AP Chem Unit 5 Review
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Kinetics
The study of the rates of a chemical reaction
Concentration, temperature, surface area, catalysts, volume
What factors affect reaction rate?
Ms⁻¹
Rate constant for 0th order
s⁻¹
Rate constant for 1st order
M⁻¹s⁻¹
Rate constant for 2nd order
M⁻²s⁻¹
Rate constant for 3rd order
Linear
Zero, first, and second order have ______ slopes on graphs
[A]
Y-axis for Zeroth order
ln [A]
Y-axis for First order
1/ [A]
Y-axis for Second order
Half-life
The amount of time it takes for a radioactive sample to decay to half its original amount
First order
Half-life is always _____ order
Exothermic
When reactants are higher than products it is a _____ reaction
Endothermic
When products are higher than reactants it is a ______ reaction
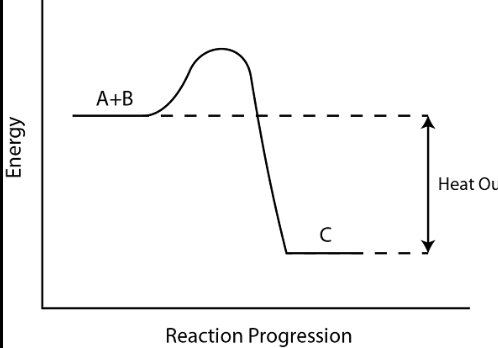
Exothermic
This is an _______ reaction
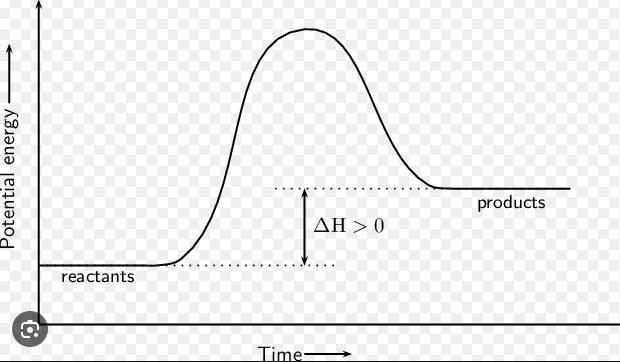
Endothermic
This is an _______ reaction
Decreases
As activation energy increases, reaction rate _______
-Molecules must collide
-Molecules must collide with sufficient energy
-Molecules must collide with correct orientation
Parts of the collision theory are ______ , ______ , _______
Speeds up a reaction
What does a catalyst do?
Beginning ; end
A catalyst is in the _____ then _____ of a reaction mechanism
End ; beginning
An intermediate is in the ______ then ______ of a reaction
SLOWEST
The rate of a reaction can never be faster than its ______ step
Highest
The slowest step has the _____ peak
Intermediates
What CANNOT show up in an overall reaction?
Reversible
When substituting use the ________ fast step
Speeds up
A catalyst ______ a reaction
Homogeneous Catalysis
A reaction in which catalysis is in the same phase as the catalyst
Heterogeneous Catalysis
A reaction in which catalysis is in a different phase as the catalyst