Physics Chapter 28 - Reflection and Refraction
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
When light reflects from a surface, there is a change in its
none of the above
3 multiple choice options
According to the law of reflection, the incident light ray, the reflected light ray, and the normal between them
lie in the same plane
Light is reflected when
incident light is returned into the medium from which it came
It is difficult to see the roadway when driving on a rainy night mainly because
the film of water on the roadway makes the road less diffuse
Your image in a plane mirror is
virtual
3 multiple choice options
The inversion of your image in a plane mirror is actually an inversion of
front-back
3 multiple choice options
Object and image for a plane mirror occur
Diffuse reflection occurs when the size of surface irregularities is
large compared to the wavelength of the light used
The shortest plane mirror in which you can see your entire image is
half your height
Light travels from one place to another along a path of least
fine
Refraction occurs when light passing from one medium to another
changes speed
When a light ray in air enters water at 15° from the normal, it
always bends toward the normal
A mirage is a result of atmospheric
refraction
Rainbows are not usually seen as complete circles because
the ground is usually in the way
Refraction causes the bottom of a swimming pool to appear
closer to the surface than it actually is
Light travels fastest in
a vacuum
The secondary rainbow is dimmer than the primary rainbow mainly because
of an extra reflection and refraction in the drops
When light passes through common windowpane, its angle of emergence is
the same as its angle of incidence
Reflection
returned into the medium from which it came
How does reflection work?
light hits a material and energizes it's electrons, the electrons release their excitement in the form of light
Fermant's Principle of Least Time
the idea that light takes the quickest path in going from one place to another
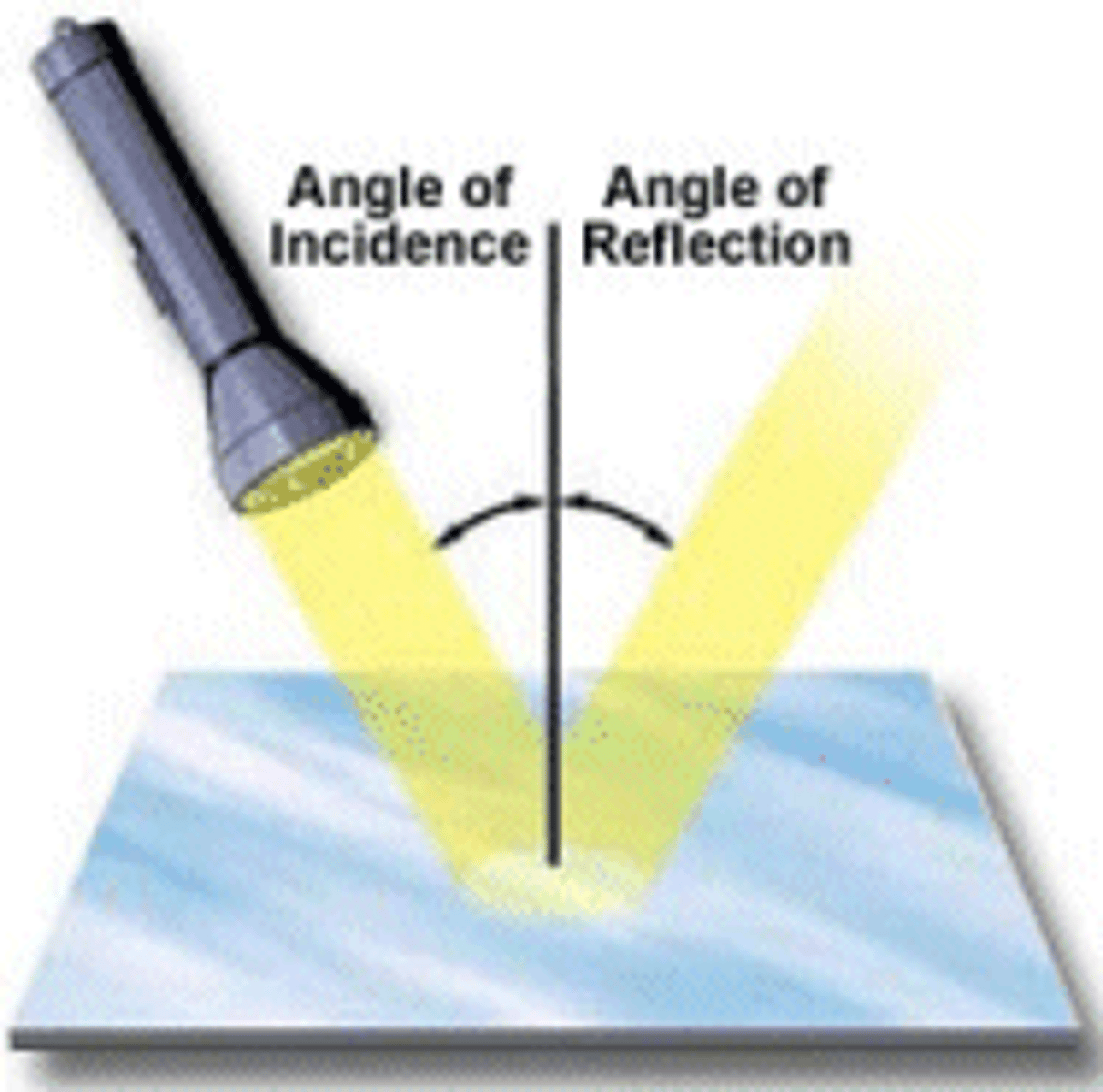
Angle of Incidence
made by the incoming ray and the perpendicular (surface)
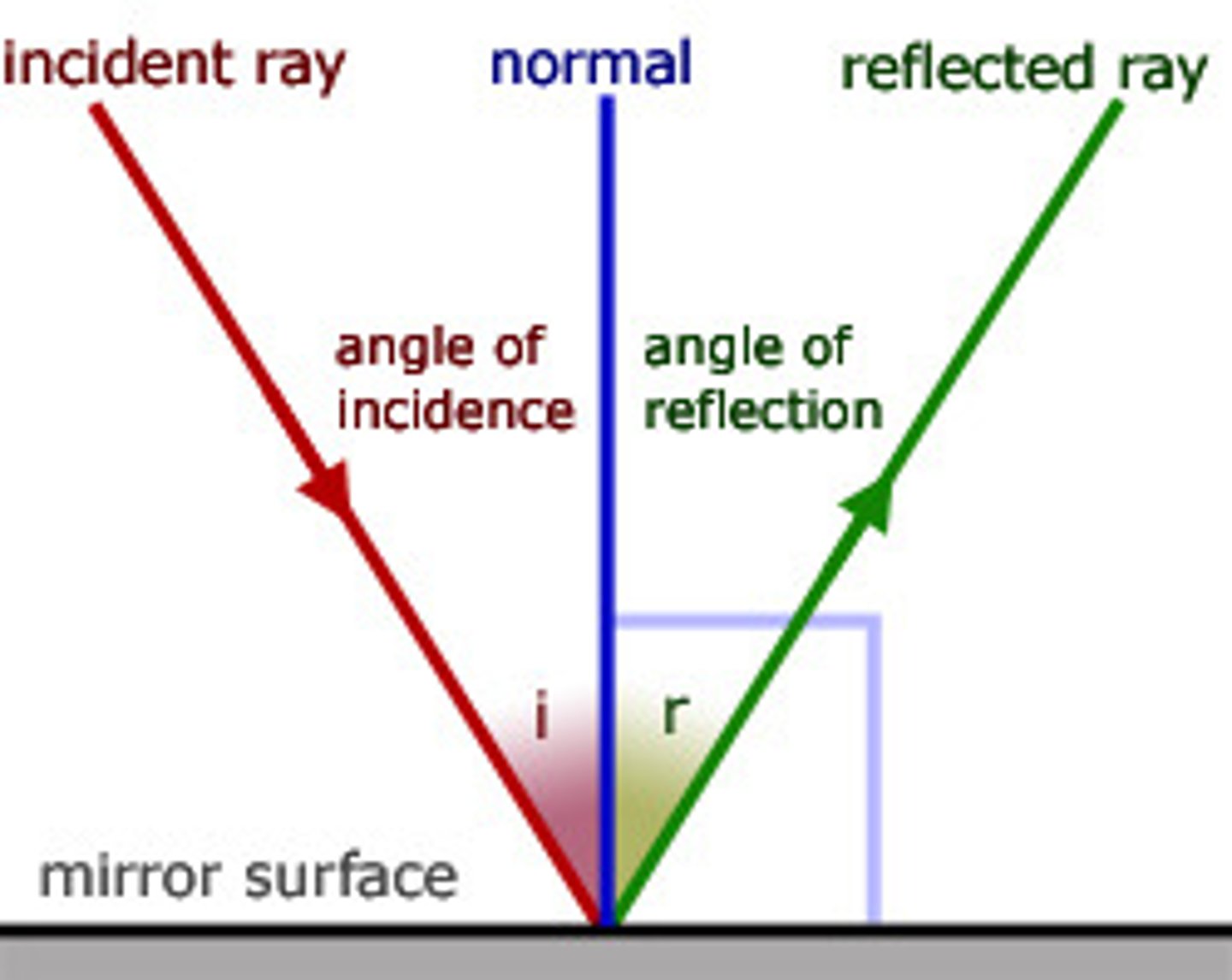
Angle of Reflection
made by the reflected ray and the perpendicular (surface)
Normal
imaginary line perpendicular to the place of the reflecting surface (lies in the same place as the incident and reflected rays)
Law of Reflection
the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence
Virtual Image
same size as an object, formed behind a mirror, and located at the position where the extended reflected rays converge is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror
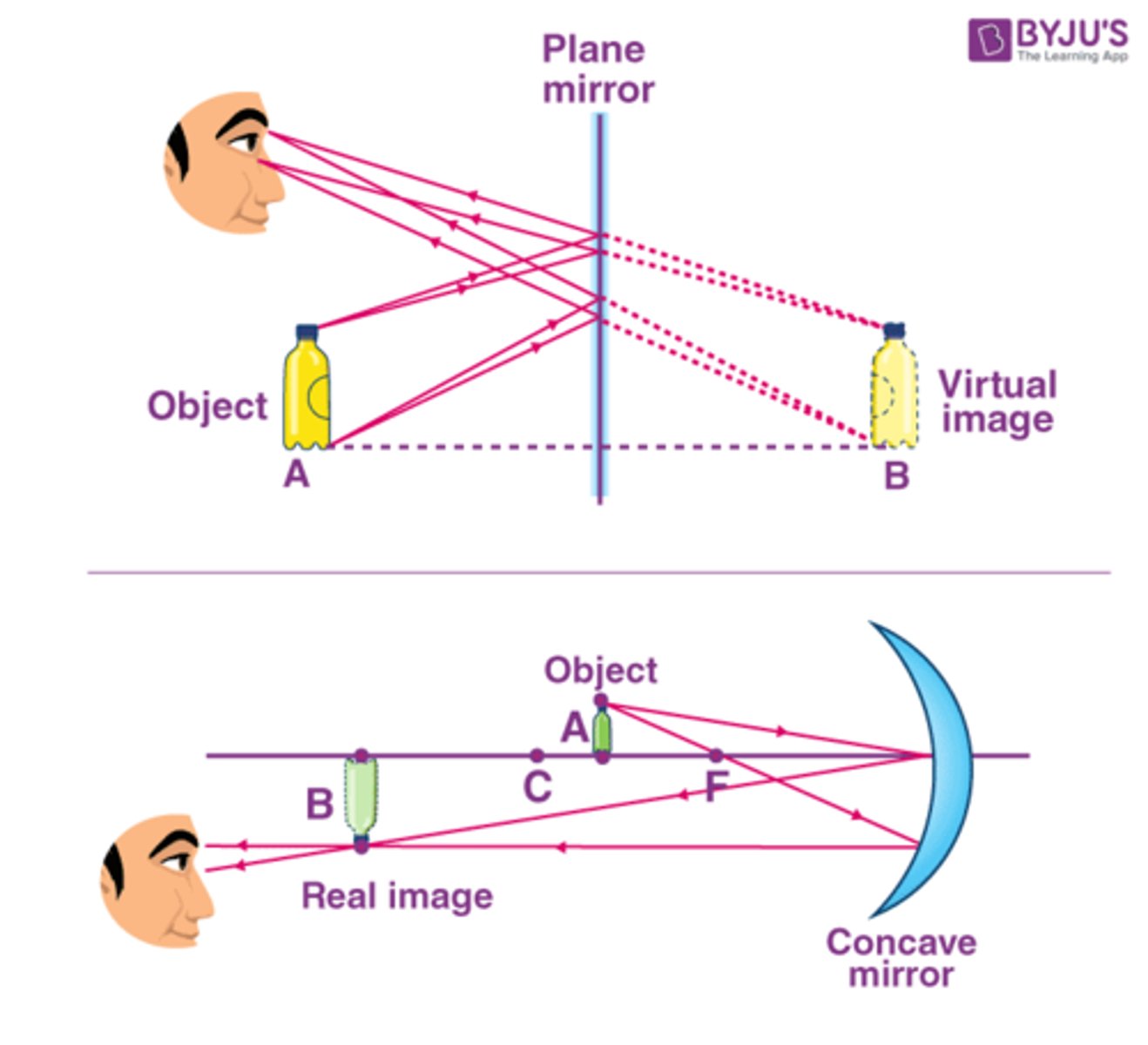
Plane Mirror
normal, regular mirror (the only axis reversed in an image is in the front-back axis)
Convex Mirror (that curves outward)
virtual image is smaller and close to the mirror than the object
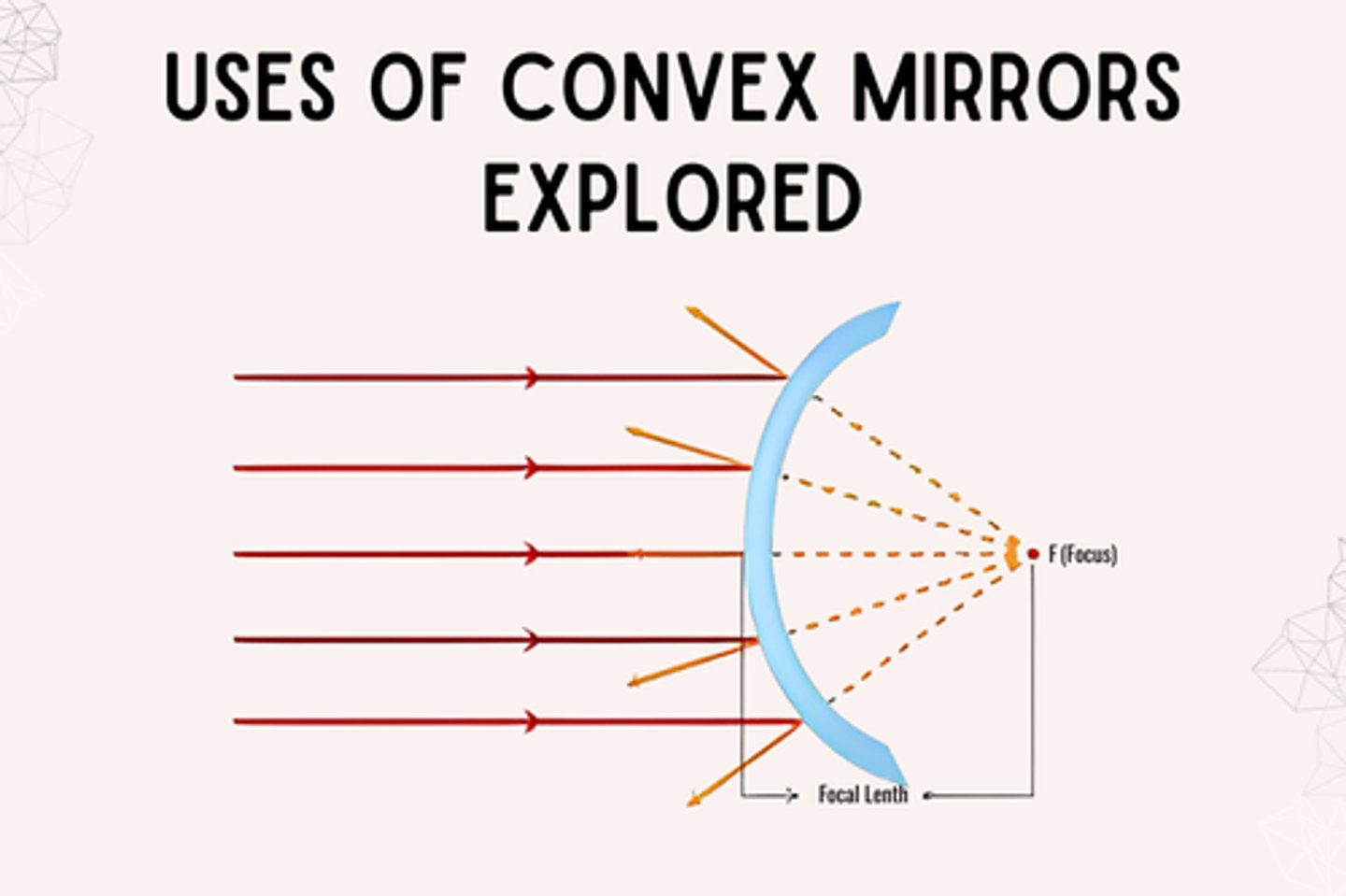
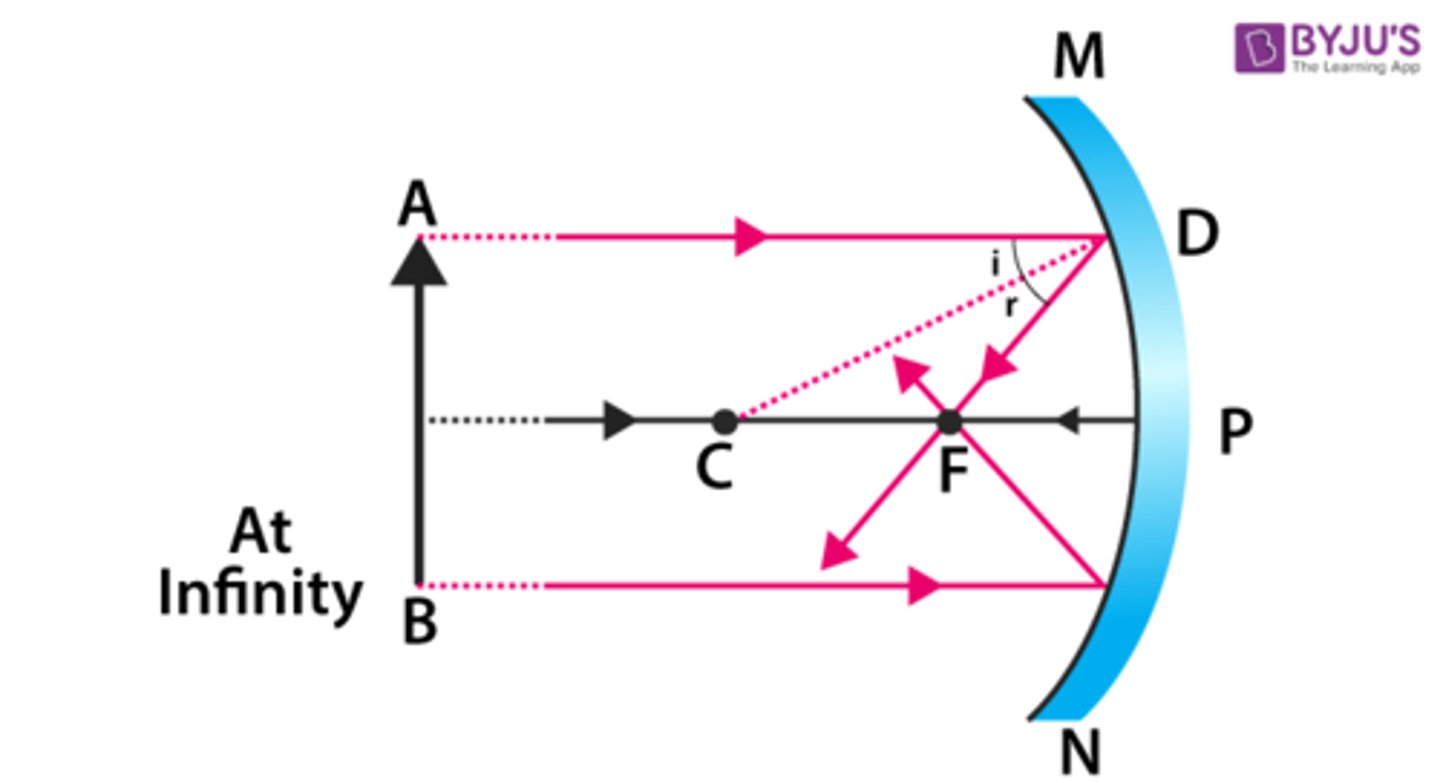
Concave Mirror (that curves inward)
virtual image is larger and farther away from the object
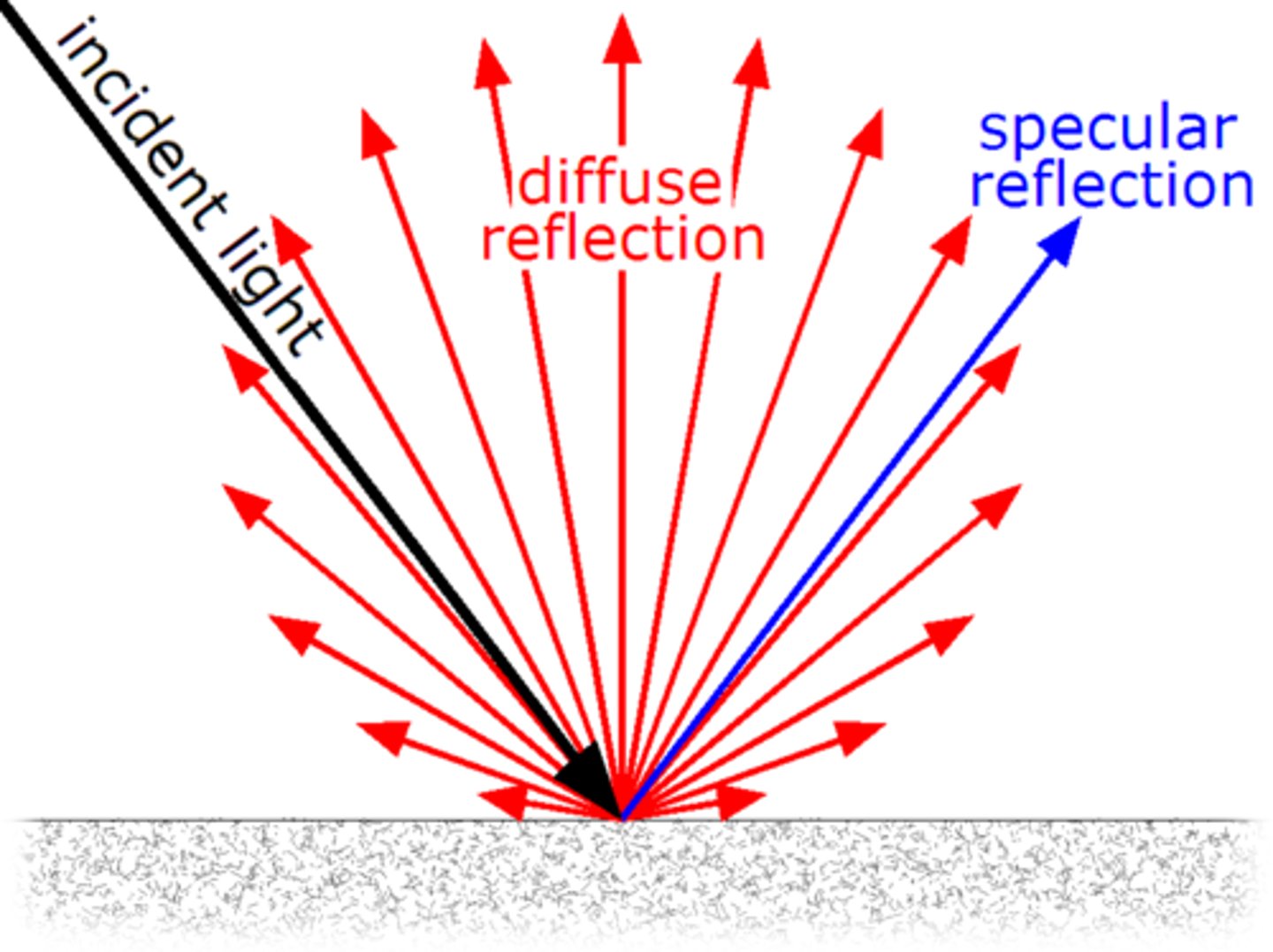
Diffuse Reflections
when light strikes a rough or irregular surface and reflects in many directions (an undesirable circumstance is the ghost image that occurs on a TV set when TV signals bounce off buildings)
Different road surfaces determine amount of
diffuse reflection
Dry Road Surface
rough because of diffuse reflection, see road ahead of car at night
Wet Road Surface
smooth because of less diffuse, reflection, difficult to see
Light bends when going in obliquely (slantwise) from
one medium to another
Refraction
bending of light when it passes from one medium to another (caused by change in speed of light)
In general, when light enters a new materials
its direction will change
Total Internal Reflection
a phenomenon that occurs when a wave, such as a light wave, traveling through a medium encounters a boundary with another medium of lower refractive index at an angle greater than the critical angle
Lower refractive indices = _______________________________
closer to the speed of light
Critical Angle
the minimum angle of which a beam of light will be internally reflected (no longer refracts into air)
Critical angles vary for
different materials
Examples of Total Internal Reflection
glass prisms, optical fibers (biomedical devices, communications, etc.)
Converging Lens (convex)
bulges out (thicker in the center than the edges) and converges light
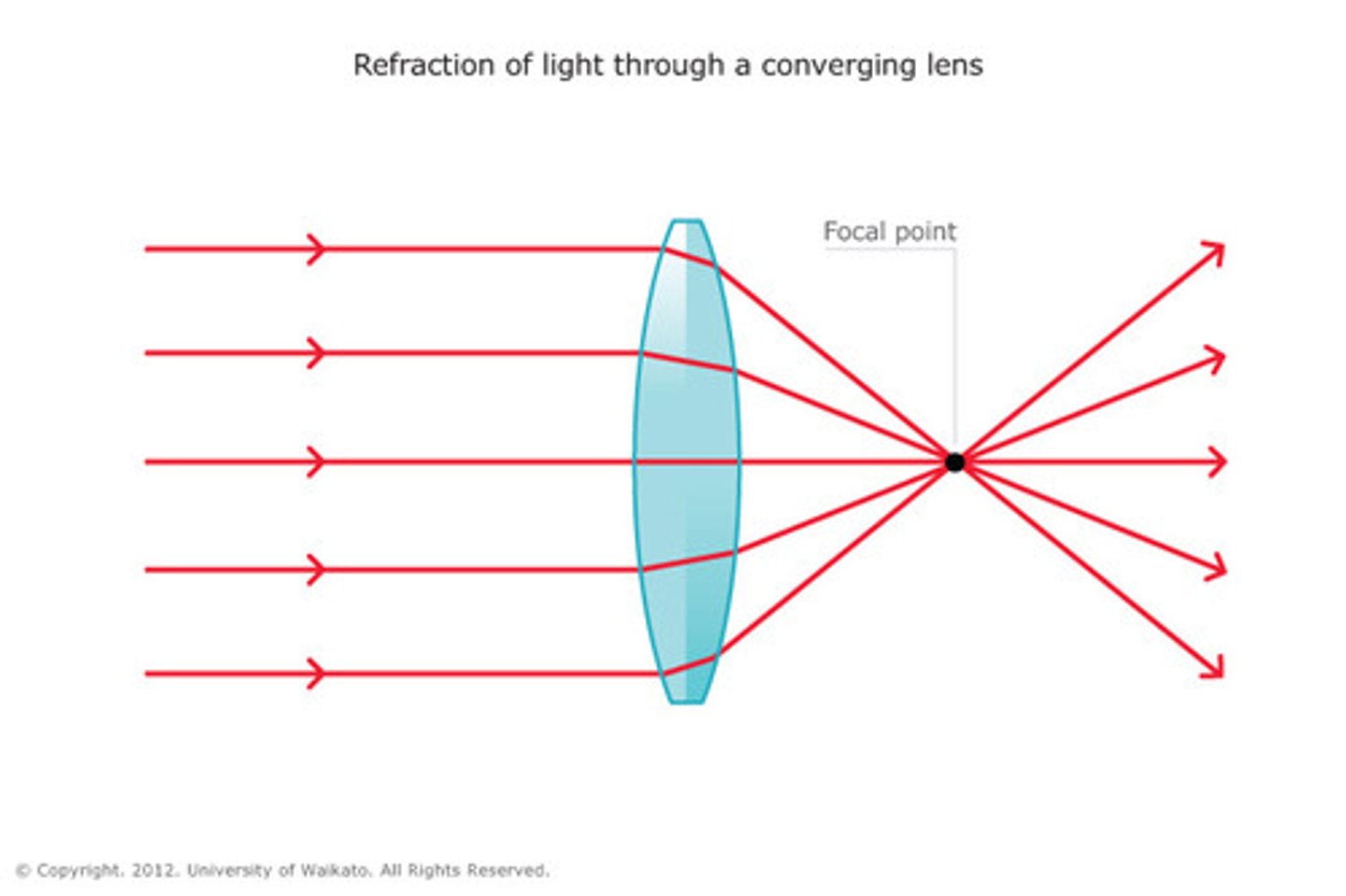
Diverging Lens (concave)
caves in (thinner in the center than the edges) and diverges lens
Principal Axis
line joining the centers of curvature of the two lens surfaces
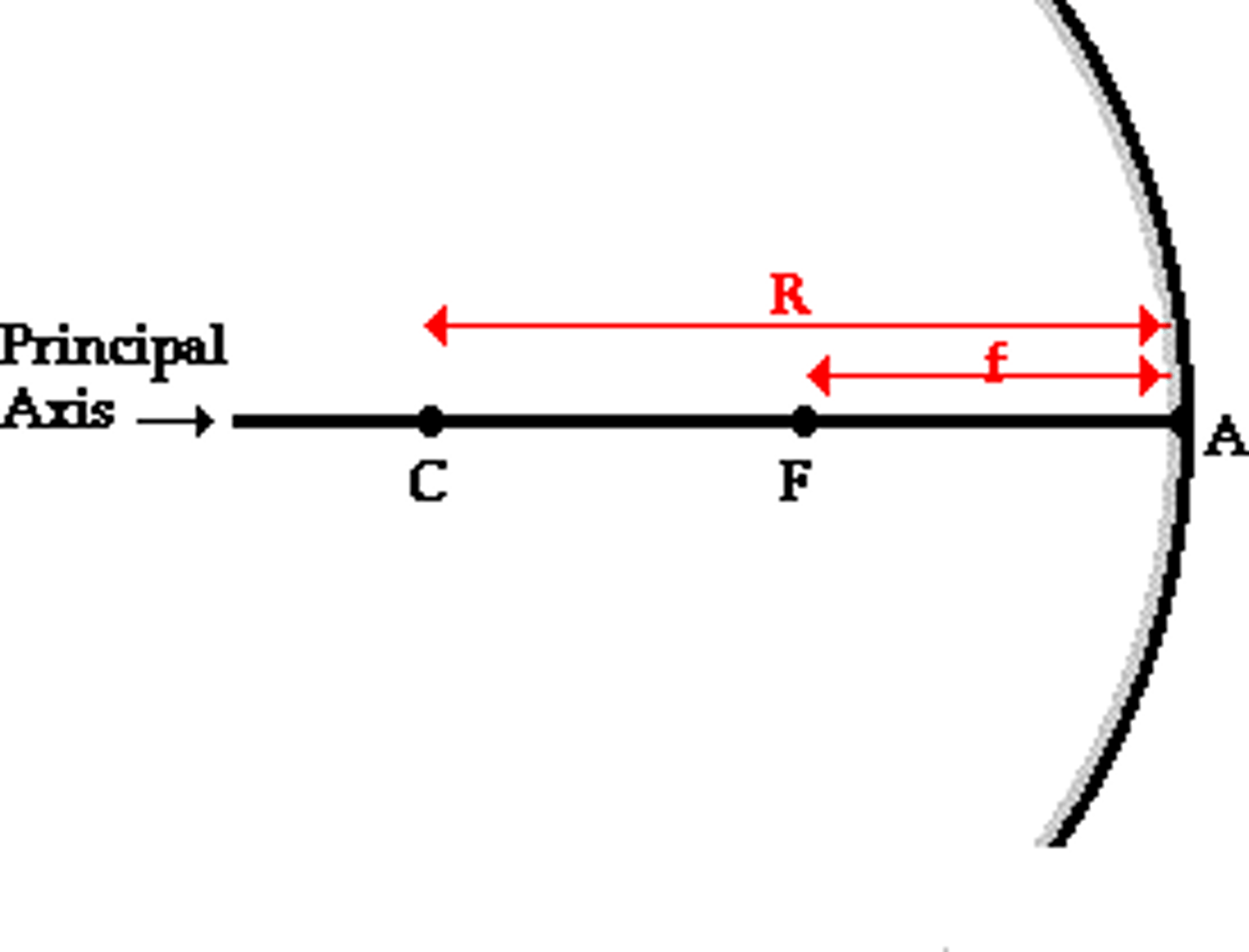
Focal Point
point at which all the light rays come together
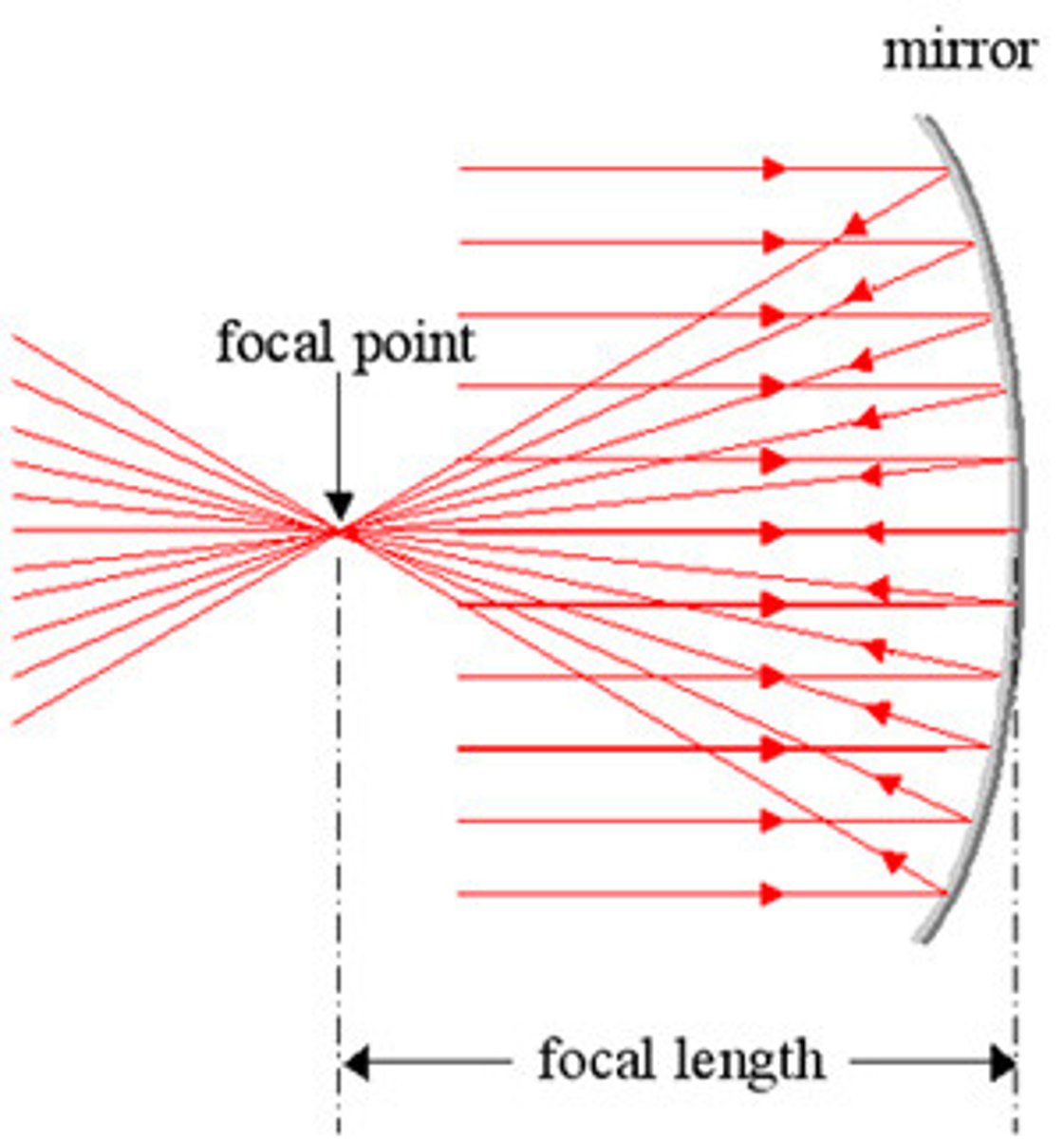
Focal Length
distance between the center of the lens and either focal point
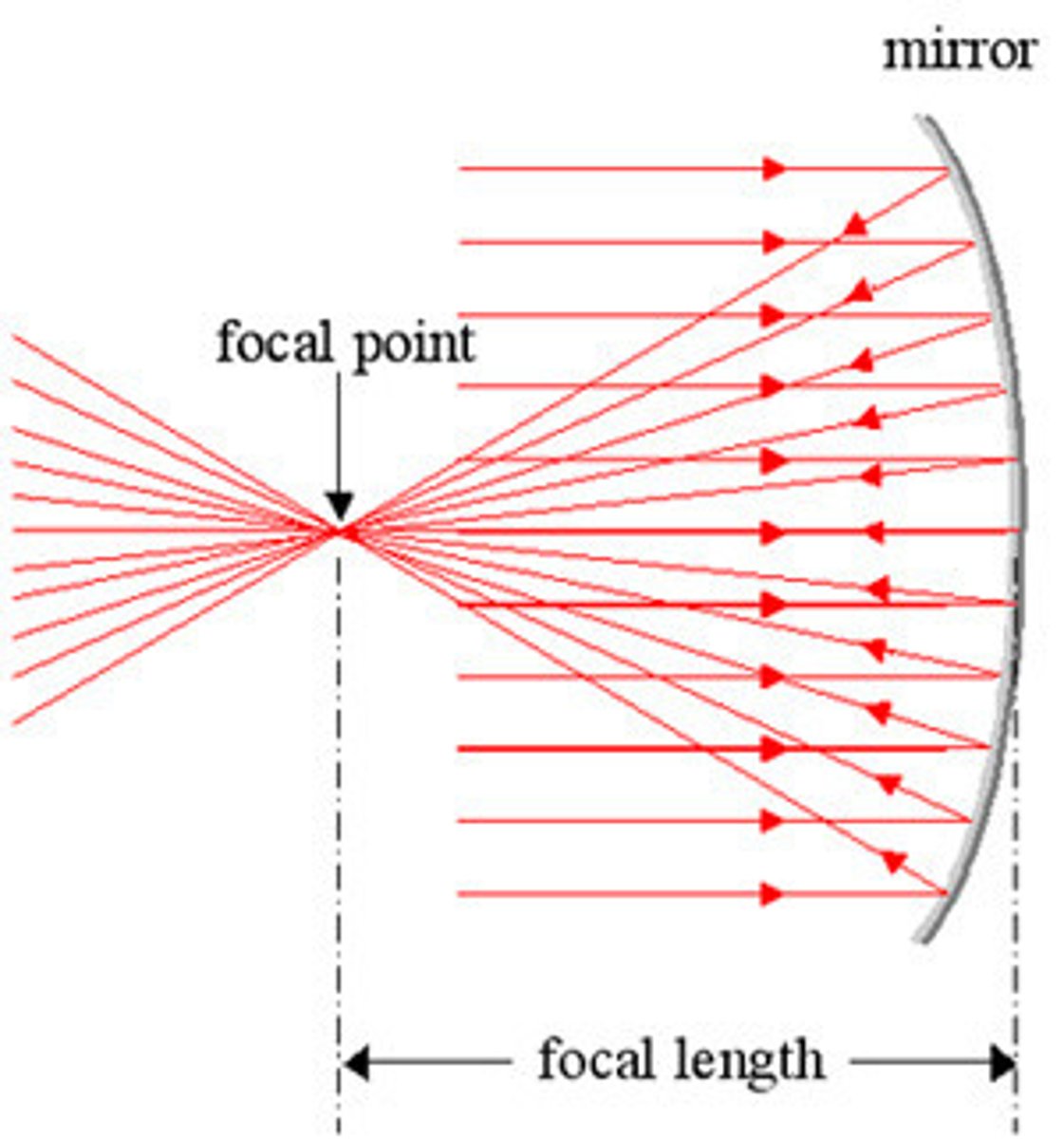
Image formation is a consequence of
light traveling in straight lines (the first camera, the pinhole camera, illustrates this fact)
A converging lens can project an
image
Real images are always
upside down