Pharm E4- Toxicology
1/144
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
Which is a constellation of specific signs and symptoms that indicate exposure to a specific toxin?
Toxidrome
What is a toxic substance produced from natural sources (ex- botox, snake venom)?
Toxin
What is the MOA of cholinergic poisoning?
Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase → too much Ach → excess nicotinic & muscarinic activation
*initially reversible but can become a permanent covalent bond → aging; takes time to produce new esterase
What are examples of organophosphates (OPs)?
Parathion, malathion, chlorpyrifos
*insectisides, really toxic
What are examples of carbamates?
Physostigmine, neostigmine, carbofuran, carbaryl
*plant sources
What are examples of nerve gasses?
Sarin, soman, tabun
*chemical / terrorist attacks
What agents cause cholinergic poisoning?
Organophosphates, carbamates, nicotine, pilocarpine, nerve gassess
Which agents that cause cholinergic poisoning cause irreversible aging?
Organophosphates (slower) & nerve gases (faster)
Which agents that cause cholinergic poisoning are reversible?
Carbamates
What is the mnemonic for muscarinic toxicity symptoms?
Defecation
Urination
Miosis
Bradycardia
Bronchorrhea
Bronchospasm
Emesis
Lacrimation
Salivation
*wet!!
What is the mnemonic for nicotinic effects?
*present first but overshadowed by muscarinic
Mydriasis
Tachycardia
Weakness
Hypertension
Fasciculations → weakness, diaphragmatic failure
What CNS effects can be seen with cholinergic toxicity?
HA, confusion, slurred speech, ataxia, delirium, psychosis, seizure
Which agent responsible for cholinergic poisoning is more lipophilic, containing hydrocarbon bases which is more likely to injure lung tissue?
Organophosphates
What is the treatment for cholinergic poisoning?
ABC’s, decontamination w/ lipid soluble compounds (mild detergent/bleach)
Antidotes: Atropine, pralidoxime
Seizures: BZDs, barbiturates, propofol
How does atropine work to treat cholinergic poisoning?
Dry pulmonary secretions → goal is clear lung exam
*just a bandaid, does not fix problem
What is the true antidote for cholinergic poisoning?
Pralidoxime → prevents covalent bond/aging, treat x 12-24 hrs post last dose of atropine
*fixes the problem
What agents cause anticholinergic toxicity?
Plants (belladonna alkaloids- scopolamine, jimson weed, angel’s trumpet), 1st gen antihistamines (cough and cold preparations), antidepressants (TCAs), 1st gen antipsychotics
What is the MOA of antimuscarinic poisoning?
Competitive blockade at postsynaptic muscarinic receptors
What is the mnemonic for anticholinergic poisoning?
Red as a beet: cutaneous vasodilation→ flushing
Mad as a hatter: CNS depression to severe psychosis / hyperexcitation, seizures at high doses
Blind as a bat: mydriasis, dec accommodation to light, blurry vision
Hot as a hare: hyperthermia
Dry as a bone: dec secretions→ dry mouth, urinary retention
Bowel & bladder lose their tone: dec motility & bowel sounds, delayed absorption
Heart runs alone: tachycardia, hypotension
Why should you listen to bowel sounds in a patient presenting with anticholinergic toxicity?
To determine if the GI tract starts back up because there may be substances in the stomach that are still not absorbed yet, so they could start to get sick again
What is the treatment for anticholinergic poisoning?
Mainstay: supportive; ABC’s, GI decontamination (charcoal)
Seizures: BZDs
Tachy: fluids & BZDs
Antidote: physostigmine (rarely used)
What drug?
acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
carbamate - reversible inhibition (no aging)
antidote for anticholinergic toxicity → indicated for refractory psychosis / seizures
stimulates muscarinic, nicotinic, & somatic receptors, affecting multiple areas
Physostigmine
What are CIs to physostigmine?
Asthma, COPD, TCA ingestions, & can cause cholinergic crisis if dose too high
*avoid unless refractory
Why should rapid administration of physostigmine be avoided?
Can cause cholinergic symptoms → bradycardia, seizures, hypersalivation
What are 3 classifications of agents that cause sympathomimetic toxicity?
Alpha agonists: PPA, phenylephrine, imadazolines
Beta agonists: albuterol, clenbuterol, theophylline/ caffeine
Mixed: epi, pseudoephedrine, ephedrine, amphetamines, PCP, MAOI, LSD, cocaine, acid
Which agents that cause sympathomimetic toxicity are direct agonists at sympathomimetic receptors?
PPA, phenylephrine, epinephrine
Which agents that cause sympathomimetic toxicity do so by increasing release of endogenous catecholamines?
Cocaine, amphetamines
Which agents that cause sympathomimetic toxicity block reuptake/ inhibit metabolism?
MAOIs, antidepressants
What symptoms are seen with alpha stimulation?
Mydriasis, arterial vasoconstriction, diaphoresis, platelet aggregation (clots, strokes, MI) → hypertension w/ normal or decreased heart rate
What symptoms are seen with Beta 1 stimulation?
Increased inotropy & chronotropy → tachycardia +/- BP effects
What symptoms are seen with beta 2 stimulation?
Smooth muscle relaxation in lungs & arteries, arterial vasodilation hypokalemia (ex: clenbuterol - shifts too much K inside cell) → tachycardia with hypotension
What agent that causes sympathomimetic toxicity is a mixed agonist that causes alpha and beta effects?
Theophylline
Anticholinergic or sympathomimetic toxicity?
disorientation
agitation
mydriasis
hyperthermia
moist mucous membranes & skin
increased intestinal motility
Sympathomimetic
Anticholinergic or sympathomimetic toxicity?
disorientation
agitation
mydriasis
hyperthermia
urinary retention
dry mucous membranes & skin
decreased intestinal motility
Anticholinergic
What is the treatment for sympathomimetic toxicity?
Supportive: ABCs, GI decontamination (depends on route), place in calm/ cool environment, evaporative cooling & icepacks
BZDs for HTN, tachy, agitation, seizures
Short acting CV agents: emolol + nitroprusside
Why should a BB never be given alone to a sympathomimetic overdose such as cocaine?
Unopposed alpha stimulation / squeeze which inc BP → give with antihypertensive (ex- esmolol + nitroprusside)
What term refers to naturally occurring alkaloids (ex- morphine & codeine derived from papaver somniferum)?
Opiate
What term refers to all non-natural substances w/ opiate like effects (ex- fentanyl, tramadol, buprenorphine)?
Opioid
What is the order from fastest onset to slowest onset for opioid intake routes?
Inhaled > IV > oral
Which has a shorter DOA, morphine or methadone?
Morphine
The following clinical presentation is associated with what toxicity?
CNS: analgesia, sedation, euphoria, dysphoria
Miosis
Pulm edema, respiratory depression (turns off brainstems response to CO2 → stop breathing)
Bradycardia, hypotension
Decreased bowel motility, N, V
Hypothermia
Opioids
What 2 agents slow down the GI tract?
Opioids & anticholinergics
What agents that cause opioid poisoning inhibit serotonin uptake?
Meperidine, dextromethorphan, tramadol
What agents that cause opioid toxicity may induce seizures?
Propoxyphene, meperidine, tramadol
What agent is a partial opioid agonist that may cause an atypical presentation in toxicity?
Buprenorphine
Which agents are detected on a UDS?
THC, cocaine, amphetamines, PCP, BZD, barbiturates
Opioids: heroin, morphine, hydrocodone, codeine
*opioids not detected: low concentrations of oxycodone, fentanyl, tramadol
What is the treatment for opioid toxicity?
ABCs, GI decontamination, naloxone
What is the best way to determine if opioids are the reason for a patient presenting with a toxidrome?
Trial naloxone & see if they respond
*if you get up to 10 mg w/ no response → different cause
How should naloxone be given?
Too much can cause withdrawal so give just enough to get them breathing to blow off CO2 / arouse to voice (sweet spot → yawning)
DOA 20-90 min, call 911 after given or give continuous drip
What agents are sedatives / hypnotics?
BZDs: alprazolam, midazolam, lorazepam
Barbiturates: butalbital, phenobarbital
Muscle relaxants: Cyclobenzaprine, carisoprodol, baclofen
Misc: ethanol, chloral hydrate, GHB
What is the MOA of sedative / hypnotive toxicity?
Activate GABA receptor → increase Cl influx → inhibit APs → depresses CNS function
The following clinical presentation is associated with which toxidrome?
CNS: depressed mentation, nystagmus, ataxia
Respiratory depression
depends on agent; BZDs alone rarely cause
Hypotension (barbiturates)
Decreased GI motility
Some have anticholinergic SEs (carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine)
Sedatives / hypnotics
What is the treatment for sedative / hypnotic overdose?
ABCs
Hypotension: fluids & pressers (NE preferred for alpha squeeze, not as much on heart)
What is the antidote for an accidental exposure to BZDs?
*do NOT use in chronic BZD use → withdrawal seizures, deadly
Flumazenil
What should be given in addition for treatment of sedative toxicity if due to phenobarbital?
Sodium bicarbonate for urinary alkalinization (spills in urine to metabolize faster) or multi-dose charcoal
What differentiates opiate withdrawal from sedative / hypnotic withdrawal?
*both have anxiety, agitation, irritability, GI hyperactivity, tachycardia, HTN
Withdrawal seizures occur with sedatives, not opiates
Which agents cause bradycardia?
Cholinergics, clonidine (dec NE release), non-DHP CCBs, BBs, digoxin (+ xanthopsia)
What agents cause tachycardia?
Sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, theophylline, iron, salicylates, antihistamines, neuroleptics
Which agents cause hypotension?
Clonidine, CCBs, TCAs, sedatives / hypnotics, iron, salicylates, digoxin, significant acidosis (NE cant bind as well)
What agents cause HTN?
Sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, nicotine, caffeine, thyroid supplements (levothyroxine abused for weight loss)
What agents cause hypothermia?
Opioids, hypoglycemics, carbon monoxide (generators / cars in garage, house fires), sedatives / hypnotics (unconscious, not physically active for long periods)
What agents cause hyperthermia?
Anticholinergics, sympathomimetics, salicylates, phenothiazines, antidepressants, thyroid preparations
What agents cause bradypnea?
Clonidine, opioids, sedatives/ hypnotics
What agents cause tachypnea?
Salicylates (early sign of poisoning), cyanide (house fires burning synthetic fibers, apples / peach pits), irritant gasses (chemical cleaners, bleach + cat urine / ammonia → chlorine gas)
What agents cause miosis?
Cholinergics, clonidine, opiates, sedatives/ hypnotics
What agents cause mydriasis?
Anticholinergics, antidepressants, sympathomimetics, phenothiazines
What agents cause diaphoresis?
Sympathomimemtics, OPs, salicylates
What agents cause bullae (pressure ulcer / blister filled with fluid from being down for long period)?
Barbiturates, carbon monoxide
What agents cause dry mucous membranes?
Anticholinergics
What agents cause flushed skin?
Anticholinergics, carbon monoxide, cyanide, boric acid (roach tablets, certain cleansers)
What smell would indicate cyanide?
Bitter almonds
What smell would indicate water hemlock?
Carrots
What smell would indicate arsenic or pesticides?
Garlic
What smell would indicate camphor?
Mothballs
What smell would indicate chloral hydrate?
Pears
What smell would indicate methyl salicylate?
Wintergreen
What smell would indicate hydrogen sulfide (or anything with sulfur)?
Rotten eggs
What agents cause a wide anion gap (> 16)?
Methanol- windshield wiper fluid
Uremia - check BMP
DKA
Paraldehyde
Isoniazid, iron
Lactic acidosis
Ethylene glycol- radiator fluid, sweet
Salicylates
Less common: cyanide, CO, alcoholic ketoacidosis, toluene (paint thinner)
What agents are radiopaque on imaging?
Chloral hydrate, heavy metals / lead, iron, phenothiazines, enteric coated product, salts (potassium)
How should areas exposed to fat soluble or oil based products be flushed?
Water with soap / mild detergent, diluted bleach solns
How do you perform ocular decontamination?
Remove contacts & use Morgan lenses connected to IV line for continuous saline flushing (or use nasal cannula if unavailable), irrigate atleast 15-30 min
*end goal → normal lacrimal pH 7.2
What decontamination agent that stimulates chemoreceptor trigger zone to initiate emesis was removed from the market d/t being ineffective, aspiration risk & causing cardiomypothay in bulimic patients?
Ipecac
How is gastric lavage performed?
Used for life threatening ingestion w/in 1 hr → left lateral decubitus position, tap water or saline instilled into stomach via NG tube & removed by gravity / suction
What are CIs to gastric lavage?
Aspiration risk, FB ingestion, toxin that is bigger than lovage tube hole, corrosive or hydrocarbon ingestions (burns)
complications → aspiration, esophageal perforation d/t corrosive ingestion (draino)
What is the time frame for activated charcoal?
Within 1 hour of ingestion
*2 hours if opioids or anticholinergics
What agents does activated charcoal (AC) NOT bind to?
Alcohol, heavy metals, iron, lithium, hydrocarbons (lighter fluid, gas from car)
What are CIs to AC?
Aspiration (make sure pt is upright & lucid), intestinal obstruction, corrosive ingestion
How is whole bowel irrigation performed?
Flush 500ml - 2L/hr of polyethylene glycol to force through tract more quickly (given through NG tube d/t bad taste) → end goal is clear recall effluent
*must confirm placement of tube in stomach w/ stethoscope (blow air & hear bubbles) to prevent aspiration
What agents would whole bowel decontamination be good for?
Heavy metals, concretions / bezoars, body packers (smuggling drugs, more well wrapped & less likely to come up in tract), body stuffers (dealing on streets & swallows drugs to hide from cops, not well wrapped, more likely to be exposed)
What toxic byproduct of APAP toxicity forms covalent bonds that causes cell death and free radical production (usually neutralized by glutathione / GSH but dangerous when stores run out)?
NAPQI
What patients are predisposed to APAP toxicity?
Inc frequency of dosing for chronic pain, prolonged use of excessive doses, chronic alcoholics w/ liver impairment, induction of CYP2E1, decrease GSH (less substrate to process APAP)
Which stage of APAP toxicity?
may be asx
no hepatic injury
N/V, malaise, pallor, diaphoresis
dec LOC & metabolic acidosis if massive ingestion
Stage 1 - 0-24 hrs
Which stage of APAP toxicity?
Transaminase elevations
Inc AST/ALT w/ actual damage to cells, but doesn’t tell you how well liver is actually functioning
Inc PT/INR, bilirubin, lactate
PT/INR better indication of liver function - not producing clotting factors (bad sign)
Stage 2 - 24-36 hrs
Which stage of APAP toxicity?
Further elevation of transaminases
if PT/INR still inc but ALT/AST dec → no enzymes left
jaundice, hepatic encephalopathy, renal failure
metabolic acidosis
death from hepatic failure: 3-5 days
Stage 3 - 72-96 hrs
Which stage of APAP toxicity?
recovery phase
weeks-months for complete resolution
rare but some may need liver transplant
Stage 4
What are the toxic levels of APAP?
Adults: 7.5 g
Kids: 150-200 mg/kg
Know the APAP nomogram
**Test Q
above line → treat; below line → do nothing
wait until 4 hrs after ingestion to draw levels
single one time ingestion only, not for chronic use**
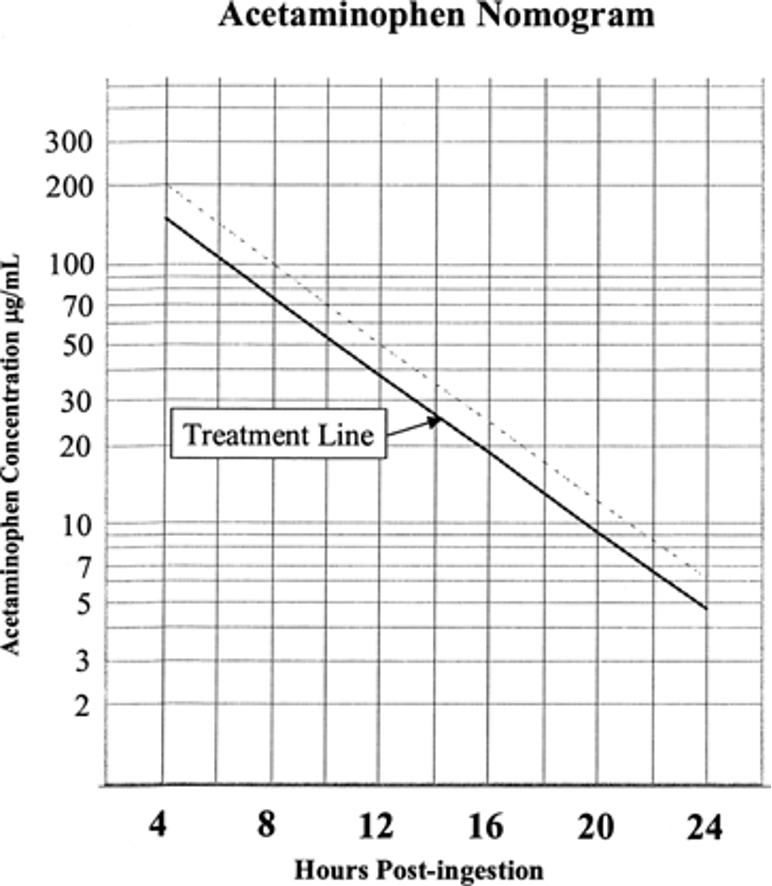
What is the treatment for APAP toxicity?
ABCs (co-ingestion), AC if appropriate (w/in 1 hr, conscious, tolerate PO), tx hypoglycemia, Vit K or blood products if coagulopathy, transplant (rare)
Antidote: n-acetylcysteine
What drug?
APAP antidote → replaces substrates in all 3 pathways that handles APAP
Substrates & precursor for GSH, donates sulfhydryl groups
smells like rotten eggs (sulfur)
IV: Acetadote- expensive; use if suicidal or noncompliant
PO: mucomyst- cheaper; mix w/ sprite & use straw/ cover to mask bad smell/ taste
stop when LFTs recovering, APAP is undetected, & PT/INR is normal
N-acteylcysteine
What is the timeframe from ingestion that N-acetylcysteine is 100% effective (pt won’t die)?
*still effective after by scavenging free radicals & limiting damage
8 hours