Chem Bonds Test
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
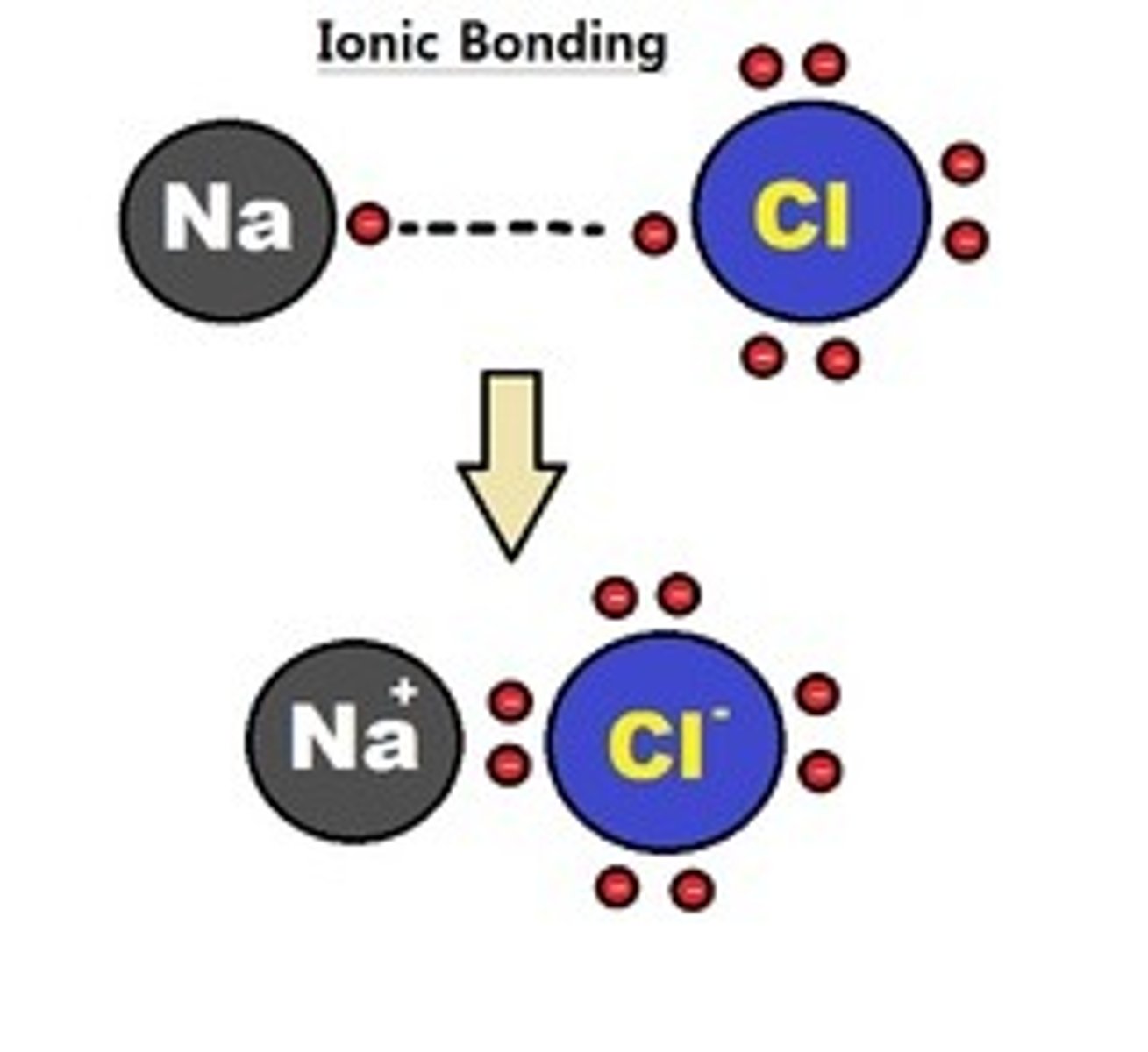
ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
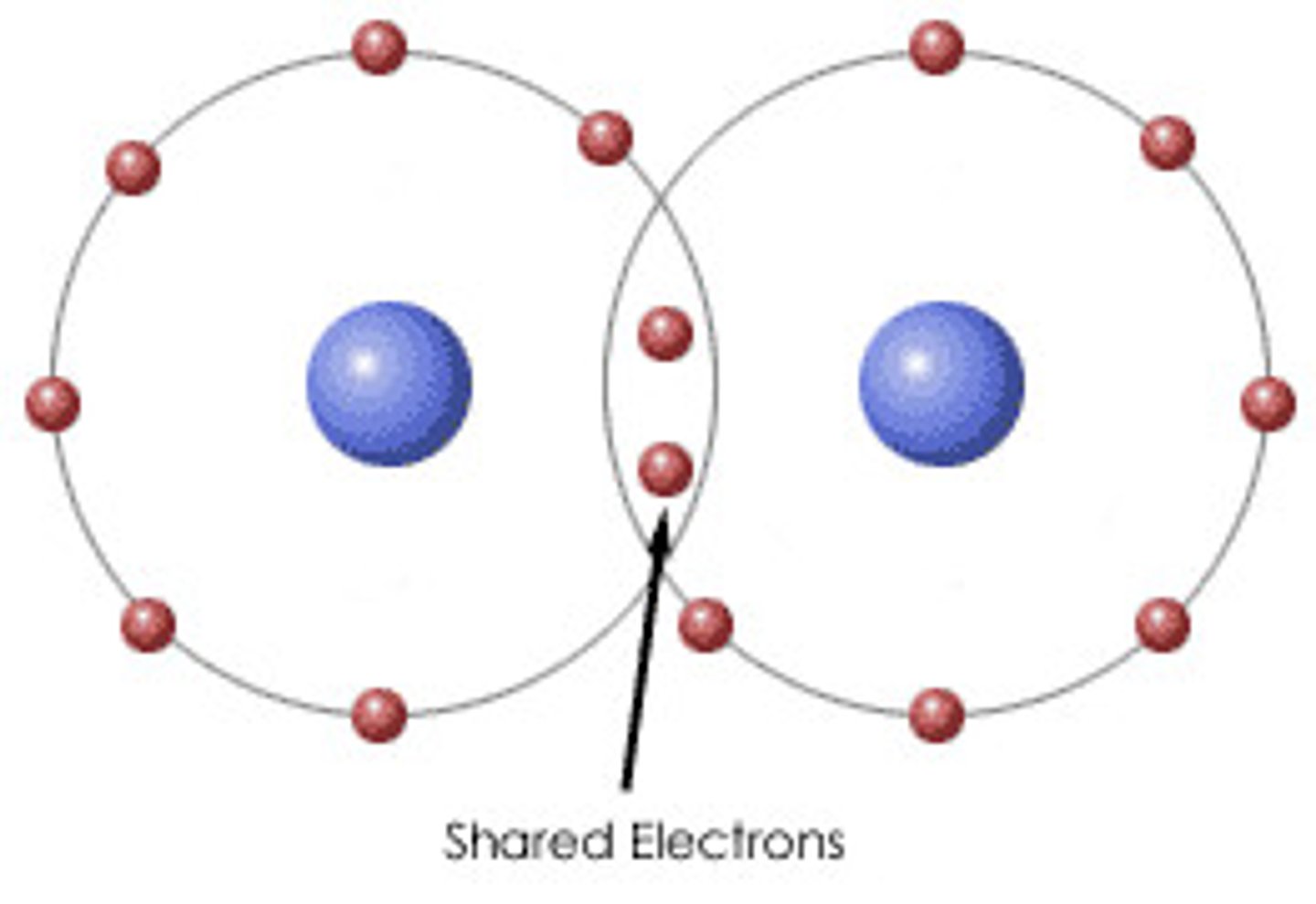
Covalent Bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
What does a larger electronegativity difference mean?
stronger attraction for electrons
What does a smaller electronegativity difference mean?
More equal sharing
Nonpolar Covalent
0.0-0.4
Polar covalent
0.5-1.6
Ionic
1.7 and up
Diatomic Molecule
2 atoms of same element covalently bonded
Explain the potential energy chart of a covalent bond.
Optimal length is lowest potential energy
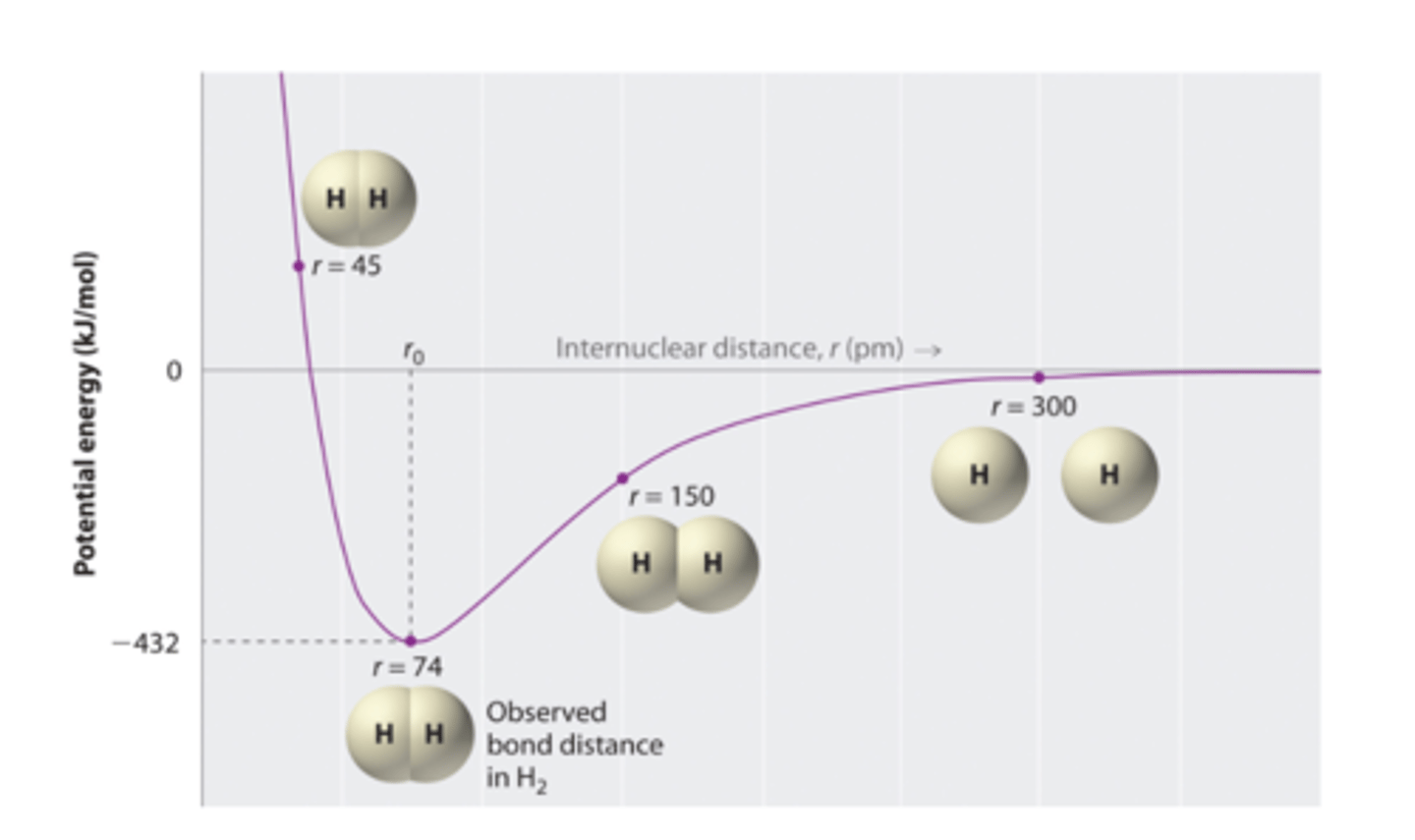
Bond length
distance between 2 bonded atoms are minimum potential energy
Bond energy
Energy required to break chemical bond
Octet Rule
States that atoms lose, gain or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons
exceptions to the octet rule
Hydrogen (2), Beryllium (4), Boron (6), Al (6)
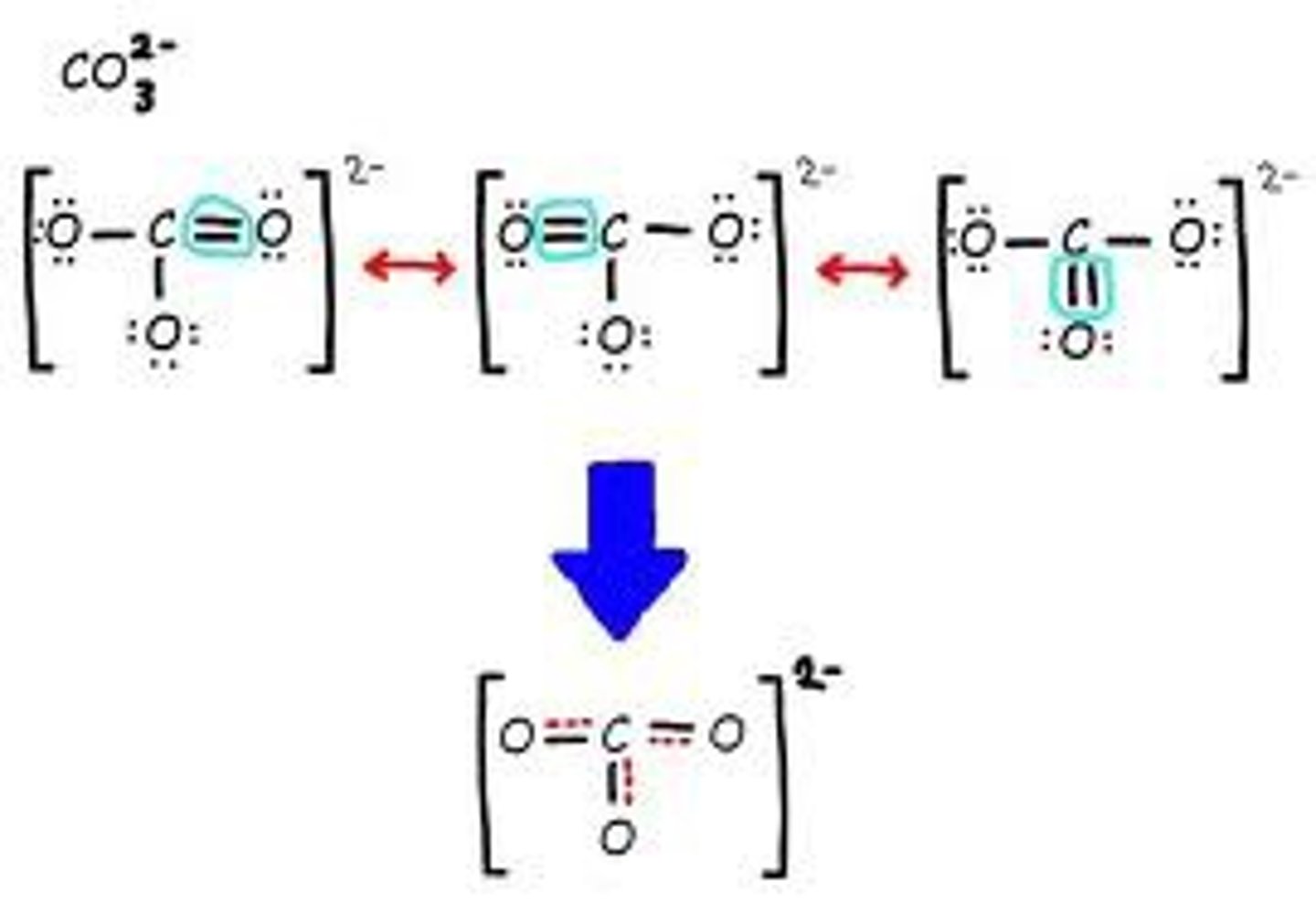
Resonance structures
structures that occur when it is possible to draw two or more valid electron dot structures
Formal Charge Equation
Valence - Nonbonding - (bonding/2)
Formula unit
lowest possible ratio of elements
Crystal Lattice
a three-dimensional geometric arrangement of particles
Lattice Energy
the energy needed to break lattice
Ionic Compound Properties
- strong electrostatic force
- high melting points
- brittle
- conductive in liquid state (mobile ions)
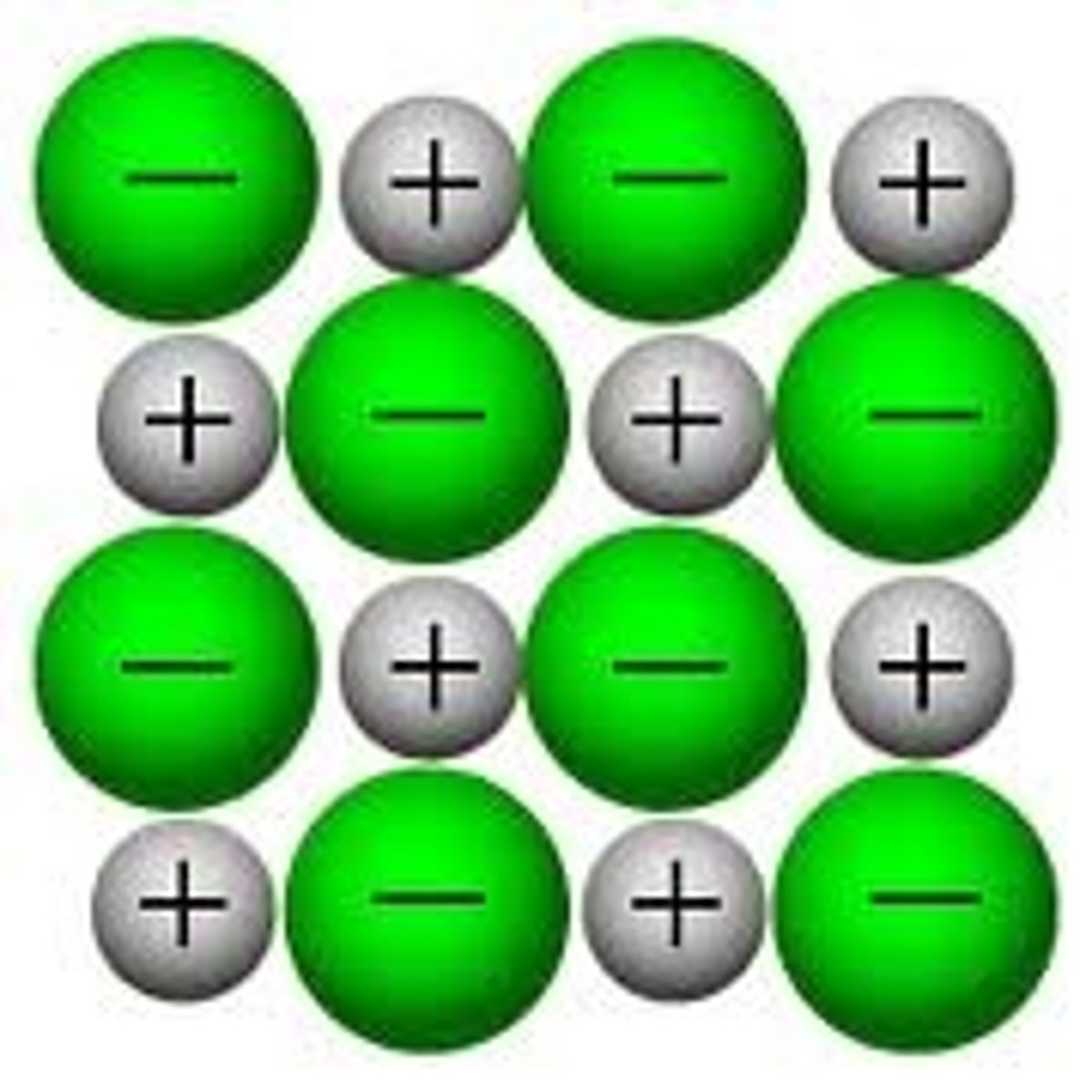
Molecular Compound Properties
- weaker attractive forces
- less brittle
- lower melting & boiling points
Sea of electrons
mobile e- around metal atoms in crystal lattice
Metallic bond
chemical bond formed from electrostatic attraction between metal atoms and sea of electrons
Shiny
when electrons absorb the light they reemit it, causing the metal to appear shiny
Why is metal malleable?
the bonds are planar, making them easier to pull away or push over
Heat of vaporization
energy to break apart metallic bonds & vaporize, usually high
VSEPR
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
How do we find electron domains?
Count lone pairs, single, double, and triple bonds on CENTRAL atom (each counts as ONE)
2 Domain Geometry
Electron: Linear
Molecular: Linear
180
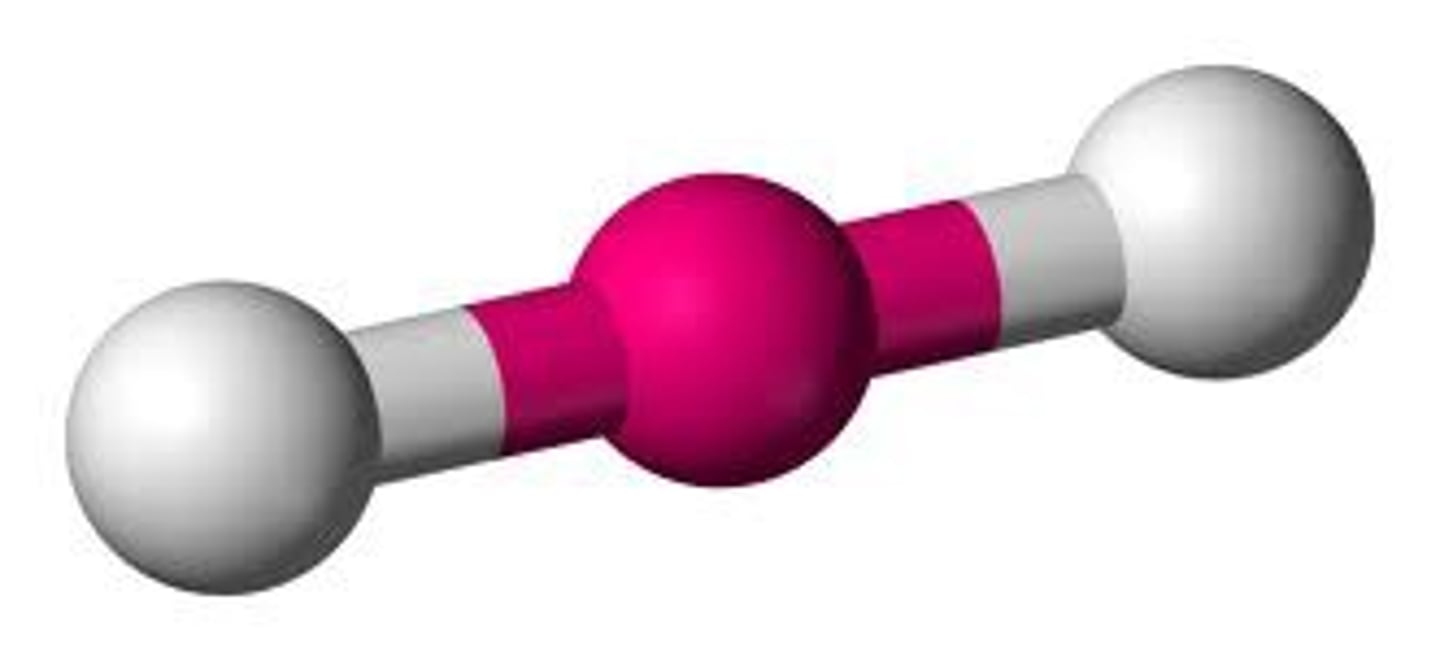
3 bonding 0 nonbonding
trigonal planar
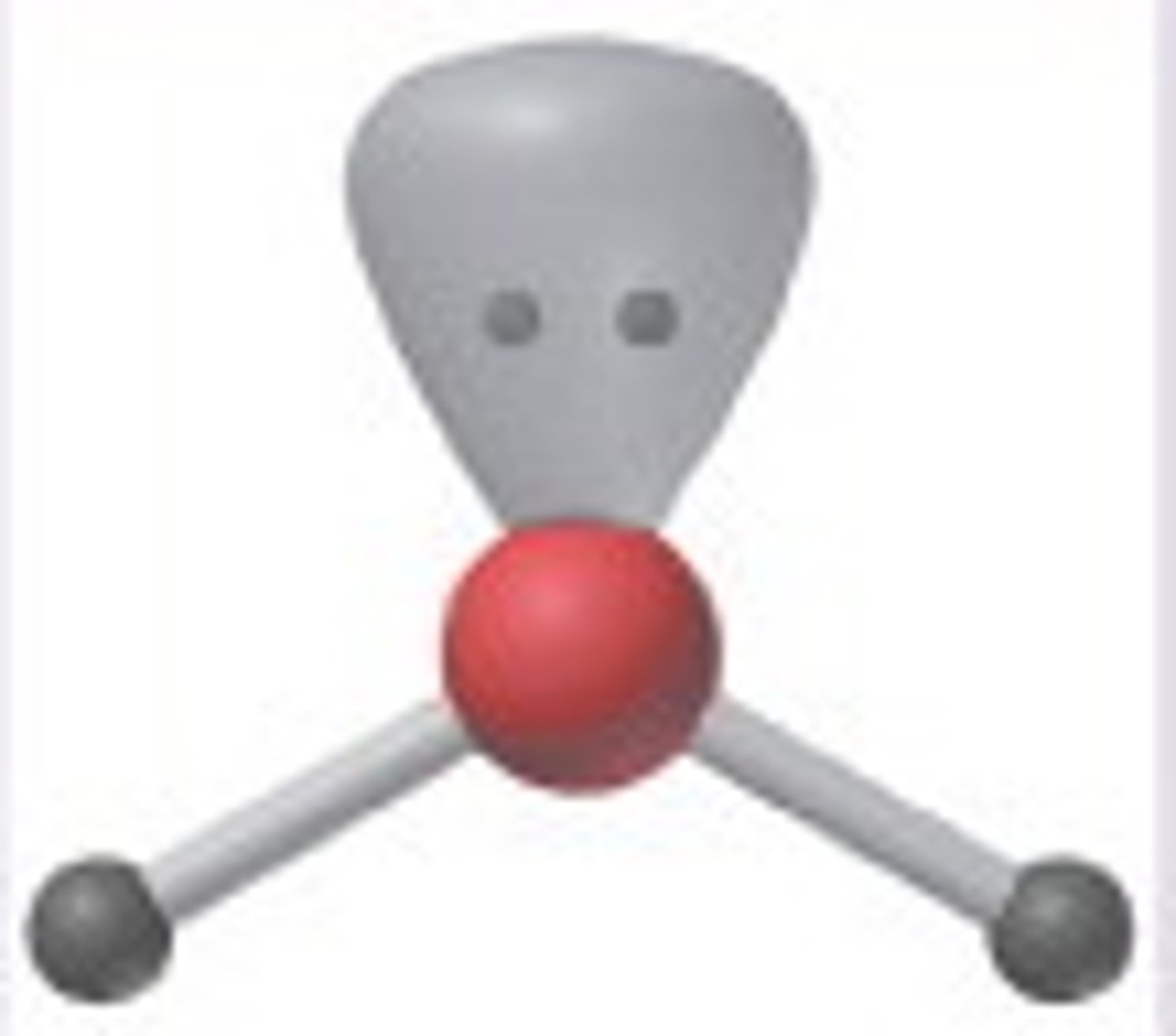
2 bonding 1 nonbonding
bent
4 bonding 0 nonbonding
tetrahedral, 109.5
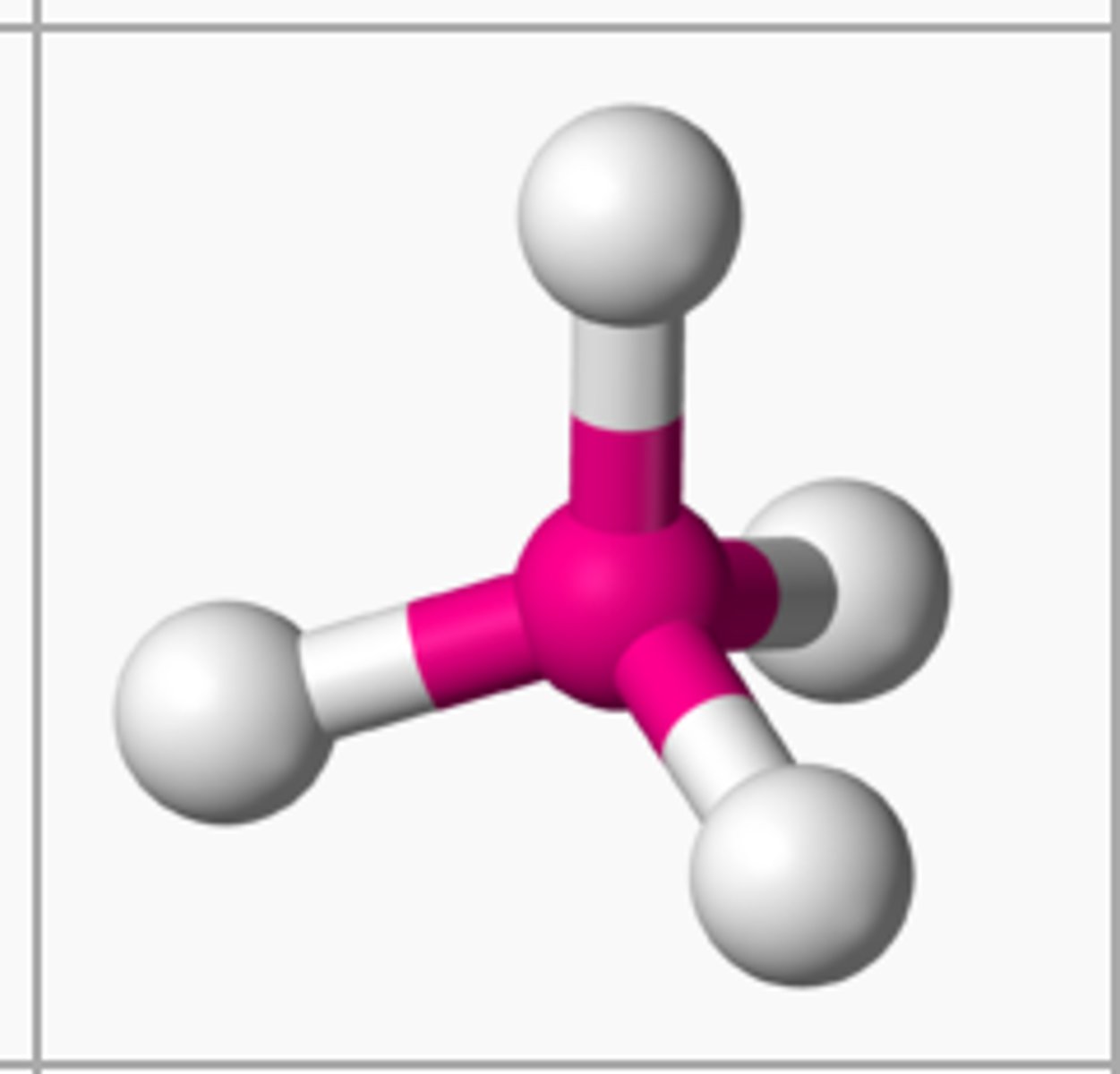
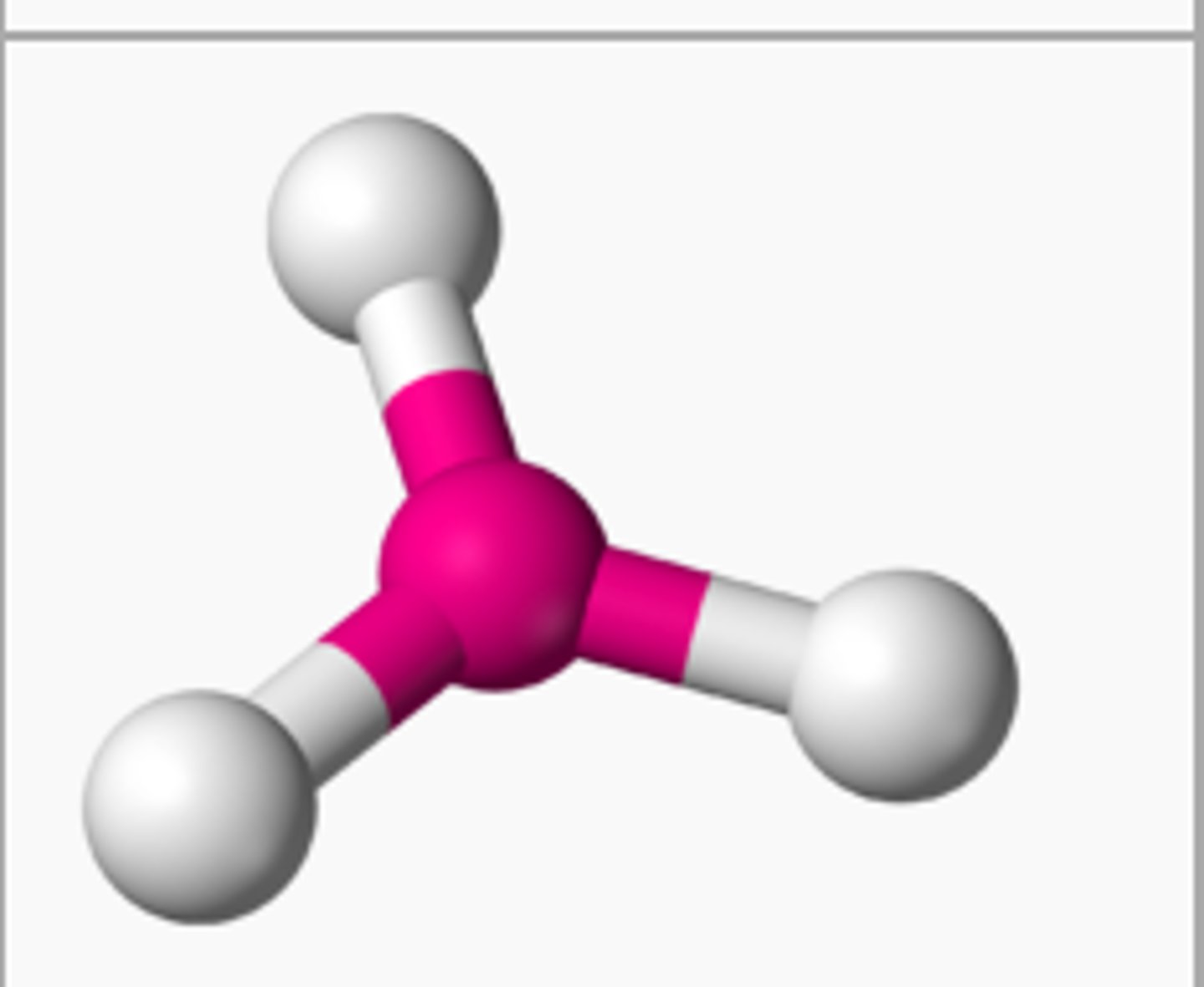
3 bonding 1 nonbonding
trigonal pyramidal
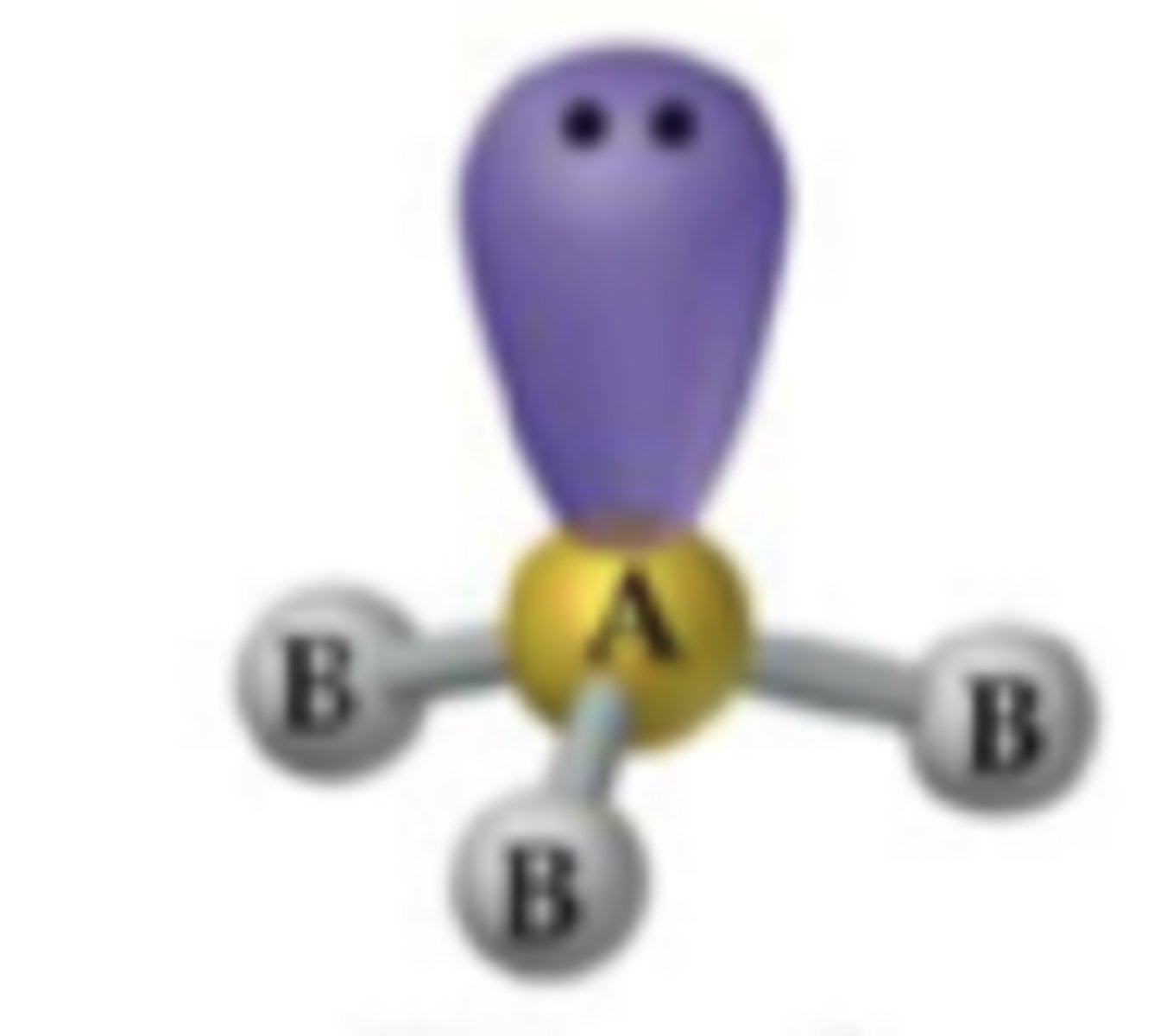
2 bonding 2 nonbonding
bent
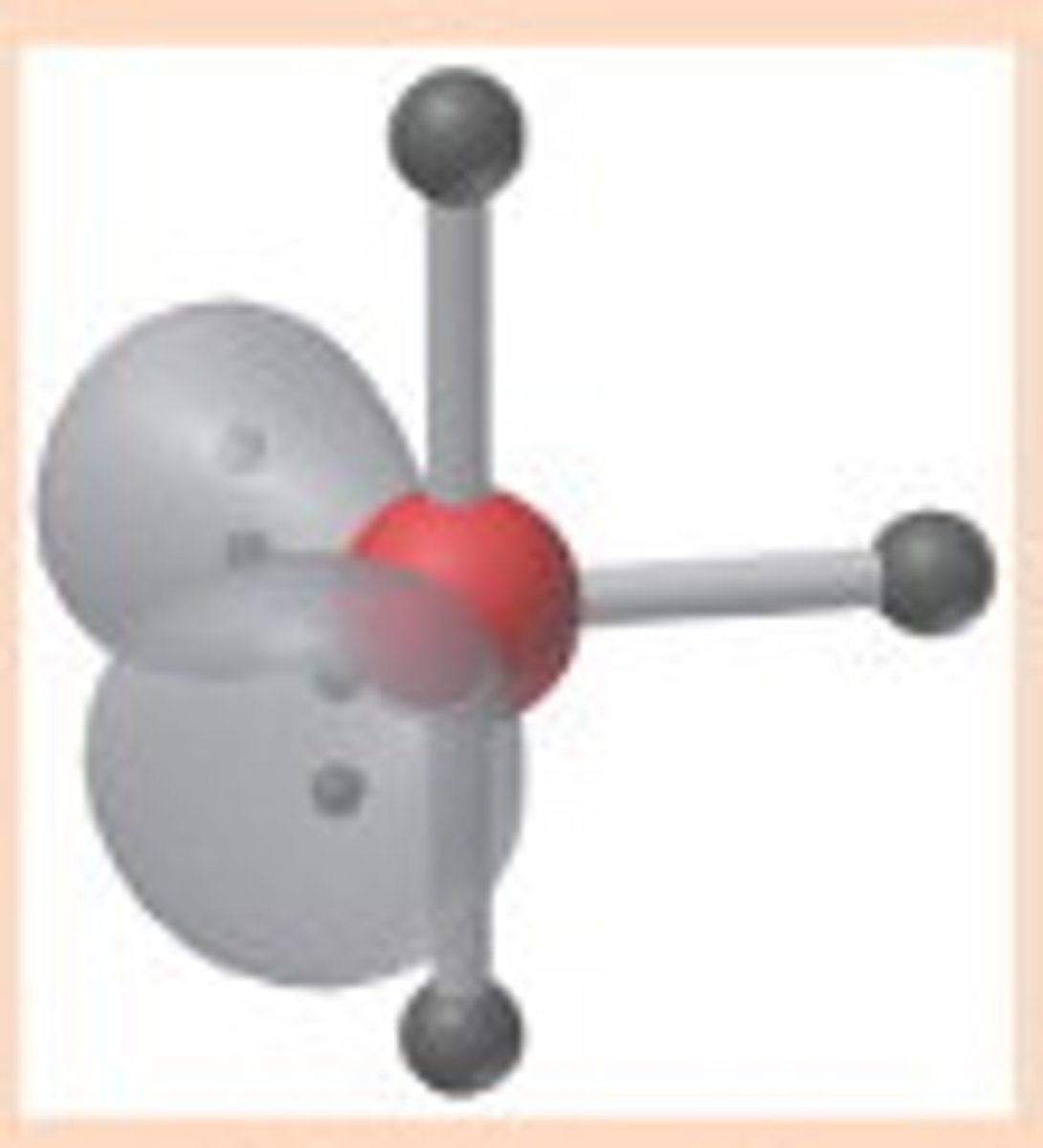
5 Electron Domains
5 bonding - trigonal bipyramidal
6 Domain Geometry
6 bonding - octahedral