Radiology - Panoramic Radiography - Principles and Technique
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Panorama Definition
an unbroken view of the whole region surrounding the observer
Tomography
image of structures lying in a predetermined plane of tissue
blurring/eliminating detail in images of structures in other planes
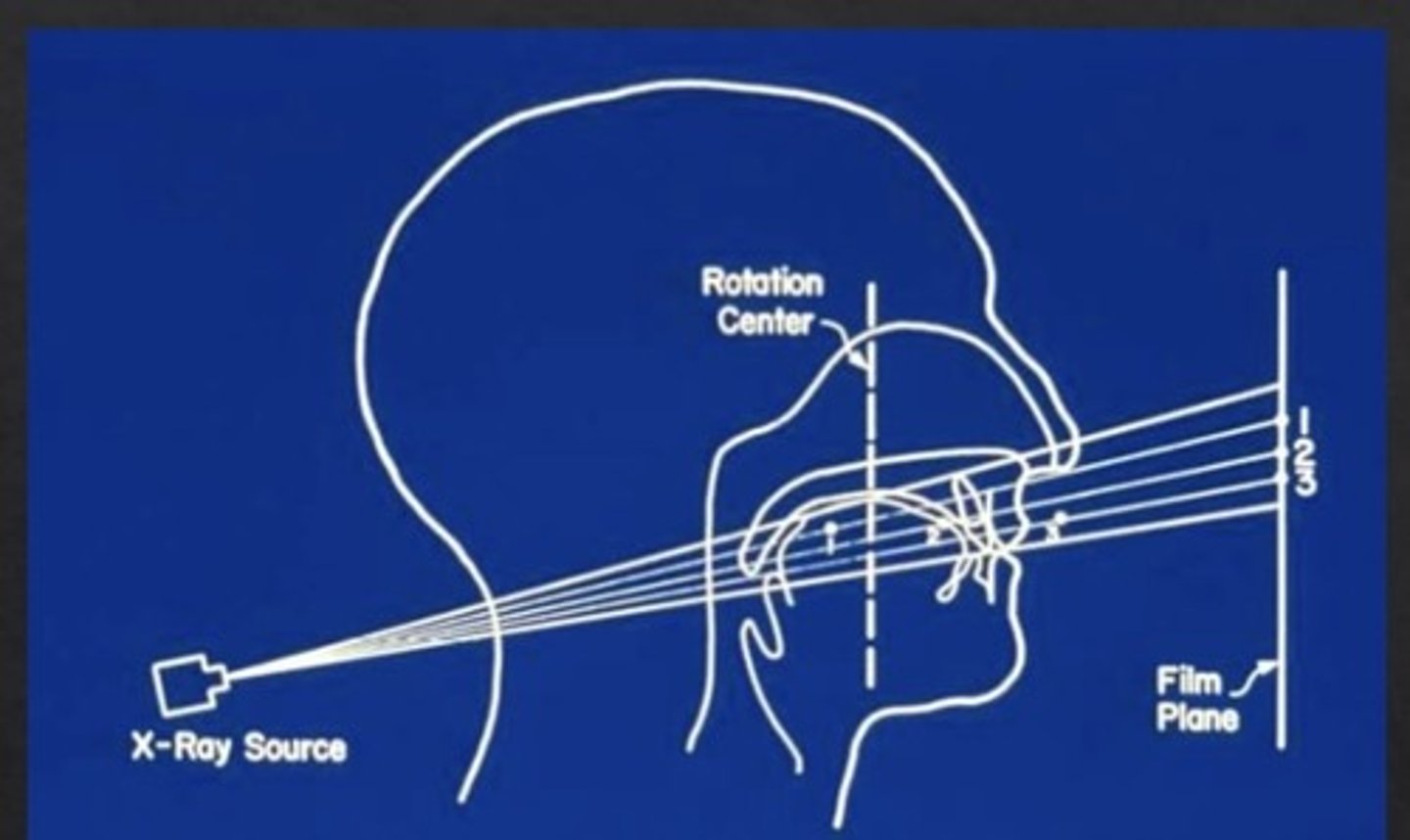
What is the rotation center?
the pivotal point or axis around which receptor and x ray tube rotate
Arcs of three circle
Because the curve of the jaw, the X ray tube and receptor rotate sequentially to three pivot points
uses fixed/stationary centers of rotation with high radiation dose
Continuously moving centers of rotation
As the x ray source moves behind the patient, the center of rotation moves forward along the arc (dotted line)
Where is the beam collimated for PANO?
at the x ray tube and detector
T/F: the basic principle of image formation is the same regardless of receptor?
TRUE
Functions of laser lights in Pano machine
Panoramic units have laser lights to position the patient's
dentition in the focal trough
Structures in the center of the wide, 3D curved zone
❑ Structures in the center of this zone cast sharper, well-defined images.
❑ Structures away are less clear
How do objects outside the focal trough appear?
blurred, magnified, or reduced in size
❑ sometimes distorted to the extent of not being
recognizable
The shape of the focal trough varies with what?
• Brand of equipment
• Imaging protocol
What structures are considered real images?
Structures between receptor and center of rotation
What structures are considered ghost images?
Structures between center of rotation and x-ray source
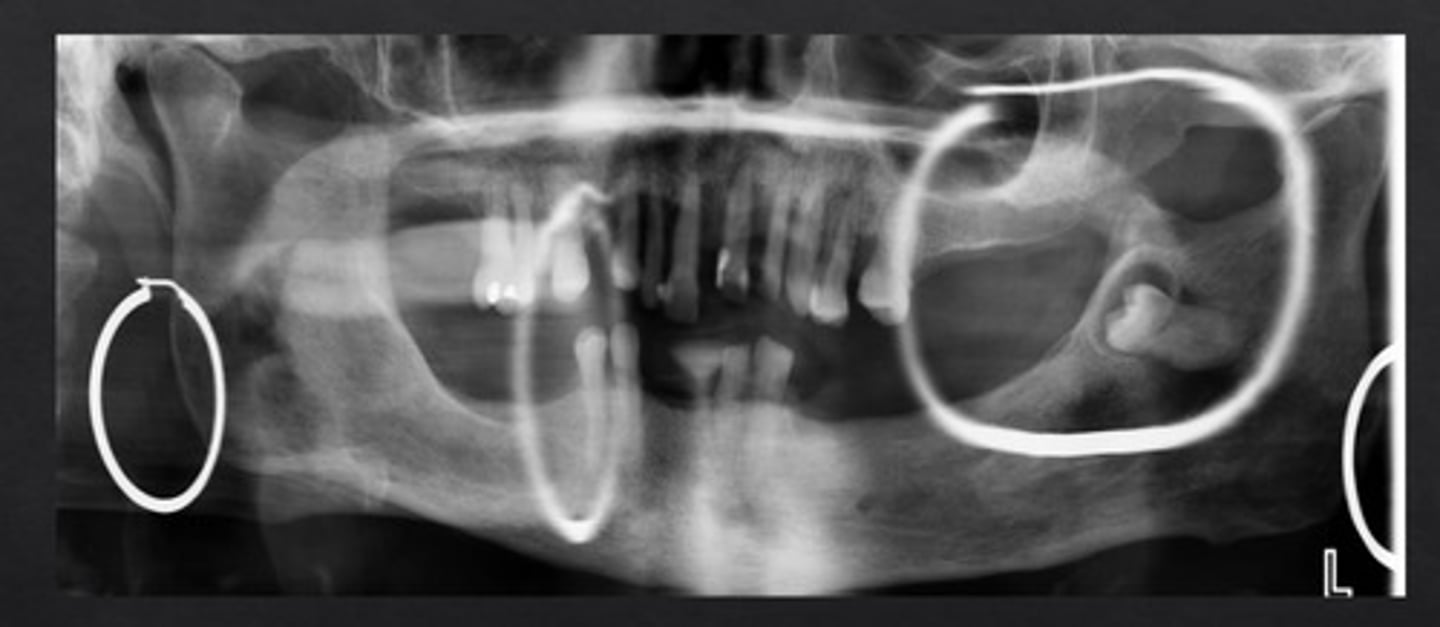
Characteristics of Ghost Images
Higher level
Contralateral
Blurred/ significantly magnified
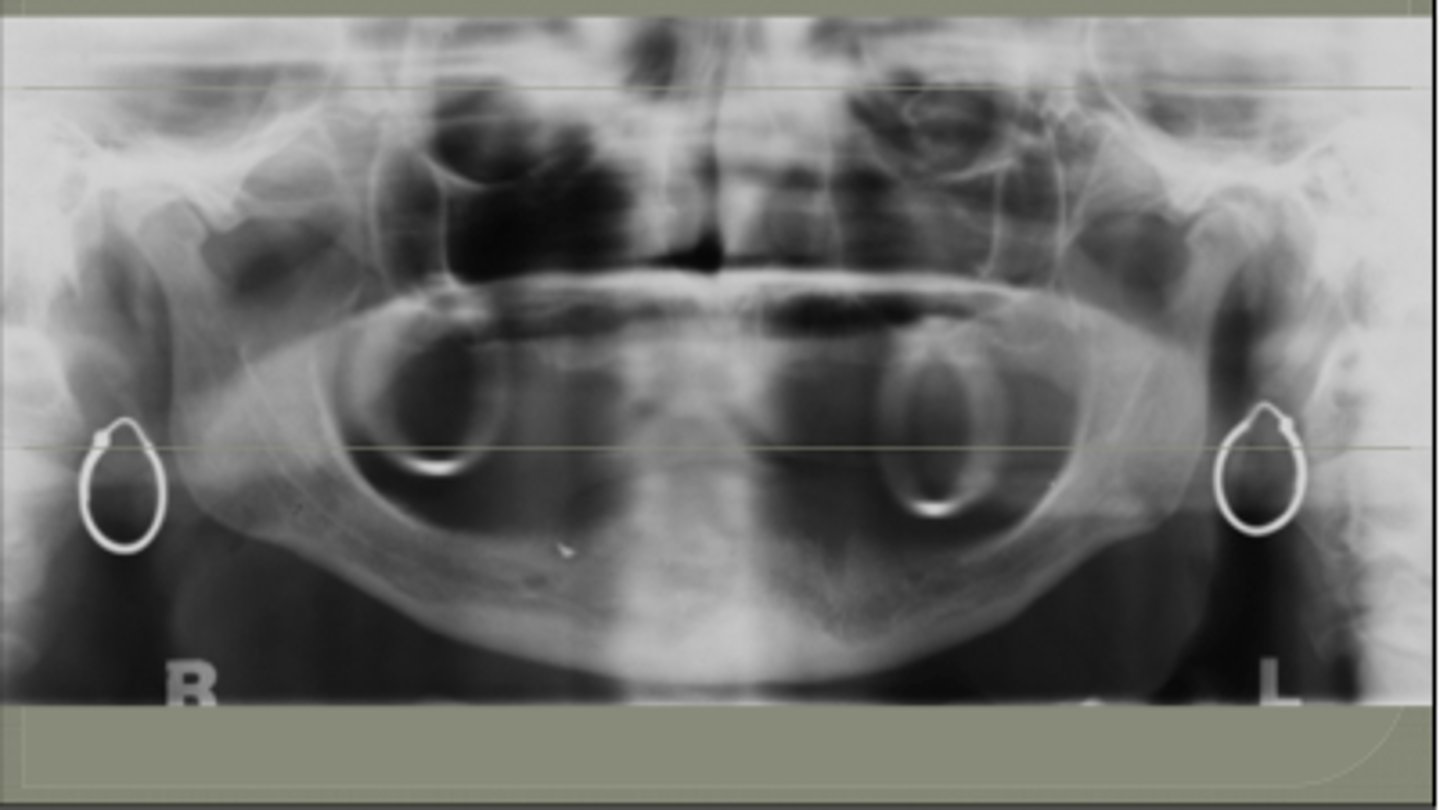
What does less magnification result in?
-Increase Source to Object distance
• Decrease in object to image receptor distance
What does more magnification result in?
- Decrease Source to Object distance
• Increase in Object & image receptor distance
Double images
Objects that lie posterior to the center of rotation are intercepted twice by the x-ray beam. E.g.: C-spine, Hyoid, epiglottis
What does image distortion depend on?
- x ray beam angulation
- x ray source to object distance
- path of rotational center
- position of the object within the focal trough
Horizontal magnification
- depends on the position of the object within the focal trough
Magnitude
distance of the object from the center of the focal trough
What happens with a negative vertical projection angle?
objects closer to the source are projected at a higher level
Advantages of panoramic imaging
- broad coverage of facial bones and teeth
- low radiation dose
- can be used in patients with limited mouth opening or in patients who cannot tolerate intraoral radiography
- useful visual aid in patient education and case presentation
Disadvantages of Panoramic Imaging
- lower resolution images rather than intraoral
- magnification approximately 20%. Unequal magnification, making linear measurements unreliable
- image is the superimposition of real, double, and ghost images
- accurate patient positioning - errors and artifacts
Patient positioning in panoramic image acquisition
- patient should be upright
- all metallic items like glasses, earrings, piercings, partial dentures, and other jewelry are removed
- patient should stay still.
Five major positioning criteria
- mid-sagittal plane (midline)
- occlusal plane or Frankfort plane (chin position)
- anterior-posterior jaw location (bite block)
- cervical neck/spine
- tongue/lip
Mid sagittal plane or midline positioning
the plane should be perpendicular to the floor
Frankfort plane
an imaginary line connecting the infraorbital margin and the external auditory meatus
occlusal plane or frankfort plane should be parallel to the floor
Anterior-posterior position
- anterior teeth should be in the bite block groove
- in edentulous patients: chin up or similar devices can be used instead of bite block
cervical spine/neck position in panoramic acquisition
for neck extension, use gentle upward force on mastoid eminences
slumping head and hands
Lip and tongue position in panoramic acquisition
instruct patient to swallow and hold the tongue against the roof of mouth
this eliminates radiolucent shadow
Diagnostically acceptable panoramic image characteristics
- condyles completely captured perpendicular to the inferior aspect of the image
- hard palate flat and parallel to the floor
- no asymmetry between left and right rami
- even and minimal distortion of teeth
- no palatoglossal air shadow
- no spinal shadow obscuring image
- air shadow not obscuring image
NOMAD PID and backscatter shield position
NOMAD PID and backscatter shield is parallel to the XCP ring
maximum protection exists when the shield is at the outer edge of the cone, closer to the subject, and parallel to the operator
Image quality versus distance in NOMAD
Image quality may degrade as you move PID and ring away from patient.
Inverse square law
The intensity of beam is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from source
When does protection diminish for backscatter shield?
1) when the shield is not at the
outer edge of the cone.
**Use positioning kits that do not require the shield to be slid back.
2) when the shield is distanced
from the subject.
**Hold the cone close to the patient.
3) when the shield is not parallel to the operator.
**Avoid this by asking the patient to slightly tilt their head.
Optimal storage for NOMAD
The optimal storage location is cool, dry, and away from direct sunlight.
Recommendations by National Commission on Radiation Protection (NCRP)

T/F: there is no need for personal radiation monitoring with handheld x ray equipment
TRUE
** as long as the whole body effective dose to the operator is <1.0 mSc y-1
What is the position of the X ray source, image receptor, and patient's head with respect to each other in panoramic radiography?
x ray source and image receptor rotate around the patient's head
What kind of image is formed by the objects that lie between the center of rotation and the receptor?
real image
What kind of image is formed by the objects that lie between the center of rotation and x ray source?
ghost image