Measuring Energy Changes
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Define Energy and its important parts
ability to do ‘work’
move an object against an opposing force
potential or kinetic
ex. heat, light, sound, electricity and chemical energy

Tell me about Heat
energy transfer due to temperature difference
produces an increase in disorder in how particles behave
increases the average kinetic energy of the molecules
What is the Chemistry Universe? What are its components?
the universe in chemistry that is split into two systems
Chemical System - area of interest/made of reactants and products
Surroundings - everything else in the universe
typically air or water
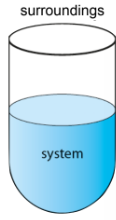
What are the two types of Systems?
Open
can exchange energy and matter with the surroundings
closed
can exchange energy, but not matter. eg. glow sticks
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed only converted from one form into another
What does the Law of Conservation of Energy tell us about chemical reactions?
energy can be exchanged between system and surroundings, but total energy cannot change during the process
Energy from the system is gained by surroundings and vice versa
eg. bbq (chemical to thermal & light)
What is Enthalpy? tell me about it.
Total Internal Heat Content (at constant pressure)(sum of kinetic and potential energy)
it is impossible to measure the enthalpy of a system
Tell me about Enthalpy Change (∆H)
measured in kJ/mol
measures amount of heat energy contained in a substance/system
result from bonds and intermolecular forces breaking and forming
measured from difference in enthalpy between reactants and products
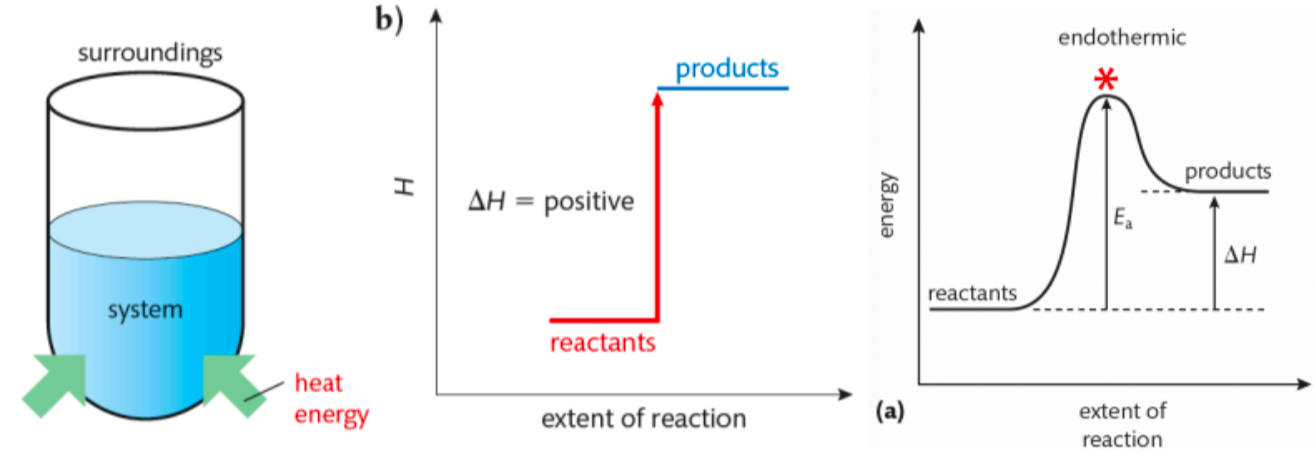
Tell me about Endothermic Reactions
net absorption of energy from surroundings
(energy absorbed to break bonds is GREATER than energy released when products form)
△H is positive
temperature of surroundings decreases
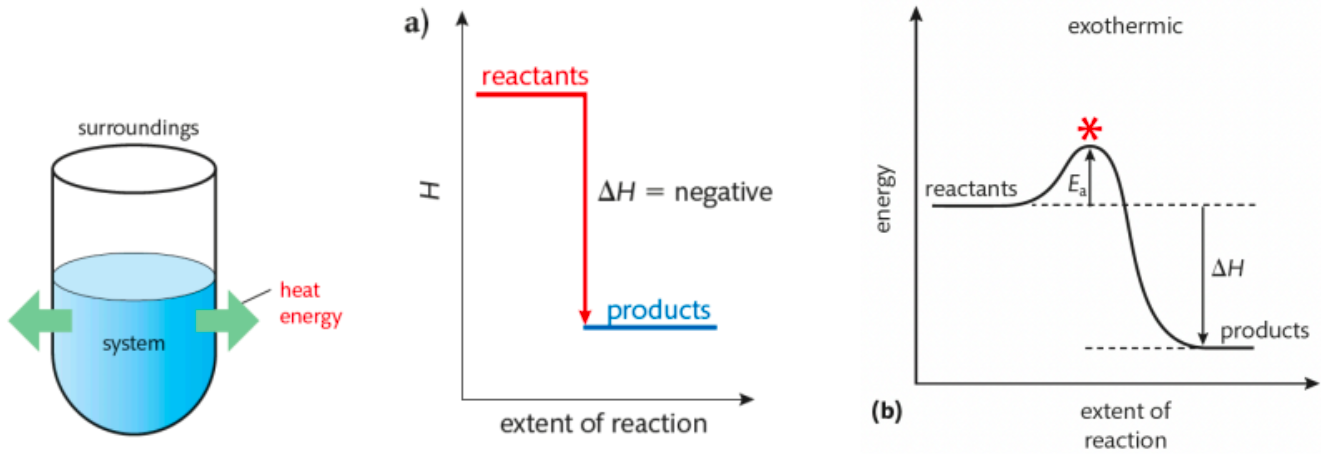
Tell me about Exothermic Reactions
net release of energy to surroundings
(energy absorbed to break bonds is LESS than energy released when products form)
△H is negative
temperature of surroundings increases
What 3 things affect Heat Change Calculations?
mass of object (g)
heat added (K)
Specific Heat Capacity
Define Specific Heat Capacity. What does it depend on? What is its equation?
amount of heat needed to raise 1g of a substance by 1°C
depends on # of particles
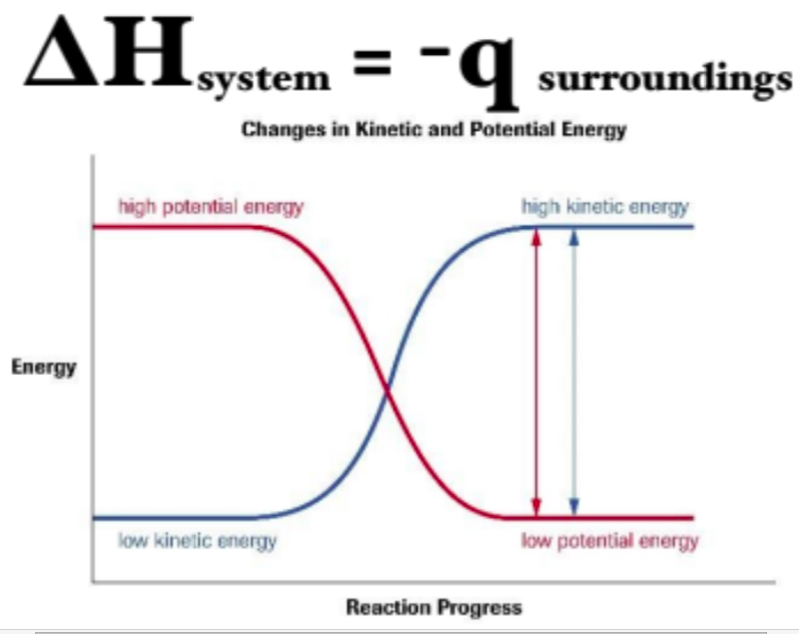
when a change occurs in a system (__), the chemical potential energy change is ___________ _____ to the ____ (_) transferred to the surroundings.
∆H
numerically equal
heat (q)
Equation for heat transfer between System and Surrounding
What do Enthalpy Changes Depend on?
the conditions of the reaction
What are standard conditions?
100 kPa (pressure)
1 mol dm⁻³ (concentration)
298 K (temp.)
How can we represent Enthalpy Change?
thermochemical equation
potential energy diagram
molar enthalpy change
(energy change that occurs when 1 mol of a substance undergoes a physical, chemical, or nuclear change)
What does a Thermochemical Equation look like?
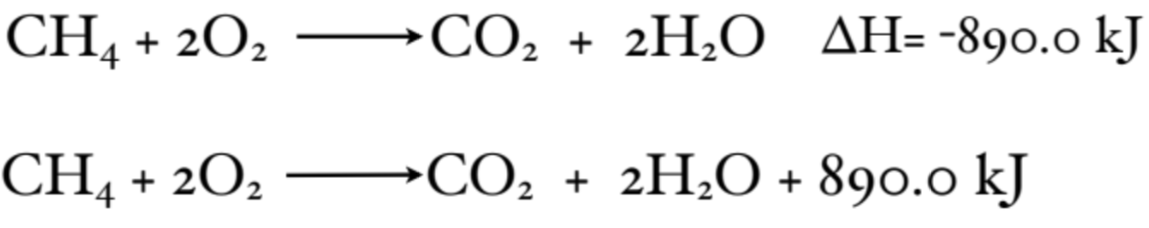
What does a Molar Enthalpy Change look like?
represented by ∆Hr
units are J/mol
*the molecule you are getting the ΔHr MUST have a coefficient of 1

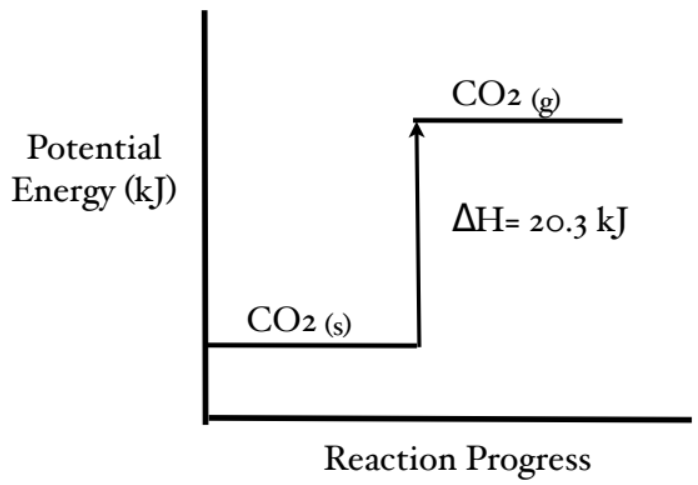
Draw a potential energy diagram for: CO₂(s) + 20.3 kJ → CO₂ (g)
Energy is on the reactant side, which means its endothermic. Product will have greater potential energy than reactants.
Tell me about Calorimetry
process of measuring energy changes during a chemical or physical change
use a device called a calorimeter
we assume the calorimeter is a closed system
surroundings is water

EXAMPLE (p.397)
A coffee-cup calorimeter was used to measure the temperature change for the reaction between zinc powder and a 1.0 mol/dm⁻³ solution of copper (II) sulphate. The following results were recorded:
Determine the amount of heat released and the enthalpy change for this reaction.
Determine Heat Change
Determine limiting reactant
Calculate molar enthalpy