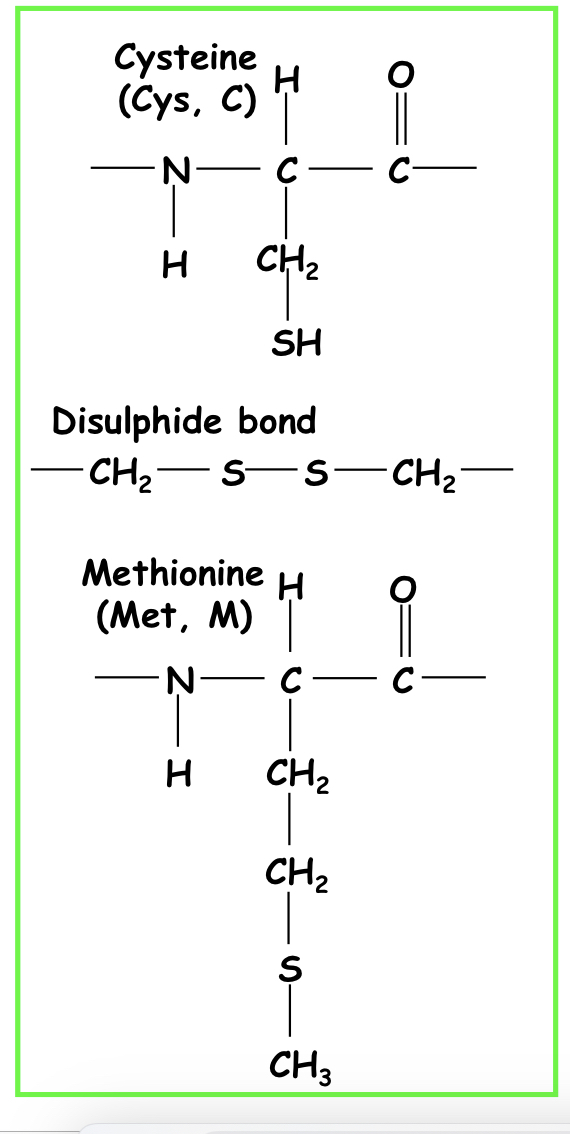
55
New cards
Aromatic side chain
Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan
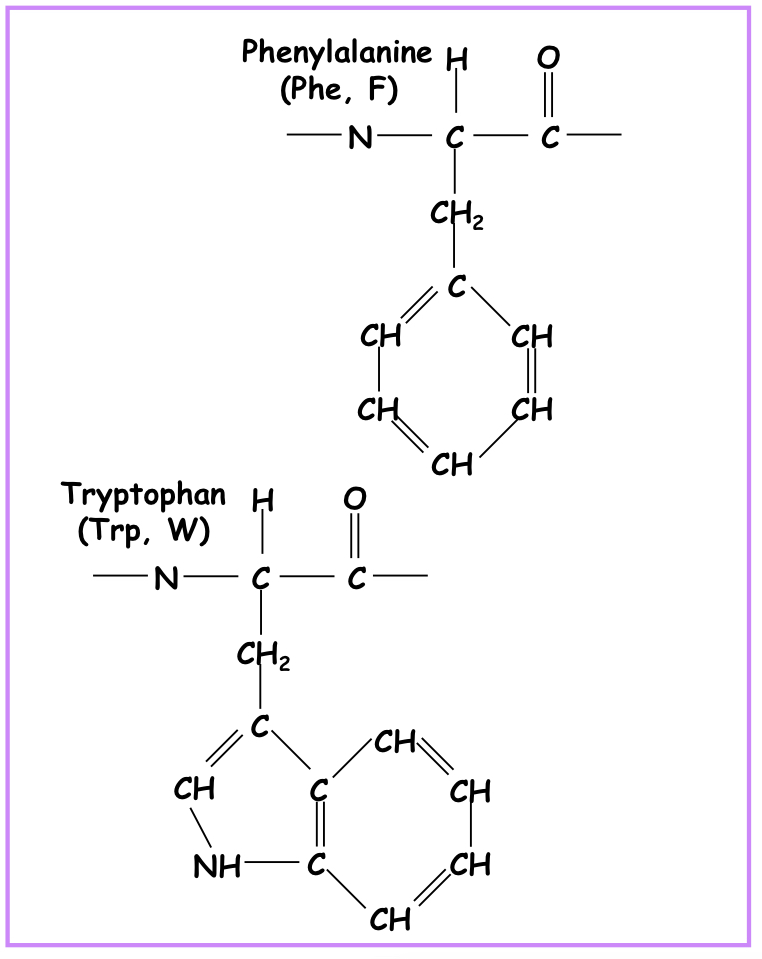
56
New cards
Polar side chain
NH₂- Asparagine and glutamine.
OH- Serine, threonine and tyrosine
OH- Serine, threonine and tyrosine
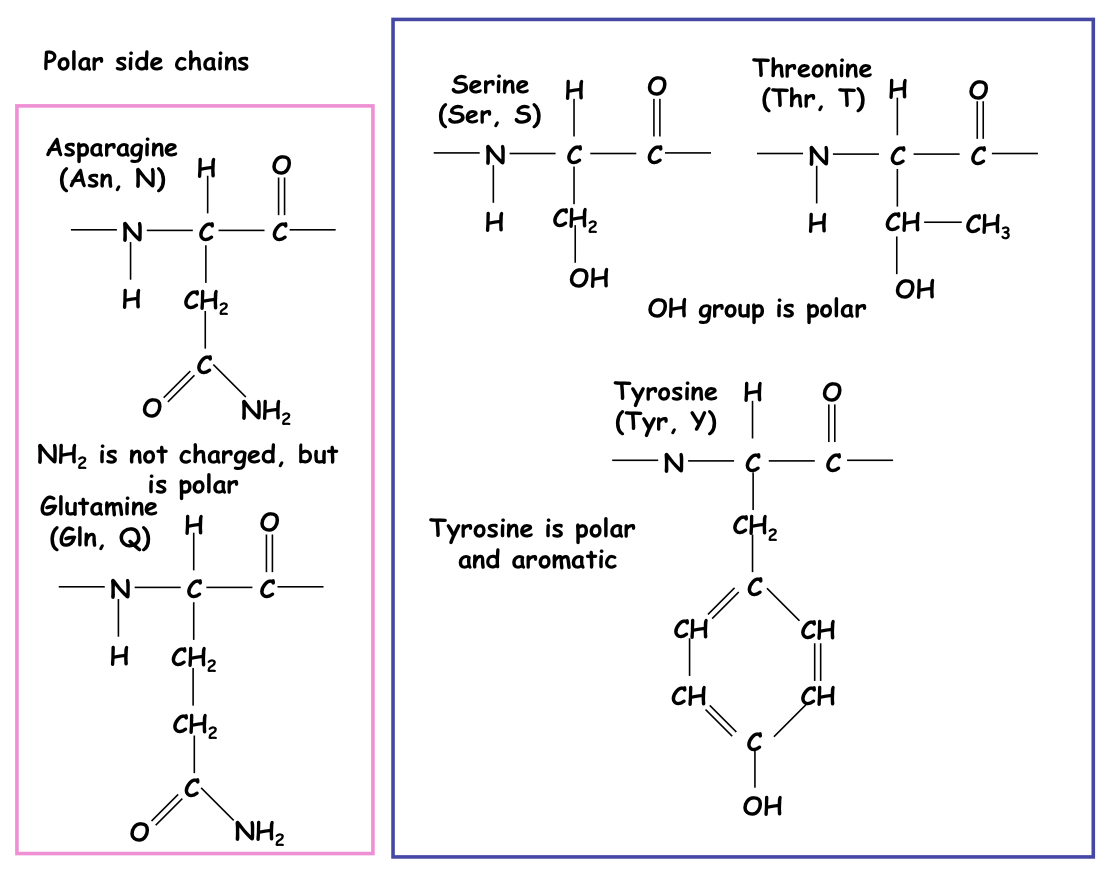
57
New cards
Zwitterion
Doubly-charged amino acid ion with negative COO⁻ group and positive NH₃⁺ group, occurs at close to neutral pH. Low pH = positive cation. High pH = negative anion.
58
New cards
pKa of amino acid
The pH of the centre point of the titration
59
New cards
Glycine
The only amino acid (out of 20 total) which does not have a chiral centre as one of its side chains is a hydrogen atom.
60
New cards
L-amino acids
Chirality of naturally-found amino acids.
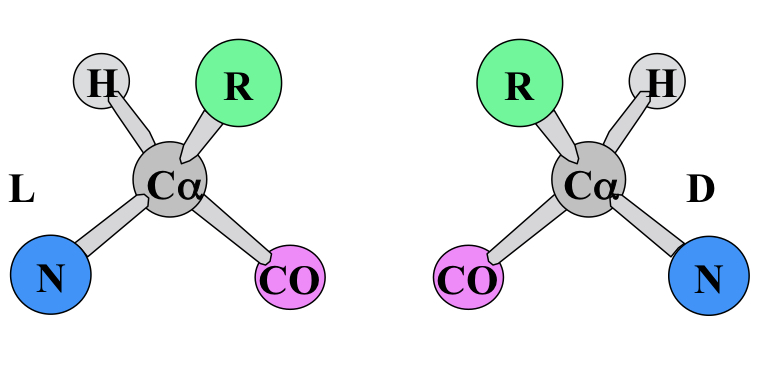
61
New cards
CORN rule
For L-amino acids, point hydrogen towards you, the groups going clockwise should spell CORN: CO, R and N
62
New cards
Peptide bond
Bond which forms via a condensation reaction, resulting in amine and carboxylate groups losing their charges. Is also rigid and planar with a little plasticity.
63
New cards
Directionality of polypeptide
Has an N-terminus (amino) and C-terminus (carboxyl), numbering and drawing is from N to C
64
New cards
Resonance hybrid
Description of a peptide due to its 40% double bond character.
65
New cards
Stereospecific
Trans peptide bonds are made to ensure sidechains on adjacent residues do not clash,describes protein biosynthesis.
66
New cards
Primary structure
Genetically defined sequence of amino acids.
67
New cards
Secondary structure
Regular structures formed by the backbone of the protein
68
New cards
Tertiary structure
3D organisation of the protein
69
New cards
Quaternary structure
Organisation of subunits in multi-subunit proteins
70
New cards
Edman degradation method
Outdated method of protein sequencing from the N-terminus only suitable for up to \~10 amino acids.
71
New cards
Disulphide bridges
The only other covalent bond in amino acids, forms between cysteine residues. (Rare in intracellular proteins due to the reducing cytoplasmic environment)
72
New cards
Phi (φ)
The angle between the nitrogen and central amino acid carbon.
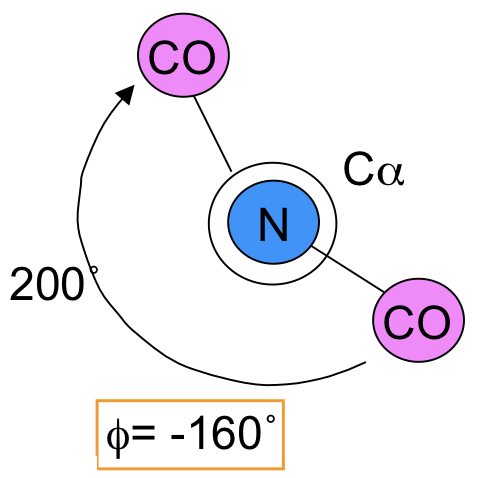
73
New cards
Psi (ψ)
The angle between the carbon of the carboxylate and the central carbon
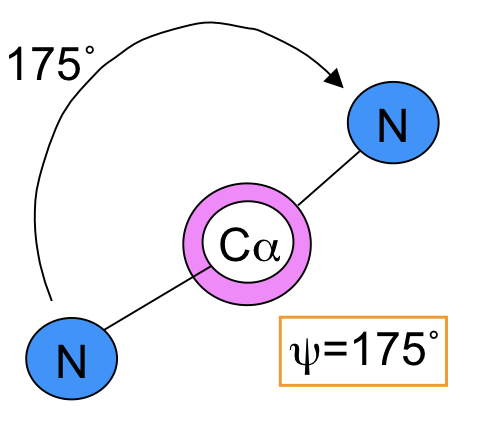
74
New cards
Steric hinderance
The process by which psi and phi bond angles are limited by the main chain and the sidechains of adjacent residues.
75
New cards
Ramachandran plot
Plot that shows possible phi and psi angle combinations for L-amino acids.
Exceptions= proline due to pyrrolidine ring of the sidechain (restricts rotation) and glycine which only has H sidechain therefore more steric freedom.
Exceptions= proline due to pyrrolidine ring of the sidechain (restricts rotation) and glycine which only has H sidechain therefore more steric freedom.
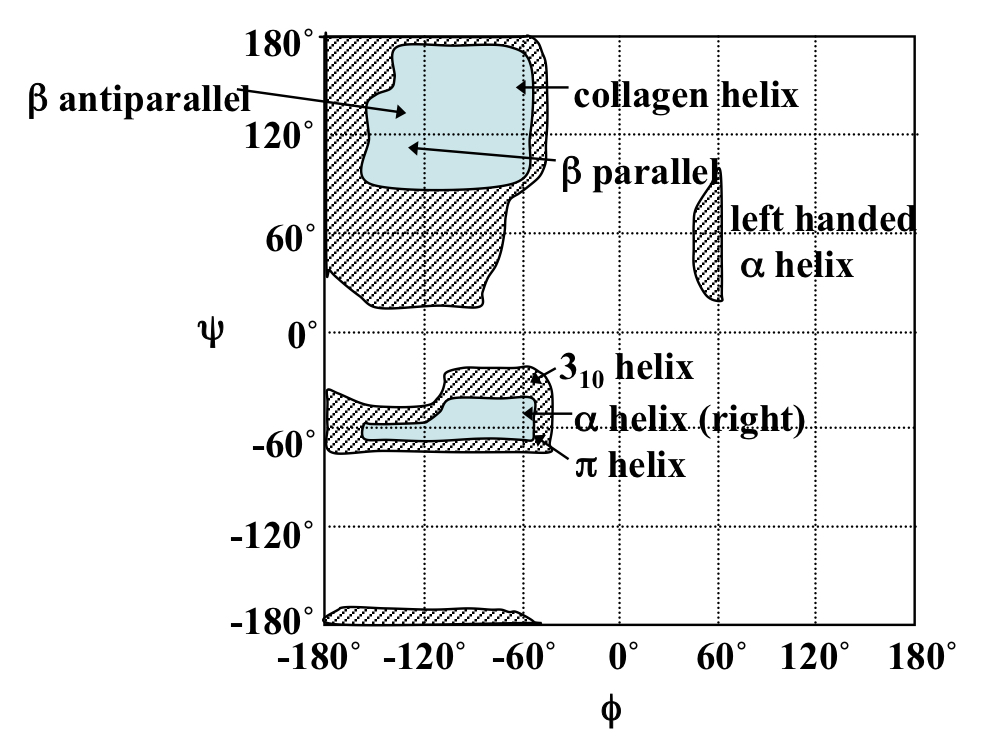
76
New cards
α-helix
Spring like structure, with main chain and side-chain R-groups protruding from the axis of the helix. Stabilised by H bonds between the NH and CO groups (i, i+4 bonding). Often occur at the first level of protein folding due to no 3D folding needed.
77
New cards
5\.4 A
The height of each complete turn of the helix
78
New cards
Helical wheel
Representation of a helix as if looking from the N-terminus, where 2 turns (7 amino acids) are represented by the letters a-g.
79
New cards
β-sheet
Extended polypeptide backbone which forms strands connected by ‘ladders’ of hydrogen bonds. R-groups alternate in protruding above/below the sheet.
80
New cards
Antiparallel
Beta sheet in which the strands run in opposite directions to one another.
81
New cards
Parallel
Beta sheet in which the strands run in the same direction as one another.
82
New cards
Ionic interactions
Interactions between amino acids with a positive (Arg, Lys) and negative (Glu, Asp) charge at physiological pH.
83
New cards
Hydrophobic interactions
Due to the preference for non-polar sidechains to associate with each other rather than the surrounding aqueous environment. (Entropic effect as increases entropy of water)
84
New cards
Van der Waals interactions
Occur when the electron distribution around one atom fluctuates, inducing fluctuations in another nearby atom.
85
New cards
Supersecondary structures
The dissection of tertiary structures into commonly-found combinations of each of the secondary structure types.
86
New cards
β-hairpin
An antiparallel β-sheet where the two strands are connected by a β-turn, involves H bonding.
87
New cards
α-hairpin
When two amphipathic alpha helices form a hydrophobic interface between each other due to hydrophobic and Van der Waals interactions that are reinforced at the edges by H-bonds and ionic interactions.
88
New cards
Four α-helix bundle motif
Motif found in proteins that bind to haem (electron and oxygen carrier). E.g. cytochrome c and myoglobin.
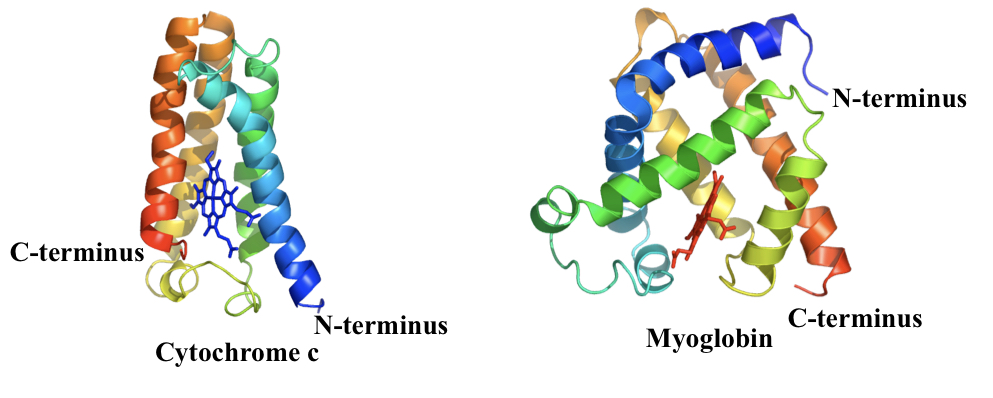
89
New cards
βαβ motif
Found in proteins with parallel β-sheets, proteins that bind to nucleotides usually have this structure in a ROSSMAN FOLD. E.g. lactate dehydrogenase which binds to NADH.
90
New cards
Greek key motif
Basis of the immunoglobulin fold, held together by hydrophobic interactions.
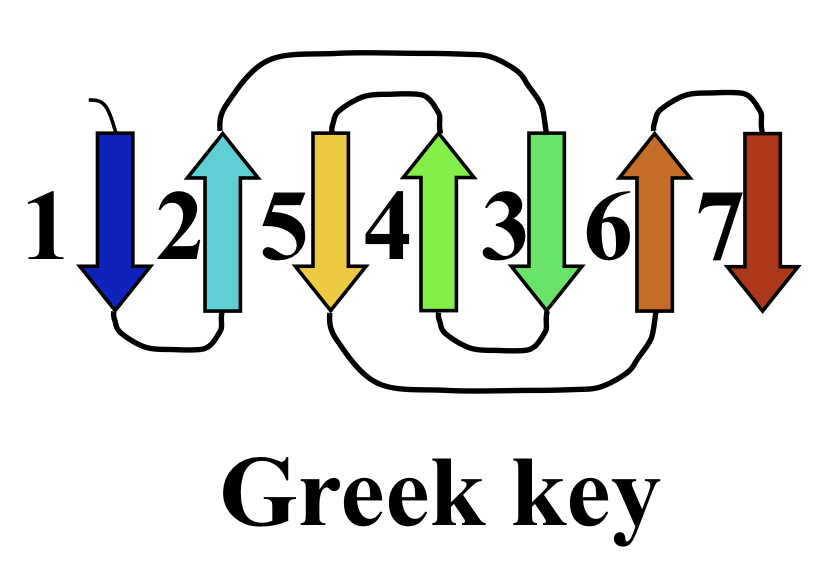
91
New cards
Cryo-electron microscopy
Sample is rapidly frozen to preserve and protect during observation, results in a 3D image
92
New cards
X-ray diffraction
Electrons in the molecule scatter the x-rays, makes a diffraction pattern to make an electron density map.
93
New cards
NMR spectroscopy
Applicable to small proteins in solution, placed into a strong magnetic field and irradiated at radio frequencies to get bond length and a 3D model
94
New cards
Atomic force microscopy
Atomically sharp tip is scanned over a surface to map the topography of the sample.
95
New cards
DNA binding proteins
Diners that can bind to the grooves in DNA. E.g. CRO from bacteriophage lamda is a 2 a-helix dimer that binds to adjacent major grooves on DNA.
96
New cards
Haemoglobin
Contains 4 myoglobin chains as a bundle protein (α-helix), arranged into a tetramer.
97
New cards
Sickle cell anaemia
Mutation on the surface of two haemoglobin monomers that replaces glutamic acid (charged) with valine (hydrophobic). Causes haemoglobin molecules to polymerise due to hydrophobic interactions, causing distortion of the cell in to a sickle shape.
98
New cards
Effects of sickle cell anaemia
Cell rupture, blocking of capillaries and a decreased ability to carry O2.
99
New cards
Ribonuclease
The enzyme that hydrolyses RNA.
100
New cards
Ribonuclease experiement
In the presence of 8M urea and β-mercaptoethanol, the protein is denatured. When they are removed, the protein can spontaneously re fold to the catalytically active form in certain conditions.