Chem Semester One
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
why are valence electrons important for stability?
as when the shell is filled, it is stable. incomplete valence shells are highly reactive and participate in various reactions
why are valence electrons shells lost so easily?
they are farther from the nucleus and experience less electrostatic attraction
shielding effect
inner shell electrons reduce the effective nuclear charge felt by outer shell electrons
electrostatic attraction
the force of attraction between oppositely charged particles, while same charges repel
4 stages of mass spectrometry
ionisation, acceleration, deflection, detection
ionisation
knocking electrons off atoms to produce ions
acceleration
charged plate accelerates cations
deflection
the ions are deflected in a magnetic field
detection
a computer analyses which isotopes are present and their abundance
chemical properties of isotopes
similar to original element due to same number of electrons
physical properties of isotopes
affects mass, which affects melting/boiling points, and densities
core charge (definition)
force felt by the valence electrons towards the nucleus
core charge (pattern)
remains constant down the group, increases across a period
describe the pattern of core charge
number of protons increases as you move left to right
atomic radius
the distance from the nucleus to the valence electrons
describe the pattern of atomic radius
as you move across a period, core charge increases and radii decreases. electrons are held more tightly towards the nucleus.
ionisation energy
energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom in a gas state
first ionisation energy (pattern)
increases across a period, decreases down a group
describe the pattern of first ionisation energy
decreases down a group due to shielding, increases across a period due to core charge
metallic character
tendency of an element to lose electrons and exhibit properties of metals, such as conductivity and malleability.
metallic character AND atomic radius
increases down a group, decreases across periods
electronegativity
tendency of atoms to attract electrons towards itself. strength depends on size of nuclear charge and radii
electronegativity (pattern)
decreases down a group, increases across a period
describe the pattern of electronegativity
decreases down a group as charge stays constant and number of shells increases. increases across a period as charge increases and pulls on the electrons stonger.
material
something which is classified as a pure substance or a mixture
element
substance which is made up of one type of atom and cannot be broken down
compound
a substance formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together
molecule
when two or more atoms join together
what is the difference between a molecule and a compound?
a molecule can consists of same or different atoms, whereas a compound consists of different types of atoms.
mixture
contains 2 or more types of matter which are not chemically bonded
homogenous mixture
a mixture that has a uniform composition throughout
heterogenous mixture
a mixture that has an uneven composition
ionic bonding
when metals and non metals transfer electrons, resulting in ions that attract each other
properties of ionic bonding
brittle, high boiling/melting points, electrical conductivity
covalent bonding
when non-metals share electrons
properties of covalent bonds
usually low boiling/melting points, poor electrical conductivity, poor conductivity of heat, depends on shape of molecule
metallic bonding
a lattice of cations surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons
delocalised electrons
electrons which are able to move freely in the lattice
why do metals have a high boiling point
the strong electrostatic attraction between the cations and delocalised electrons requires a large amount of energy to overcome
why are metals a good conductor of electricity
the sea of delocalised electrons provide free flow of electric charge and will flow towards a positive electrodee
how are metals malleable and ductile
due to the nondirectional bonding, allowing the layers of atoms to slide over another without breaking the entire bond
non directional bonding
where the forces between atoms do not have a specific direction, enabling atoms to rearrange without fracturing the material.
how are metals good conductors of heat
when an atom is heated, the electron gains energy and vibrates more frequently, being able to transmit energy rapidly through the lattice
alkane
saturated and cannot fit anymore H bonds
alkene
unsaturated and can fit more H bonds
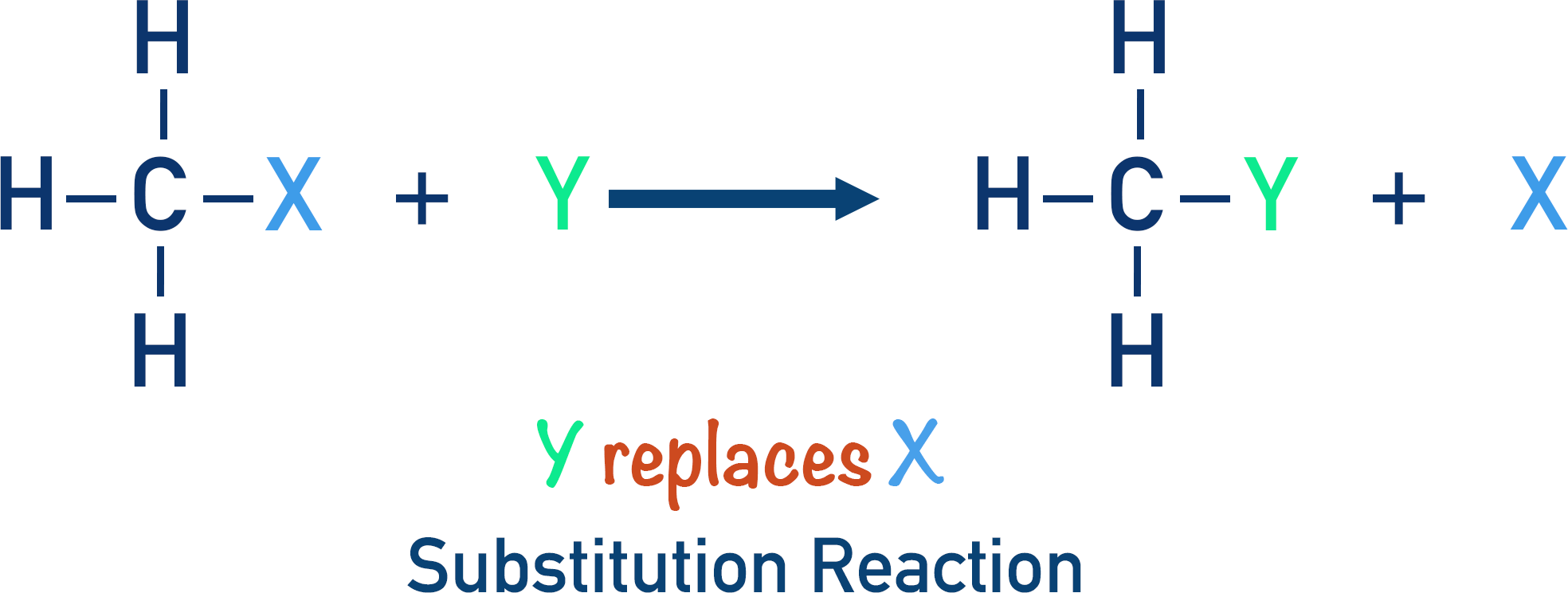
substitution reaction
requires UV and occurs in alkanes or benzenes
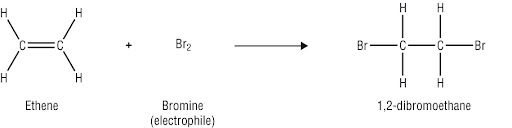
addition reaction
this reaction breaks double bonds, is quicker, and occurs in alkenes
nanoparticle
an atom with a diameter between 1-100 nm
how is nanoparticle coating superior to corrosion?
as the coating provides a uniform layer, leading more particles to react with the surface.
endothermic reaction
occurs when more energy is required to break the bonds in the reactants.
exothermic reaction
occurs when more energy is released to create new bonds than to break the original bonds
biofuel
fuel derived from biological sources
fossil fuels
non-renewable source of energy formed from things in sediment
advantages of biofuels over fossil fuels
sustainable, less CO2 emission, less environmental destruction
advantages of fossil fuels over biofuels
cheaper, available everywhere