UCI Chem 1LD Practical
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What factors determines whether a solute will dissolve in a solvent?
imf's, molecular dipoles, molecular geometry, electrostatic attraction
What is the strongest imf that must be overcome when melting menthol?
hydrogen bonding

A —> solid
B —> liquid and solid
C —> liquid
D —> gas and liquid
E —> gas
F —> boiling point
G —> melting point
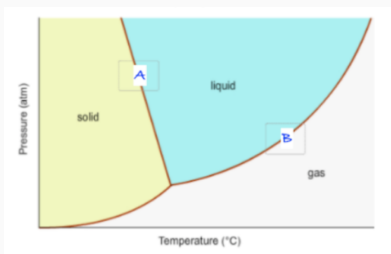
Label A and B. Which direction does each line shift when solute is added?
solid-liquid coexistence line —> A
liquid-gas coexistence line —> B
A shifts left
B shifts right
How do impurities affect melting point? By what colligative property does this occur?
lower the melting point
freezing point depression
A solution is created when a small amount of solute dissolves in a large amount of _________
solvent
What is concentration of a solvent reported as?
molality or molarity
A solutions concentration is reported in _______ per ________
moles of solute per kilogram of solvent
moles of solute per liters of solution
What should you do to respond to an emergency?
know where the stairwells are
all laboratories must have two exits
stay calm
turn off lab equipment before leaving lab for a fire alarm
True or false: cinnamic acid dissolves in melted menthol
true
True or false: cinnamic acid does not stay dissolved in solid menthol
true
How will a weak acidity affect the freezing point depression?
The solution freezing point is lower than it should be
Why does the freezing point of a solution decrease as a result of weak acidity?
particles in the solution are greater due to dissociation
Under what conditions are the values of molarity and molality very different?
high concentrations
Why is molality used instead of molarity in this project?
volume changes with temperature —> change in molarity
name common household products that contain flammable chemicals
rubbing alcohol, gasoline, antifreeze, nail polish remover
ways to stop a fire
place beaker over an open flame to remove oxygen
ground metal container to prevent static electricity
remove ignition sources
limit quantities of flammable substances in work area
what is true about flammability?
1. inflammable is another word for flammable
2. a fire cannot start above or below a vapor's flammability limits
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) diamond has a [A] section for flammability. If the number [B] appears in this section, the chemical is extremely flammable. If the number [C] appears in this section, the chemical is a combustible, it will catch fire when heated. The Global Harmonized System (GHS) symbol is a picture of a [D]. If the hazard category is [E], the chemical is extremely flammable. If the hazard category is [F], the chemical is combustible.
red
4
2
fire
HC1
HC4
best piece of glassware to measure out volumes for TLC eluent ratios is __________
graduated cylinder
polar spots in TLC
are attracted to the silica plate and travel short distances up the plate
non-polar spots in TLC
are attracted to the eluent and travel farther distances up the plate
What is true about fume hoods
room air should be drawn into the fume hood
The window on the front of the fume hood is called a sash.
All work should be done at least 6 inches inside the hood.
A tissue paper held at the bottom of a sash should blow into the hood.
PEL
permissible exposure limit
odor threshold
gas concentration that 50% of the population can detect
odor fatigue
decreased sensitivity to odors over time
IDLH
Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health
OEL
Occupational Exposure Limit
what is the major underlying principle of chromatography?
separation will be achieved if one component adheres to the stationary phase more than the other component does
what is a stationary phase?
silica TLC plate, likely solid
what is a mobile phase
eluent (heptane/acetone mixture), likely liquid or gas
Why does most of the TLC plate turn pink in permanganate dip?
unreacted permanganate is pink
Why do TLC spots turn yellow after dipping in permanganate?
the compound has double bonds
What is true about gloves?
1. gloves should be removed when they come in contact with any hazardous chemicals
2. no glove material protects against all chemicals
permeation
ability of a chemical to penetrate the glove material through small pores
degradation
destructive change in the glove material
breakthrough time
time for the first appearance of a chemical on the other side of the glove
rate of transfer
speed at which chemical appears on the other side of the glove
lab coats
sleeves should never be rolled up
should never be worn outside of lab
nitrile gloves
protect well against aliphatic hydrocarbons like heptane and limonene
nitrile gloves can be degraded by acetone (a ketone)
What of the following guidelines should be followed to protect your skin in the chemical laboratory?
1. wear a lab coat
2. wear clothing that covers most of your body
3. wear sturdy closed toed and heel shoes
4. use gloves when appropriate to do so.
toxicology
the study of the adverse effects of chemicals
toxicity
ability of a chemical to damage an organ
toxicant
chemical producing toxic effects
toxin
toxic substance made by plant, animal, fungi, or bacterium (living organisms)
acute toxicity
ability of a chemical to do damage with a single dose
chronic toxicity
ability of a chemical to do damage after multiple doses
LD(50)
lethal dose that kills 50% of a population
LC(50)
lethal concentration that kills 50% of a population
what factors influence toxicity
the dose makes the poison
age —> very young and very old more susceptible to toxic effects
animal models are not always a good representation of human responses
Acetaminophen’s (tylenol) fate in the human body
metabolized and removed by the liver
DDT fate in the human body
bioaccumulation - stored in fat
ethylene glycol fate in the human body
metabolized to calcium oxalate —> forms crystals in kidneys
example of a sensitizer
formaldehyde
example of a asphyxiant
carbon monoxide
example of a teratogen
acrylonitrile
example of a carcinogen
benzene
example of a organ toxicant
ethanol
example of a neurotoxin
acetone
example of a poison
cyanide
what assumptions can be made if the solid does not melt in the digi-melt?
digi-melt does not reach high enough temp to melt the solid or it is broken
what is the role of vanillin?
limiting reagent
what is the role of acetic acid?
source of H+ for redox balance
what is the role of hydrogen peroxide?
oxidizing agent
what is the role of horseradish peroxidase?
catalyst
hazard
A potential source of danger
risk
probability of suffering harm
risk level
hazard severity x exposure probability
risk assessment
identification of sources of danger and probability of harm
risk management
wearing PPE, avoiding spark sources, using smaller amounts
What affects the probability of a lab accident
how other people behave, how chemicals are used, how the physical environment is controlled
factors to probability of exposure to a hazard (5)
1. amount of chemicals used
2. type of PPE needed
3. routes of exposure
4. containment of chemicals
5. personal knowledge of the hazards
what determines the severity of a hazard?
1. GHS symbols
2. chemical amount used
3. PELs
4. LD50 values
5. NFPA fire ratings
zero risk
no hazards are present
balancing
risk allowed increases with benefit of chemical use
technology-based
exposure level is set to level it can be reduced to
eye hazard
causes irreversible damage to cornea or iris
sensitizers
cause hypersensitivity to lungs or skin
mutagens
produce genetic defects
carcinogens
substances that (presumably) cause cancer in humans
reproductive toxins
cause birth defects
target organ toxicants
cause damage to certain organs, affecting their ability to carry out normal functions
aspiration hazards
can be fatal if swallowed or inhaled
acute toxicants
Are fatal if exposed to the smallest amounts
corrosives
cause severe skin burns and eye damage
what makes good sunscreen
high percent yield
broad absorbance of uv light
low hazard starting materials
melting point value
ambient reaction conditions (little to not heat or pressure needed)
color and feel
filtration terms. what type of mixture is being separated?
filtrate, vacuum, buchner funnel
heterogenous mixture
TLC terms. what type of mixture is being separated?
eluent, silica plates, solvent front
mixture with components of different polarities
crystallization terms. what type of mixture is being separated?
temperature dependent solubility, no agitation
product with impurities
green chemistry
uses materials and processes that are intended to prevent or reduce pollution at its source
what applies to green chemistry
1. high yield reactions
2. methods used to eliminate hazards during chemical use and manufacturing
3. use less hazardous reagents
4. choose reactions that can be done at room temp and pressure
5. recycle reagents and solvents
How does 1LD use green chemistry
using starting reagents from renewable feedstocks
sunscreen synthesis did not require heat
atom economy
MM of product / MM of all reactants * 100