Unit 3.1
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
marketing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
segmentation
categorizing of customers based on certain characteristics
segmentation examples
income
age
gender
location
purpose of segmentation
basis for product development
targeting customers
meeting specific needs/wants
target market
the main customers a business aims for
disposable income
how much a person has left after paying taxes, bills & needs
pros of segmentation
recognizes different needs/wants of groups
less expensive/wasteful than wider product marketing
altering of product
loyalty from specific needs being me
cons of segmentation
risk of over generalization
not all segments are mutually exclusive/difficulty in identifying
requires more detailed research taking more time/costly
segments may be too small for catering
primary research
gathering information for the first time
field research, first hand
types of primary research
observing consumer actions
surveying first hand via phone, focus groups, door to door
direct customer feedback
pros of primary research
tailored to business
up to date
deeper insight
cons of primary research
expensive
misleading results if general group is incorrectly represented
longer process
requires expertise(good questions + avoiding bias)
secondary research
using data that already exists
desk research, second hand
types of secondary research
any form of existing documentation
printed press/magazines
census/government archives
internet research
pros of secondary research
gathered quickly & cheaply with many reliable sources
info on larger sections of population
useful starting point
spotting broader patterns
cons of secondary research
not tailored to businesses
out of date with market needs
varying quality due to wide range of sources
2 types of data
qualitative(opinions)
quantitative(#)
market research
process of gathering, analyzing & processing data relevant to marketing decisions
examples of info
shopping patterns
frequented locations
competitor products(price/packaging)
success of promotions
purpose of market research
measure:
demand
market share
competition
target market
demand
size & growth of market, different segments that exist within the market as a whole
competition
the number & size of competitors & their share of total market sales
market share
the percentage of sales in a particular market for a specific business
market share equation
business profits/ total market profit
market growth
the percentage growth in the size of the market, measured over a specific period
market growth equation
change in market size/ og market size * 100
market size
total volume of a given market
market size equation
measured by value/volume of sales
marketing mix (4Ps)
combination of product, price, place and promotion for each business venture
they are all interrelated
product
function/appearance of goods/services
price
payment for the product
promotion
customers’ informed-ness of the product(persuade,remind,inform)
place
point where products are made available to customers
factors of marketing mix
competition
product
target customer
brand image
main features of a product
quality
image
technology
value for money
reliability
design
packaging
factors of product development
design
durability
demand
development costs
price
USP
m1- what makes a product special
m2- provide CSD such as special warranty
new products
product designed to fit change in customer needs
high-risk element on brand rep + investment
alters existent model/introduces new product
product life cycle
the stages a product goes through from their initial launch to the point they are discontinued
product life cycle diagram
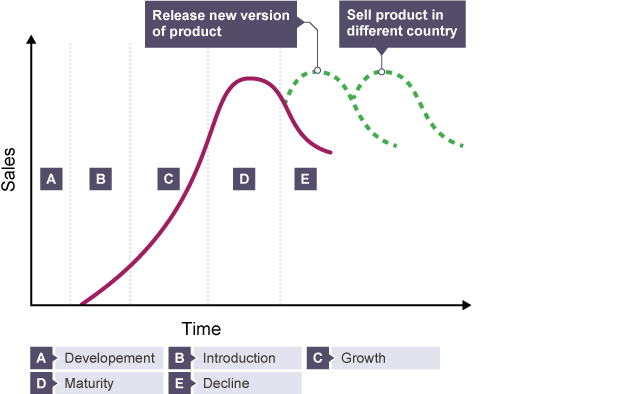
development
no sales = no value to company’s revenue
needs suitable development time but is generally minimized
launch/introduction
sales are relatively low as visibility is low, resulting in heavy advertising
growth
rapid increase of sales as demand increase and become established
maturity
the market is established
copycats may arise from rivalry USPs
market becomes flooded/saturated, leading to a fall in demand
decline
sales and profits fall, often leading to a product’s discontinuation
extension
company uses extension strategies to lengthen its product life cycle
extension strategy examples
rebranding product
updating the package
finding larger market
pricing strategy
brand
naming a product to differentiate it
easily recognized
builds an image
higher pricing
loyalty booster
own brand
a product sold under a supermarket chain/other retailers, rather than that of a manufacturer
cheaper as costs are lowered from collateral promotions
branding
involves the consistent range of color or logos
pros of the brand
higher price
loyalty
successful names can link to a product
purchasing complimentary products (shampoo, brush)
cons of the brand
bad name if quality falls
development cost
can be copied/near copied
product portfolio
collective name for every product that a company produces
boston matrix
analyzes a product portfolio by categorizing into one of four areas.
informs decisions of marketing strategies
low/high market share/growth
boston matrix diagram
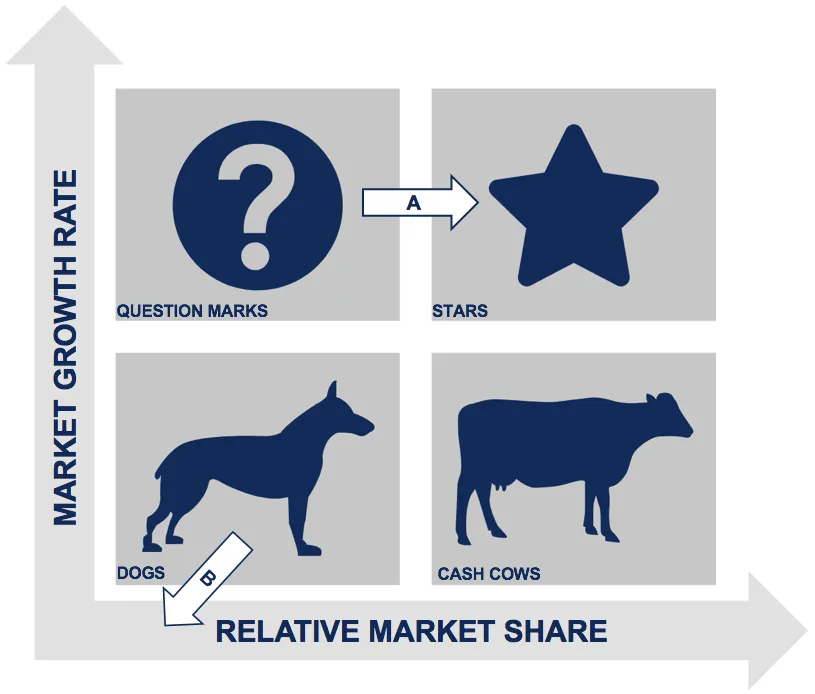
stars
high market growth + share
potential for high revenue growth
new products i.e. mcflurry when it first came out
cash cows
low market growth, high share
maturity phase with positive cash flow
low maintenance, high revenue
i.e. big mac, fries
?/problem child
high market growth, low share
future potential, negative cash flow, development cost
dogs
low market growth + share
negative cash flow, large sums of $ to support
limitations of the boston matrix
no predictions of future
no account of business environment
inadequate measure of market attractiveness to a new business
market share inequal profitability
ignores sustainable competitive advantages/life cycle variations per product
cost plus
adding on a profit margin on top of the cost of production
penetration
a low price when entering a new market/as a less well-known company
skimming/premium
high price when things are new/exclusive
opposite to penetration
competitor
having similar pricing to your competition(sometimes lower)
promotional
special offers of pricing to entice customers, i.e. discounts
psychological
making things appear cheaper i.e 99p to £1.00
differential
different prices for the same thing (train tickets for adults v kids)
loss leader
pricing below costs to attract customers buying products that correlate
i.e. printers at a loss, cartilages at a profit
promotional mix
blend of promotional activities a marketing department uses to enable promotion achieving business goals
reasons to promote
inform about the business
persuade purchase
reminds about product advantage
factors impacting promo
finance
cost
nature of product/market
competitiors
advertising
to communicate the product of a business via:
telly ads, posters, etc
sales promotions
short term incentives to encourage customer purchases (i.e. discounts)
public relations
using media to communicate with customers
press release, competitions, stories
sponsorship
paying to have the brand associated with something
kpop groups, sports team, programme
after-sales service
help & advice at a later date that product purchase
guaranteed refunds, check-ups
merchandising
producing associated products with the brand
t-shirts, plushies, crockery
loyalty cards
rewards for purchasing with the same business more than once
eg free gift
direct selling
having a sales person visit customer to sell
trades/fairs
a location where businesses or customers interested visit with intention of purchasing
distribution channel
how the ownership of a product passes from the producer to the final customer
wholesaler
buying in large quantities from a producer and selling to retailers
retailers
shops selling directly to customer
intermediary
a link in the distribution chain between producer and customer that results in a higher price
types of distribution channels
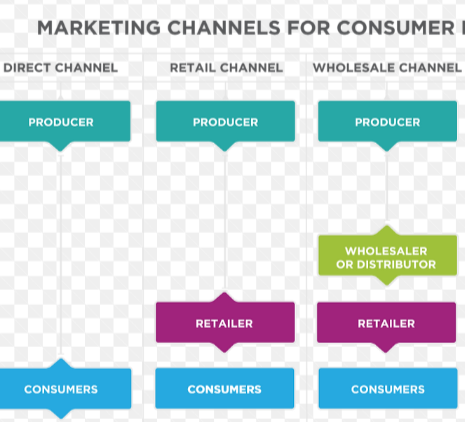
e-commerce
the act of buying/selling a product using electronic system such as the internet
m-commerce
the buying/selling of goods via a wireless handheld device
e.g. smartphones
pros in e-commerce
global everywhere
open 24/7
professional image at low cost
wide product range
price comparison is easier
cons of e-commerce
worldwide competition
delivery issues
online security
lack of personal contact/physical viewing of product
pros of m-commerce
mobile devices increase = more accessibility
easier to track data on mobile