Pharmacology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
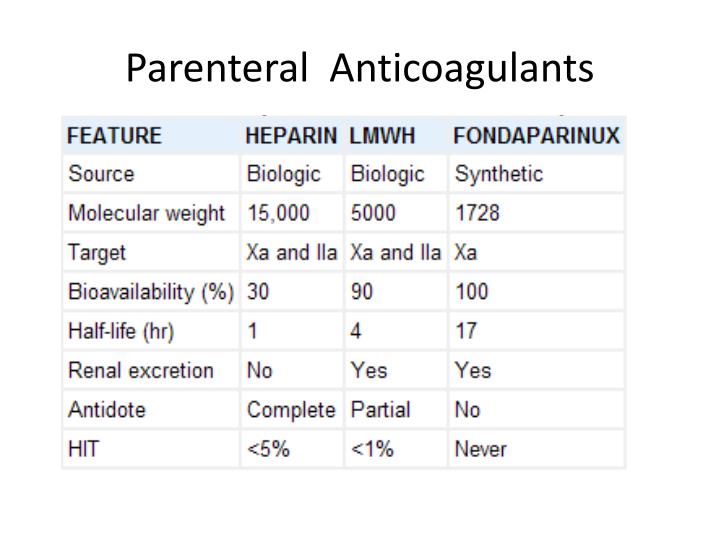
parenteral anticoagulant
unfractionated heparin (indirect)
LMWheparin (Indirect)
fondaparinux (Indirect)
bivalirudin (direct)
oral anticoagulant
warfarin
dabigatran
rivaroxaban
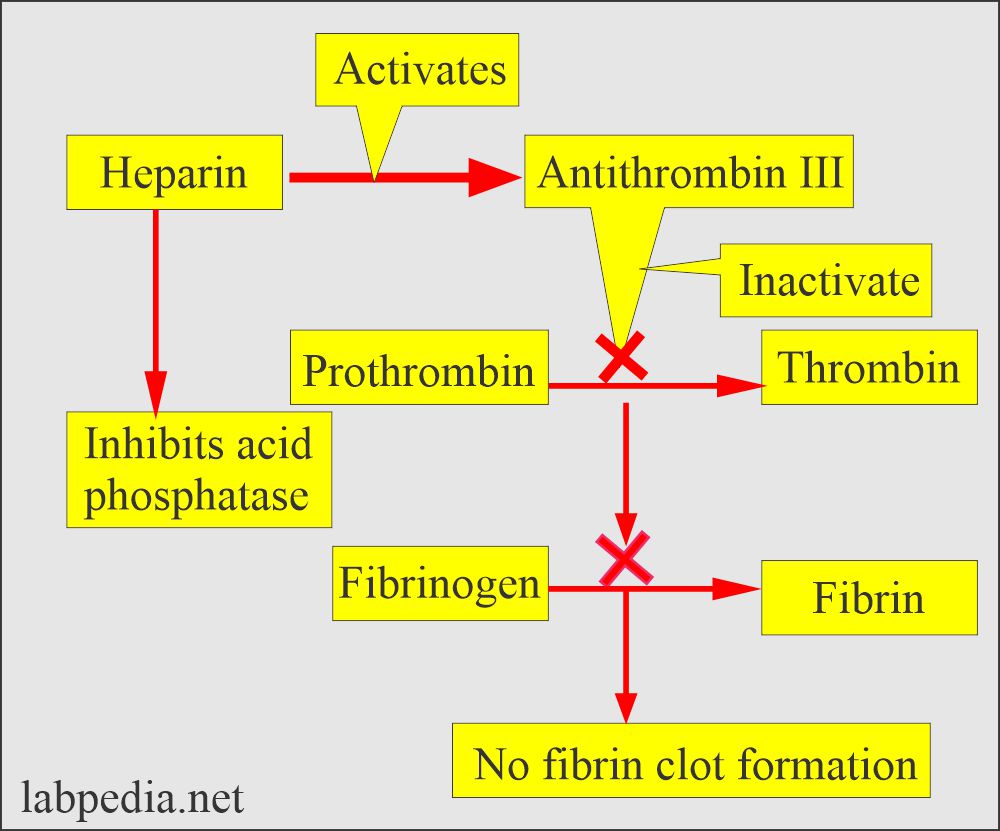
unfractionated heparin
parentral
high bound to plasma proteins
low bioavailabiliy
rapid
short half life
no need for dose adjustment in renal failure
safe during pregnancy and lactation
antidote: protamine sulfate
mechanism of action:
bind to antithrombin3
inhibit factors 2,10,11,12,13
inhibit free thrombin only
monitor by aPTT, CT
adverse effects of heparin
bleeding
re thrombosis
HITT
osteoprosis
cutaneous necrosis
hyprekalemia
LMWH
enoxaparin
bind more to factor Xa than to thrombin
can be given outside the hospital
no need for regular monitoring
adjusted in renal insufficiency and obesity
longer duration of action
less tendency to develop bleeding and HITT

factor Xa inhibitors
used as subsitiuation for heparin in patients with HITT
not improved during pregnacy
no need for regular monitring
need adjustment in renal impairment
indirect: fondaparinox:
parentral IV or SC, good bioavalibility, long half life
direct: revaroxaban:
oral, once or twice daily, metabolized by CYP3A4, antidote: andexanet
direct thrombin inhibitors
used instead of heparin in patients with HITT
not approved during pregnancy
avoided in severe renal impairment
no need for regular monitoring
inhibit free or fibrin bound thrombin
parentral: bivalirudin
cardiac intervention, eliminated by kidney and liver
oral: dabigatran
pro drug, renally excreted, antidote: idarucizumab
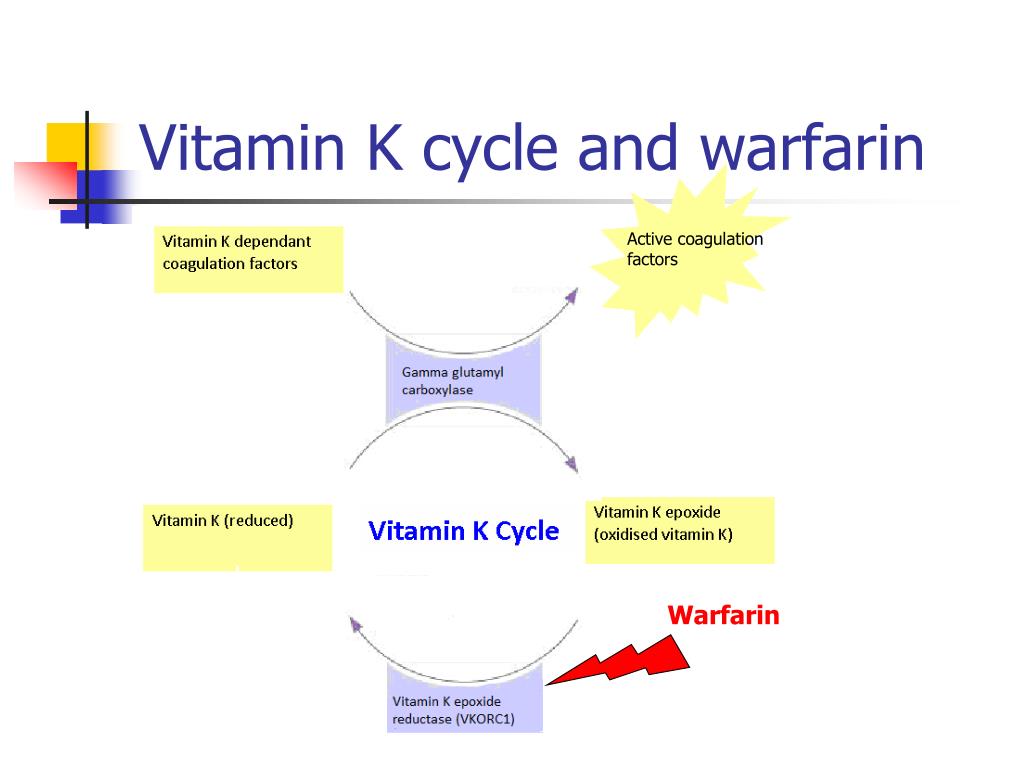
warfarin
high bioavailability
high bound to plasma proteins
onset of action 72 hours
metabolized by cytp450
teratogenic
inhibit vit k reductase enzyme
need bridging time with parentral anticoagulant
monitored by PT, INR
adverse effect of warfarin
bleeding (fresh frozen plasma)
teratogenic
skin necrosis (rare)
vit k to reverse its effect, it take 6 to 12 hours
drugs cause warfarin toxicity
broad spectrum antibiotics
cytp450 inhibitors: clarithromycin
aspirin (bound to plasma proteins)
drugs decrease efficacy of warfarin
vit k
cholestyramine decrease absorption
cytp450 inducers: carbamazepine
estrogen, oral contraceptive increase synthesis of vit k
thromboxane A2 inhibitors
ASA, aspirin
iriivrsible cox1 inhibitor
its inhibition sustained throughout life span of the platelet
small dose of aspirin will not suppress prostacyclin (325 mg)
in acute conditions (ACS, stroke) use chewable forms
DAPT with ADP antagonist for secondary prevention
long term use cause peptic ulcers, use enteric coated aspirin
use with ibuprofen result in aspirin resistence
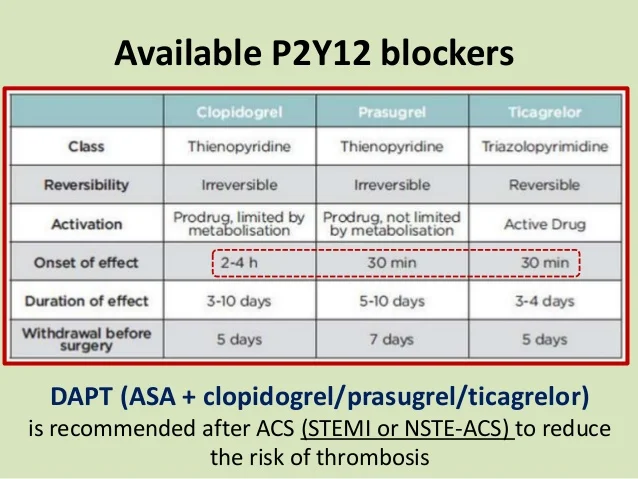
ADP receptors antagonists
clopidogrel, ticagrelor (clop, tic)
antagonists to ADP receptors subtype (P2Y12)
clop: irreversible, prodrug, give loading dose, DAPT
tic: active, reversible, vasodilating, faster, induse dyspnea
glycoprotein 2b 3a receptors antagonist
tirofiban
reversible, competitve inhibitor of GP 2b3a receptors
inhibit final common step in thrombus formation
IV infusion, during and after PCI
must be adjusted in renal insufficiency
protease activated receptor 1 antagonist
vorapaxar
oral, selective antagonist
indicated in myocardiac infarction and during cardiac intervention
PAR1 is platelet thrombin receptor
fibrinolytic drugs
cleave plasminogin ino plasmin, hydrolyse fibrin
recently formed thrombus within 6/12 hours
fibrin specific agents: alteplase, non antigenic, fibrin bound plasminogen
non fibrin specific: streptokinase, synthesized by streptocci, act on both circulating and fibrin bound plasminogen
hemostatic drugs
vit k:
factors 1972
anaphylactic reaction may occur with too rapid IV injection
antiplasmin:
aminocapric acid, tranexamic acid
inhibit plasminogen activator
V2 agonist:
desmopressin
increase von willebrand factor and factor 8
used in patients with hemophilia A or von willebrand disease
V1 agonist
terlipressin
potent vasoconstriction
used in acute variceal hemorrhage
resistant hypertension
failure to reach goal BP in patients adhering 3 or more drugs including a diuretic
causes: poor compliance, alcohol, high salt intake, diabetes, obisity, concomitant drugs such as sympathomimetics, NSAIDs, corticosteroid
treatment of hypertension
nonpharmacological treatment: exercise, dietry, decreased salt intake, increased k intake
pharmacological treatment: first line: thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blocker,angiotensin blocker
thiazide diuretics
moderate natriuretic effect
most frequently used diuretic in treating hypertension
effective in low doses
first response: reduction in plasma volume and cardiac output
continued use: vasodilatation, decrease PVR (reduce NA content in arterial smooth muscle
don’t work in renal diseases
loop diuretic
more natriuresis than thiazide
less effective in treating hypertension
preferred in patients with renal insufficiency
more potential to cause hyponatremia
RAAS
ACE enzyme convert angiotensin1 to angiotensin2
induce vasoconstriction, aldosterone secretion, breakdown of bradykinin
ACEIs: captopril, lisinopril, prodrug enalapril
ARBs: candesartan, losartan
the drugs of choice in diabetic hypertensive patients, because they reduce proteinuria without adverse metabolic effect
ACEIs used for diabetic patients regardless of hypertension
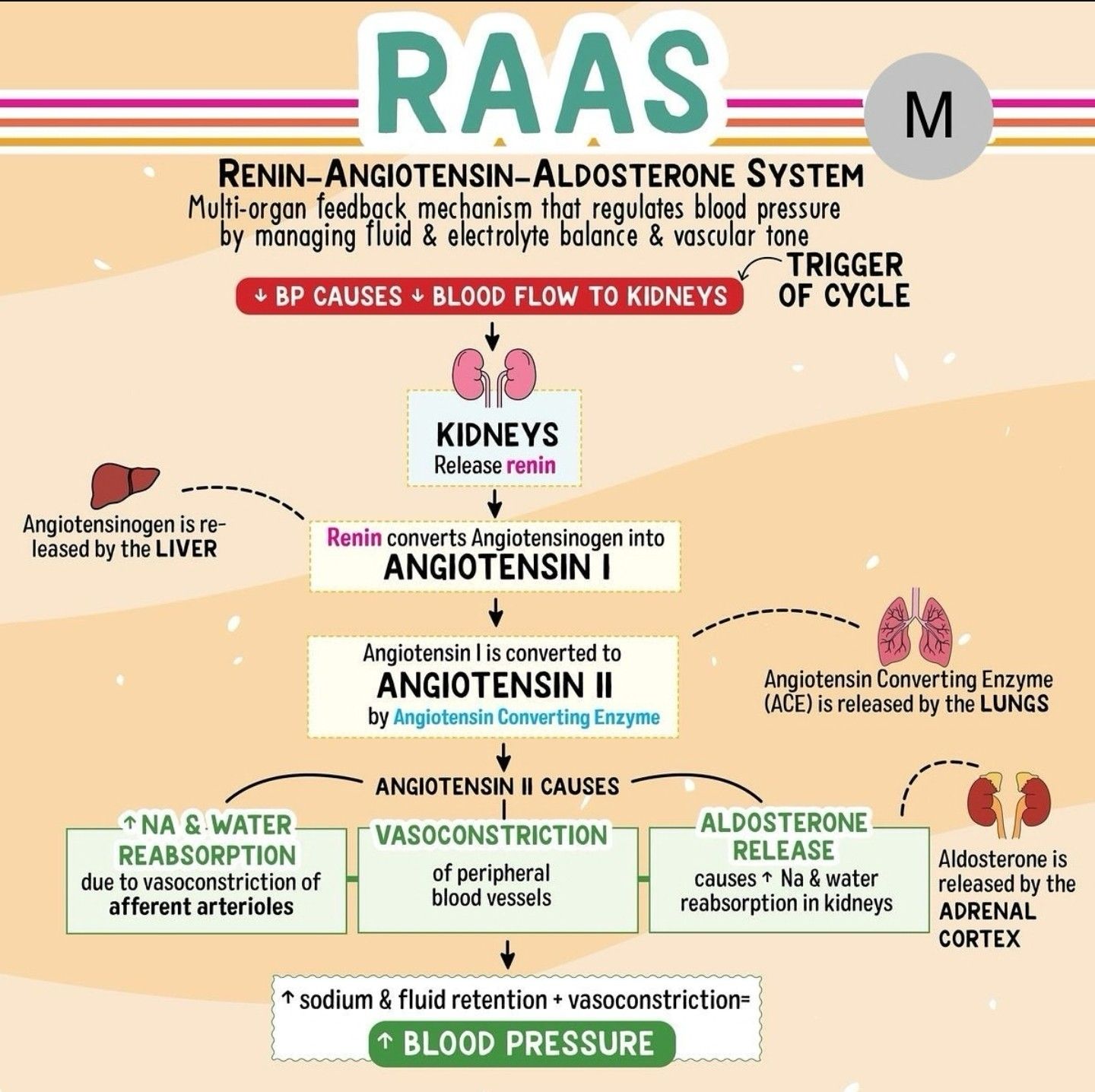
pharmacological effect of RAAS
vasodilatation of arteries and veins
decrease NA reabsorption
decrease intraglomerular pressure, dilate efferent more than afferent
decrease left ventricular hypertrophy
decrease adrenergic activity > suppress reflex tachycardia
adverse effect of RAAS and drug interaction
hypotension
hyperkalemia
teratogenic
reversible decline in renal function
persistent dry cough and angioedema
drug interaction:
potassium sparing diuretics
NASIDs (may cause acute renal damage
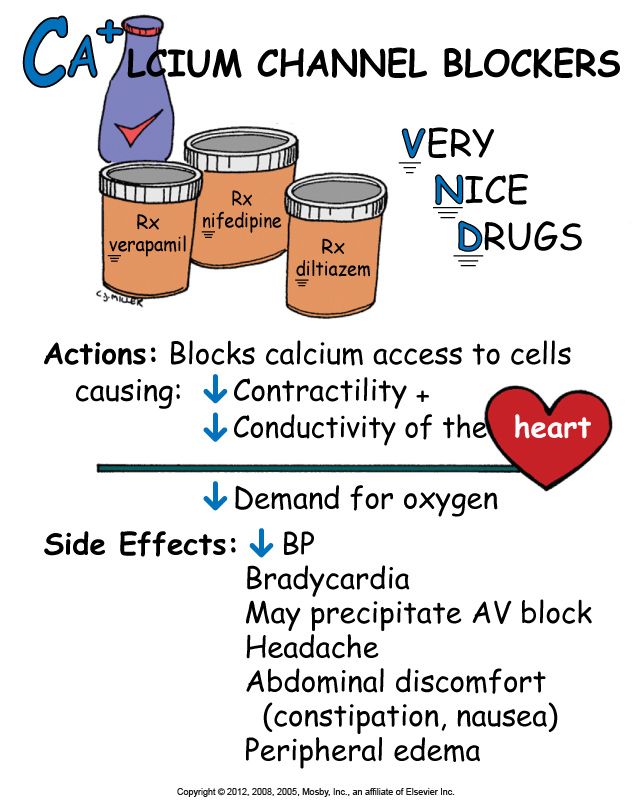
CCBs
bind to L type calcium channel
reduce cytosolic ca
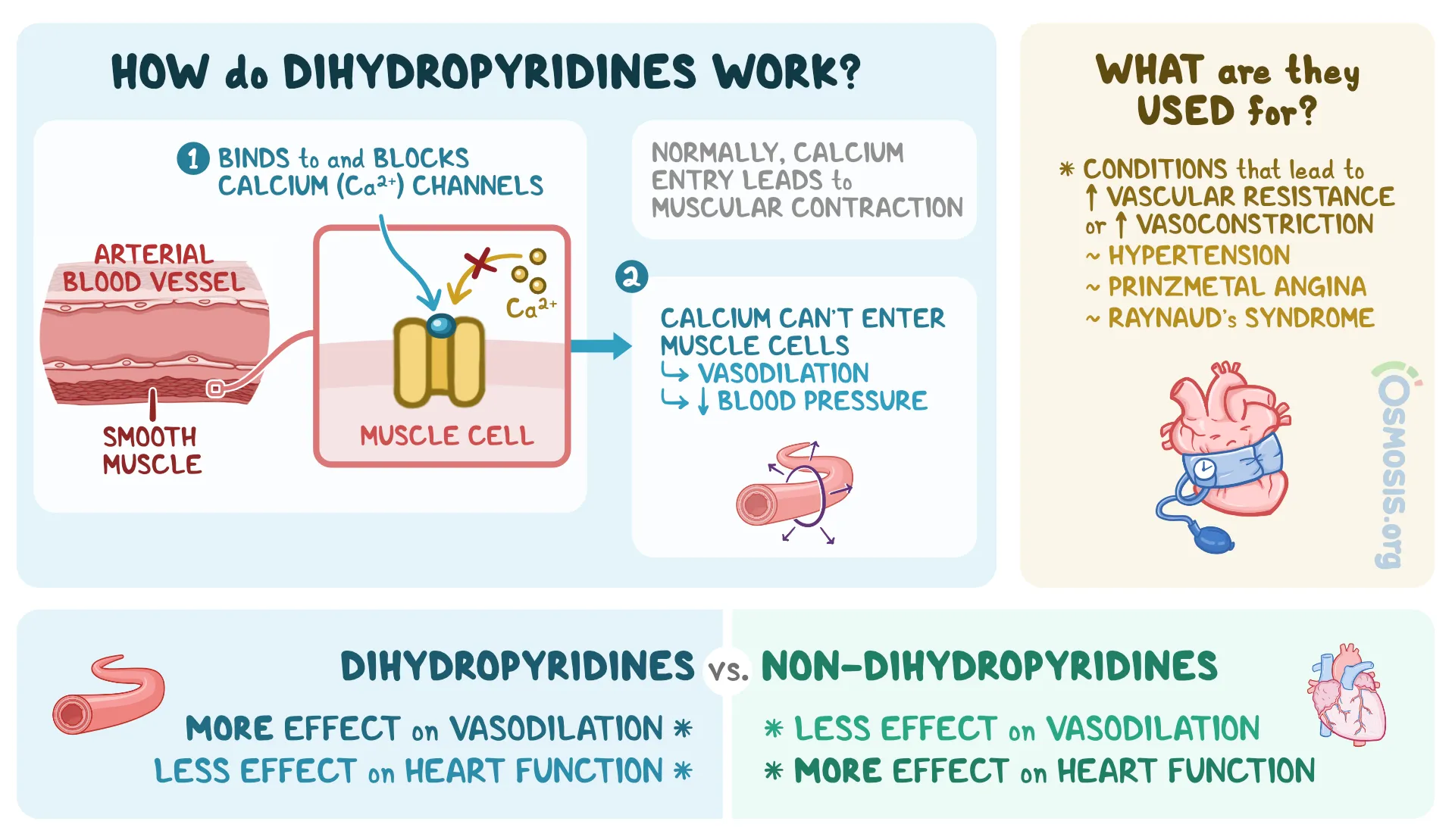
dihydropyridines: short: nifedipine, long: amlodipine
non dihydropyridine: verapamil, diltiazem
dihydropyridines
block ca channels in arterial smooth muscle
arterial vasodilation
coronary vasodilation
no effect on veins
cardiac effect: reflex tachycardia
therapeutic uses: 1. hypertension, 2. IHD
adverse effect: 1. hypotension, 2. tachycardia, 3. flushing, headache, 4. ankle edema
contraindication: 1. hypotension, 2. tachyarrhythmia
can be combined with beta blocker
non dihydropyridines
block mainly ca channels in cardiac muscle
less arterial vasodilation, coronary vasodilation
cardiac effects: decrease (HR, conduction, contractility)
therapeutic uses: 1. hypertension, 2. IHD, 3. atrial tachy arrythmia
adverse effects: 1. hypotension, 2. bradycardia, 3. heart block, 4. constipation
contraindications: 1. hypotension, 2. bradycardia, 3, HF
can’t be combined with beta blocker
beta adrenoceptors blocking drugs
not used as first line
used in compulsory indications: hypertension with cardiac or non-cardiac conditions angina, HF, glaucoma, pregnancy
all generations decrease HR, contractility
suppress release of renin
inhibit sympathetic outflow from CNS
3rd generation has vasodilator effect
alpha 1 adrenergic receptor blockers
doxazosin, prazosin
vasodilation
may be used in resistant hypertension
adverse effect: postural hypotension
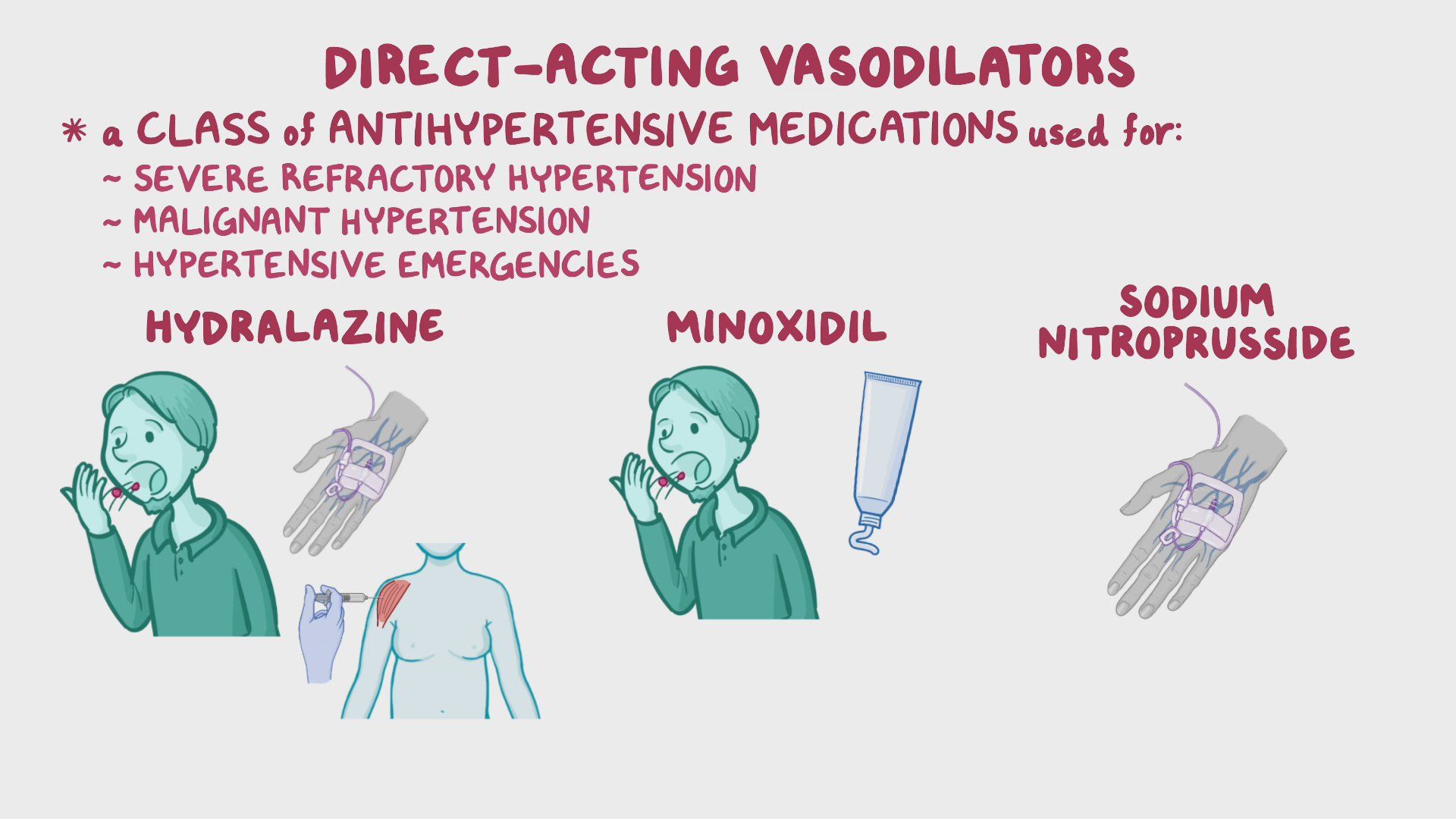
vasodilators
hydralazine, sodium nitroprusside
hydralazine:
induce arteriolar vasodilation, release NO, used in resistant hypertensin, IV in urgency or emergency,
adverse effect: reflex tachycardia, salt water retension, reversible lupus erythematosus
sodium nitroprusside:
potent venodilator, rapid, short duration, used as IV infusion in emergency
adverse effect: hypotension, reflex tachycardia, cyanide toxicity in prolonged infusion
alpha2 adrynegic receptor agonist
clonidine, methyldopa, moxonidine
reduce sympathetic outflow from CNS, reduce BP
clonidine: only in resistant hypertension
methyledopa: safe during pregnancy
moxonidine: more specific in imidazoline1 receptors than a2, used in management of hypertension when other treatments are not sufficient
adverse effect: sedation, postural hypotension