Force vs Resistance/Magnitude vs Frequency
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Aeolian
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Sediment motion
Depends on the forces applied by agents of transportation and the resisting strength of the materials involved
Sediment flux
The movement of sediment through a system and is controlled by the balance between resisting and driving forces
Driving/motivating forces
-Shearing forces
-Gravitational force (influences weight)
-Lift force (fluids only)
-Buoyancy (fluids only)
Resisting/impending forces
-Gravitational force
-Intrinsic strength (varies according to material properties, especially grain size and moisture content)
-Friction and cohesion
Shear Stress
The force per unit bed area exerted by the shearing action of a mass moving over a surface (e.g. glacial/water/air/lava motion)
Shear Stress Equation
p= fluid density
g= gravity
D= thickness/depth
S= slope
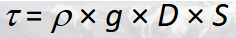
Shear Strength
Measures the ability of a material to withstand a shearing stress
Threshold
A condition which must be achieved for a system to pass from one state to another.
Threshold of Motion
The critical value of applied force required to overcome the resistance to motion. The particle(s) will start to be transported when this threshold of stress is exceeded. The lower velocities and larger grain size, the higher the threshold.
Cohesive Materials
Materials that predict the onset/spatial distribution of landsliding (such as muds, silts, clays)
Non-cohesive/granular materials
Materials that predict the onset of sediment transport in water/air flows (such as sand, gravel)
Sediment transport rate
A non-linear function of the variable flow discharge. Where there is an unlimited supply, observations show sediment transport increases rapidly with increasing flow/wind strength. However, it's very dependent on the capacity and supply, with a minimum threshold flow is needed to transport material
Other Factors Controlling Effectiveness of Geomorphic Events
– Sequencing
– Recovery, or Relaxation, versus Persistence
– Sediment availability
Complex Systems
A set of objects or characteristics which are related to one another and operate together as a complex entity
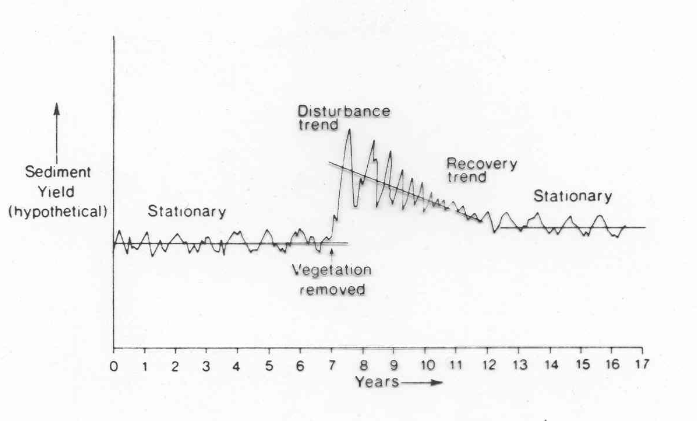
Equilibrium
The balance between form and process (includes static and dynamic equilibrium)
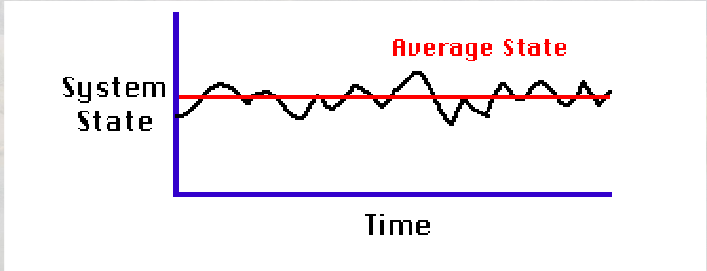
Steady State Equilibrium
Over time changes occur but these are very small and never cross the threshold (e.g. seasonal change)
Dynamic Equilibrium
Changes are big but not really changing the system
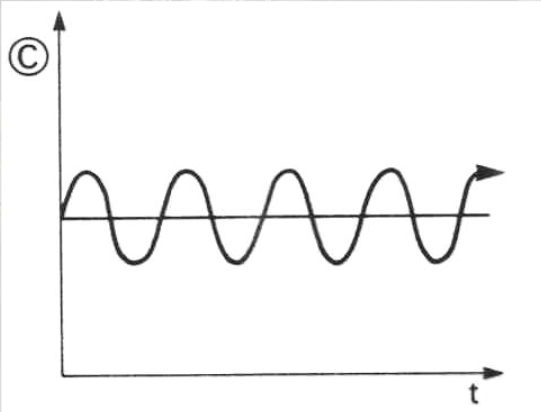
Periodic change
Constant and expected changes in a system (e.g. the tidal changes)
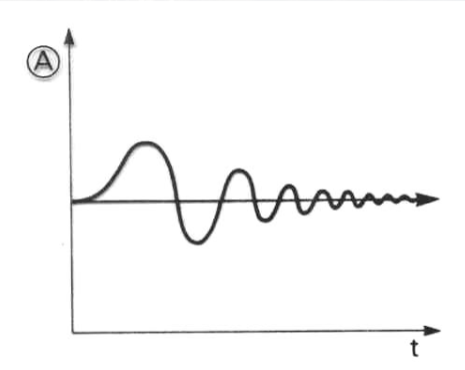
Dampened Behaviour
Sudden shock to the system which the system then adapts to
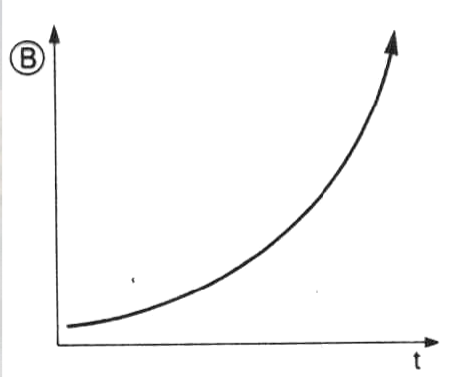
Explosive Behaviour
Some sudden/dramatic change in the system
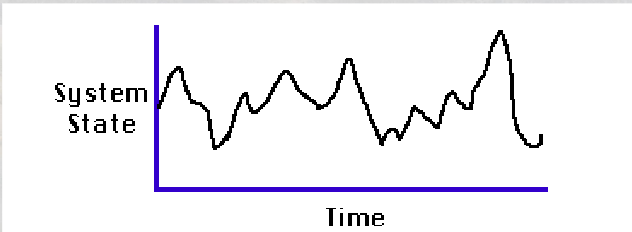
Unsystematic Behaviour
Behaviour that is unpredictable, such as unexpected consequences to change (due to interdependence)