Mass Spectrometer
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
manipulate, charged particles
The ability to ________ and sort _______________ allows deeper experimentation to understand what matter is made of.
Mass spectrometer
A device that separates ions according to their charge-to-mass ratios
Source
(1)
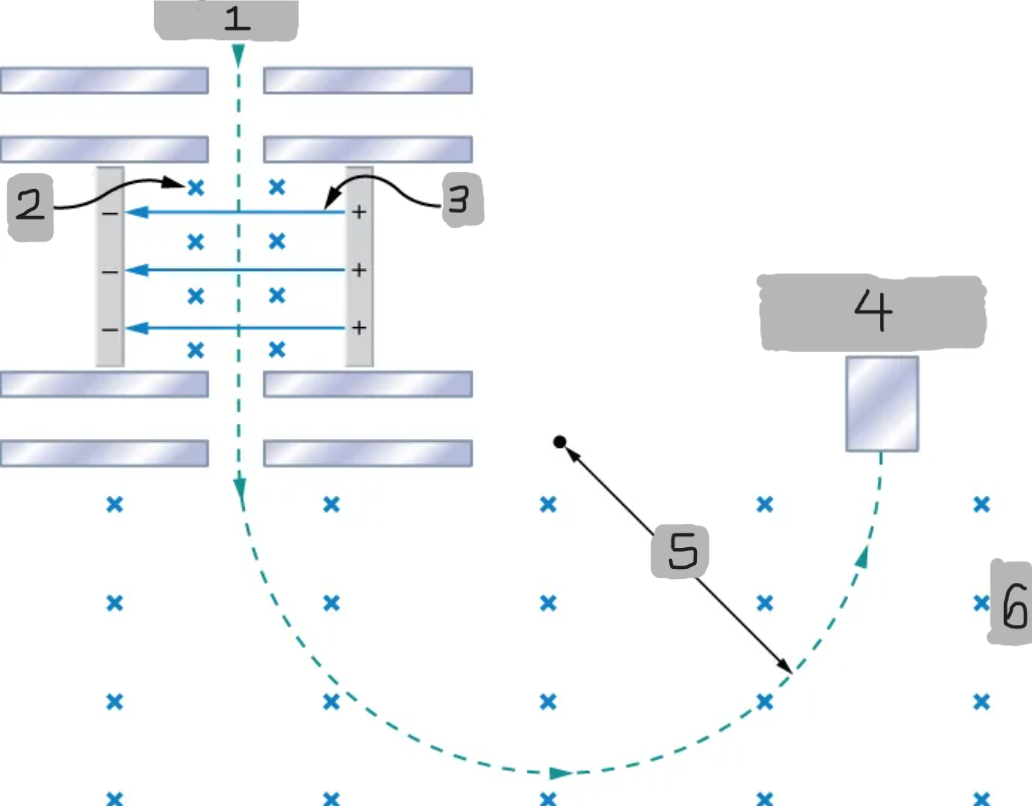
B
(2)
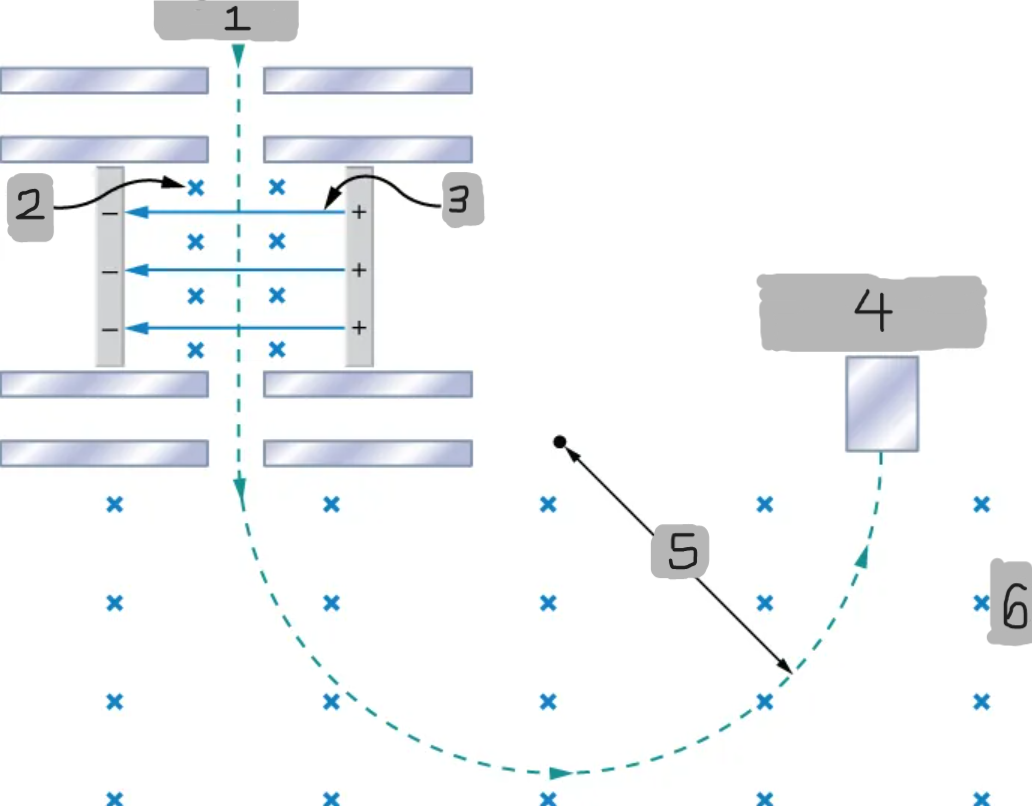
E
(3)
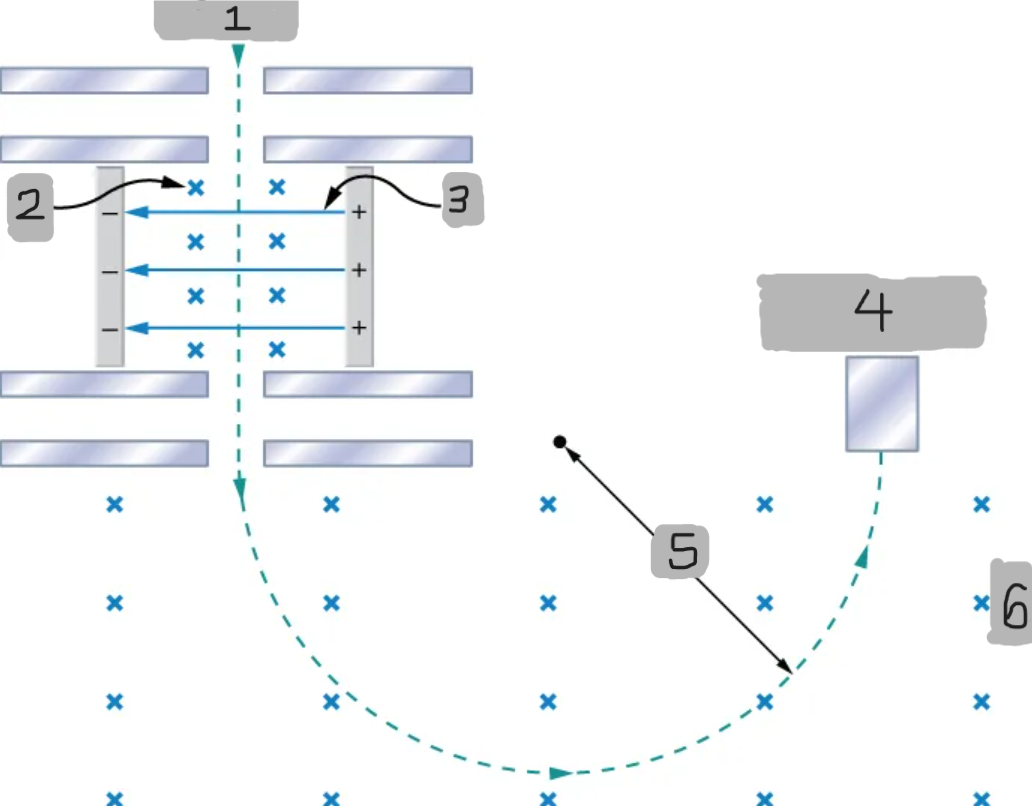
Particle detector
(4)
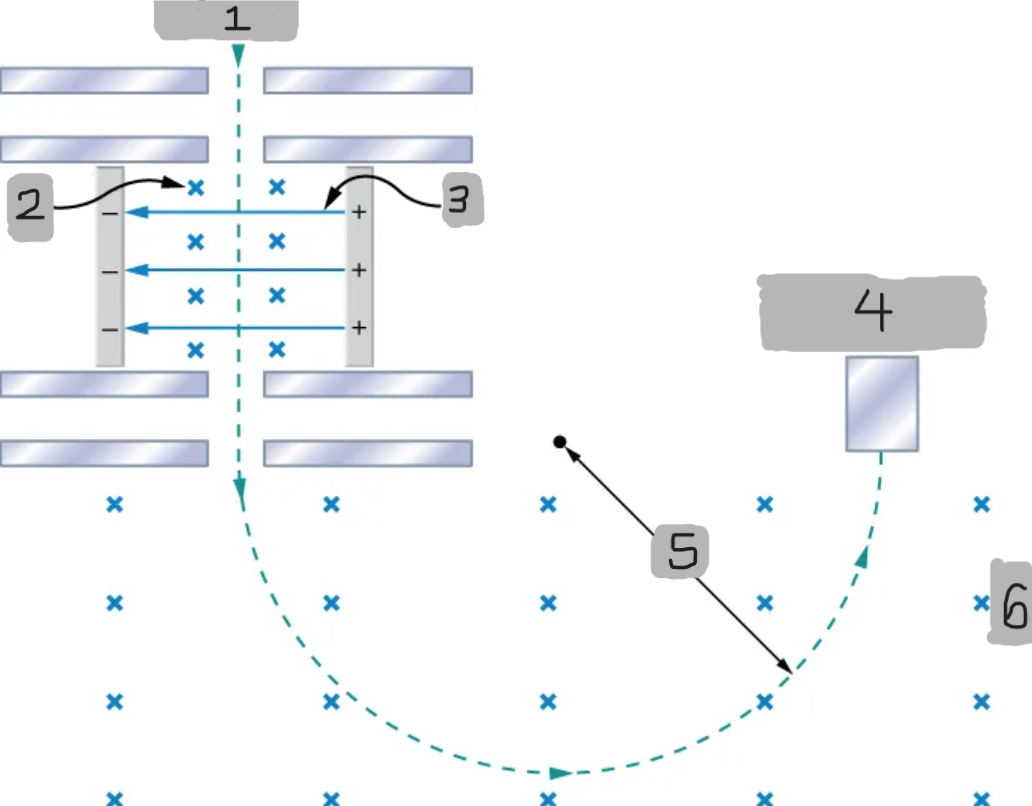
R
(5)
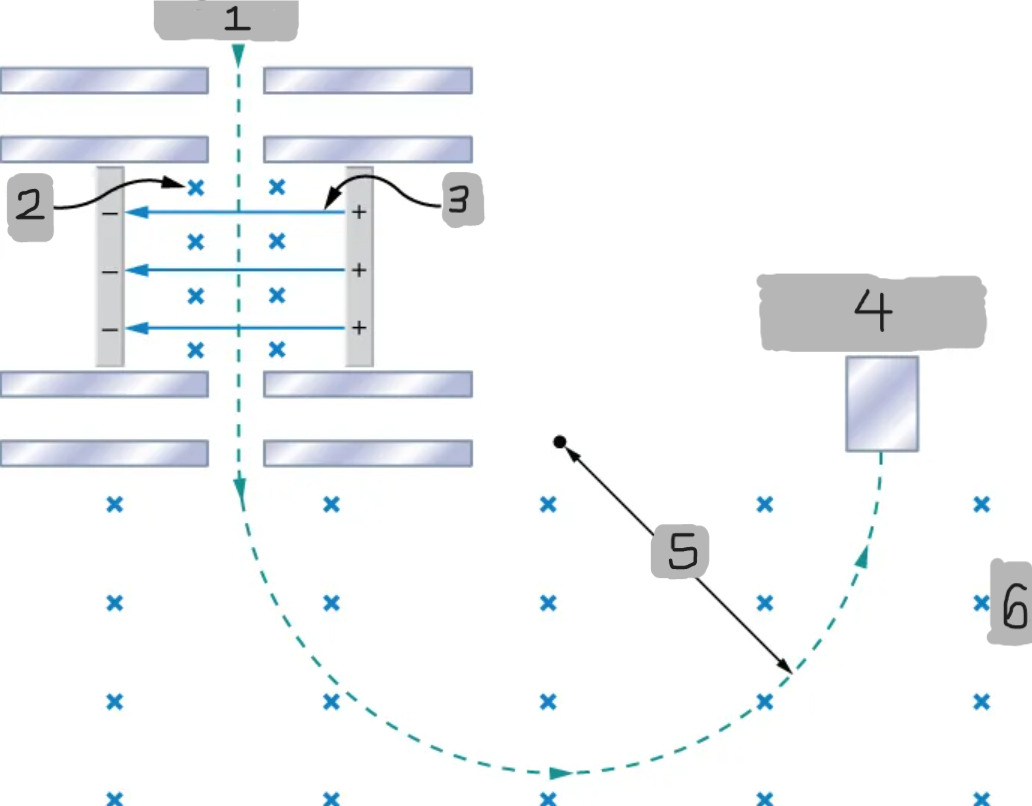
B0
(6)
Bainbridge mass spectrometer
The mass spectrometer type that uses the combination of the electric and magnetic field to deflect the ions.
velocity selector, magnetic force, electric force
Ions produced at a source are first sent through a _________________, where the ______________ is equally balanced with the ______________.
v = E/B, electric, magnetic, blocked
All the ions being sampled in the mass spectrometer emerge with the same speed (_______) since any ion with a different velocity is deflected preferentially by either ________ or ______________, and ultimately _______ from the next stage.
uniform magnetic field
The ions enter a _____________________ where they travel in a circular path with a radius, which gets measured by the particle detector
Q/m = E/BB0R
Equation for relationship between the charge-to-mass ratio and the radius
Most ions are singly charged
The mass-to-charge ratio and radius relationship equation can be used to measure the values of the radius because…
Yes, it is true
Is it true that spectrometer is also a part of system that detects very small leaks in a research apparatus?
Dilution Refrigerator
A devices in low-temperature physics laboratories to reach temperatures well below 1 K.
Cryogen
A substance which is usually a liquified gas that is used to produce very low temperatures (below 123 K or -150 °C)
Helium-3
The isotope which is the heart of the dilution refrigerator, it provides the cooling power in the mixing chamber
Is the light isotope of the Helium atom, that mixes with the Helium-4 isotope very at low temperatures.
Helium-4
The normal helium atom that is mixed with the Helium-3 isotope (the two system forms below around 0.87 K).
Helium-3 isotope atoms moving between the dilute and continuous phases provide a continuous cooling.
Liquid Helium Bath
A reservoir of liquid helium (often of Helium-4) that cools the entire refrigerator down to around 4.2 K before dilution cooling takes over.
Cryogen bath cooling or Precooling
Terms that are given to the cooling caused liquid helium bath
Dilution cooling
The ultra-low-temperature stage in a dilution refrigerator. This cooling occurs when the Helium-3 atoms cross the concentrated phase into the dilute liquid phase of a Helium-3 and helium-4 mixture, absorbing heat and reaching below 0.01 K
Pulse-Tube Cryocooler (PTC)
A refrigerator that reaches cryogenic temperature (around 2 to 4 K) without using liquid cryogens, by cycling high pressure helium gas (not liquid) through a special tube system.
compressed, expanded
Inside the PTC, helium gas is repeatedly ___________ and ________ to create cooling.
Compressor
A room temperature unit inside the PTC that compresses helium gas to high pressure, then sends it into the Cold head.
Provides the energy for the cooling cycle.
Cold head
Consists of the regenerator and the pulse tube where the cooling in PTC actually happens.
Regenerator
A material (often packed with the Bronze or copper powder or lead spheres) that temporarily stores and releases heat making the cooling cycle efficient.
Pulse tube
A hollow tube where pressure oscillations in the helium gas create a temperature gradient.
Phase shifter
Controls the timing phase between pressure and flow in the helium gas. Ensuring that the gas expands at the cold end (absorbing heat) and compresses at the warm end (releasing heat) and dumps heat to the environment.
PTC first stage cooling (40 to 50 K)
PTC intercepts most of the cooling.
PTC second stage cooling (3 to 4 K)
PTC cools the mixing chamber of the dilution refrigerator.
leak
The performance of these refrigerators is severely hampered if even a minute ____ between various component occurs.
Leak Test
A check done before cooling the dilution refrigerator, to make sure there are no leaks between compartments.
Test gas
A small amount of helium gas is injected into one compartment, because helium atoms are tiny and can slip through even the smallest leaks.
Detection setup
An adjacent compartment is connected to a high-vacuum pump that carries any leaked helium toward a mass spectrometer
Ionization step
A heated filament inside the detector ionizes helium atoms, turning them into charged particles (ions)
Leak indication
If the mass spectrometer detect helium atoms, it proves helium has crossed compartments, which means that a leak exists.
Inert gas
A gas that doesn’t easily react with other substances. Like helium, nitrogen, and argon, which are used as the carrier gases in gas chromatography because they won’t interfere with the sample.
Gas Chromatography
A technique used to separate and analyze mixture of gases or vapors. The sample is carried by an inert gas through a column, where different components move at different speeds and come out at different times (retention times)
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
A combined technique where gas chromatography separates a sample into parts, and a mass spectrometer identifies those parts.
Role of gas chromatography
Breaks down a mixture into its components by making them travel through a column at different speeds.
Role of Mass Spectrometer
Takes the separated components, ionizes them, and sorts them by mass-to-mass charge ratio to identify what molecules they are.
Arson investigation
Investigation used to detect the traces of accelerants like gasoline or alcohol in burned materials, helping investigators determine if a fire was started deliberately.
Applications of GC-MS
Used in arson investigation (fire debris), drug identification, security screening for explosives, and medical testing.