Semester 1 Final Review
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
Responsible for decision making (prefrontal cortex)
Broca’s area- responsible for speech production
Voluntary movement
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for sensing body position
Somatosensory cortex-processes sensations: touch, pressure, pain, and temperature (excludes smell)
Parietal Lobe
Responsible for visual processing
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for auditory processing
Wernicke’s area-responsible for speech comprehension
Responsible for smell processing
Temporal Lobe
Responsible for processing new memories
Hippocampus
Body temperature, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal
Hypothalamus
Master Gland of endocrine system
Pituitary Gland
Relay station for all sensory info except smell
Thalamus
Fear and aggression
Amygdala
Responsible for speech production, located in frontal lobe
Broca’s Area
Responsible for processing language, located in temporal lobe
Wernicke’s Area
Located in parietal lobe, responsible for sensing touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
Somatosensory Cortex
The brain’s ability to change and adapt due to experience
Neuroplasticity
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion; rewarding sensation
Dopamine
Neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure
Endorphins
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter
GABA
Helps control alertness and arousal
Norepinephrine
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
Serotonin
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory
Acetylcholine
A major excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory
Glutamate
A molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action, ie: Morphine
Agonist
A molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter’s action, ie: Botox
Antagonists
A condition that affects nerves in your central nervous system, caused by a breakdown of myelin sheath on a neuron
Multiple Sclerosis
A language disorder that affects a person’s ability to communicate, caused by damage to Wernicke’s Area
Aphasia
Chemicals that alter the brain by producing changes in perceptions and mood. ie: alcohol, caffeine, nicotine, marijuana
Psychoactive Drugs
The adaption of the body to the repeated use of a drug (meaning it no longer produces the naturally existing neurotransmitter that is being replaced by the drug)
Dependence
Physical conditions caused by chronic use of a tolerance-forming drug in which abrupt or gradual drug withdrawal causes unpleasant physical symptoms
Physical Dependence
Psychological need to use a drug, such as to relieve negative emotions; addiction.
Psychological Dependence
Symptoms that occur when a person ends the use of an addictive substance
Withdrawal
Enables the maintenance of balance in part controlled by the semicircular canals, which contains receptors that detect motions of the head
Vestibular Sense
Our movement sense, responsible for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts
Kinesthetic Sense
Auditory
Canal
Eardrum
Ossicles
Has (Hammer, Anvil, Stirrup)
Oval
Window
Cochlea
Hair cells
Auditory
Cortex
Auditory Sense Structures
Cornea
Pupil
Lens
Retina
Rods
Cones
Bipolar cells
Ganglion cells
Optic Nerve
Thalamus
Visual Cortex
Visual Sense Structures
A sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings. Treatment includes respiration machine (CPAP).
Sleep Apnea
A disease marked by sudden and irresistible onsets of sleep during normal walking periods. Treatment includes medication, changing sleep patterns, and naps during the day
Narcolepsy
Body does not become paralyzed during dreams, which may cause you to act out the actions of your dreams. Could result in sleep walking. Treatment includes medication or supplements.
REM Sleep Disorder
Inability to fall asleep or stay asleep. Treatment includes reduction of caffeine, set sleep schedule, etc.
Insomnia
It allows researchers to see genetic and environmental influences.
Identical Twins in Psychological Research
The minimum stimulus energy needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
Absolute Threshold
Minimum difference required to notice a difference between two stimulus
Difference Threshold
The process of turning one form of energy (sound wave, light, smells) into neural impulses our brain can interpret
Transduction
Information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
Top-Down Processing
Analysis that begins with the sensory receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information
Bottom-Up Processing
Theory that states our retina contains three different types of color receptors that can be stimulated in combination to create any color
(Red-green, blue-yellow, white-black)
Opponent Process Theory
Theory that states our retina contains three different types of color receptors that can be stimulated in combination to create any color (Red, Green, Blue)
Trichromatic Theory
The belief that after learning something we would have been able to guess that/ we already knew what we were being told
Hindsight Bias
The average of a distribution, calculated by adding up all the numbers in a data set and dividing by the number of values
Mean
The middle score in a distribution, calculated by arranging the data from least to greatest and choosing the middle number(s)
Median
The most frequently occurring score(s) of a distribution, is calculated by identifying the most frequently occurring number in a data set
Mode
The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
Range
A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score. Large standard deviation means the data is more spread out, and small standard deviation means the data is closer together
Standard Deviation
Indicates that there is a larger concentration of data points on the right side with fewer extreme values on the left side
Negative Skew
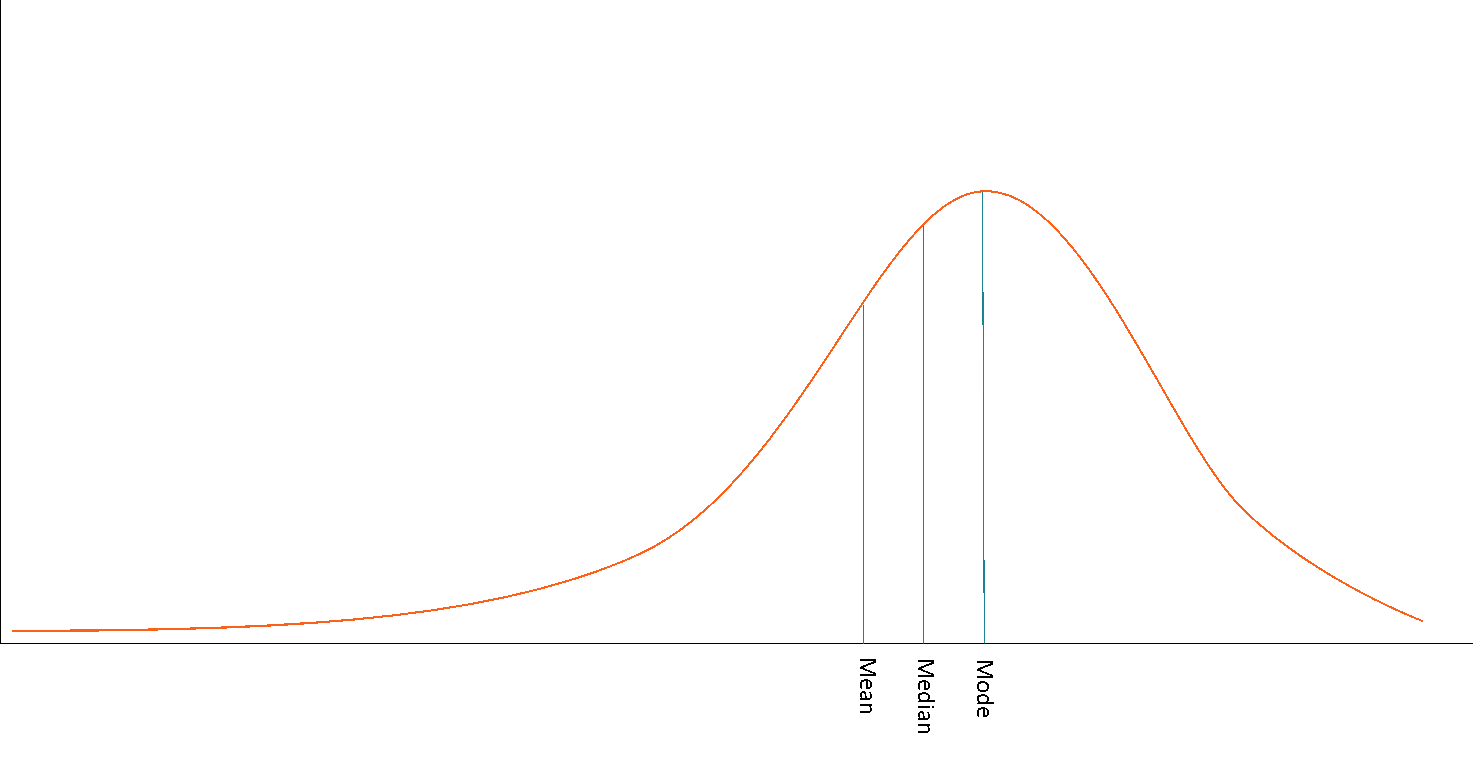
The majority of the data cluster towards the left side with few significant values on the right, creating a tail
Positive Skew
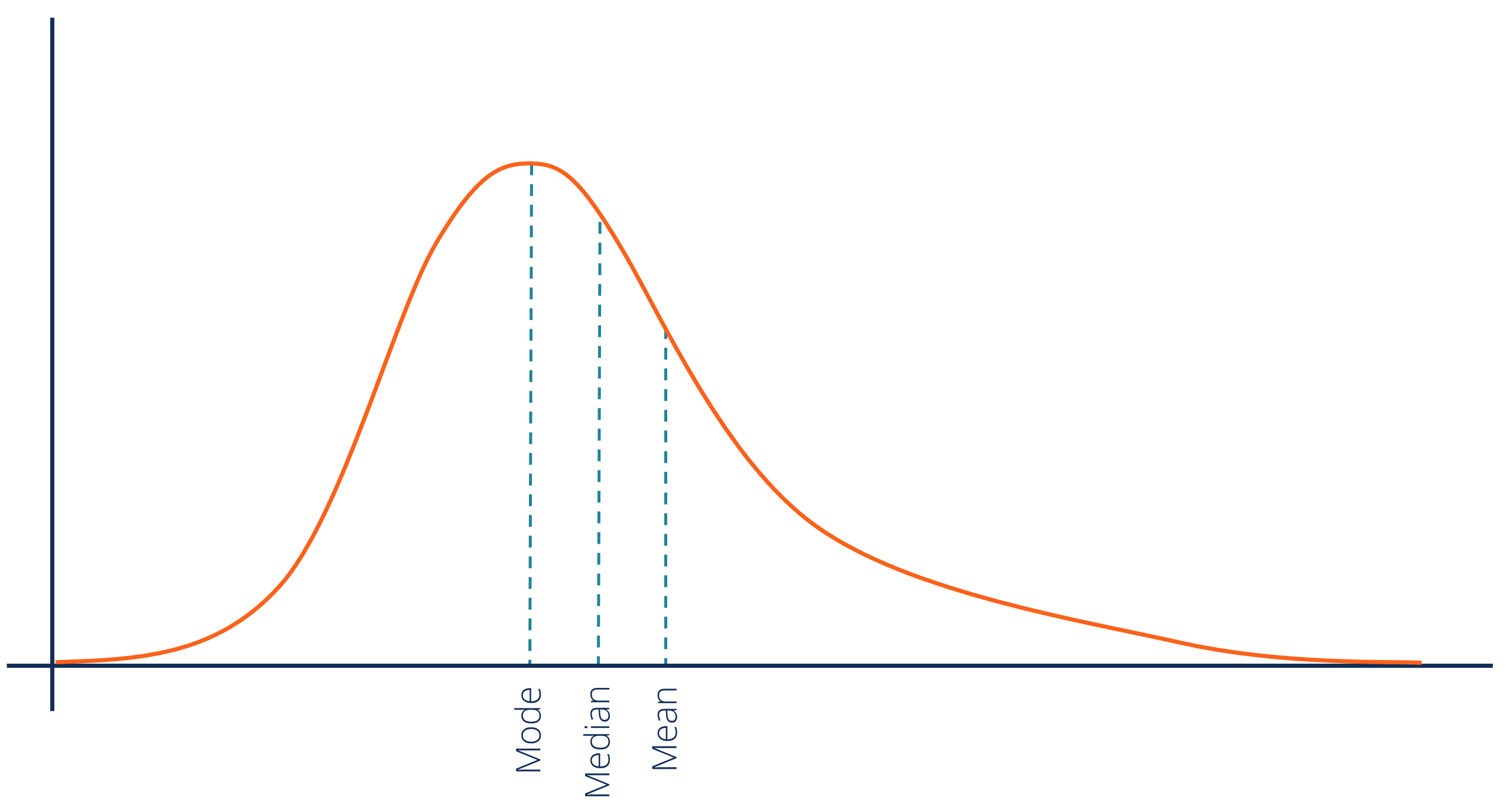
Displays a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve
Normal Distribution
Its purpose is to test cause and effect and explain it
Experiment
(Cause). Variable that is manipulated by the experimenter. Ie: Antidepressent
Independent Variable
(Effect). The factor that may change in response to the independent variable. Ie: Depression
Dependent Variable
Group that does not receive the treatment
Control Condition
Outside factors that affect research
Confounding/Third Variables
After a sample is obtained, randomly assigning participants to experimental or control groups. This eliminates any bias or pre-existing differences
Random Assignment
A method of selecting participants for a study where every individual from the population has an equal chance of being chosen, ensuring that the sample group accurately represents the larger population being studied
Random Sampling
Carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used in a research study, allows for replication
Operational Definitions
Occurs when participants are blind, or uninformed about what treatment, if any, they are receiving
Single Blind
When neither the research staff or research participants know whether the research participant have received a treatment or a placebo
Double Blind
Appropriate: Must be for a valid purpose
Beneficial: For the greater good
Caring: Food/water/shelter/protection from harm
Ethical Guidelines: Animal Experimentation
Informed consent
Protection from harm
Debriefing
Confidentiality
Right to withdrawal
Ethical Guidelines: Human Experimentation
Non-experimental research where a researcher measures two or more variables and assesses the statistical relationship (correlation) between them and how they change together without establishing causation
Correlational Research
When one variable increases, the other also increases
Positive Correlation
Relationship between two variables where one variable increases as the other decreases, meaning they have an inverse relationship
Negative Correlation
No relationship between two variables, change in one does not affect the other
No Correlation
Compares different population groups at the same time. Ie: Studying men and women and measuring the relationship between sleep deprivation and stress levels among each group
Cross-Sectional Design
Measures the relationship between two variable within the same population over a long period of time
Longitudinal Study
The statistical description of how likely it was that something occurred by chance. If something is less than 5% likely that it occurred by chance, then it is statistically significant
Statistical Significance
68% of scores fall 1 standard deviation from the mean
95% of scores fall 2 standard deviation from the mean
99% of scores fall 3 standard deviation from the mean
Standard Deviation %
Depth cues available to both eyes separately
Monecular Depth Cues
Depth cues that depend on both eyes
Binocular depth cues
The slight difference between the right and left retinal images. The brain automatically combines the images when both eyes are open
Retinal Disparity
The cognitive process of selectively focusing your attention on one aspect of your environment while ignoring other things
Selective Attention
Ability to hear one specific voice amongst many others
Cocktail Party Effect
Intentional or conscious recollection of memory; deliberately trying to remember something. Located in hippocampus.
Explicit memories
The unconscious or automatic recall of information and skills without a conscious effort to retrieve it. Located in cerebellum.
Implicit Memories
A situational predicament in which people are or feel themselves to be at risk of conforming to stereotypes about their social groups
Stereotype Threat
When old information interferes with or blocks the retrieval of new information
Proactive Interference
When new information interferes with or blocks the retrieval of old information
Retroactive Interference
Inability to remember ongoing events after the incidence of trauma
Anterograde Amnesia
The inability to remember events that occurred before the incidence of trauma or the onset of disease that caused the memory loss
Retrograde Amnesia
Humans’ tendency to organize pieces of information into a meaningful whole
Gestalt Psychology
Perceptually filling gaps to create a complex project
Closure
Perception of patterns as smooth and continuous
Continuity
Grouping nearby figures together
Proximity
A tendency to approach a problem one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past
Mental Set
A tendency to search for information that supports our pre conceptions and to ignore info that contradicts our beliefs
Confirmation Bias
The improved recall of specific episodes or information when the context present at encoding and retrieval are the same
Context Effects
Tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one’s mood
Mood Congruent
Memory retrieval is most efficient when an individual is in the same state of consciousness as they were when the memory was formed
State-Dependent Memory
Providing cues to stimulate memories
Priming
The tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions
Functional Fixedness
The trend of increasing intelligence scores as time passes
Flynn Effect
The accumulation of knowledge, facts, and skills that are acquired throughout life
Crystallized Intelligence
Ability to decipher information and make decisions which is more difficult at an old age
Fluid Intelligence