epithelial and connective tissues (with pictures!!)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:56 PM on 9/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
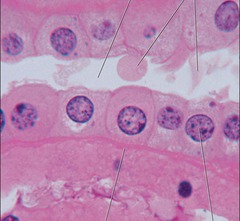
simple cuboidal epithelium
Function: secretion and absorption
Location: kidney tubules and ovary surface
Location: kidney tubules and ovary surface
2
New cards
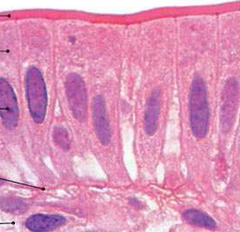
simple columnar epithelium
Functions: absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and
other substances; ciliated type propels mucus or reproductive cells by ciliary action
• Location = Non-ciliated
form lines digestive tract, gallbladder, ducts of some glands, ciliated form lines small bronchi, fallopian tubes, and uterus
other substances; ciliated type propels mucus or reproductive cells by ciliary action
• Location = Non-ciliated
form lines digestive tract, gallbladder, ducts of some glands, ciliated form lines small bronchi, fallopian tubes, and uterus
3
New cards
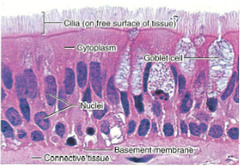
pseudostratified (ciliated) columnar epithelium
Function - secretion of mucus; propulsion of mucus by cilia • Locations = Non-
ciliated type is in ducts of male reproductive tubes and ducts of large glands; ciliated variety lines trachea and most of upper respiratory tract
ciliated type is in ducts of male reproductive tubes and ducts of large glands; ciliated variety lines trachea and most of upper respiratory tract
4
New cards
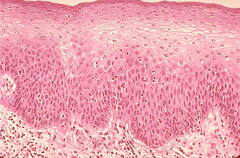
stratified squamous epithelium
Specific types = Keratinized - contain the protective
protein keratin; surface cells are dead and full of keratin; Non-keratinized - forms moist lining of body openings
• Function - Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to
abrasion
• Location = Keratinized -
forms epidermis, Non-keratinized - forms lining of esophagus, mouth, and vagina
protein keratin; surface cells are dead and full of keratin; Non-keratinized - forms moist lining of body openings
• Function - Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to
abrasion
• Location = Keratinized -
forms epidermis, Non-keratinized - forms lining of esophagus, mouth, and vagina
5
New cards
simple squamous epithelium
Specific types = Keratinized - contain the protective
protein keratin; surface cells are dead and full of keratin; Non-keratinized - forms moist lining of body openings
• Function - Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to
abrasion
• Location = Keratinized -
forms epidermis, Non-keratinized - forms lining of esophagus, mouth, and vagina
protein keratin; surface cells are dead and full of keratin; Non-keratinized - forms moist lining of body openings
• Function - Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to
abrasion
• Location = Keratinized -
forms epidermis, Non-keratinized - forms lining of esophagus, mouth, and vagina
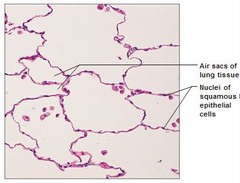
6
New cards
stratified columnar epithelium
Function - protection and secretion • Location = found in male urethra and large ducts of some
glands
glands
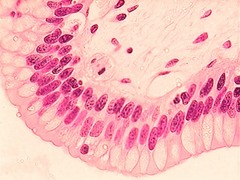
7
New cards
stratified cuboidal epithelium
Function - protection
• Locations = forms largest ducts of sweat glands and
forms ducts of mammary glands and salivary gland
• Locations = forms largest ducts of sweat glands and
forms ducts of mammary glands and salivary gland
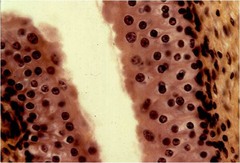
8
New cards
transitional epithelium
Function - stretches and permits distension of urinary
bladder causing thinning (from 6 to 3 layers when filled with urine)
• Location = Lines ureters, urinary bladder and part of
urethra
bladder causing thinning (from 6 to 3 layers when filled with urine)
• Location = Lines ureters, urinary bladder and part of
urethra
9
New cards
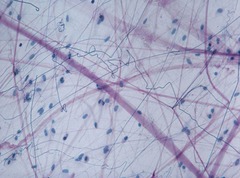
areolar connective tissue
stain clearly
paint brush strokes
------------------------------
Description = Gel-like matrix with all three fiber types, cells
include - fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, white blood cells
• Functions = Wraps and cushions organs,
holds and conveys tissue fluid, important role in inflammation
• Location = widely distributed under
epithelia, packages organs, surrounds capillaries
paint brush strokes
------------------------------
Description = Gel-like matrix with all three fiber types, cells
include - fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, white blood cells
• Functions = Wraps and cushions organs,
holds and conveys tissue fluid, important role in inflammation
• Location = widely distributed under
epithelia, packages organs, surrounds capillaries
10
New cards
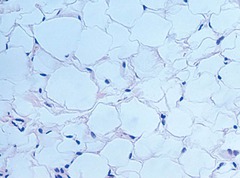
adipose tissue
doesn't uptake color as well as others
----------------------------------
•Functions = provides reserve food fuel, insulates
against heat loss, supports and protects organs
• Locations = under skin,
around kidneys, behind eyeballs, within abdomen and in breasts
----------------------------------
•Functions = provides reserve food fuel, insulates
against heat loss, supports and protects organs
• Locations = under skin,
around kidneys, behind eyeballs, within abdomen and in breasts
11
New cards
Mesenchyme
the same embryonic for connective tissue
12
New cards
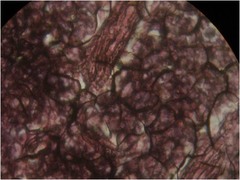
reticular connective tissue
geometric RECT-angle style
-----------------------------------
• Function - form a soft, internal skeleton (stroma) - supports
other cell types
• Location - lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow,
and spleen)
-----------------------------------
• Function - form a soft, internal skeleton (stroma) - supports
other cell types
• Location - lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow,
and spleen)
13
New cards
regular connective tissue
packed with collagen fibers and follows a parallel pattern
----------------------------------
• Functions = Attaches muscle to bone (tendons), attaches
bone to bone (ligaments); withstands great stress in one direction
• Locations = Tendons and ligaments, aponeuroses (sheet-
like tendons), fascia (membranes) around muscles, nerves, and large vessels
----------------------------------
• Functions = Attaches muscle to bone (tendons), attaches
bone to bone (ligaments); withstands great stress in one direction
• Locations = Tendons and ligaments, aponeuroses (sheet-
like tendons), fascia (membranes) around muscles, nerves, and large vessels

14
New cards
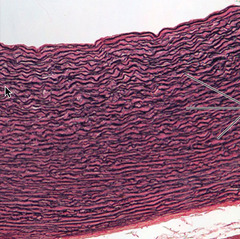
elastic connective tissue
takes up so much dye looks like purple squiggly lines
--------------------------------
--------------------------------
15
New cards
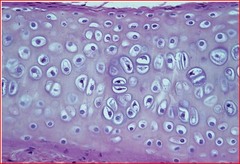
Hyaline Cartilage
glassy or hazy , fibers do not stain clearly but cells do!
-------------------------------
• Functions = Supports and reinforces, resilient cushion,
resists repetitive stress
• Locations = Fetal skeleton, ends of long bones, costal
cartilage of ribs, cartilages of nose, trachea, and larynx
-------------------------------
• Functions = Supports and reinforces, resilient cushion,
resists repetitive stress
• Locations = Fetal skeleton, ends of long bones, costal
cartilage of ribs, cartilages of nose, trachea, and larynx
16
New cards
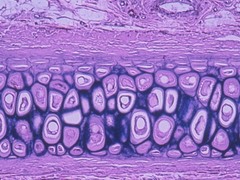
elastic cartilage
elastic stains very dark purple but reveals very big cells
------------------------------------
• Functions = Maintains shape of structure, allows great
flexibility
• Locations = Supports external ear, epiglottis
------------------------------------
• Functions = Maintains shape of structure, allows great
flexibility
• Locations = Supports external ear, epiglottis
17
New cards
fibrocartilage
hideous fuchsia pink
--------------------------------
• Function = Tensile strength and ability to absorb
compressive shock
• Locations = Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of
knee joint
--------------------------------
• Function = Tensile strength and ability to absorb
compressive shock
• Locations = Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of
knee joint
18
New cards
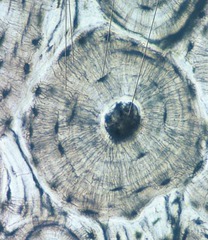
osseous (bone) tissue
looks like a tree or an OY-ster
--------------------------------
• Functions = Supports and protects organs, provides levers
and attachment site for muscles, stores calcium and other minerals, stores fat, marrow is site for blood cell formation
• Location = Bones
--------------------------------
• Functions = Supports and protects organs, provides levers
and attachment site for muscles, stores calcium and other minerals, stores fat, marrow is site for blood cell formation
• Location = Bones
19
New cards
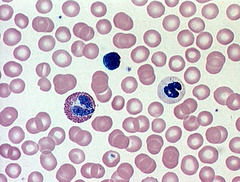
blood cells
LARGE purple dots are white blood cells
Pink are blood cells
LITTLE purple ones are platelets
Pink are blood cells
LITTLE purple ones are platelets
20
New cards
epithelial tissue def.
sheets of cells covering body surface or lining a body cavity
21
New cards
connective tissue
provide support
22
New cards
muscle tissue
includes skeletal, cardiac, smooth
---------------------------------------
Functions = Propels substances along internal passageways,
involuntary control
• Location = mostly walls of hollow organs (digestive,
urinary, uterus, and blood vessels
---------------------------------------
Functions = Propels substances along internal passageways,
involuntary control
• Location = mostly walls of hollow organs (digestive,
urinary, uterus, and blood vessels
23
New cards
nerve
main component of the nervous system: provides control
-----------------------------------
• Functions = Transmit electrical signals from sensory
receptors to effectors
• Location = Brain, spinal cord, and nerves
-----------------------------------
• Functions = Transmit electrical signals from sensory
receptors to effectors
• Location = Brain, spinal cord, and nerves
24
New cards
Epithelial tissue FACTS
-cellularity: composed almost entirely out of cells
-polarity: apical(upper free) and basal (lower attached) surfaces
-avascular (no blood vessels) but innervated (supplied by nerves)
*supported by connective tissue
-highly regenerative
-polarity: apical(upper free) and basal (lower attached) surfaces
-avascular (no blood vessels) but innervated (supplied by nerves)
*supported by connective tissue
-highly regenerative
25
New cards
endothelium (simple squamous)
slick lining of hollow organs
26
New cards
mesothelium (simple squamous)
lines peritoneal, pleural and pericardial caviities
27
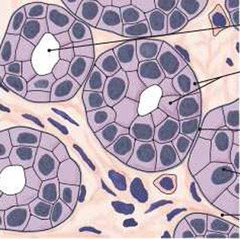
New cards
Unicellular Exocrine Glands (The
Goblet Cell)
Goblet Cell)
Scattered throughout epithelial
lining of intestines and respiratory tubes, between columnar cells
protects and lubricates many internal body surfaces
lining of intestines and respiratory tubes, between columnar cells
protects and lubricates many internal body surfaces
28
New cards
Cell Junctions
factors holding epithelial cells together
29
New cards
Tight junctions (zona
occludens)
occludens)
belt-like proteins in plasma membrane of adjacent cells are fused
close
off extracellular space
close
off extracellular space
30
New cards
Adherens junctions (zonula adherens)
with tight junctions, form the tight junctional complex
around apical lateral borders of epithelial tissues
around apical lateral borders of epithelial tissues
31
New cards
Desmosomes
anchoring
junction; two disc-like plaques connected across intercellular space
junction; two disc-like plaques connected across intercellular space
32
New cards
Gap junctions = nexus
tunnel-like passageway between two adjacent cells
33
New cards
Basal Lamina
34
New cards
Basal lamina and reticular layer
form the basement membrane
35
New cards
Microvilli
FINGER LIKE
extensions of plasma membrane; abundant in epithelia of small intestine and kidney; maximize surface area across which small molecules enter or leave
extensions of plasma membrane; abundant in epithelia of small intestine and kidney; maximize surface area across which small molecules enter or leave
36
New cards
Cilia
WHIP LIKE
highly motile
extensions of apical surface membranes
• Flagellum
highly motile
extensions of apical surface membranes
• Flagellum
37
New cards
Flagellum
38
New cards
(made of actin and myosin proteins)
39
New cards
-blast
immature
40
New cards
-cytes
matture
41
New cards
apical
top
42
New cards
avascular
no blood exchange
43
New cards
inervated
has nervous system exchange