Factor Markets microeconomics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Perfectly competitive labor market
-Many small firms are hiring workers
-Many workers with identical skills
-Wage is constant
-Workers are wage takers
profit maximization
MRP=MRC
Monopsony
Market with only one buyer
factor markets vs product markets
Factor markets are where the factors of production are sold by households to businesses. Product markets are where goods/services ares old by businesses
four factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
why is the demand for labor downward sloping?
The number of workers that businesses are willing to hire increases as the wage falls.
Why is the supply for labor upward-sloping?
The number of workers that are willing and able to sell their labor increases as the wage increases
unemployment
caused by binding minimum wage
shifters of labor demand
1. Change in the demand for the product
2. Change in the productivity of the resource
3. Change in the price of related resources (substitute
and complementary resources)
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
The extra revenue generated when an additional worker is hired
Firms will hire workers up until MRP = wage
Marginal Resource Cost (MRC)
The additional money a worker adds to the total cost of production also known as marginal factor cost (MFC)
Least cost rule formula
MPx/Px = MPy/Py
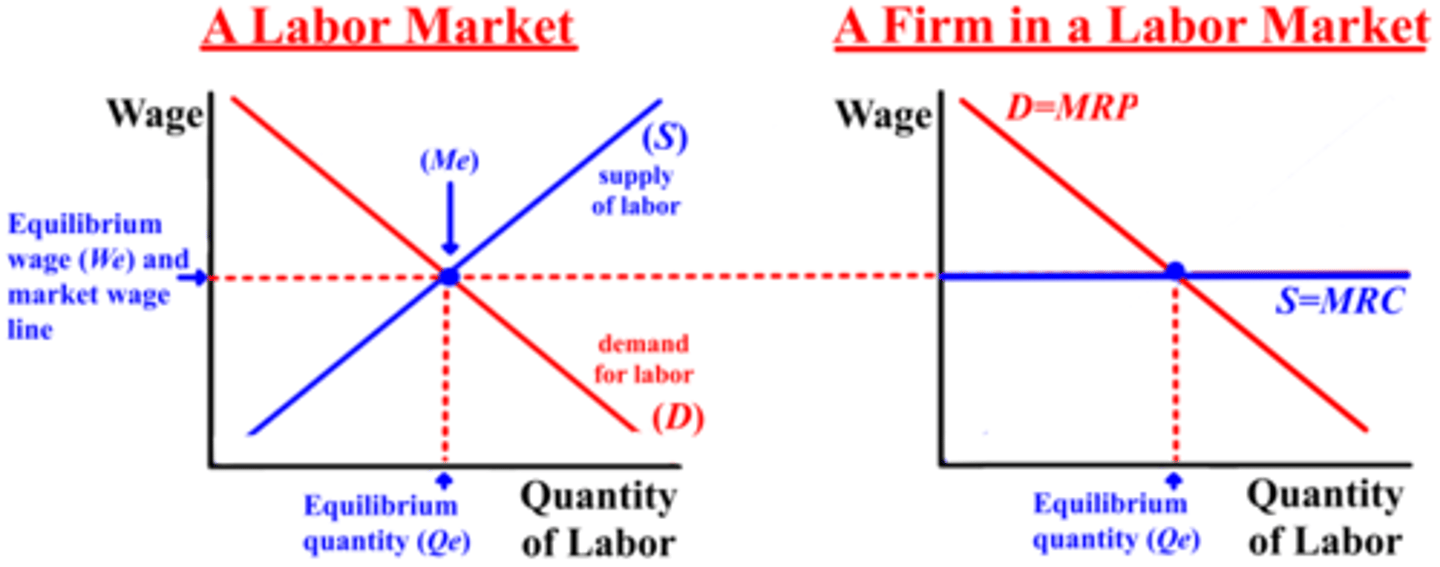
Competitive labor market and firm
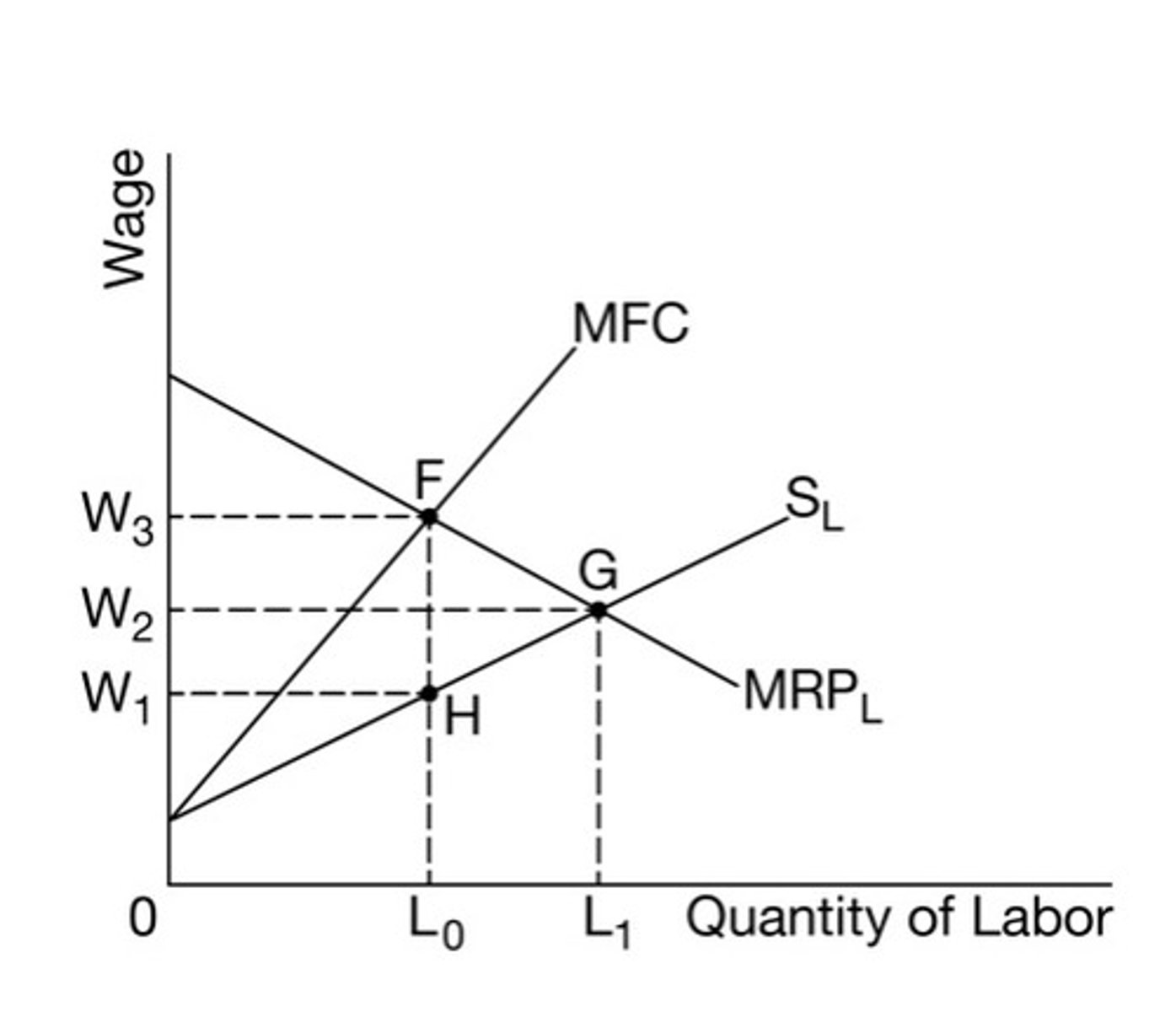
Monopsonistic market graph
least cost rule
Always buy more what gives you more MP per dollar
other names for MP
MPP
MPL
MPPL
another name for MRP
Value marginal product (VMP)
MRC
wage
MRP>MRC
keep hiring