Exam 2 Computer Science
1/66
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
File
An Area in secondary storage used to hold information.
C++ Standard Template Library includes a header file for file I/O: fstream
Header to only use input from a file: ifstream
Header to only use output to a file: ofstream
File I/O

Strings Continued

Command Line Arguments
A parameter supplied to the program when it is invoked.
Using Command Line Arguments

List
A collection of components arranged one after another
(1D)Array
A list containing a collection of a fixed number of components of the same data type.
Arrays

Accessing Information in Arrays

Processing Arrays Types
1. Initializing an array
2. Reading data into an array
3. Printing an array
4. Finding the sum/average of an array
5. Finding the largest/smallest element in an array
Initializing an Array

Reading Data Into an Array

Printing an Array

Finding the Sum/Average of an Array

Finding the Min/Max of an Array

In-Bound Index
An index that is 0 <= index <= arraySize -1.
Out-Of-Bounds Index
An index that is index < 0 or arraySize - 1 < index.
Array Out of Bounds

Copying One Array Into Another Array

Two-Dimensional Array
A collection of a fixed number of components arranged in rows and columns, wherein all the components are of the same data type.
2D Arrays

Void Functions
Functions that do not have a return type. These functions do not return a value or use a return statement.
Value-Returning Functions
Functions that have a return type. These functions return a value of a specific data type using the return statement.
Void Functions Without Parameters

Void Functions With Parameters

Value-Returning Functions

Formal Parameters
A variable declared in the function heading.
● The formal parameters are the parameters you can use only in your user-defined function.
● General syntax (Formal Parameter List): dataType identifier, dataType identifier, …
Actual Parameters
A variable or expression listed in a call to a function.
● The actual parameters are the parameters you can use only in your calling function.
● General syntax (Actual Parameter List): expression or variable, expression or variable,
Scope
Where in the program an identifier is accessible (visible).
Local Identifier
Identifiers declared within a function or block of code. These identifiers are not accessible outside of the function or block of code they are declared in.
Global Identifier
Identifiers declared outside of every function definition. These identifiers are accessible from any function in your program (but not without side effects).
Rules when accessing identifiers:

Function Prototype
The function heading without the body of the function or identifiers of the formal parameters.
Function Prototype Page

Value Parameters
A formal parameter that receives a copy of the value of the corresponding actual parameter.
Value Parameter Page

Reference Parameters
A formal parameter that receives the address (memory location) of the corresponding actual parameter.
Reference Parameters Page

Default Parameters

Function Overloading
Creating several functions with the same name.
Function Overloading Page

Control Structures

While Looping
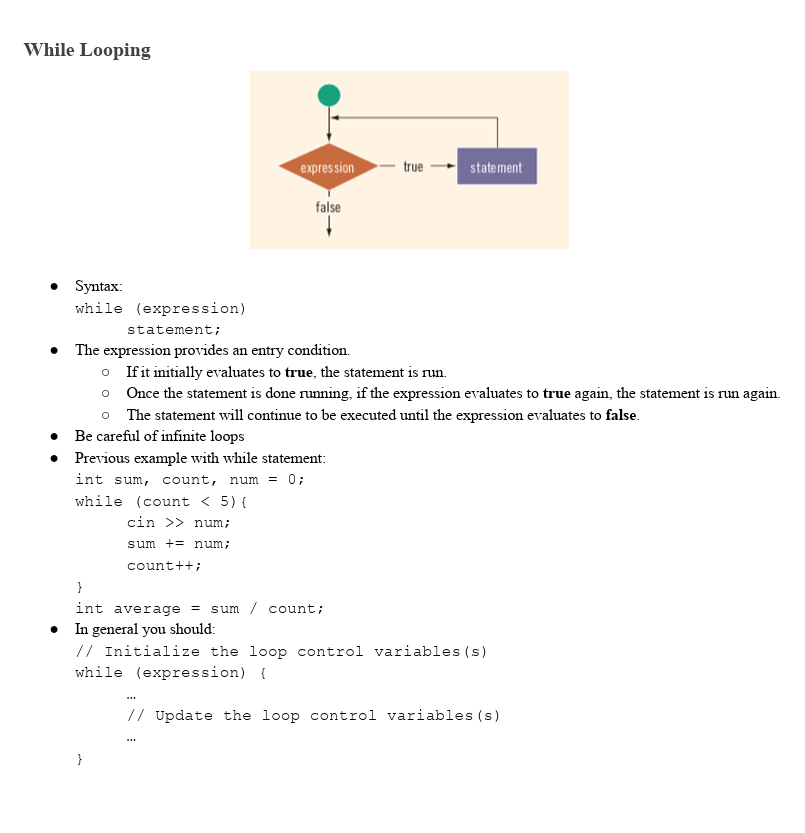
Types of While Loops

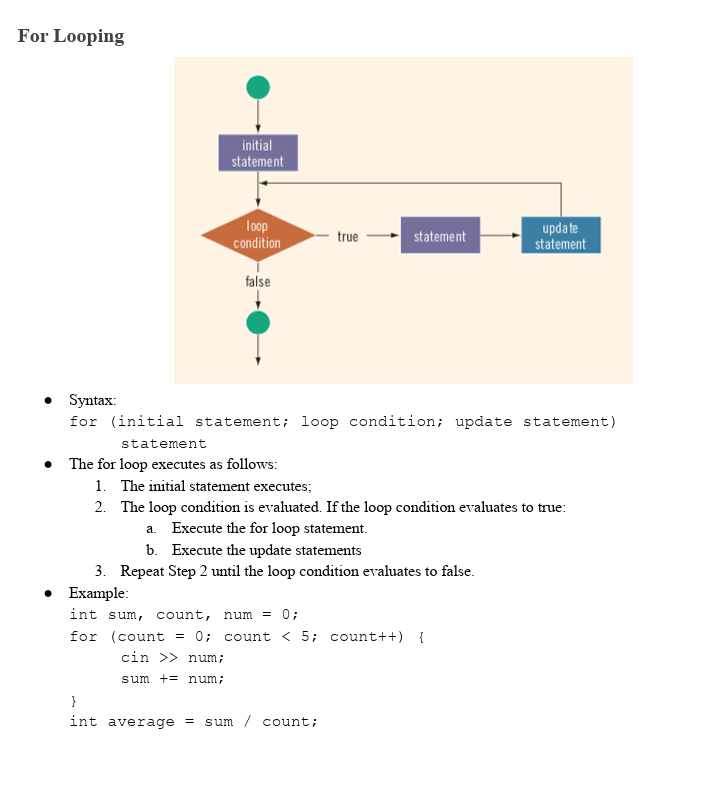
For Looping
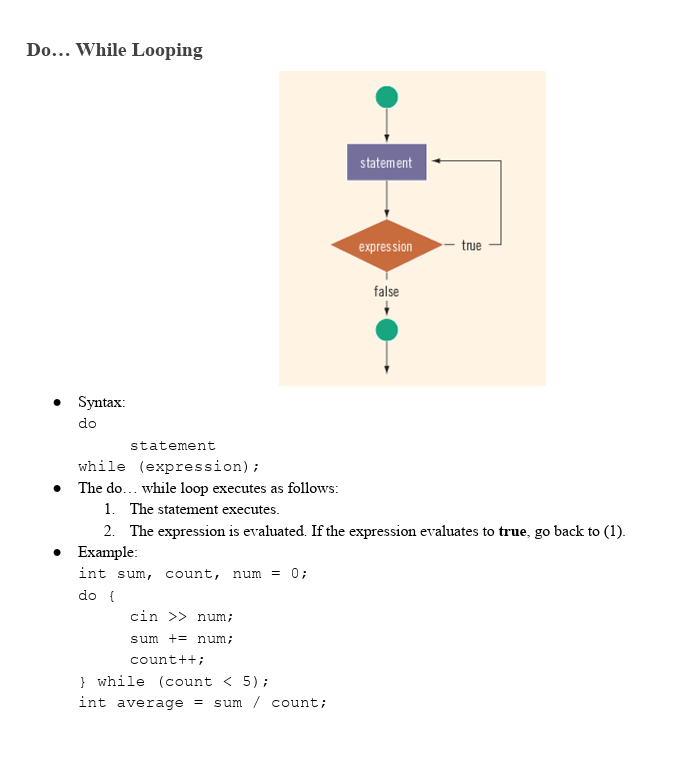
Do While Looping
Break and continue

Nested Control Structures

Explain the difference between break and continue statements in a loop.
The break statement is used to exit a loop prematurely, whereas the continue statement is used to skip the rest of the loop's code and move to the next iteration.
What loop is best to use when you know the number of iterations?
For loops
What loop is best to use when you at least want one iteration?
Do ... while loop.
Why should we not use global variables in our program?
If you use a global variable throughout your program, it can be very hard to track down bugs with them. Problems caused by a global variable in one part of a program may be understood as problems in other parts of a program. Since the variable scope is larger, that means more code to surf through.
Given the following code snippet, what is the output after execution?
int n = 3;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) {
cout << j << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
1
1 2
1 2 3
In a few lines of code, verify if the file was open.
Explain the purpose of the library in C++.
Used for file input and output operations. It provides classes like ifstream (input file stream) and ofstream (output file stream) that enable reading from and writing to files
Create an 2D integer array named arr with 5 columns and 3 rows.
const int rows = 3;
const int columns = 5;
int arr[rows][columns];
With a few lines of code, print all elements of an array named values with 8 elements.
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
cout << values[i] << " ";
}
Why is it important to be cautious about accessing elements beyond the bounds of an array in C++?
Accessing elements beyond the bounds of an array in C++ can lead to undefined behavior, including segmentation faults (seg faults). This occurs because memory outside the allocated array space may not belong to the program, causing unexpected results or crashes.
List the general steps of reading data from a text file into a one-dimensional array in C++.
1. Include Necessary Headers: #include <fstream>
2. Declare an Input File Stream
3. Open the File
4. Declare and Initialize the Array
5. Read Data from the File
6. Close the File
Provide the function signature for each function.
void acc(int id, char alpha, double cash);
int fire(float radius, float temperature = 60);
string ice(int temp = 31, bool shard = 29);
void bomb(int time[], int power, double radius);
void shift(int x, int pos[], double z);
acc(int, char, double)
fire(float, float) fire(float)
ice(int, bool) ice(int) ice()
bomb(int[], int, double)
shift(int, int[], double)
For a function: int findArea(int length, int width), provide an example that uses function overloading.
int findArea(int radius)
For the following program, correctly label the function prototype, body, call, and header.
1. Prototype
2. Call
3. Header
4. Body

Why are arrays always passed by reference to functions?
Arrays are a contiguous block of memory. Passing them by reference (by providing the memory address) avoids the overhead of copying the entire array, making function calls more efficient.

(Ideas on how to approach this but not perfect)
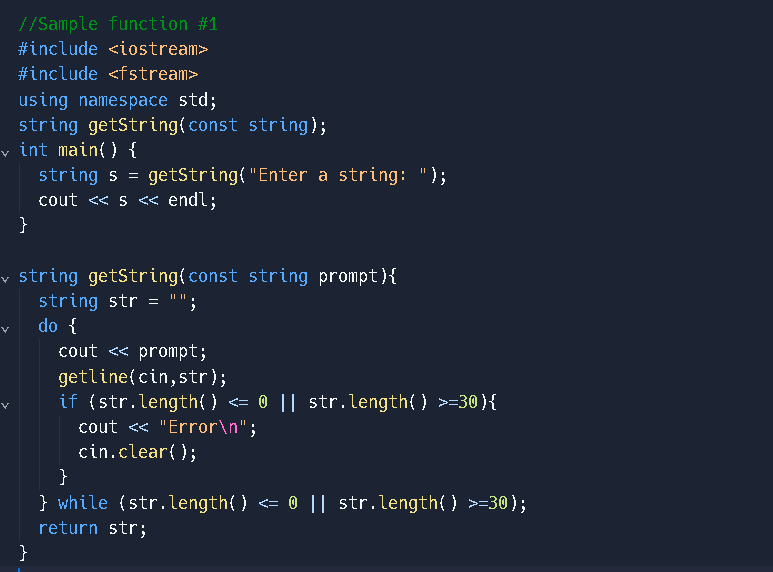

(Ideas on how to approach this but not perfect)
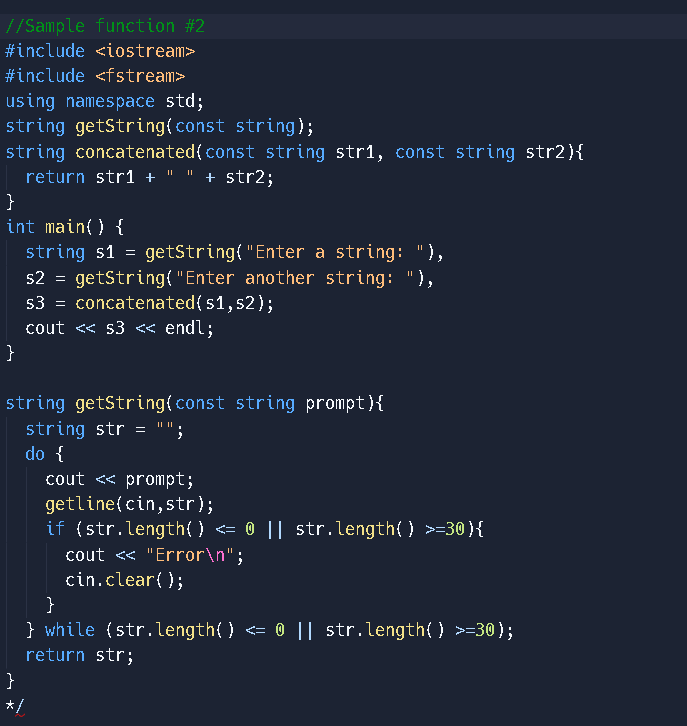

(Ideas on how to approach this but not perfect)
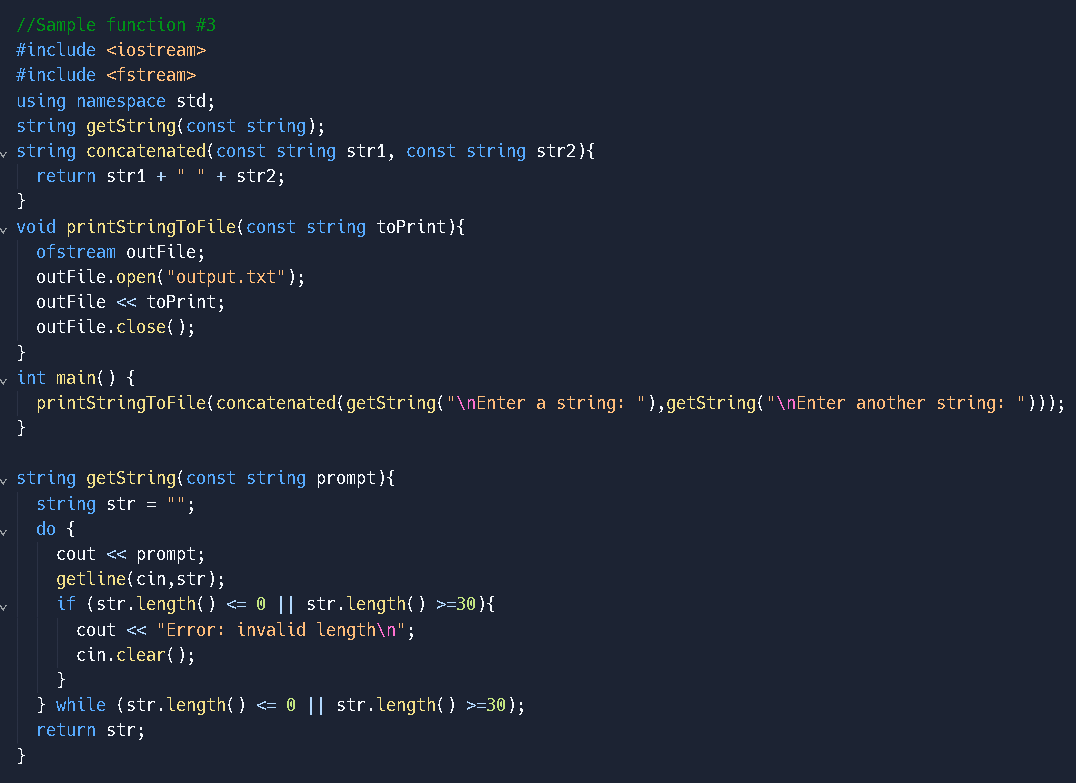
Function Signature
The function name and formal parameter list data types. The signature does not include the return type of the function.