Thermodynamics
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the zeroth law of thermodynamics?
Objects are in thermal equilibrium when they are at the same temperature
Describe objects in thermal equilibrium.
They experience no net exchange of heat energy
What does the zeroth law state?
Transitive property in thermal systems: If a = b and b = c, then a =c
What is temperature?
- qualitative measure of how hot or cold an object is
- quantitatively, it's related to the average kinetic energy of the particles that make up a substance
What type of property is temperature? Explain.
- physical property of matter
- related to average KE of particles
- differences in temp determine direction of heat transfer
Absolute zero in ˚F, ˚C and K
-460
-273
0
Freezing point of water in ˚F, ˚C and K
32
0
273
Boiling point of water in ˚F, ˚C and K
212
100
373
What does thermal expansion describe?
How a substance changes in length or volume as a function of the change in temperature
What is a thermodynamic system?
The portion of the universe that we are interested in observing
What do surroundings include?
Everything that is not part of the system
What are 3 kinds of systems?
1. isolated
2. closed
3. open
Describe isolated systems.
They do not exchange matter or energy with the surroundings
Describe closed systems.
They exchange energy but not matter with their surroundings
Describe open systems.
They exchange both energy and matter with their surroundings
What are examples of process functions?
- work
- heat
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
A statement of conservation of energy: the total energy in the universe can never decrease or increase
Describe total internal energy in a closed system.
It's equal to the heat flow into the system minus the work done by the system
What is an increase in total internal energy of a system caused by?
Transferring heat into the system or performing work ON the system
When would the total internal energy of a system decrease?
When heat is lost from the system or work is performed BY the system
What is heat?
The process of energy transfer between two objects at different temperatures that occurs until the two objects come into thermal equilibrium (reach same temp)
What is specific heat?
The amount of energy necessary to raise one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius or one unit kelvin
What is the specific heat of water?
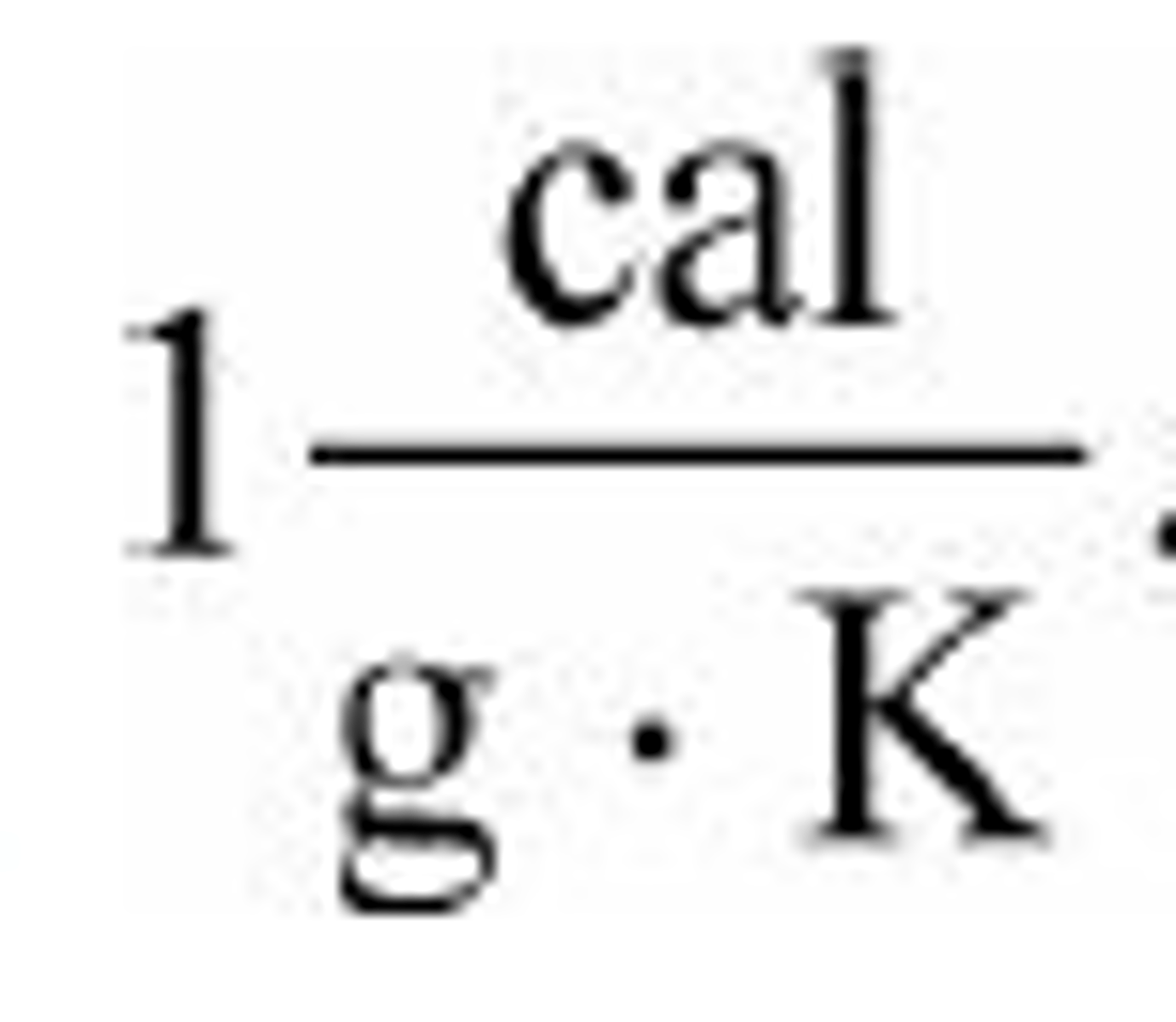
What is one calorie (little c)?
The amount of heat required to raise 1 g of water one degree Celsius
What is one Calorie (big C)?
The amount of heat required to raise 1 kg of water 1 degree Celsius, equal to 1000 calories
Explain what heat of transformation is.
- during a phase change, heat energy causes changes in the particles' potential energy and energy distribution (entropy), but not kinetic energy
- there is no change in temperature
What are the four special types of thermodynamic systems in which a given variable is held constant?
1. isothermal processes
2. adiabatic processes
3. isobaric processes
4. isovolumetric (isochoric) processes
Describe isothermal processes.
- temperature is constant
- change in internal energy is therefore 0
Describe adiabatic processes.
No heat is exchanged
Describe isobaric processes.
The pressure is held constant
Describe isovolumetric (isochoric) processes.
- volume is held constant
- work done by or on the system is 0
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
In a closed system (up to and including the entire universe), energy will spontaneously and irreversibly go from being localized to being spread out (dispersed)
What is entropy?
A measure of how much energy has spread out or how spread out energy has become
What increases entropy? Explain.
- as the number of available microstates increases, the potential energy of a molecule is distributed over that larger number of microstates
- increasing entropy
Describe the universe and what you know because of it.
- universe is a closed, expanding system
- entropy is always increasing
- more space that appears with the expansion of the universe, the more space there is for the entire universe's energy to be distributed and the total entropy of the universe to increase irreversibly
What is irreversible?
Every natural process
What can be reversible? Explain.
Under highly controlled conditions, certain equilibrium processes such as phase changes can be treated as essentially reversible
How is the first law of thermodynamics calculated?
ΔU = Q - W
What is the equation to describe heat gained or lost (with temperature change)?
q = mcΔT
What is the equation to describe heat gained or lost (phase change)?
q = mL
How is entropy and heat calculated?
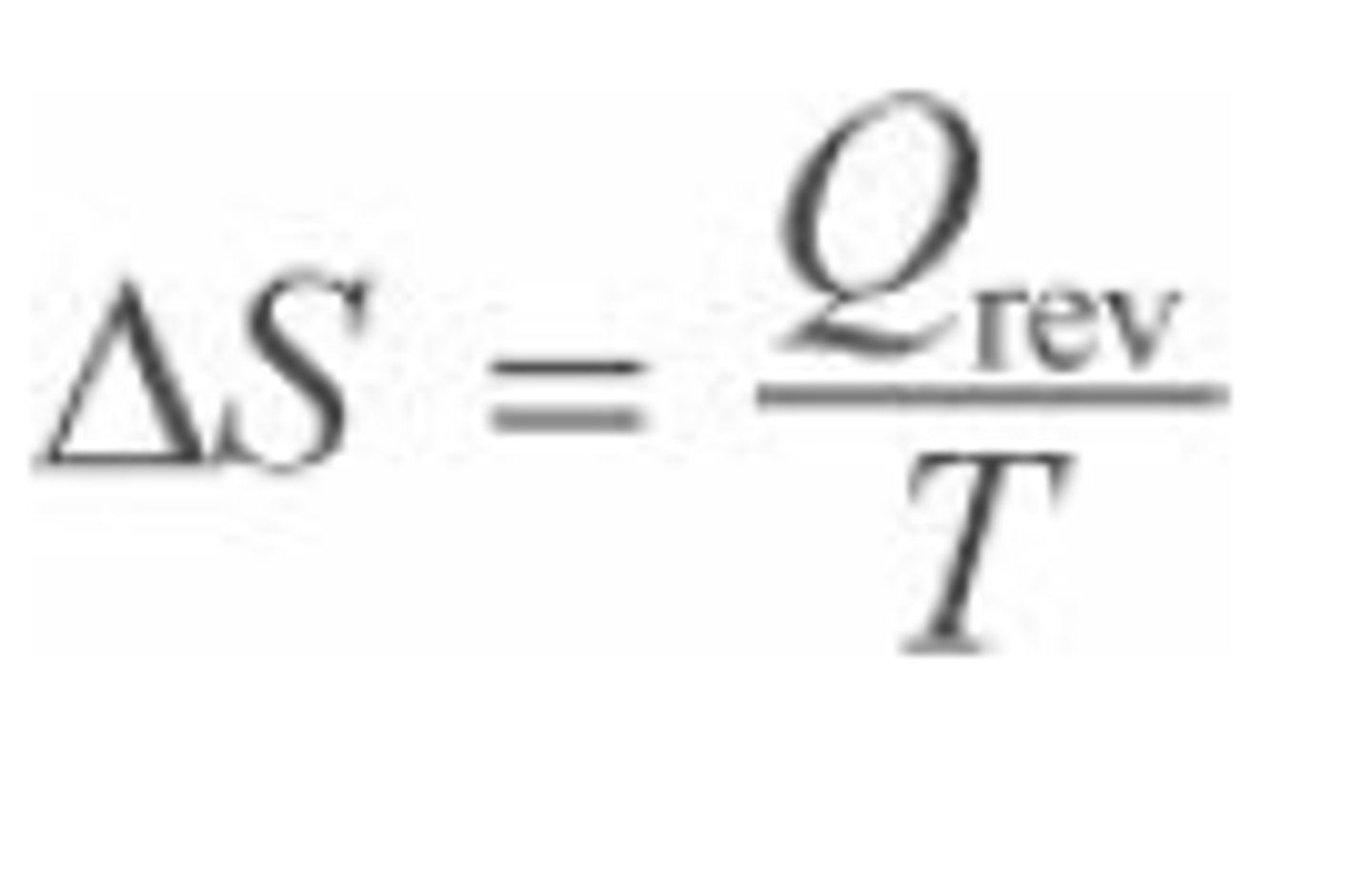
Thermodynamics
The study of heat.
Kinetic-molecular Theory
In a hot body the particles move faster and thus have greater kinetic energy than particles in a cooler body.
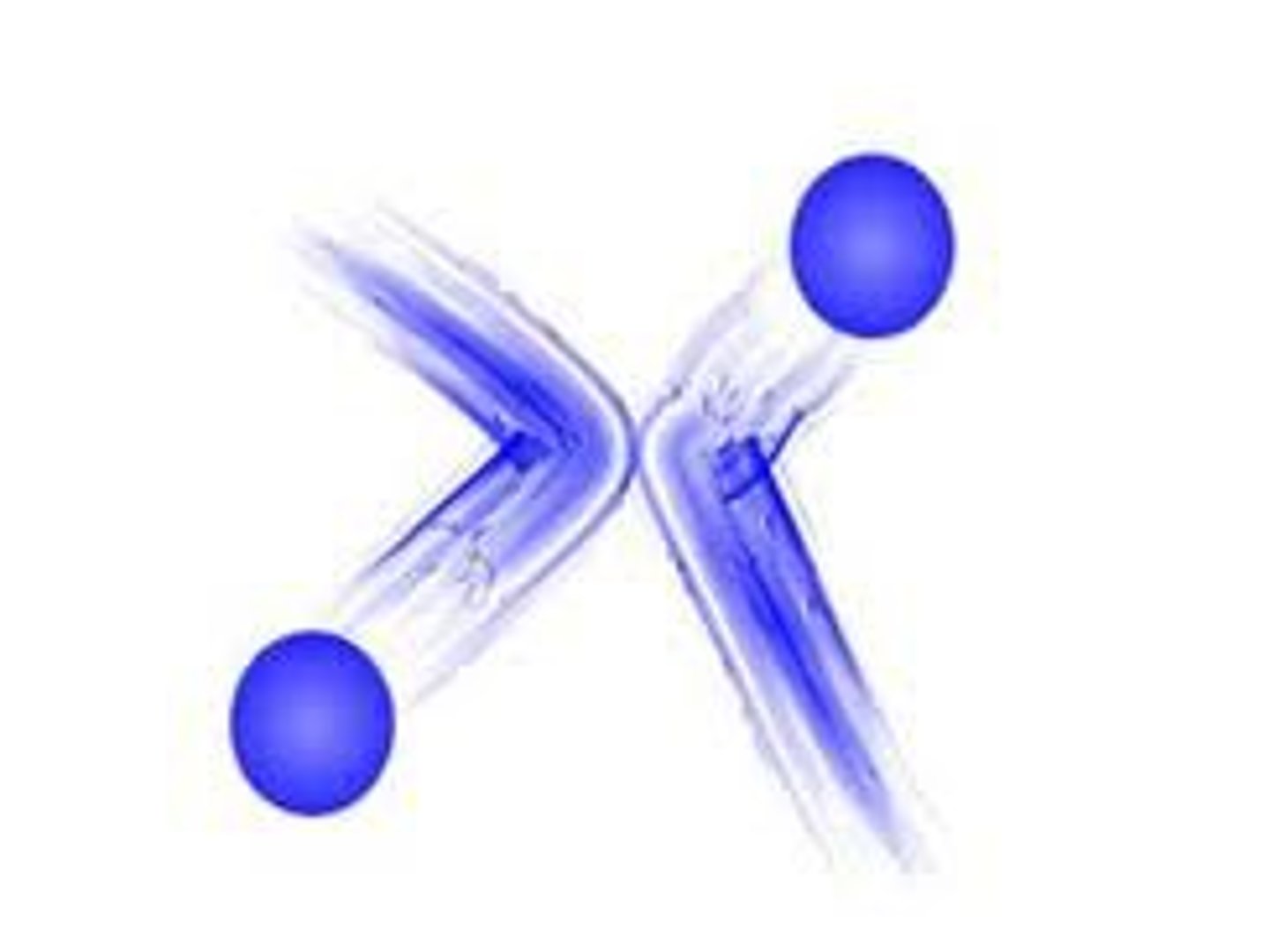

Thermal Energy
The overall energy of motion of the particles that make up an object.
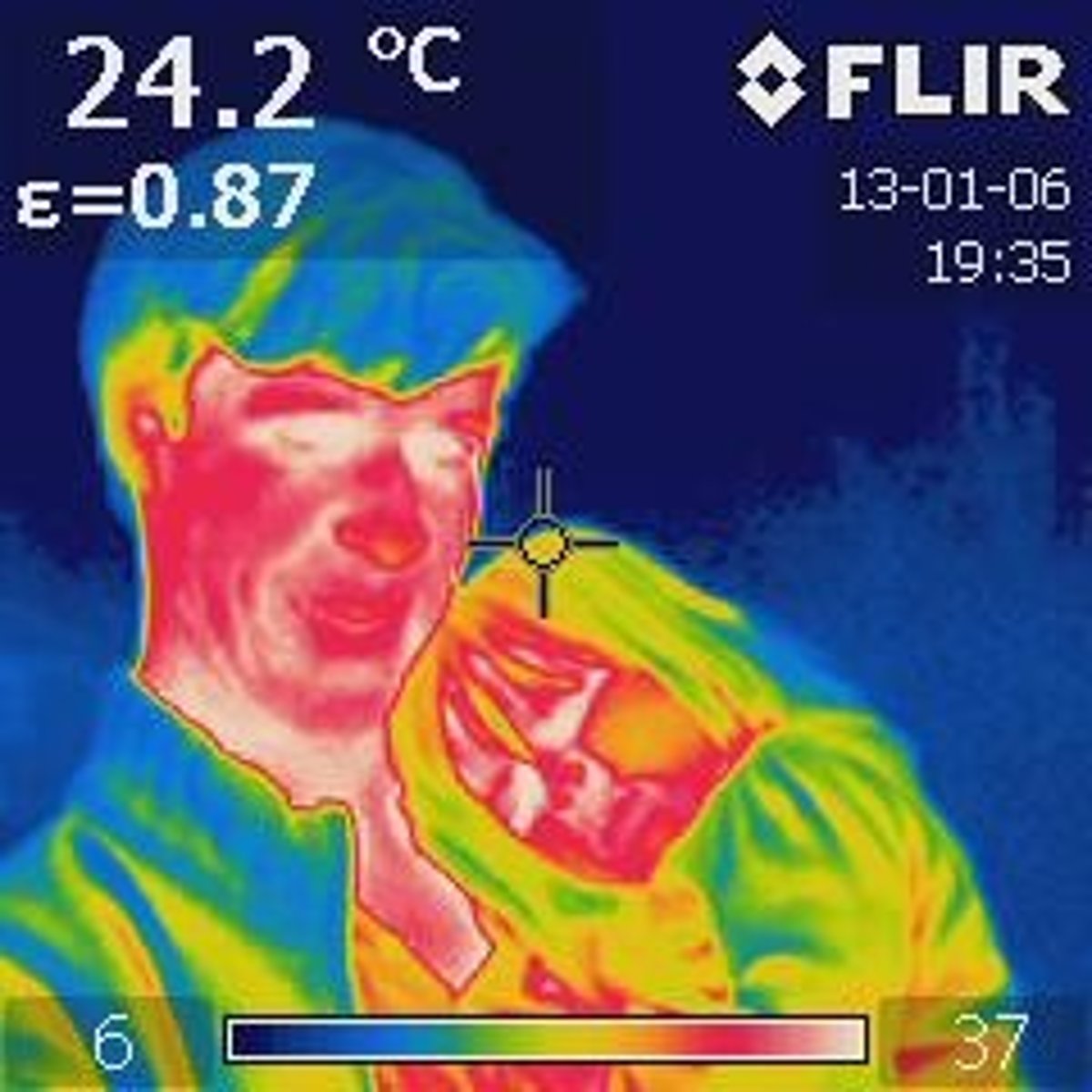
Temperature
The hotness of an object. It represents the average kinetic energy of particles in a object.

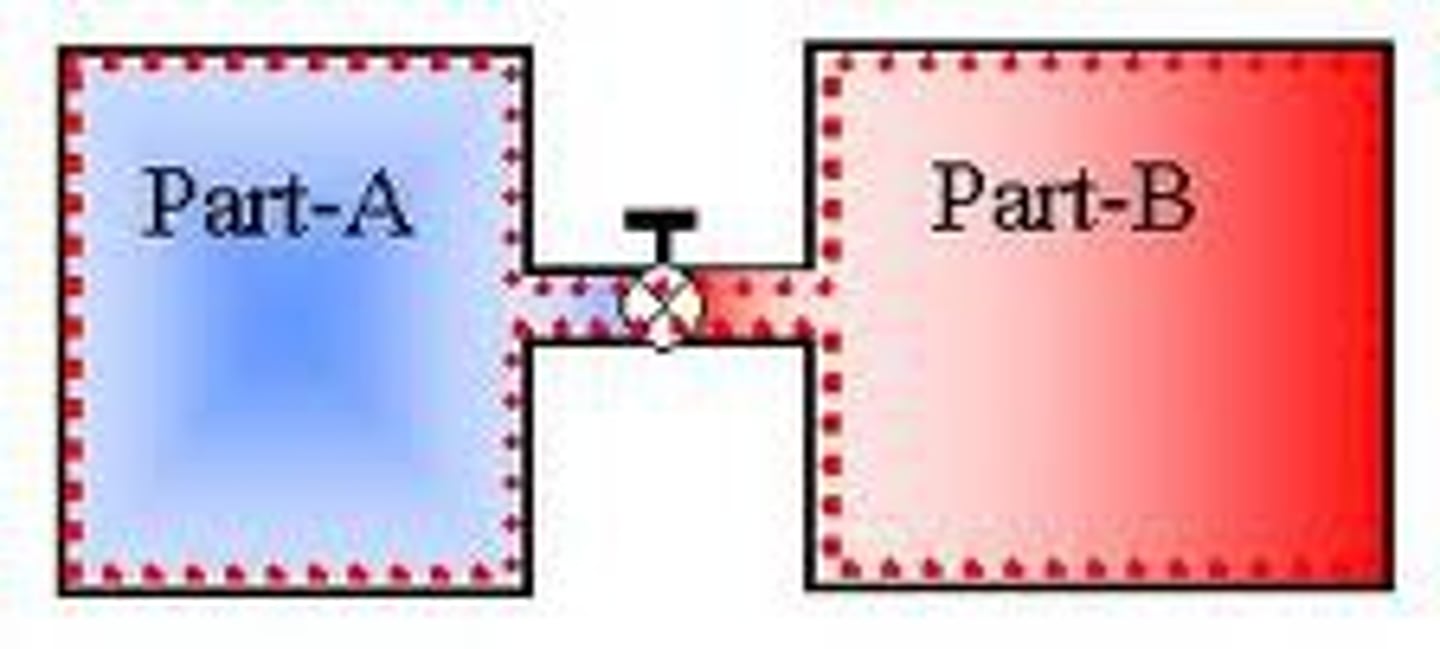
Heat
The energy that flows between two objects as a result of a temperature difference.

Thermal equilibrium
When the rate of transfer of thermal energy between two objects is equal.
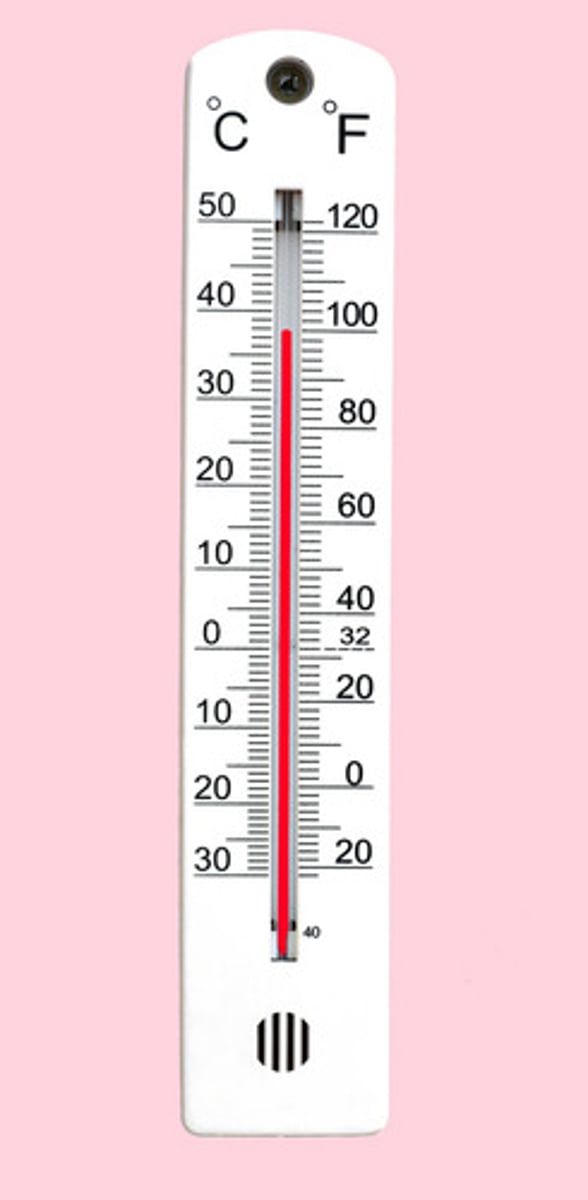
Thermometer
A device that measures temperature. It relies on thermal expansion of a fluid in a sealed tube.
Absolute zero
The temperature at which particles have zero kinetic energy. That is, particles stop moving. Its equal to -273 degrees Celsius.

Kelvin
A temperature scale used by scientists to measure thermal energy.

conduction
The transfer of thermal energy when particles collide.

Convection
The transfer of thermal energy in a fluid.

Radiation
The transfer of thermal energy through empty space.
Specific Heat
The amount of energy that must be added to raise the temperature of a unit of mass one temperature unit.

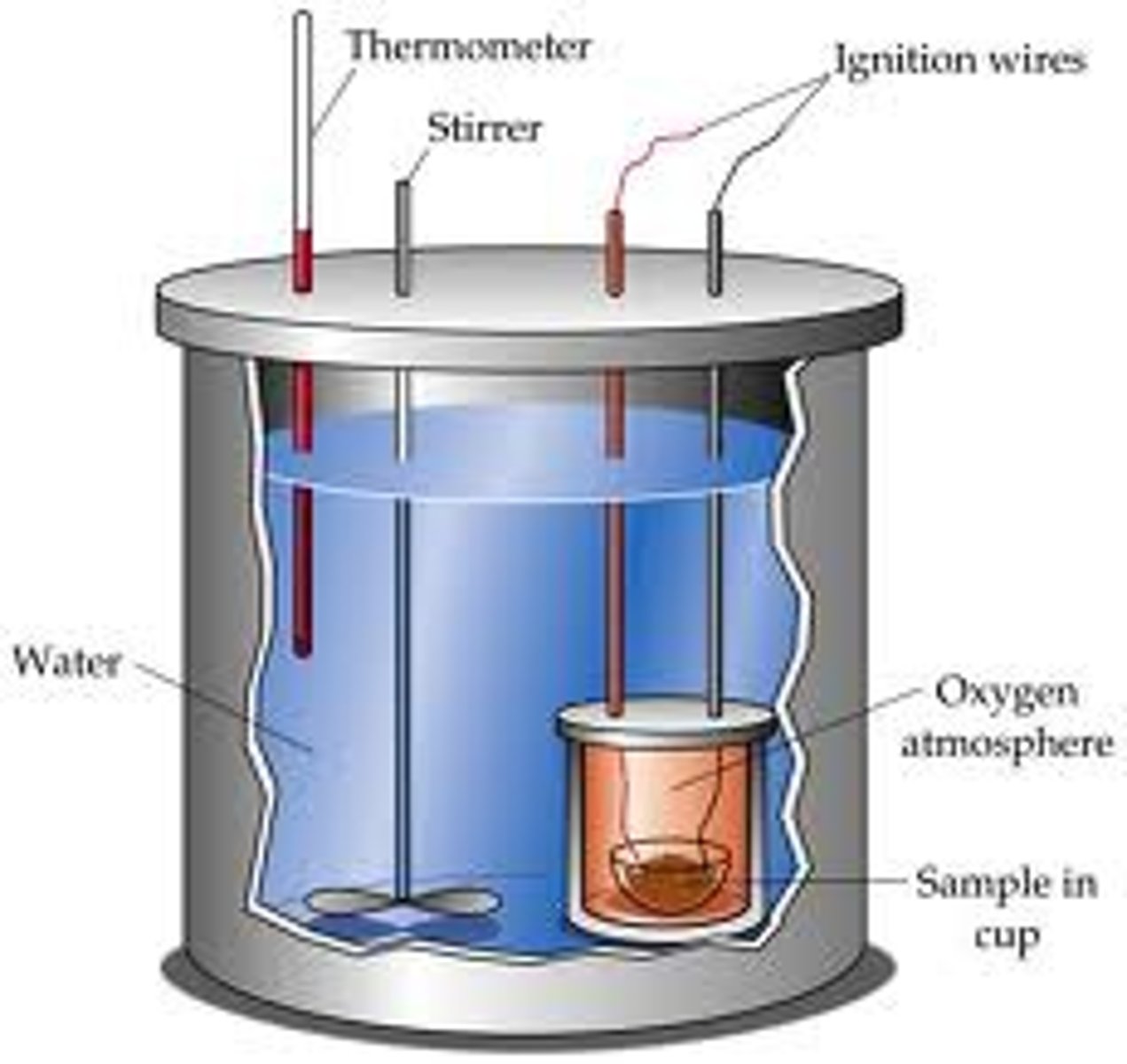
Calorimeter
A device used to measure changes in thermal energy.