BIO 426: ELISA
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
ELISA
what it is.
give function
different types
WHAT IT IS:
- enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
- uses a 96 well plate
- utilizes antibody and antigen recognition (IgG for long term seroconversion, IgM for short term seroconversion)
- utilizes amplification molecule (label) for fluorescence
FUNCTION:
- uses antigen recognition to produce amplification of signal with molecules using fluorescence and this signal is detected.
- well plate is coated and uses primary antibody conjugate, capture antibody, secondary antibody conjugate
TYPES:
- direct ELISA
- indirect ELISA
- sandwich ELISA (indirect and direct)
- competitive ELISA (indirect and direct and sandwich)
describe the materials and the function of a:
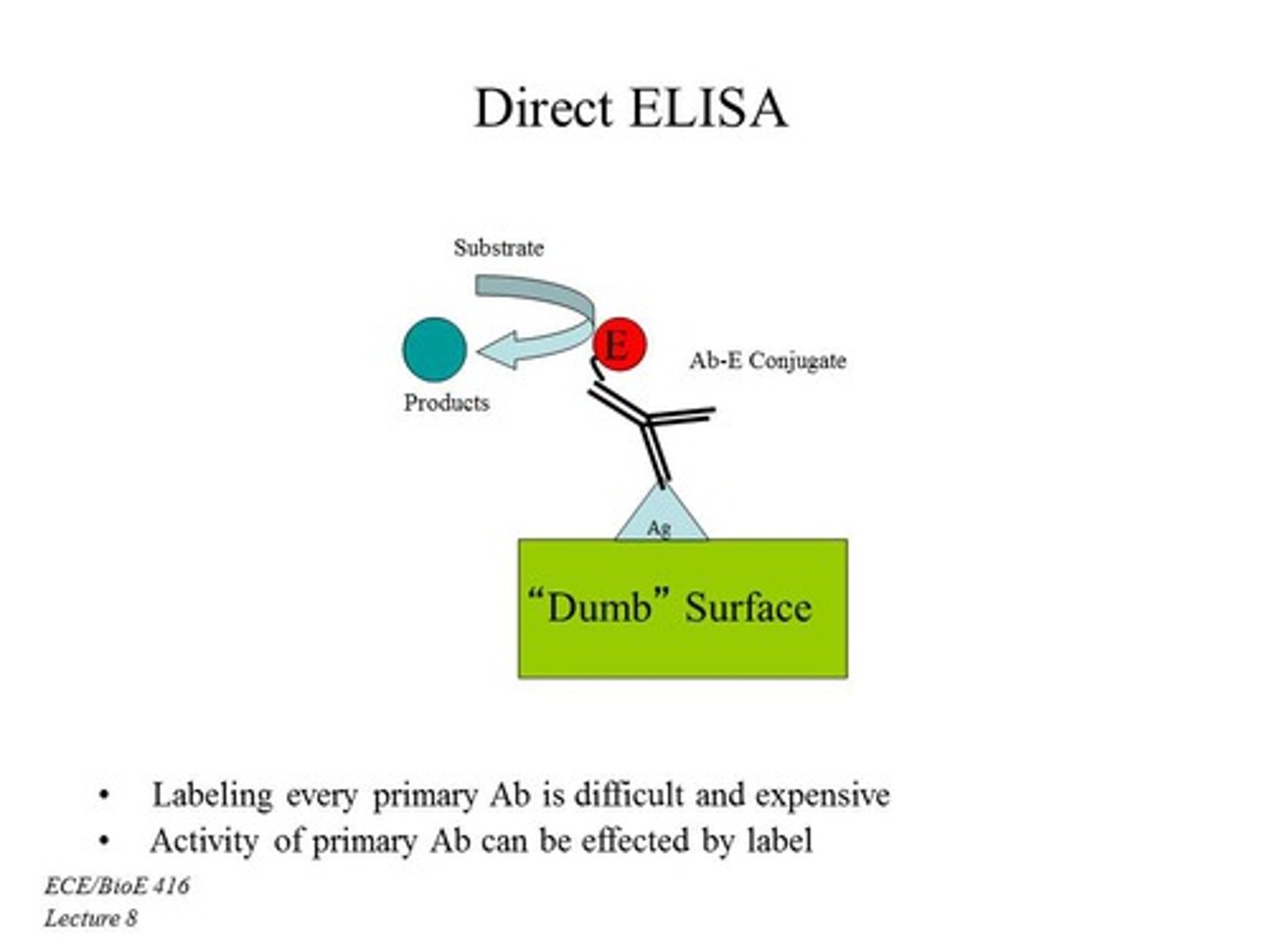
Direct ELISA
MATERIALS
- antigen (analyte) annealed to the plate
- primary antibody conjugate with fluorophore (amplification molecule)
FUNCTION
- uses amplification molecule that binds to the primary antibody
- helps quantify antigen present in sample
- less sensitive than indirect because less primary antibodies bind to antigen
- only done with high antigen concentration (mmol or micromolar)
- a lower signal = lower antigen concentration
a higher signal = greater antigen concentration
describe the materials and the function of a:
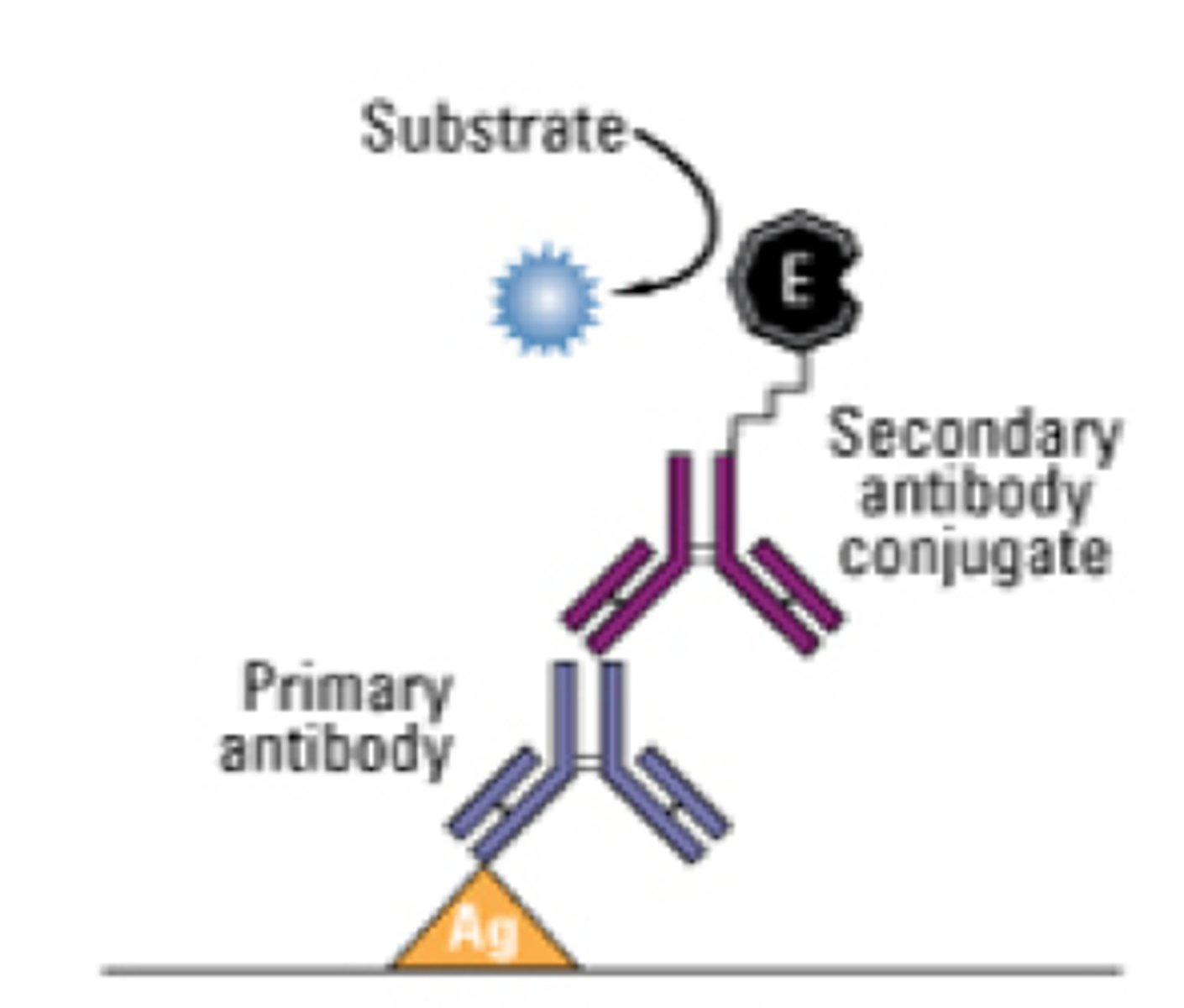
Indirect ELISA
MATERIALS
- antigen (analyte) annealed to the plate
- secondary antibody conjugate with a fluorophore (amplification molecule) that binds to the Fc region of the primary antibody
FUNCTION
- amplification molecule binds to the secondary antibody and looks for antigen concentration
- can be used if primary antibody is not available for sale
- allows for greater ELISA breadth to make more ELISA kits because of the greater availability
- more sensitive and more amplification than direct because you can get multiple secondary antibodies binding to primary antibodies
- also looks for seroconversion of primary antibodies by using recombinant antigen on a plate and applying serum (with primary antibodies) and then adding secondary antibodies
- a lower signal = lower antigen or antibody concentration
a higher signal = greater antigen or antibody concentration
describe the materials and the function of a:
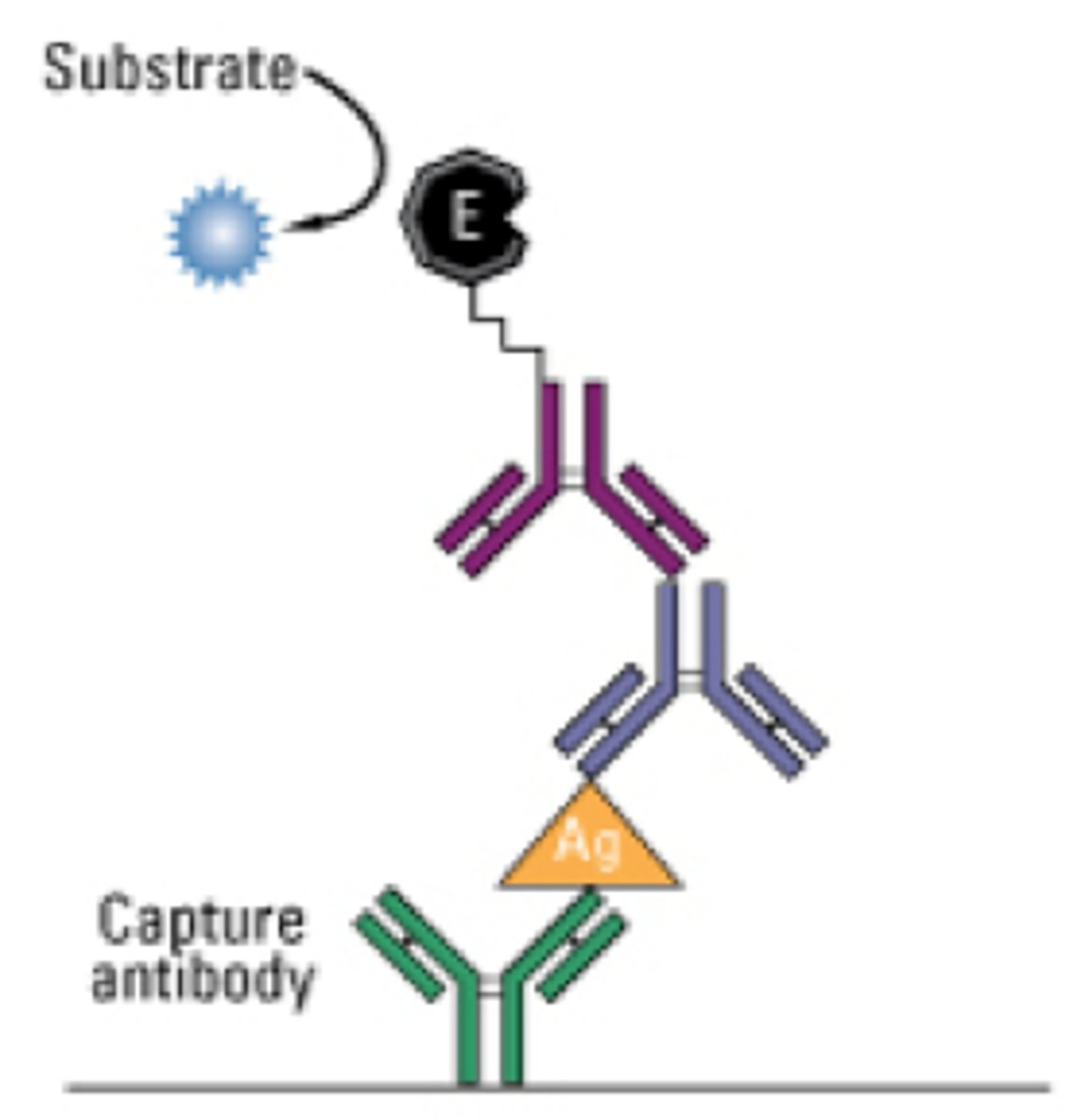
Sandwich ELISA
Indirect Sandwich ELISA
Direct Sandwich ELISA
MATERIALS
- capture antibody annealed to the plate
- analyte binds to the capture antibody
- Indirect = secondary antibody conjugate with fluorophore (amplification molecule) that binds to the Fc region of the primary antibody
- Direct = primary antibody with amplification molecule
FUNCTION
- called a sandwich ELISA because the antigen is sandwiched between antibodies
- used to get quantitative data on small amounts of antigen present (10^-15)
- has the greatest sensitivity and specificity out of all of the ELISAs
- incubate serum with antigen on plate
- a lower signal = lower antigen concentration
a higher signal = greater antigen concentration
describe the materials and the function of a:
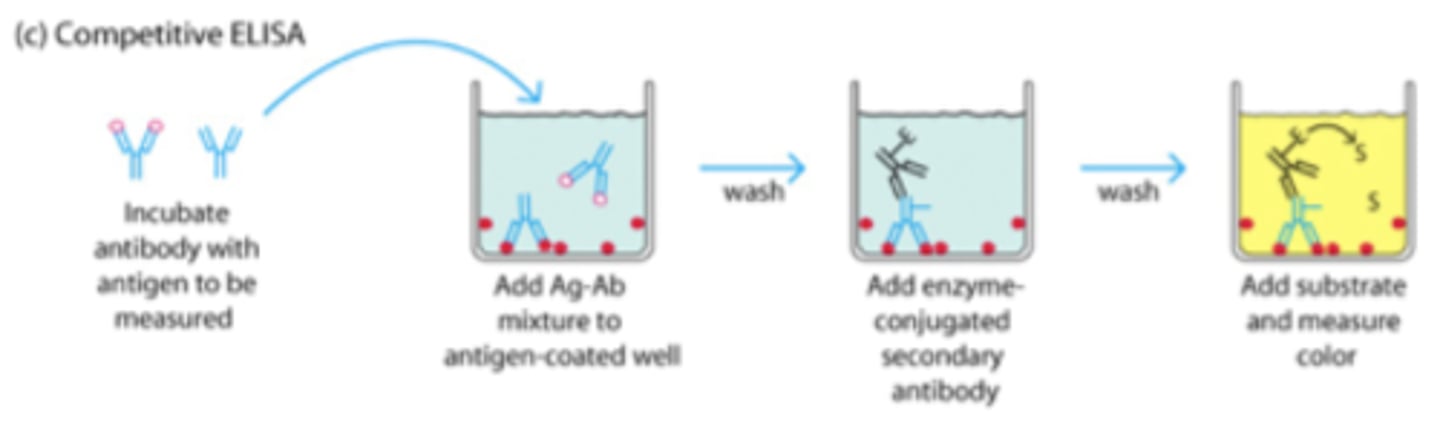
Competitive ELISA
Indirect Competitive ELISA
Direct Competitive ELISA
Sandwich Competitive ELISA
MATERIALS
- antigen (analyte) annealed to the plate
- inhibitor antigen also on plate
- Indirect: secondary antibody conjugate with fluorophore (amplification molecule) that binds to the Fc region of the primary antibody that binds to the antigens
- Direct: primary antibody binds to the antigen
FUNCTION
- usually incubate the sample antigen with known concentration of antibody
- antibodies will bind to the antigen first and remaining will bind to the recombinant antigen on the plate.
- a lower signal = greater antigen concentration
a higher signal = lower antigen concentration
describe the general procedure of an ELISA
1. add blocking protein and other molecules to increase binding to well (ex. streptavidin)
2. immobilize antigen or antibody (sandwich) on the plate
3. add Patient serum
4. add primary antibody / capture antibody / secondary antibody as needed
5. incubate and wash off excess with a wash
6. add substrate (reacts with the amplification molecule)
7. keep wells in dark because the amplification molecule can be photosensitive and then add Stop Solution
8. Use spectrophotometer to read absorbance
what is the sensitivity of the ELISA used in lab
usually in pg/mL
The lowest concentration that can be determined to be statistically different from a blank at a 99% confidence level
what is the range of the ELISA sensitivity
0.312-20 ng/mL
The upper and lower limits of quantification
what are the plate coating conditions
- plate must be a flat, bottom, clear, polystyrene plate that isn't tissue treated
- protein binding capacity has a minimum of 400 ng/cm squared
- you want a <5% coefficient of variance (this means that there is a less than 5% variation between the well makeup
- incubate about 210 mg/ml antigen in the well overnight. add blocking buffer that usually has 5-10% BSA (bovine serum albumin)
why is polystyrene used in the well plates
it's hydrophobic and it's good with binding to proteins
HRP
- horse radish peroxidase
- a colorimeter
- useful in reduction of H peroxide by being catalyzed by peroxidase
- substrate is TMB
TMB structure and how it affects its fluorescence
- 2 benzine rings (benzine rings usually means that color is given off because of the electrons)
- 2 amines at the ends
- photosensitivewh
TMB structure and the interaction with HRP and H peroxidase
TMB donates electron in the presence of HRP and H peroxidase
TMB becomes an intermediate of 1 imine and 1 amine OR unstabilized diimines
there's a bluish color (OD: 370-650 nm) at this stage. it's very unstable and should be stopped after 30 min.
should be stopped with a stop solution (H2SO4) where it loses another electron to be a stabilized diimine (yellow color here ; OD:450 nm)
what is the standard LDH curve and how do you use it to find your Pt serum's LDH significance
- linear relationship between concentration (ng/mL = x axis) vs. average absorbance (y axis) after an ELISA
- use linear equation and plug in the average absorbance of the Pt serum to find the concentration
- need an enzymatic assay to determine the significance of the ELISA because LDH is measured in U/L
When using TMB as a substrate in a colorimetric ELISA (HRP) without stop solution, what happens
The multi-well plate will remain colorless
When using TMB as a substrate in the presence of hydrogen peroxide and horse-radish peroxidase (HRP), the TMB is:
oxidized
ABTS is one of many alternative chromogenic substrates to TMB when using an HRP/ H2O2 assay readout. Describes the use of ABTS by comparing it the TMB
ABTS is less sensitive than TMB with or without employing stop solution
in an ELISA using TMB and HRP, what spectrophotometer setting would you utilize if you did not have Stop solution
available?
at 370-650 nm because it'll remain blue.
what is LDH and why is it significant to observe in patients
- a glycolytic oxidoreductase enzyme that catalyzes the reversible conversion of pyruvate to lactate resulting in the oxidation of NADH to NAD+.
- found in most tissues, yet concentrated in muscle, kidney and liver cells.
- Malignant cells release intracellular enzymes through damaged cell membranes via mitochondrial machinery alteration and apoptosis dysregulation.
- increased LDH is usually recognized as a tumor marker
- elevated serum LDH at the time of initial diagnosis have inferior survival outcomes
how is LDH used in International Prognostic Index (IPI)
LDH level is a clinical tool for predicting the prognosis of patients with aggressive malignancies.