States of matter
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is plasma?
How does it differ from a gas (3)?
An ionised gas, consisting of free electrons and ions
conducts electricity
affected by magnetic fields
requires significant energy to form under terrestrial conditions
What are liquid crystals?
How does it compare to other states of matter?
How does it react to applied fields?
Fluid with a small degree of solid-like order
flows like a liquid but with optical properties of a solid
typically responsible to applied fields e.g. electrical/magnetic
What is a phase transition?
A transformation of a substance from one state of matter to another, in response to changes in its environment e.g. temperature or pressure
What is fusion another word for?
Melting
What is solidification another word for?
Freezing
What is vaporisation another word for?
Boiling / evaporating
Energy in endothermic processes?
Name 3 endothermic processes
Energy absorbed to overcome IMF
melting, vaporisation, sublimation
Energy in exothermic processes?
Name 3 exothermic processes
Energy is released as IMF form
freezing, condensation, deposition (gas to solid)
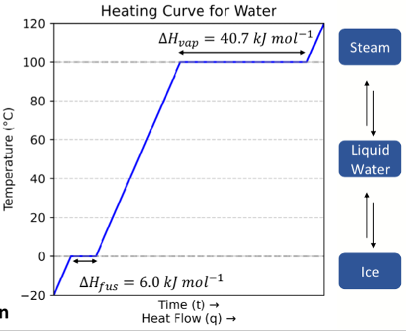
Heating curve
What is the equation?
What does the slope represent?
What happens at a phase transition?
q=mCΔT
Slope is heat capacity
At a phase transition, temperature is constant (gradient is zero), input energy is used to overcome IMF
there is a mixture of both phases
What systems does the Lennard-Jones Potential model not work for?
It only works for non polar systems
more complex interactions lead to complex phase behaviour
What is on the axes of a phase diagram?
Pressure vs temperature
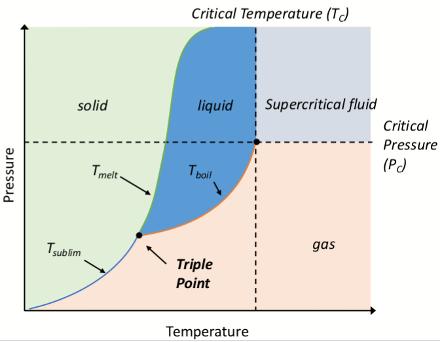
What is the triple point on a phase diagram?
When solid, liquid, and gas phases coexist in equilibrium
the only set of conditions under which phases are equally stable
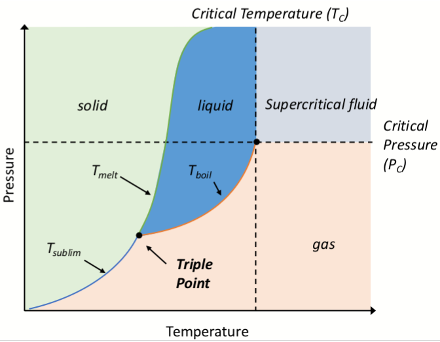
What is the critical temperature Tc on a phase diagram?
The highest temperature at which a substance can exist as liquid, regardless of pressure
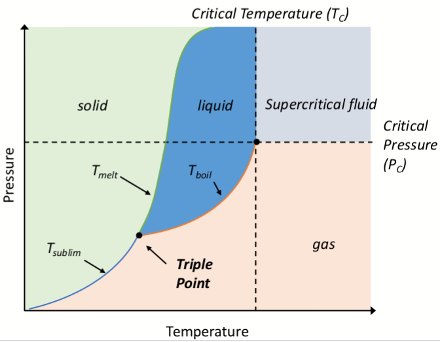
What is the critical pressure Pc on a phase diagram?
The pressure required to liquefy a gas at the critical temperature
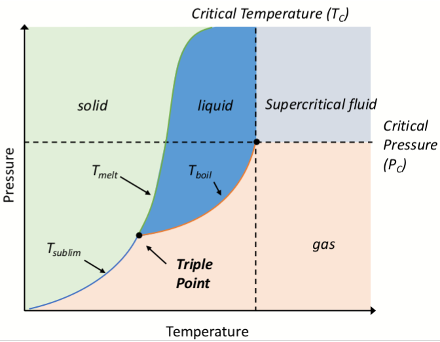
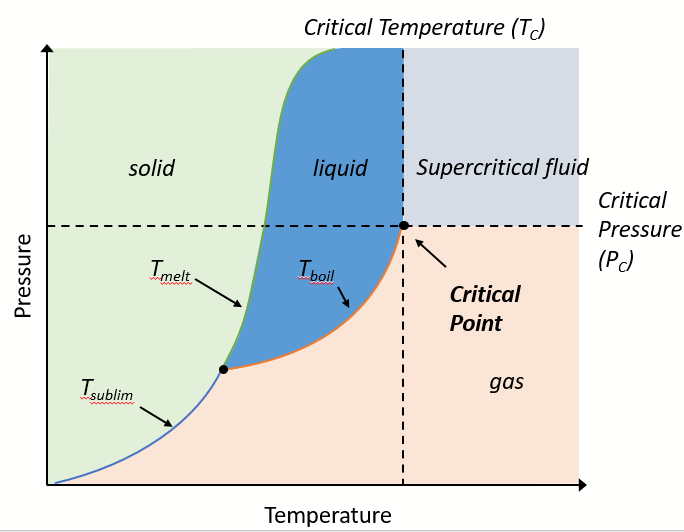
What is the critical point?
The highest temperature and pressure at which a liquid and gas can coexist
Supercritical fluids
viscosity?
density?
solvation power?
Low viscosity of a gas, high density of a liquid
Can have good solvation power for small molecules and polymers (can be dissolved)
How to change solvent properties of supercritical fluid?
What does this enable?
By varying pressure and temperatures near the critical point
this enables selective extraction of specific compounds
Advantages of supercritical CO2?
abundant / inexpensive (waste product)
nonflammable, nontoxic
easily removed, captured and reused
low critical pressure and temperatures
What are the 3 assumptions the ideal gas law makes?
gas molecules/atoms have no volume
no IMF between molecules/atoms
perfectly elastic collisions
What is Z, what does it represent?
The compressibility factor
For an ideal gas, Z = 1
For a real gas, Z<1 at low pressure and Z>1 at high pressure
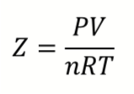
Why does Z change for real gases with pressure?
Attractive forces dominate at low pressure
Repulsive forces dominate at high pressure
What is van der Waals equation?
a = magnitude of attractive IMF
b = effective (excluded) vol of gas molecules/atoms
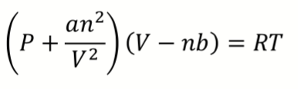
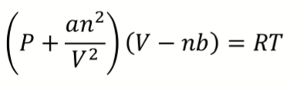
What happens to van der Waals equation when V is larger?
both terms become negligible
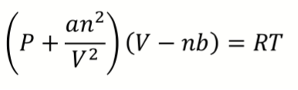
What does n2/V2 represent in van der Waals equation? How does it change with pressure (number of molecules per volume)?
Represents the probability of molecules interacting = increases with the number of molecules per volume
What happens to Gibbs free energy of two phases at a phase transition?
The Gibbs free energy is equal
What is the Clapeyron equation? What does it show?
It quantifies how pressure and temperature change along a phase boundary
calculates slope of phase boundary
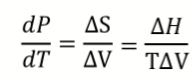
What is Clausius-Clapeyron equation? What does it apply to?
Only applies to vaporisation and sublimation
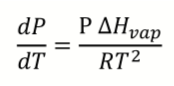
When solute is added to system of two immiscible liquids, what happens?
Distributed between two liquid phases
depends on solubility of solute in each solvent
What is the partition coefficient, KD?
The equilibrium distribution of the solute between two phases
Corg is conc of solute in organic phase
Caq is conc of solute in aqueous phase
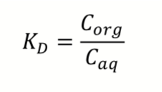
How to calculate mass balance of single extraction step of liquid liquid extraction (when volume is equal)?
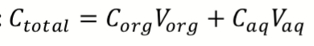
Why are repeated extractions useful in liquid-liquid extraction?
Some material usually remains in the aqueous phase after the first extraction
more material isolated after each extraction