[BOTAONE] LE1
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
Photosynthesis
(Biological Process) Capture of light energy and its transformation into chemical energy of organic molecules that are manufactured from carbon dioxide and water
Cellular Respiration
(Cellular Process) Energy of organic molecules is released for biological work
Tropism
Growth toward or away from stimulus
Hypothesis
Educated guess based on previous observation that is testable by observation and experiments
Theory
Widely accepted explanation supported by a large body of observations and experiments
Consistent, Observable, Natural, Predictable, Testable, Tentative
Criteria of Science (CONPTT)
Atom
Smallest unit of matter
Matter
Consists of chemical elements.
Element or Substance
Pure form cannot be broken down to other substance by chemical reaction
Compound
Two or more elements combined in a fixed ratio
Electron (-), Proton (+), Neutron
Atom Structure
20-25% ; 92 ; 17
About ___% of the ___ natural elements are essential to life (___ for plants)
Oxygen, Hydrogen, Carbon, Nitrogen
4 elements that make up 96-99% of living matter
True
(True/False) Plants have more carbon percentage
Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Calcium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sulfur, Sodium & Chlorine, Magnesium
Naturally occurring elements in the living system
Inorganic (water, salts, ions) molecules ; Organic molecules
Cell contains both __ and __
Water (H2O)
Biological medium that supports all life
True
(True/False) Not all compounds with Carbon are organic
Hydroxyl
—OH, Alcohols, Ethanol
Carbonyl
>CO, Ketones;Aldehydes, Acetone, Glucose
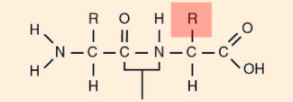
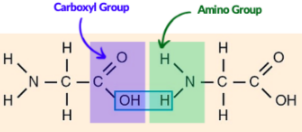
Carboxyl
—COOH, Organic acids, Acetic acid
Amino
—NH2, Amines, Amino acids
Phosphate
—PO4, Organic phosphates, Glycerol phosphate
Carbon
Can form chemical bonds with 4 other atoms including same element
4 electrons (outer shell) ; 4 bonds form Tetrahedron
Carbon’s bonding pattern
Functional Groups
Special cluster of atoms that performs a useful specific function
Cohesion
Water is attracted to water
Adhesion
Water is attracted to other substances
Oxygen
__ can form two hydrogen bonds
water
Arrangement of __ changes constantly
Hydrogen-bond
Each water molecule can __ to several others
Water polar molecules
__ are attracted to ions and polar substances that can form hydrogen bond
Hydrophilic
Substances that have affinity to water
Hydrophobic
Substances that do not have affinity to water
Power of Hydrogen
pH
pH level
Amount of hydrogen ion (-log [H+])
pH scale
Relative concentration of H+ and OH- in a solution
Acidic
more H ions (0-6)
Basic
Less H ion (8-14)
7
Neutral in pH scale
Polymer
Long molecule consisting of many identical building blocks (Carbohydrates, Protein, Nucleic Acids)
Monomer
Building blocks of Polymers linked by covalent bonds (Lipids)
Carbohydrates
Serve as fuel and building materials. Includes sugars, polymers of sugars (starch and cellulose)
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars, monomers for more complex carbohydrates
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharide units, double sugars
Polysaccharides
Many monosaccharide units, carbohydrate polymer
Aldehyde ; Alcohol
Monosaccharides include a Carbonyl group __ and Hydroxyl group __
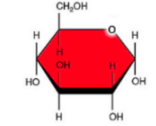
Glucose Structure [C6H12O6]
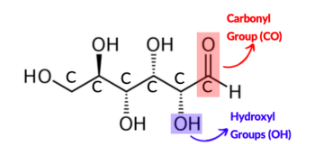
Glucose molecules
During cellular respiration, the cell extracts energy from __
Glucose
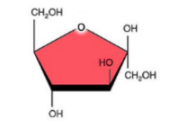
Fructose
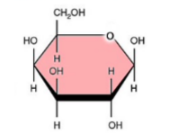
Galactose
Glycosidic linkage
Two monosaccharide (disaccharide) units are joined by a __: acovalent bond by dehydration
Sucrose ; Glucose ; Fructose
Most prevalent disaccharide also known as table sugar. It is made up of two monomers __ and __
Sucrose
Plants generally transport carbohydrates in the form of __
Broken down into monosaccharides
Disaccharides must be __ to be used for energy by organisms
Storage Polysaccharides
Storage materials, hydrolyzed as needed to provide monosaccharides for cell. Stores sugar for later use (stores starch for plants)
Storage Starch
A polymer of glucose monomers, granules within cellular known as Plastids
Structural Polysaccharide
Building material for structures that protect the cell/whole organism
Cellulose
Consists of repeating units of glucose, reinformed by numerous hydrogen bonds between glucose molecules. (unbranched)
Microfibrils
Cellulose are grouped into units called __
Proteins
macromolecule encoded by the organism’s genome
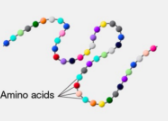
Peptide bonds
Proteins are composed of amino acids joined by __
Enzymes
Macromolecule that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reaction by lowering its activation energy
Amino acids
Organic molecule with both an amino group and a carboxyl group
Polypeptide
Proteins are made up of one or more __ folded and coiled into a specific structure
Primary protein
Sequence of a chain of amino acid
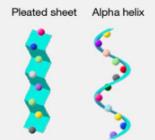
Secondary protein
Sequence of amino acids folds into a 3D shape. Stabilized by hydrogen bonds
Tertiary protein
Mature protein folds upon itself

Quaternary protein
Protein consisting of more than one polypeptide chain (Ribosome, site of P synthesis)

Normal binding
Substrate can bind normally to the active site of an enzyme
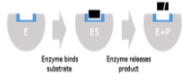
Competitive inhibition
Competitive inhibitor mimics the substrate, competing for the active site
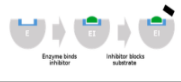
Noncompetitive inhibition
Binds the enzyme away from the active site, altering shape of enzyme so even if substrate can bind, the active site functions less effectively if at all

Nucleic acid
Store, transmit and help express hereditary information. Controls cell’s life processes
DNA
Transmits information from one generation to the next. Directs RNA synthesis
RNA
Involved (controls) in protein synthesis
Gene expression
Process of synthesizing DNA to RNA to protein
Nucleotides
Repeating units that form nucleic acids. Its order in a nucleic acid chain determines the specific information encoded
Pyrimidines
Six-membered rings of C and N atoms
Uracil
Pyrimidine found only in RNA
Thymine
Pyrimidine found only in DNA
Cytosine
Pyrimidine found in both RNA and DNA
Purine
Six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring
Adenine and Guanine
two purines found in both RNA and DNA
Lipids
Macromolecules not soluble in water (hydrophobic). Main non-polar component of cells. Mostly hydrocarbons (no oxygen)
Fats (Triglycerides)
Composed of 3 fatty acids attached to a molecule of gycerol
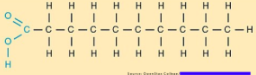
Fatty acids
Long hydrocarbon chains with an acid group at one end, usually 16-18 carbon atoms in length
Glycerol
3 carbon carbohydrate. It has 3 alcohol (—OH) groups which link up with the acid groups in the fatty acids
Saturated fats
Hydrocarbon chains with all single bonds. Solid in room temperature
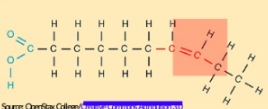
Unsaturated fats
Fats with double bonds. Liquid in room temperature. Can be obtained from plants and fishes
Trans fats
Hydrogenated fat that produced unsaturated fats with trans double bonds and solidified to a saturated fat (ex. margarine)
Glycerols with 2 fatty acids, phosphate containing head group, phospholipid bilayer
Main component of cell membranes
Plant waxes
Retards water loss from plant
Steroid hormones
Hydrocarbons with carbon atoms arranged in a set of 4 linked rings
Cholesterol
Common steroid that is an essential component of animal cell membranes
Secondary Metabolites
Product of cells’ metabolic activities. Responsible for bright colors of flowers, bitter taste in certain plants
Terpenoids
Dimers and polymers of 5-C called isoprene units
Phenolic compounds
Formed by a benzene ring, carboxyl group and one or more hydroxyl groups in their molecules, giving them antioxidant properties (ex. Lignins, Flavonoids)
Naturally occurring organic nitrogen-containing bases (Morphine, Caffeine)
Energy
Ability to do work, capacity to cause change