chem - energetics
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
define temperature
the average kinetic energy of molecules (K)
define heat
the amount of energy exchanged due to a temperature difference between two substances (J)
define thermochemistry
the study of the energy changes that accompany physical or chemical changes in matter
define a chemical system
a set of reactants and products under study, usually represented by a chemical equation
define enthalpy
the amount of energy or heat content of a substance
where is energy stored in a substance? what energy is included?
in the chemical bonds. includes kinetic and potential energy and is not measured directly but changes are measured (J)
define standard enthalpy change of reaction. what are standard conditions?
the diff between the enthalpy of the products and the enthalpy of the reactant
SC: 298K and 1 × 105 Pa
what is the equation for change in enthalpy?
change in H = Hproducts - Hreactants
if change in H is negative, what type of reaction is it?
exothermic
if change in H is positive, what type of reaction is it?
endothermic
what does it mean about the substance when the enthalpy is high?
less stable
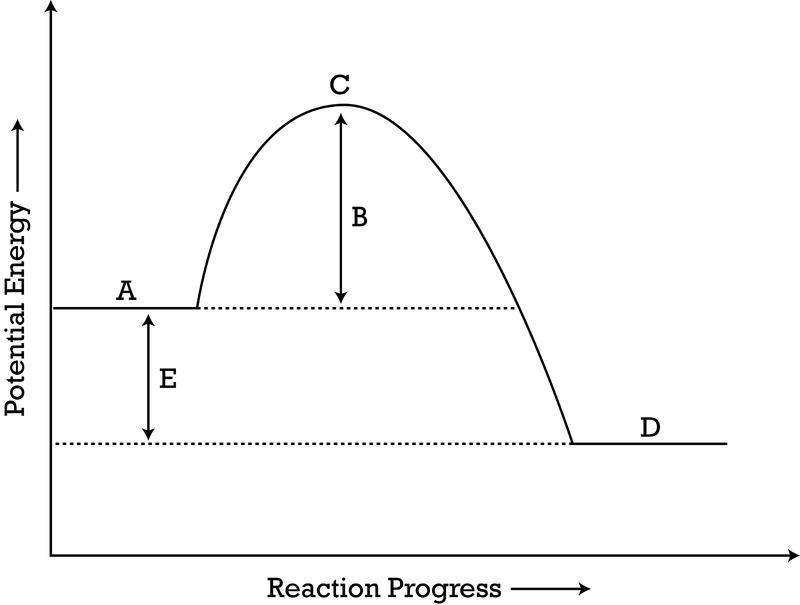
what does E represent? is this reaction endothermic or exothermic?
E represents change in energy - reaction is exothermic
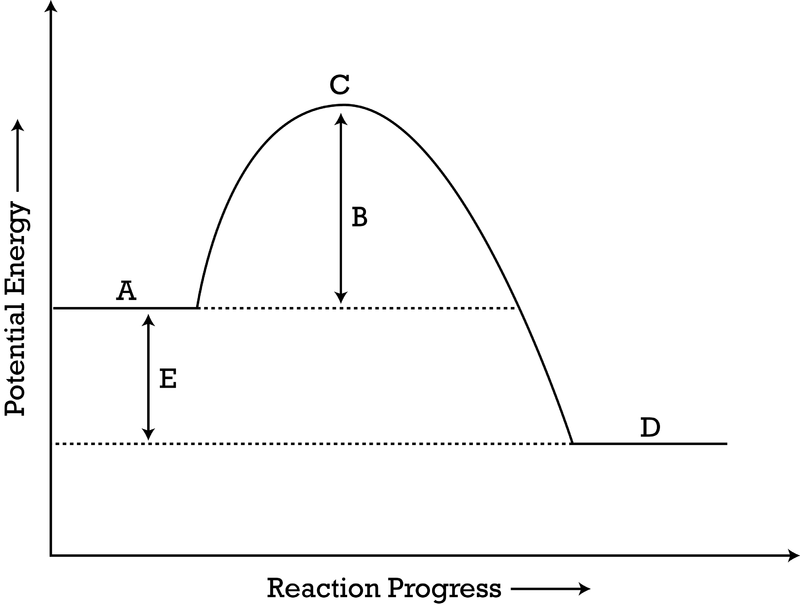
are reactants or products more stable?
products
name two examples of exothermic reactions. what are three characteristics about exothermic products?
combustion reactions
neutralization reactions
have less stored energy
more stable
have stronger bonds
what is the equation for energy? what are the units for each?
Q=mc(change in temperature)
m = mass in g
c= specific heat capacity of substance JK-1g-1
T= change in temperature in K
how is energy of surroundings related to energy of the system
qsurroundings = -qsystem
what are four examples of kinetic energy
electron motion in an atom
vibrations of atoms connected by chemical bonds
rotation of molecules
translation of molecules; motion of molecules through space
what are four examples of potential energy?
forces of attraction between molecules
chemical bond energy present within the molecule
energy associated with electrons
forces holding nuclear particles together
what does Hess’ Law state?
the value of change in H for any reaction that can be written in steps equals the sum of the values for change in H for each of the individual steps
What are the two rules for Hess’ Law?
if the rxn is reversed, H sign is flipped
if the rxn is multiplied by a factor, H is multiplied by same factor
define the standard enthalpy change of formation (H0f)
the enthalpy change that results when one mole of a compound is formed from its element at 298K and 1 × 105 Pa and at their standard states.
how do you calculate change in H using bond enthalpies?
H = BEbroken - BEformed
define average bond enthalpy
the amount of energy required to break one mole of bonds in the gaseous state averaged across a range of compounds containing that bond
what is the Born-Haber Cycle?
elements from standard states through multiple steps to form the solid compound
What are the 3 steps of the Born-Haber Cycle?
1) elements to gases (standard enthalpy change of atomisation)
Na(s) —> Na(g)
Cl2(g) —> 2Cl.(g) —> breaking bond energy, not state change
2) gas atoms to anions (electron affinity)
Cl. —> Cl-
3) metal atoms to cations (ionization energy)
Na —> Na+
define lattice enthalpy
the energy required to convert 1 mole of the solid compound into gaseous ions
draw the Born-Haber Cycle
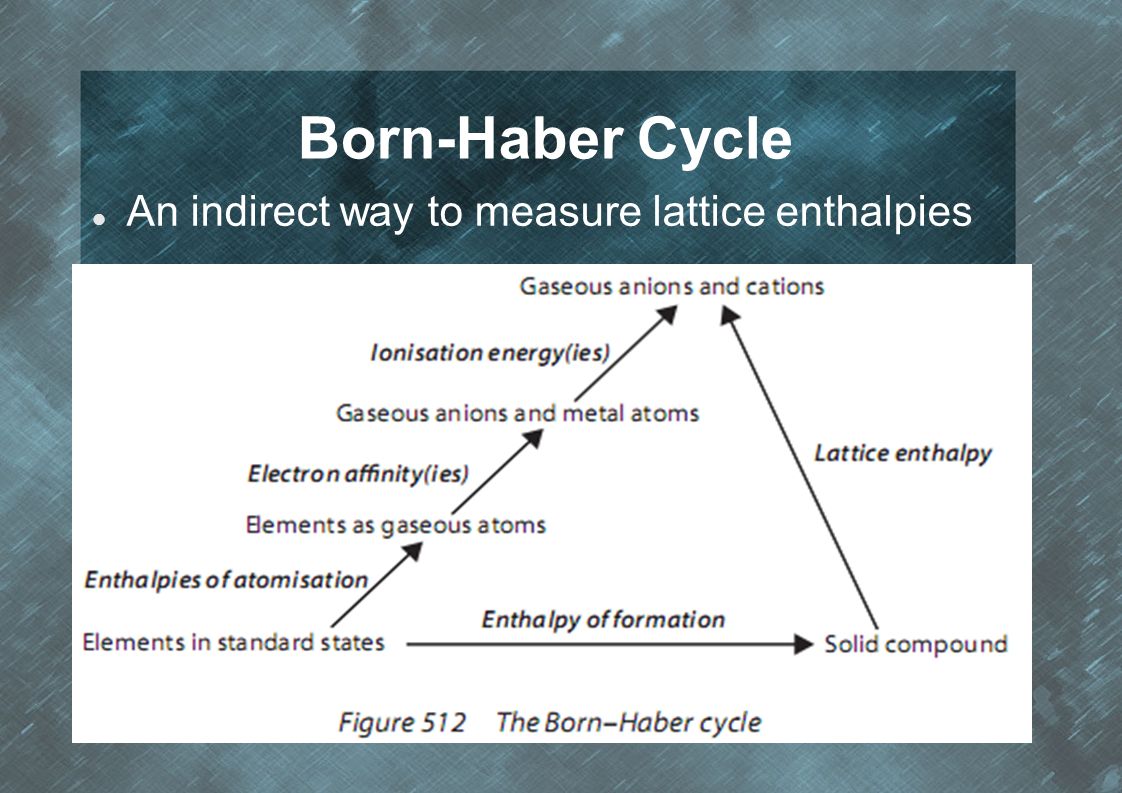
give the equation of the Born Haber cycle
H0atom + EA + IE = H0f + H0LE
define enthalpy of atomisation
the energy change required to change one mole of atoms from their standard states to their gaseous states
define ionization energy
minimum energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of atoms or positive ions in the gaseous state