Neuro - cranial nerves - quiz 2
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
Brainstem general functions
conduit, CN III - XII, integrative - reticular formation
divisions of the brainstem
midbrain, pons, medulla
regions of the brainstem
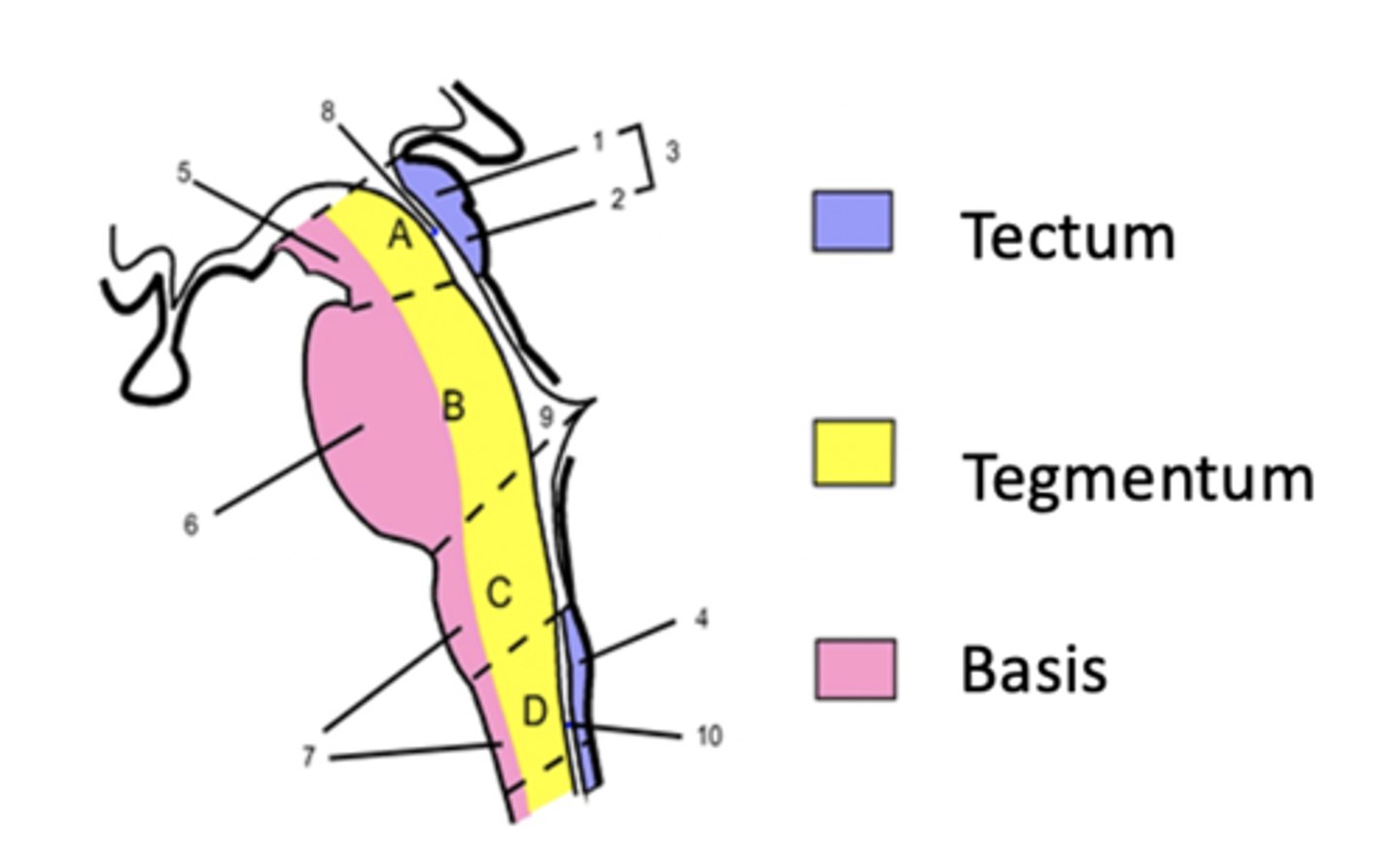
basilar, tegmentum, tectum
Basilar brainstem
ventral surface
motor aspect of the brain
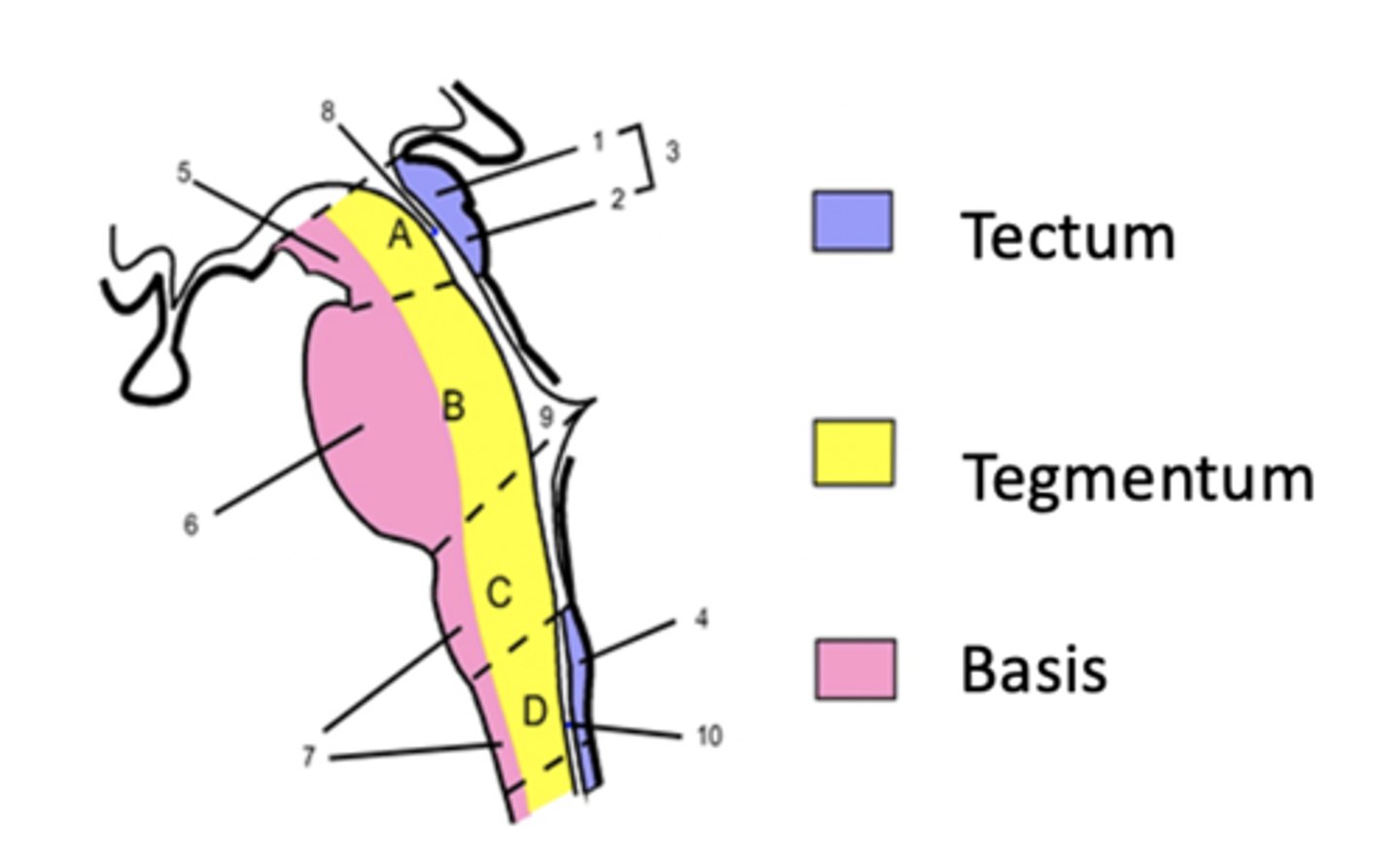
tegmentum region of the brainstem
nuclei of CN III - XII
reticular formation
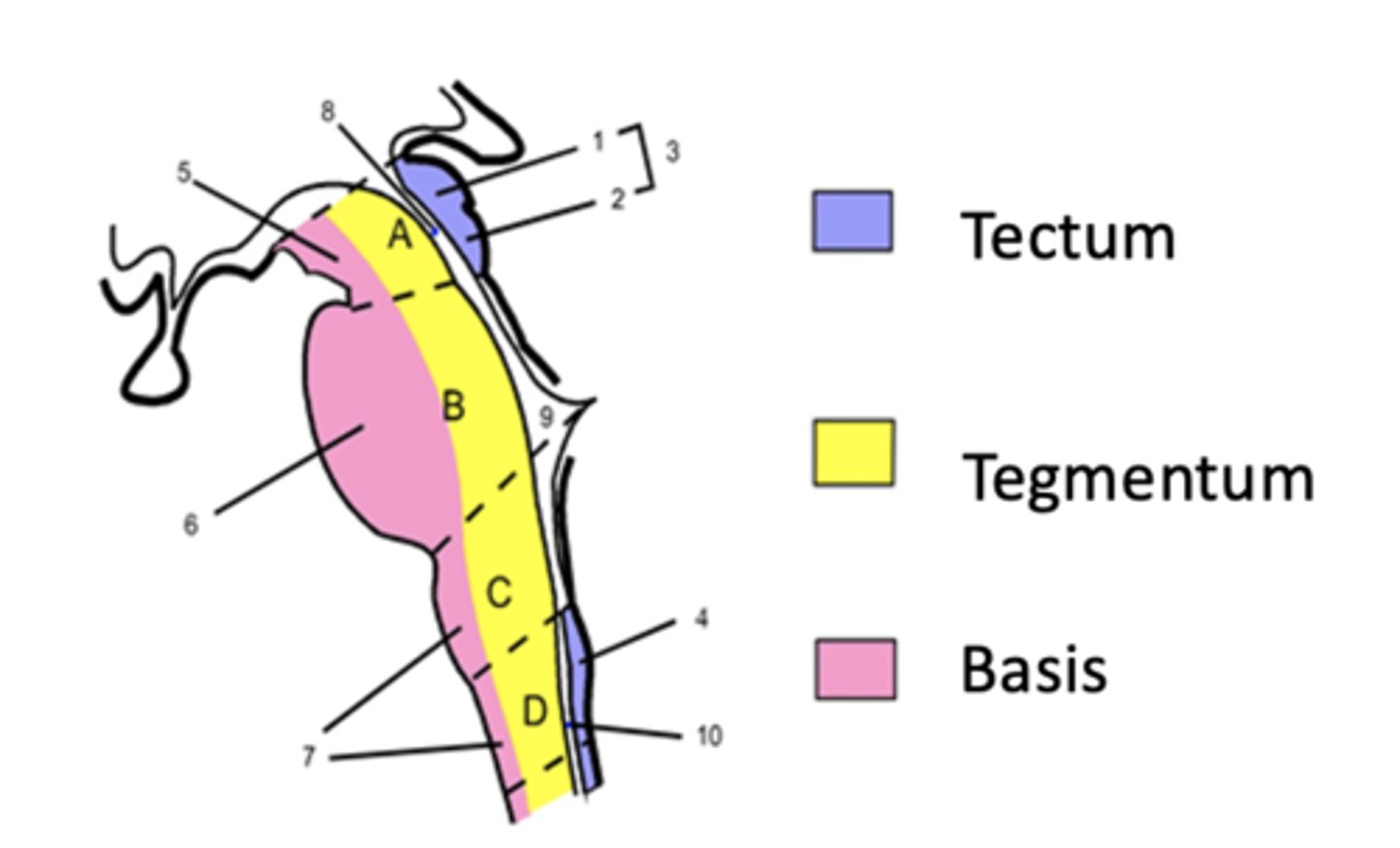
Tectum region of the brainstem
midbrain only
dorsal to cerebral aqueduct
cerebellum is the chamber of what ventricle?
ventricle 4
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
12
all of the CN are visible on the inferior view of the brain except
CN IV
the CN are generally numbered in order from
rostral (CN I) to caudal (CN XII)
all CN innervate structures in the head and neck EXCEPT
CN X (vagus)
axons and receptors outside of the brainstem/cerebrum are part of
the PNS
nuclei organization - dorsal structures are associated with _____ processing
central
nuclei organization - ventral structures are associated with _____ processing
motor
CN I
Olfactory
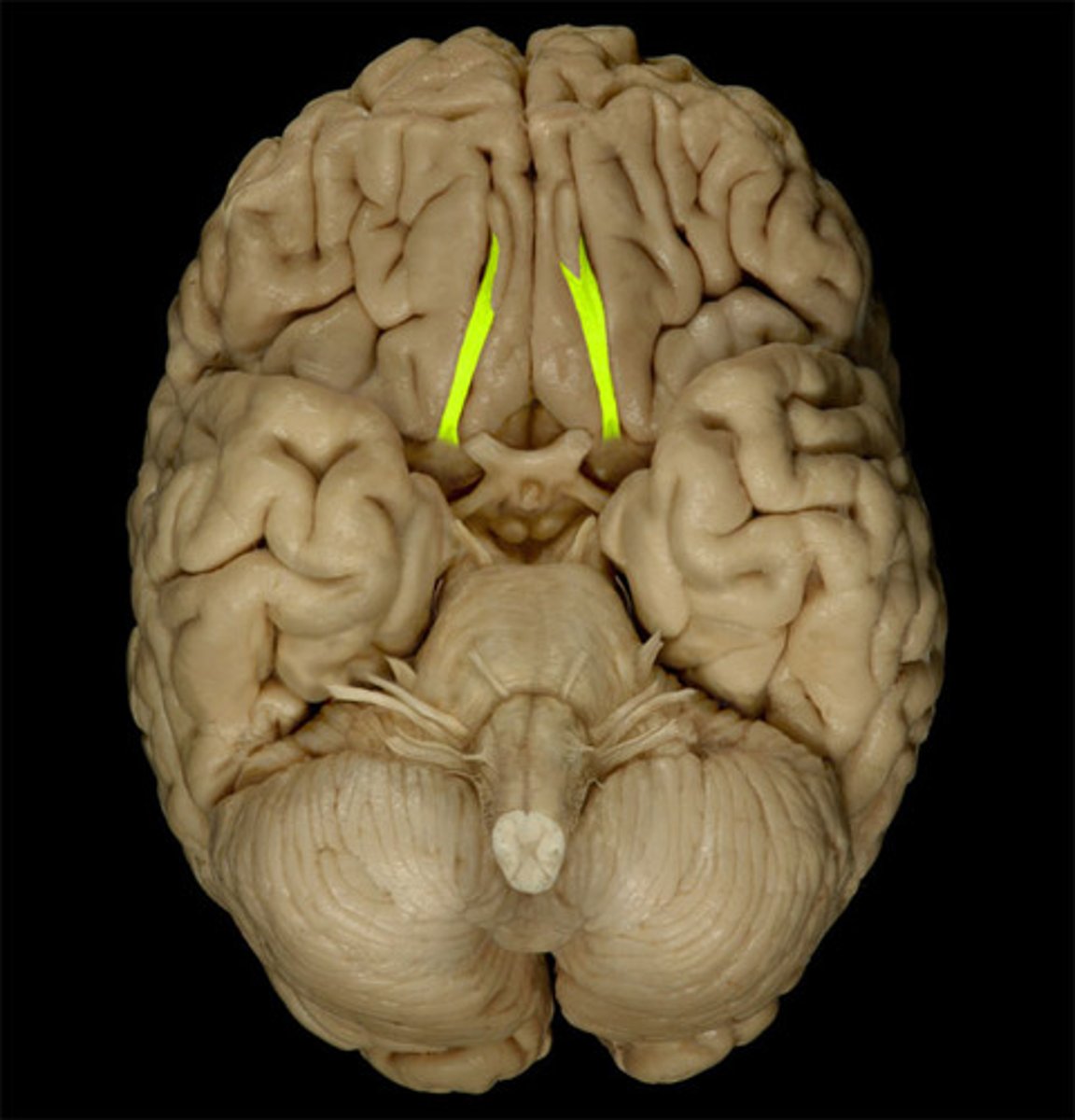
CN I sensory function
Smell: the only sensory system that does not transmit sensory information through the thalamus.
CN I motor function
none
CN I - CNS entry/exit location
inferior frontal lobe
pathway of CN I
nasal chemoreceptors in the olfactory mucosa (olfactory epithelium) connect via the olfactory nerve through the cribriform plate > olfactory bulb > olfactory tract (some fibers go to the anterior olfactory nucleus)
THEN 2 options
2 options of CN I pathways following intial
OPTION 1: medial olfactory stria > anterior commissure > contralateral olfactory bulb (bulbs ultimately receive information from both sides)
or
OPTION 2: lateral olfactory stria > olfactory tubercle; medial temporal lobe, & amygdala
All sensory information is sent to the thalamus EXCEPT
olfaction
CN I - testing
Using familiar, non-irritating odors: coffee, vanilla, etc.
Test one nostril at a time
Pathology of CN I
Anosmia - loss of sense of smell
Hyperosmia - increase in olfactory sensitivity
Trauma - fracture of cribriform plate, possible CSF leakage (pathway for meningitis)
Infection, neoplasm, metabolic disease, drug ingestion
CN II
Optic
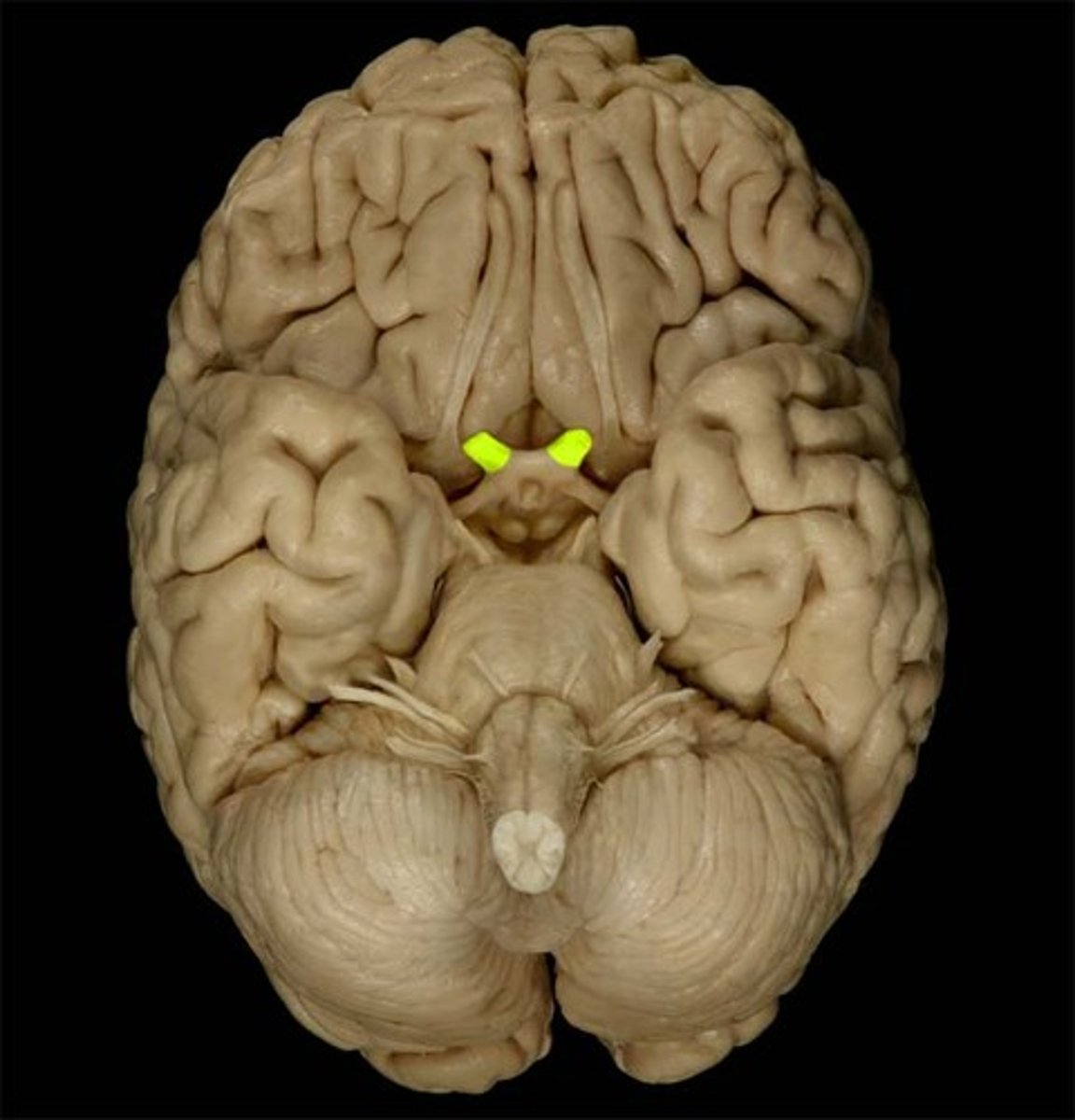
sensory function of CN II
vision
motor function of CN II
none
CN II - CNS entry/exit location
diencephalon
CN II pathway
Retinal cells > optic nerve > optic chiasm > optic tract >
Lateral geniculate body (part of the thalamus) > optic radiation > primarily visual cortex (vision)
or
brainstem nuclei (midbrain): pupil reflexes, light/dark awareness, and head orientation in space
T/F: you are not consciously aware of what you are seeing until it reached the occipital region of occipital lobe (area 17 of brochman's area)
TRUE
CN II - testing
field of view (lateral ~90 degrees, medial ~60 degrees)
pupil reflexes (light reaction) ; consensual (opposite eye)
accommodation: eyes adjusting to nearby objects (adduction, pupils constrict, the lens becomes more convex)
CN II - pathology
blindness, hemianopsia, loss of 1/2 visual field
CN III
Oculomotor
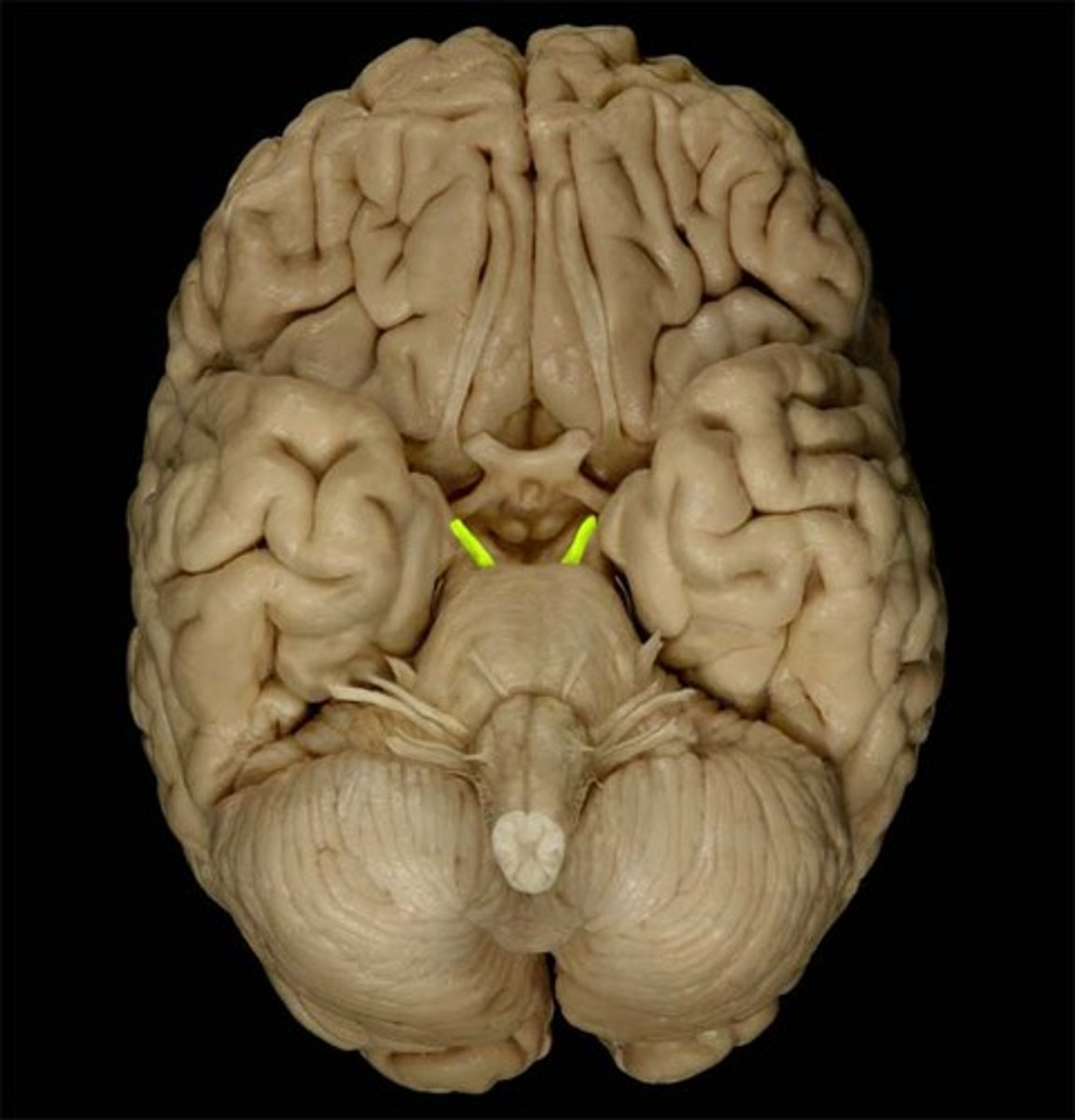
sensory function of CN III
none
motor function of CN III
Levator palpebrae superioris m. (lifts upper eyelid) and all extraocular eye m. except for the lateral rectus and superior oblique
sphincter pupillae (constriction of the pupil), ciliary mm. (contraction thickens the lens)
CN III - CNS entry/exit location
ventral midbrain (cerebral penducles between the PCA & SCA arteries)
CN III pathway
2 nucleis that play a part: come out between cerebral penducles > enter superior orbital fissure > from there is depends on the muscle it is going to:
Oculomotor nucleus (GSE; rostral midbrain; motor part) > superior orbital fissure > extraocular muscles
Oculomotor nucleus (GVE; midbrain; parasympathetic part)(Edinger-Westphal nucleus; posterior to motor part of the oculomotor nucleus) > ciliary ganglion & pupillary sphincter > intrinsic muscles of the eye.
CN III - testing
finger following test
pupil size and pupil reflex
opening eyelid
CN III - pathology
diabetes mellitus vascular lesions
external (lateral) strabismus (visual axis of eyes not parallel; misaligned) : eyeball deviating laterally (outward or abducted) due to unopposed lateral rectus
diplopia (double vision)
paralysis of medially directed gaze
ptosis ('drooping' eyelid)
dilation of the pupil (mydriasis)
CN IV
Trochlear
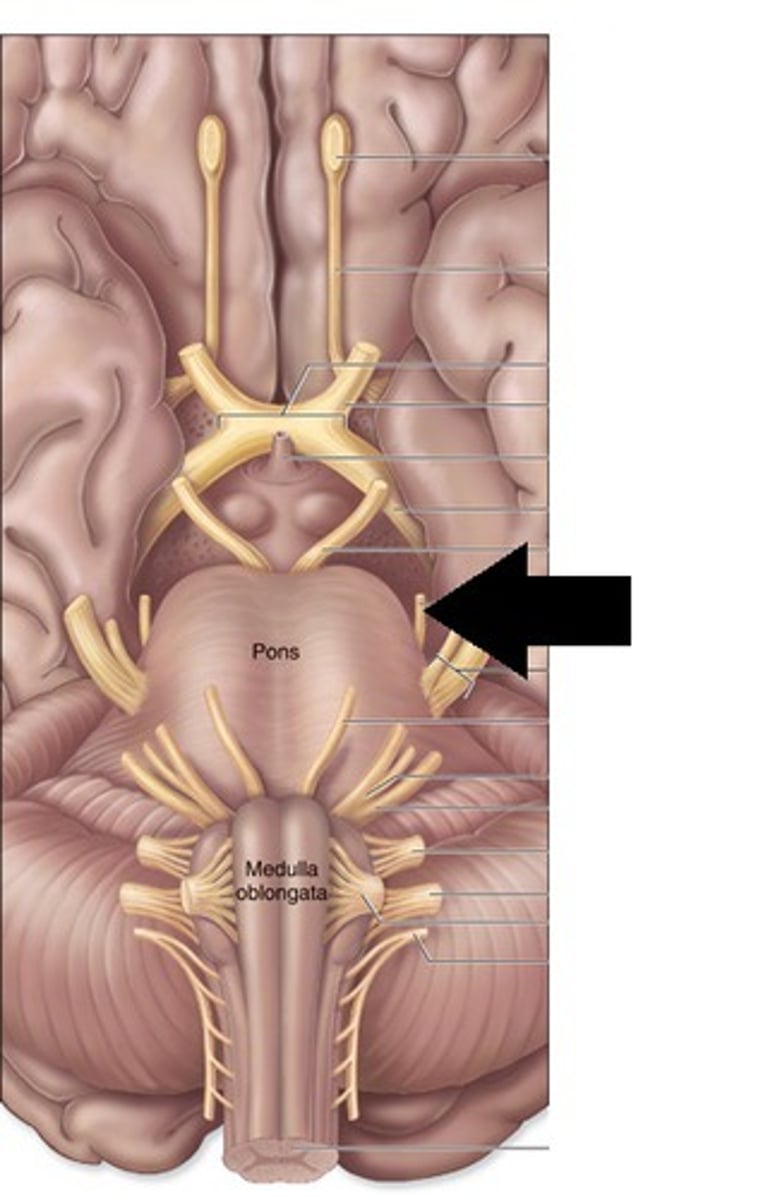
sensory function of CN IV
none
motor function of CN IV
Superior Oblique m. (contralateral to the nucleus)
Moves eye inferio-medially
if the eye is adducted the superior oblique will
turn pupils down
if the eye is abducted, superior oblique will
rotate the eye
CN IV - CNS entry/exit location
posterior (dorsal) midbrain
CN IV - pathway
Contralateral trochlear nucleus ( midbrain; level of inferior colliculus) runs dorsally from the nucleus and decussates in anterior medullary velum > emerges from posterior tectum (caudal to inferior colliculi) > through the superior orbital fissure to the superior oblique m.
Decussating fascicles of CN IV
where R and L pieces of CN IV cross
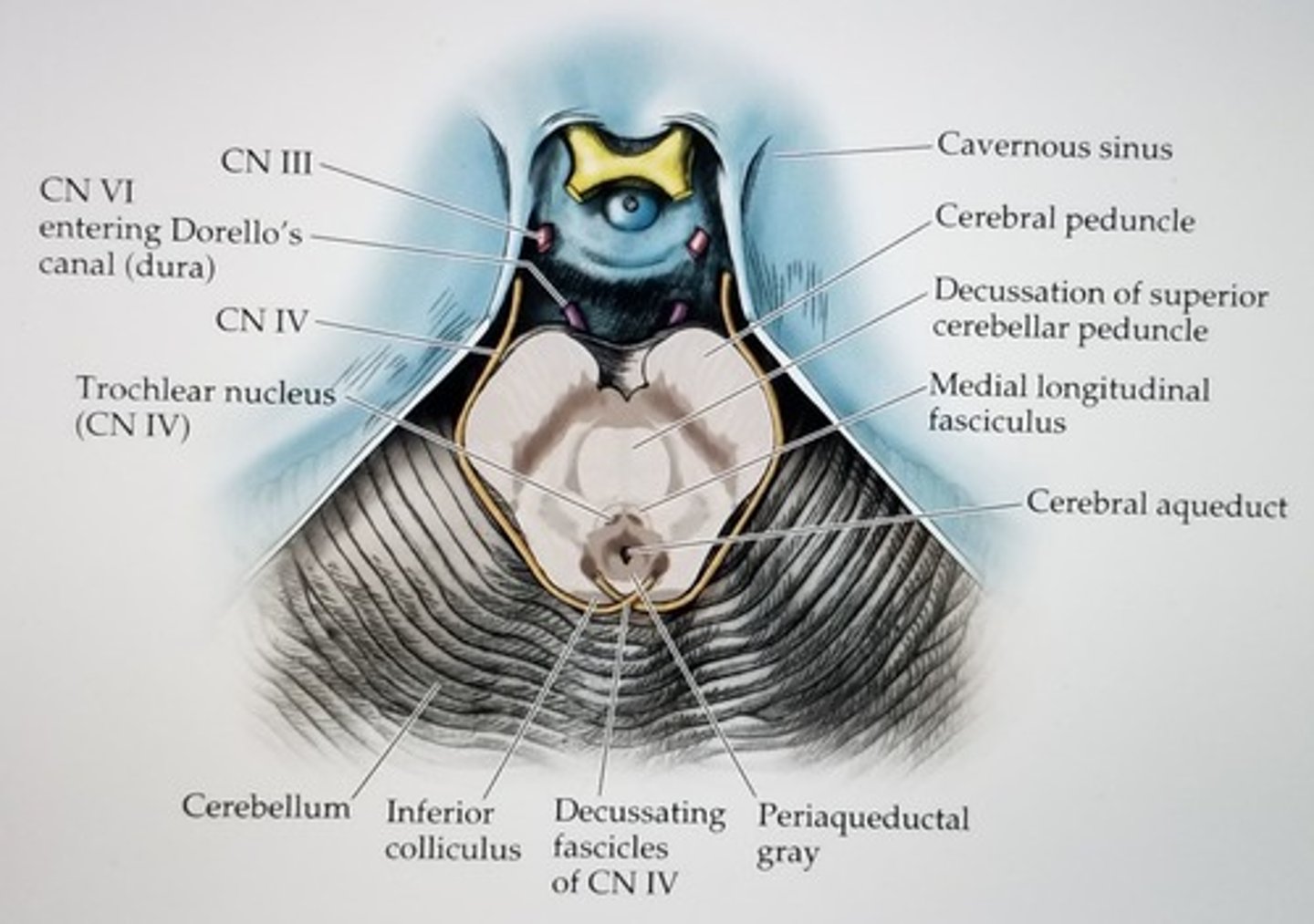
CN IV - testing
Finger following test: pt. adducts the eye and then rotates it downward
note head alignment- anterior view, head may deviate opposite side
CN IV - pathology
rarely have lesions that are limited to only the trochlear nerve.
Impaired down and in gaze; Diplopia (double vision from eyes no longer being parallel) > difficulty descending stairs
CN V
Trigeminal
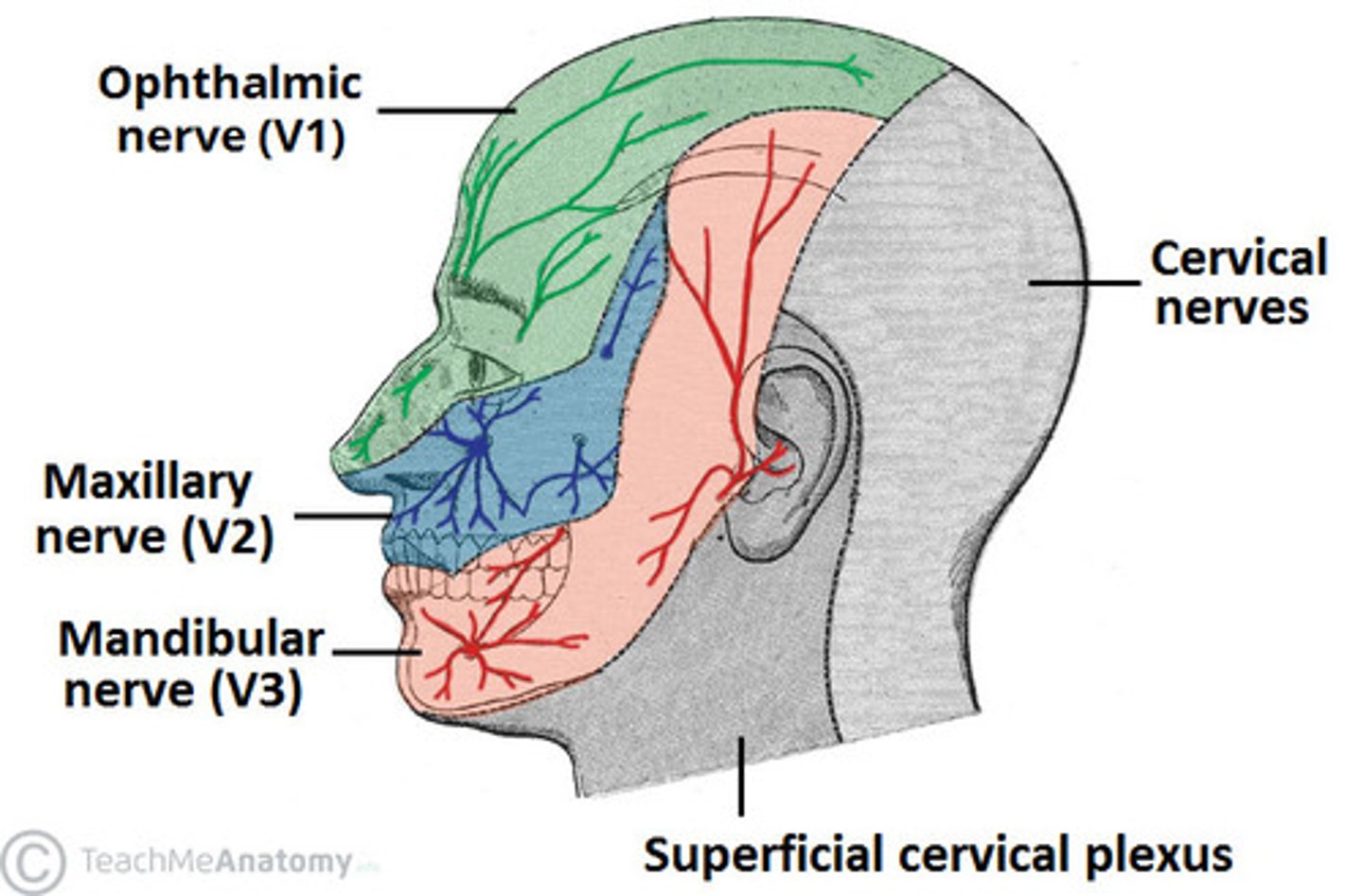
3 branches of trigeminal nerve
ophthalmic (V1) : forehead
maxillary (V2) : mid face
mandibular (V3) : lower jaw
sensory function of CN V
touch, pain, temperature, position for face (cornea)
Anterior 2/3 tongue touch
Nasal sinuses and cornea
meninges
motor function of CN V
muscles of mastication and tensor tympani
CN V - CNS entry/exit location
mid-lateral pons
Motor pathway of CN V
Right and left motor cortex--(UMN) > Motor nucleus V (lateral tegmentum; rostral pons) > mandibular branch > m. of mastication (temporalis; masseter; med/lat pterygoid; tensor tympany; and others)
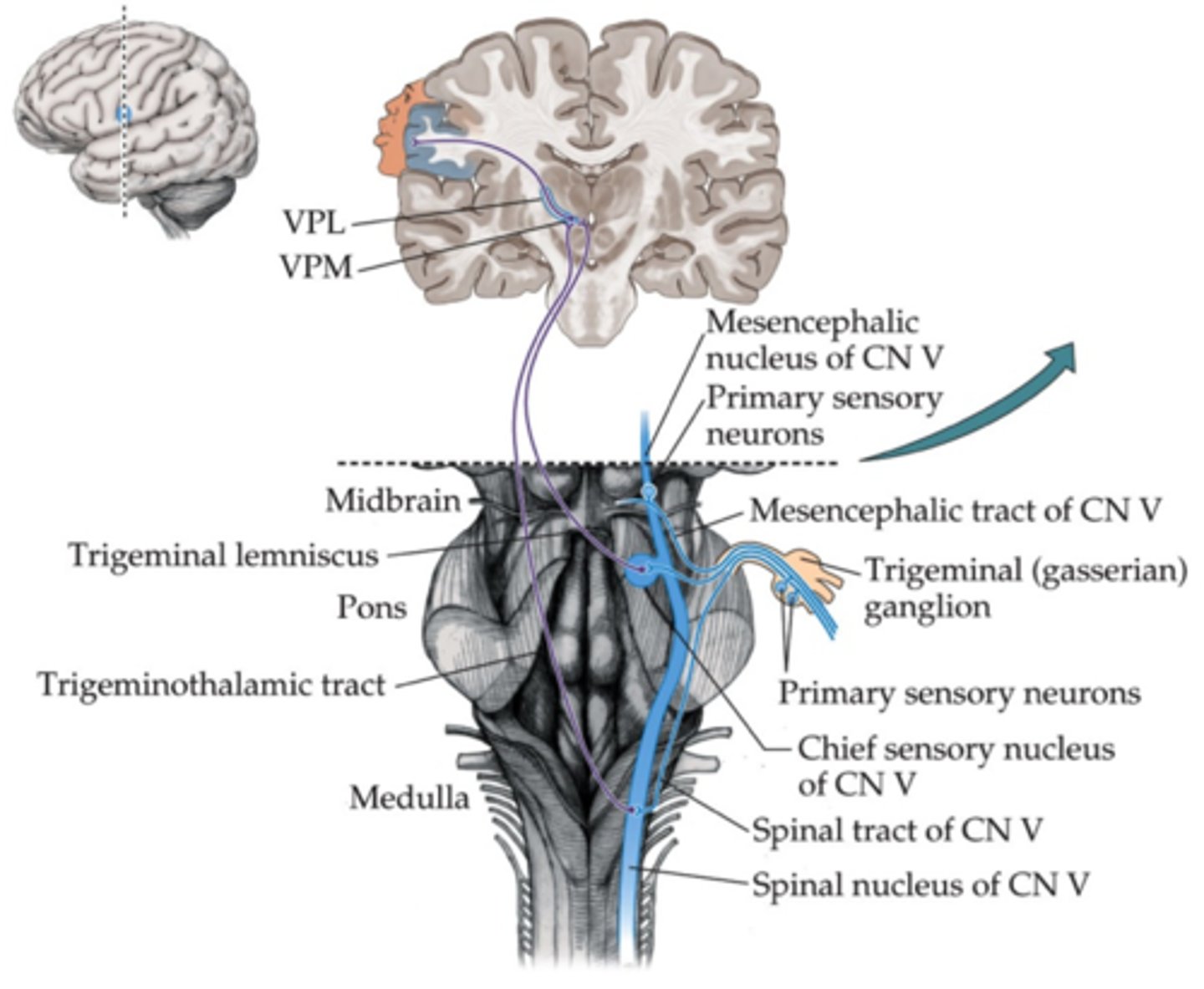
Sensory touch pathway of CN V
innervated tissue > trigeminal ganglion (primary cell bodies) > main sensory nucleus V (mid pons) > cross midline & travel with contralateral medial lemniscus fibers > thalamus (VPM) > SI cortex (also some uncrossed fibers that travel to ipsilaterally VPM)
sensory proprioception pathway of CN V
M. of mastication (ipsilateral; innervated tissue) > mesencephalic nucleus (dorsolateral tegmentum; location of the neuron cell body in the brainstem; unusual for primary nerves) with axon to motor nucleus V (reflex) > reticular formation
sensory nociceptive pathway of CN V
Pain receptors > trigeminal ganglion (primary cell bodies) > enter and descend and form the spinal tract of trigeminal n. > cross midline > thalamus (VPM) > SI (primary somatosensory cortex) > reticular formation
specific nuclei in the thalamus:
VPM - ventro-posterior medial : sensory info from the face
VPL - ventro-posterior lateral : sensory info from the body
CN V - testing
Jaw jerk
Corneal reflex
CN V - pathology
Hyperaccusis (tensor tympani)
weakness and atrophy of mastication m.
Lateral medulla + lower pons: loss of ipsilateral pain and temp.
Lesion in upper pons/midbrain: contralateral anesthesia
Trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux): unbearable pain over the n. distribution; trigger zone in sensory distribution pattern
CN VI
Abducens
CN VI sensory function
none
CN VI motor function
lateral rectus m. > abducts the eye; ipsilateral to the nucleus
CN VI - CNS entry/exit location
between pons and medulla (pons-medulla junction) at the pyramids
CN VI pathway
Abducens nucleus (dorsal and caudal pons in pontine tegmentum) > emerges between pons and pyramids > superior orbital fissure > lateral rectus m.
CN VI - testing
Finger following test , abduction
CN VI - Pathology
Internal/medial strabismus 2 to unopposed medial rectus à eye deviates medially
Diplopia
Nuclear lesion: lateral paralysis à disruption of the nucleus itself causes ipsilateral lateral gaze paralysis
In testing; medial strabismus shows at rest, lateral paralysis shows in finger following test
what CN help to regulate eye movements
3, 4, 6
CN VII
Facial
CN VII sensory function
Outer ear (touch, pain, pressure) - spinal trigeminal (V) nucleus (STTN)
Special -taste (anterior 2/3 of tongue; solitary nucleus)
CN VII motor function
Closes eyes (orbicularis oculi), moves lips, muscles used for facial expression, and Stapedius
salivary & lacrimal glands
CN VII - CNS entry/exit location
between pons and medulla (lateral)
CN VII - facial motor nucleus pathway
§ Facial motor nucleus (caudal pontine tegmentum) > passes dorsally encircling (internal genu) abducens nucleus > emerges in the junction between pons and cerebellum (cerebellopontine angle) > internal auditory canal > facial canal > stylomastoid foramen > muscles used for facial expression. [Stapedius, too, but it comes off earlier in the facial canal]
CN VII - UMN motor pathway
· Part of the Facial motor nucleus controlling the upper face (above the eyes) - receives UMN neuron input from the bilateral motor cortex
· Part of the Facial motor nucleus controlling the lower fact (below the eyes) receives UMN neuron input only from the contralateral cortex
CN VII - parasympathetic pathway
Superior salivary nucleus (medulla; preganglionic cell bodies) > Nervus Intermedius (smaller of two divisions of VII) > internal acoustic meatus > facial canal (geniculate ganglion located in a sharp bend in the canal) > chorda tympani and lingual nerves > salivary, nasal, and lacrimal glands
CN VII - taste pathway
Taste receptors on the tongue > facial canal (geniculate ganglion located in a sharp bend in the canal) > internal acoustic meatus) > Nervus Intermedius (smaller of two divisions of VII) > Solitary tract nucleus (in the reticular formation)
4 different nuclei
facial motor
STTN (spinal trigeminal nucleus)
Solitary nucleus
Superior salivatory nucleus
facial motor nucleus
same level as abducens level ; big player in motor control of facial muscles
STTN
through facial nerve before now coming here
Solitary nucleus
sensory information (taste)
superior salivatory nucleus
parasympathetic, distributed to salivary and lacrimal glands
CN VII - testing
taste (anterior 2/3 of the tongue, sweet and salt)
Corneal blink reflex: touch the cornea, and the eyes blink automatically
Close eyes, smiling (facial expressions)
CN VII - pathology
Cheeks puff out, lack of facial expression
Bell's palsy: loss of function overnight; swelling in the distal facial canal; spon. recovery in 1-2 mo.
Proximal lesion (ipsilateral):
hyperacusis: secondary to stapedius m paralysis
Absent taste anterior 2/3 tongue
Disturbed secretion of tears and salivation
LMN: paralysis or weakness
UMN (corticobulbar; 'bulbar' loosely refers to the brainstem) lesion:
Sparing of forehead/brow area - receives input from bilateral cortex
Involuntary contraction still possible (reflexes)
Lower parrt of the face is driven ONLY by ______ side of brain
contralateral
Peripheral lesion of facial nerve
Lesion B - both top and bottom affected
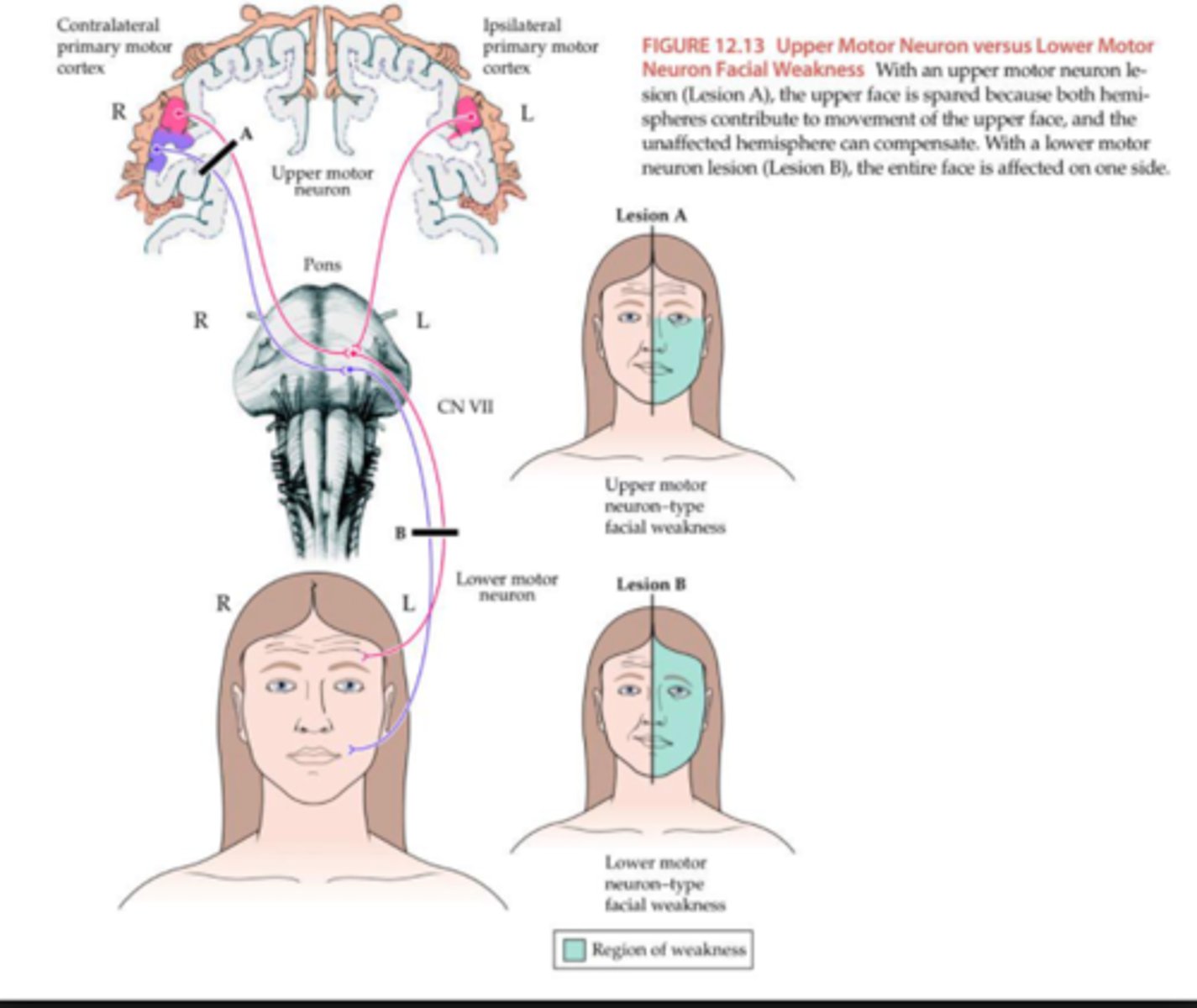
UMN lesion of facial nerve
only contralateral lower face affected
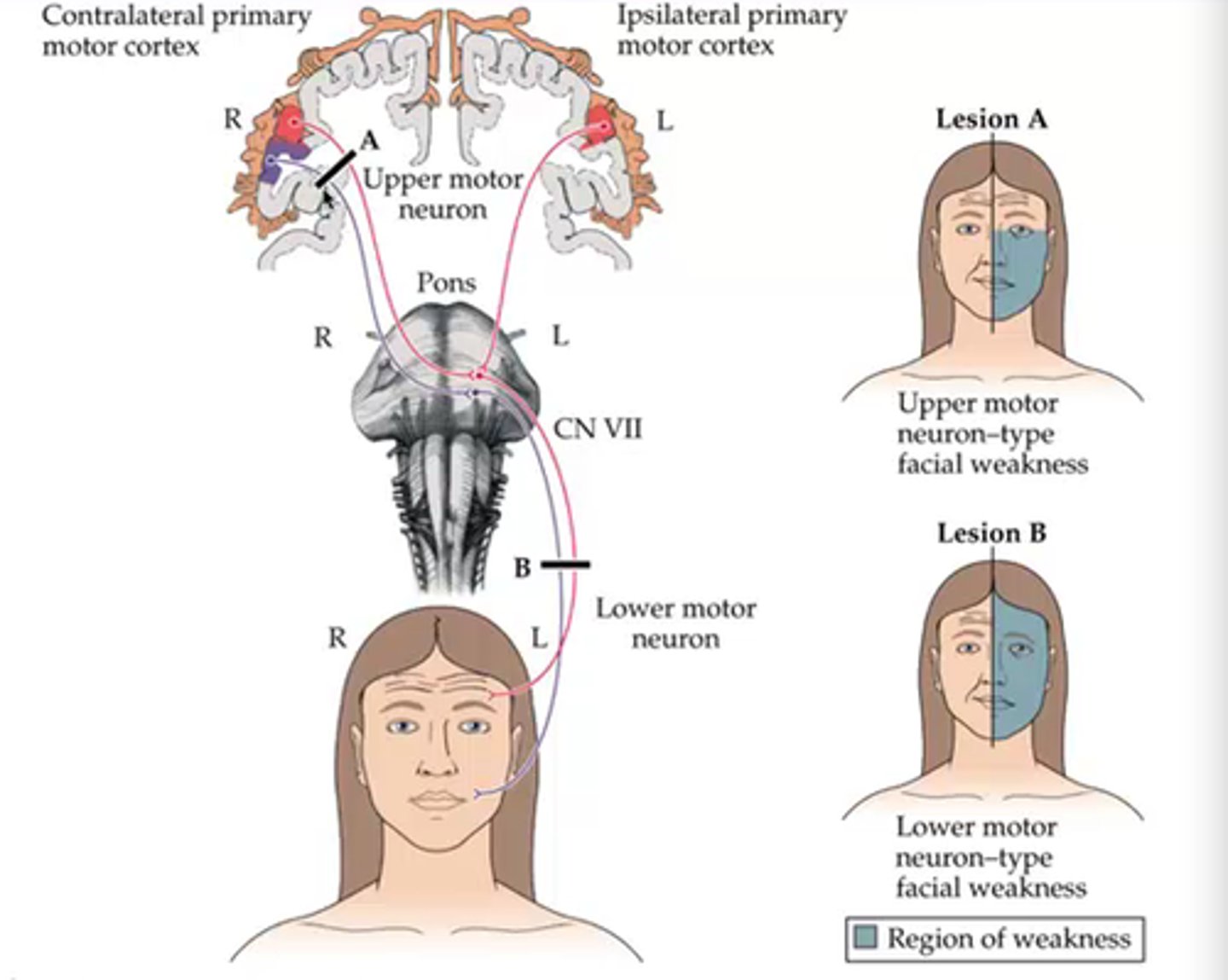
CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear
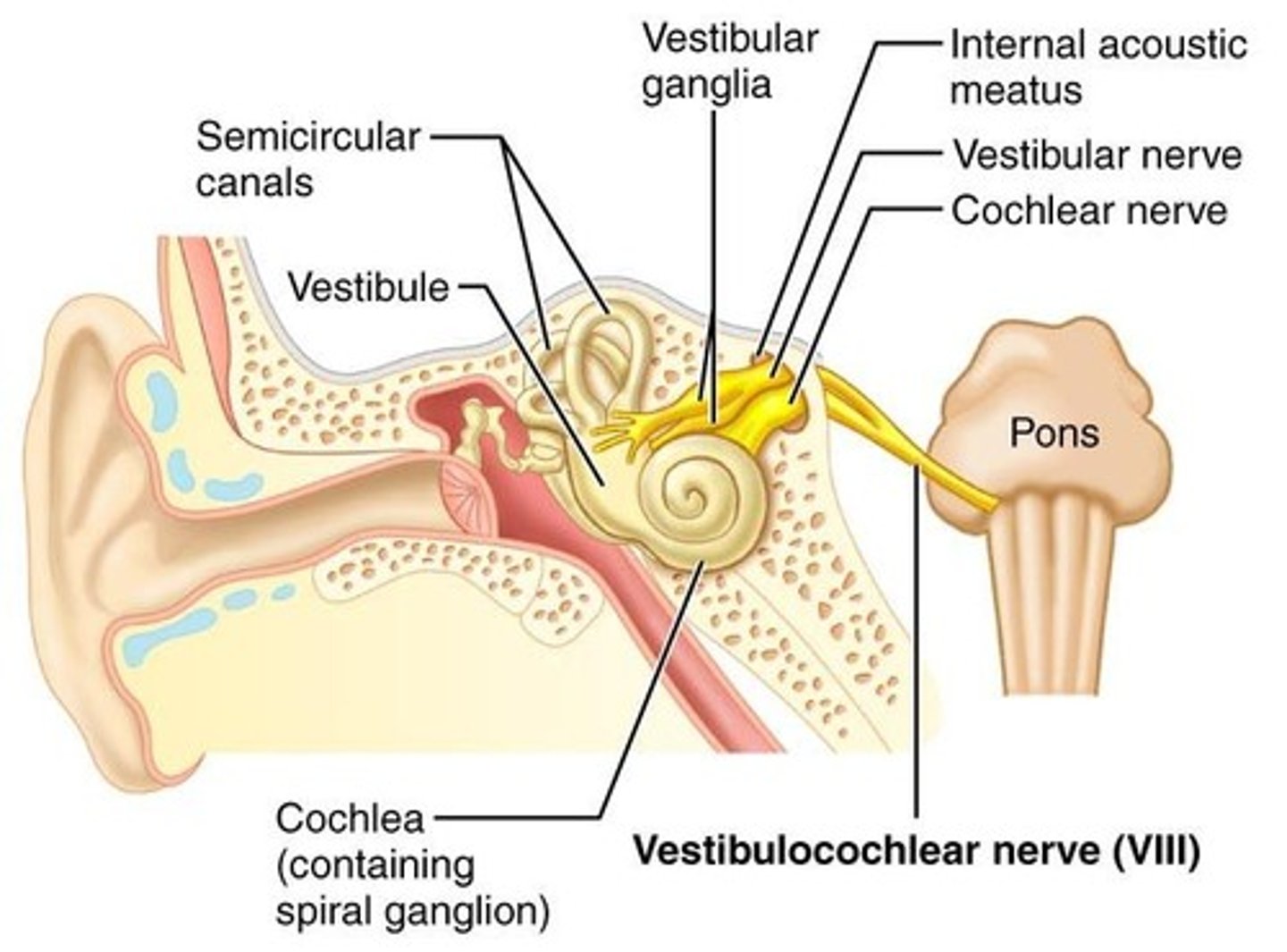
sensory function of CN VIII
Cochlear: hearing (ipsilateral nuclei)
Vestibular: head position/ movement; equilibrium (ipsilateral nuclei)
motor function of CN VIII
none
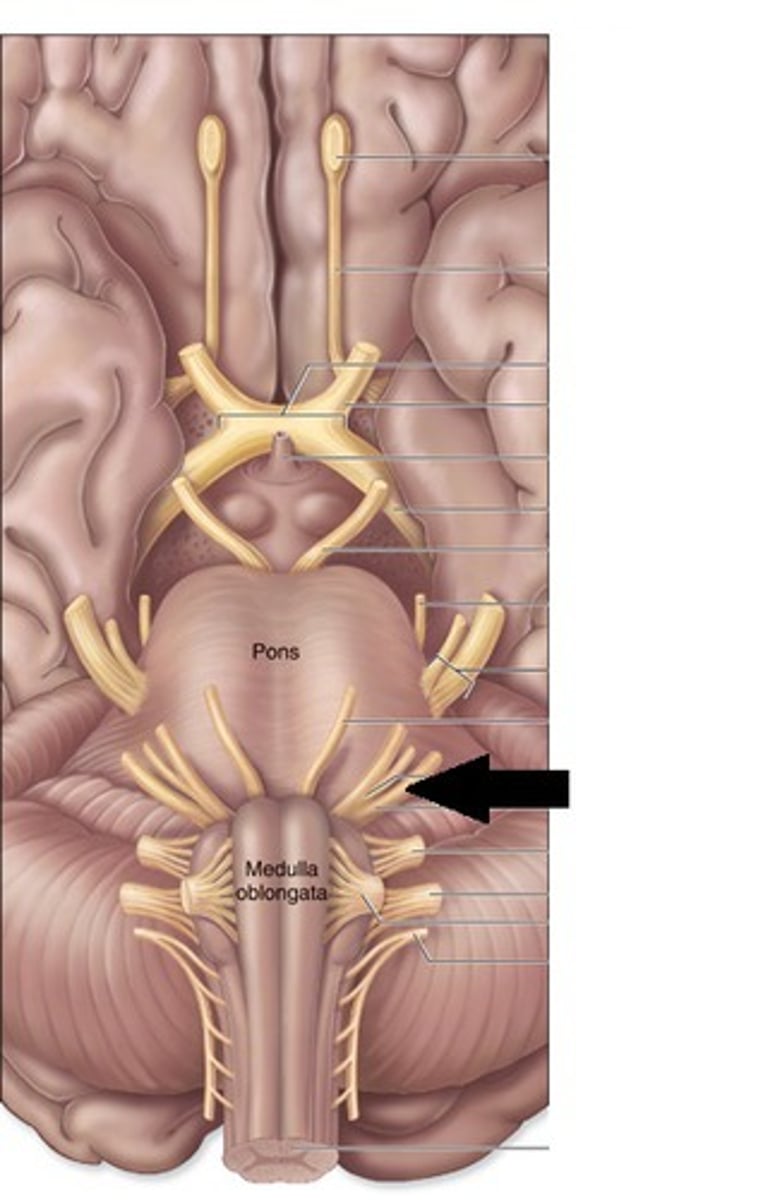
CN VIII - CNS entry/exit location
between the pons and the medulla (most laterally)
Hearing pathway of CN VIII
Hair cells in the cochlear duct > internal auditory meatus > connects to Cochlear nuclei > becomes bilateral at this point (auditory info goes up on both side of the nervous system)
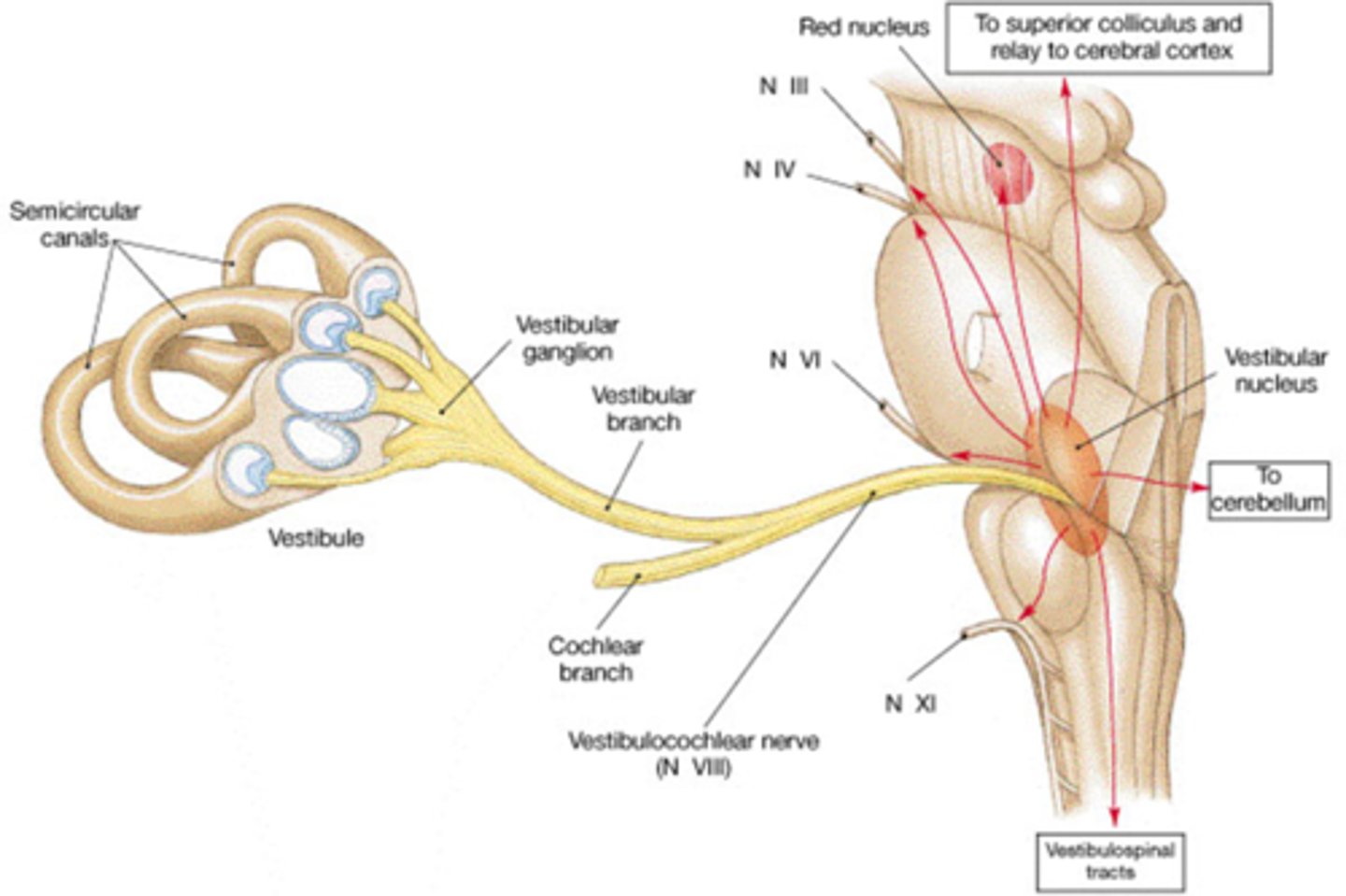
vestibular pathway of CN VIII
semicircular canals (hair cells in the maculae of the utricle and saccule; cristae in the ampullae) > internal auditory meatus > Vestibular nuclei (four)
CN VIII - testing
Hearing (tuning fork, snapping, may need an audiologist)
Vestibular for postural control (put in different positions, balance testing)
CN VIII - pathology
loss of hearing
vertigo; disequilibrium
once you get to CN VIII and its totality you may have a combo of both hearing and vestibular impairment (at apparatus level = may have only one)
cerebellopontine angle
this angle is where you describe CN VIII exiting
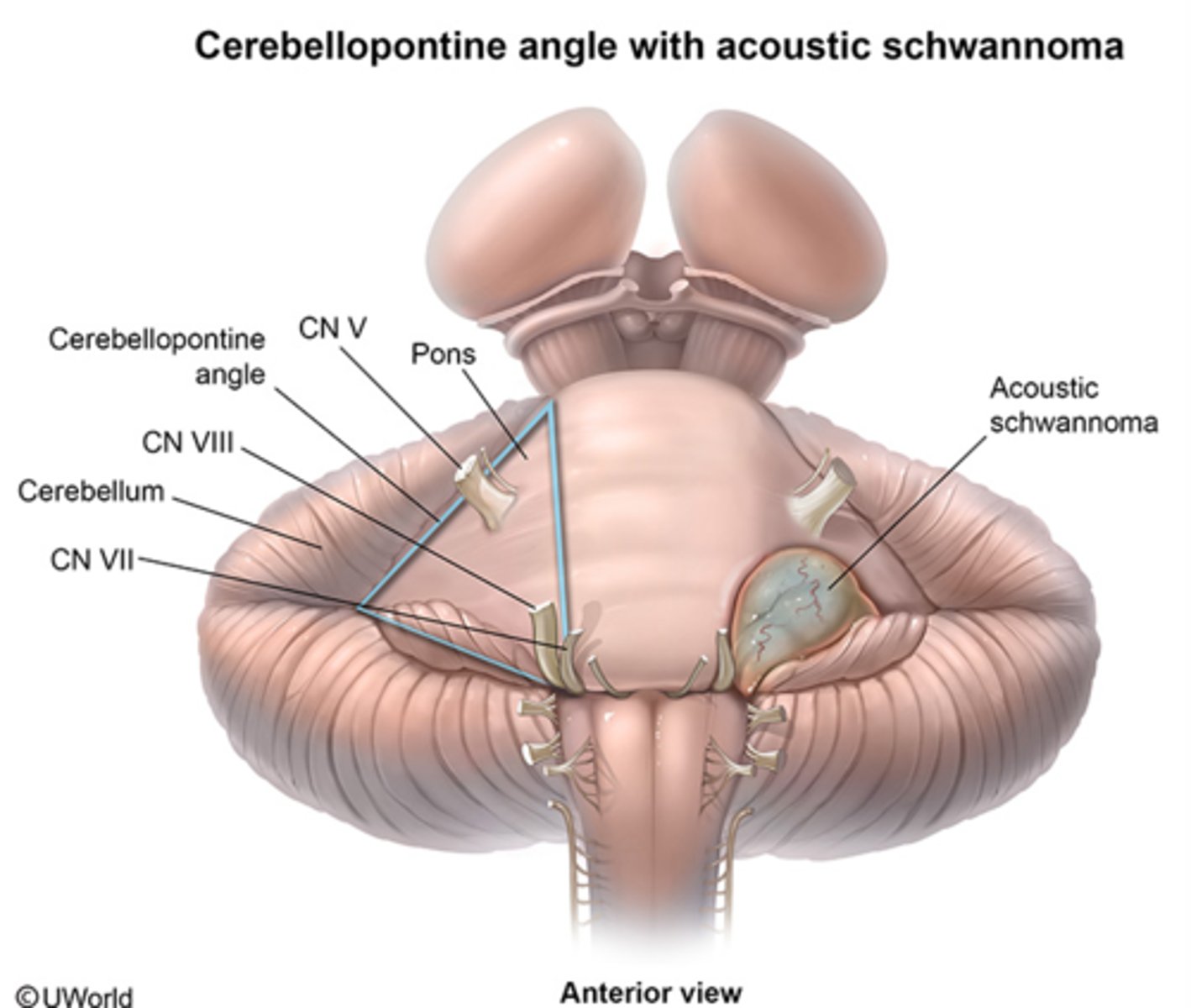
CN IX
Glossopharyngeal
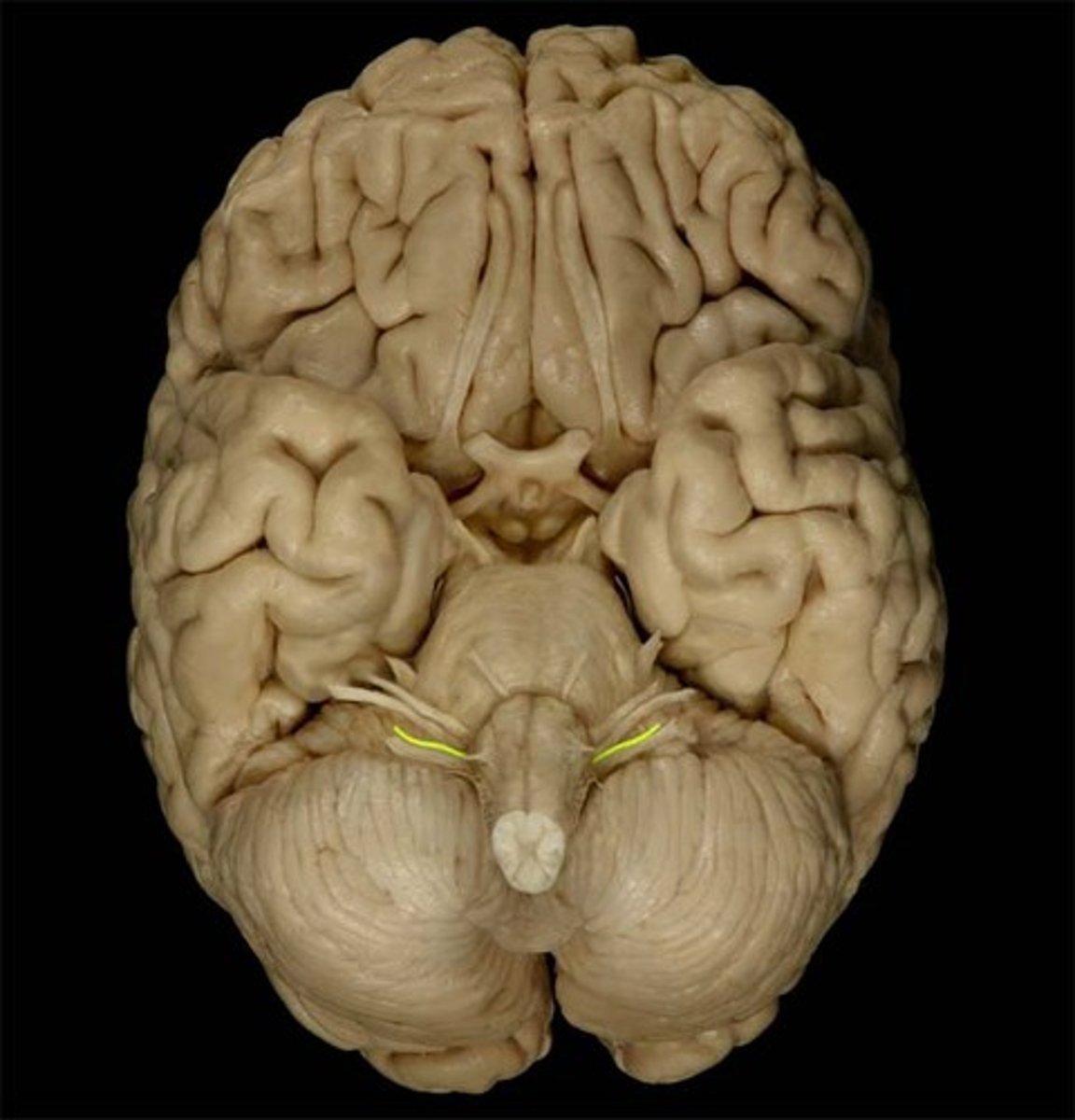
CN IX sensory function
Outer Ear (STTN - spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus) - CN 7, 9, 10
middle ear, pharynx, touch post. 1/3 tongue (Sol. N. & STTN)
carotid body & sinus (Sol. N.)
chemoreceptors - posterior 1/3 tongue. (Sol. N.)
CN IX motor function
Stylopharyngeus m. (elevates pharynx) (Nucleus Ambiguus)
parotid salivary gland (Inf. Salivatory N)
CN IX - CNS entry/exit location
medulla
Five branches of CN IX pathway
inferior salivatory
solitary nucleus
STTN
nucleus ambiguus
solitary nucleus