Chapter 9: Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microbiology Exam 2 Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Paul Enrich
worked with dyes that specifically bind to microbial cells, reasoned that dyes could selectively destroy pathogens but not harm human cells, developed treatment for syphilis
The first antibiotic was ___ and it was rediscovered by ____
penicillin, Alexander Fleming
Selective toxicity
ability of a chemotherapeutic agent to kill or inhibit a microbial pathogen while providing little to no damage to the host
Antibiotics are produced by ____
fungi/bacteria
How is degree of selective toxicity expressed?
Therapeutic dose
Toxic dose
Therapeutic index
Therapeutic dose
drug level required for treatment of a particular infection
Toxic dose
drug level at which agent is too toxic for the host
therapeutic index
ratio of the toxic dose to the therapeutic dose
The (smaller or larger) the therapeutic index, the better the chemotherapeutic agent?
the larger the index, the better the agent
narrow spectrum drugs
drugs only effective against a limited variety of pathogens
broad spectrum drugs
target many different kinds of bacteria
True or False: Although a cidal agent kills the target pathogen, it may be static at low levels
True: remember the concentration of the microbial agent effects the affectiveness
minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
lowest concentration of a drug that prevent the growth of a particular pathogen
minimal lethal concentration (MLC)
lowest drug concentration that kills the pathogen
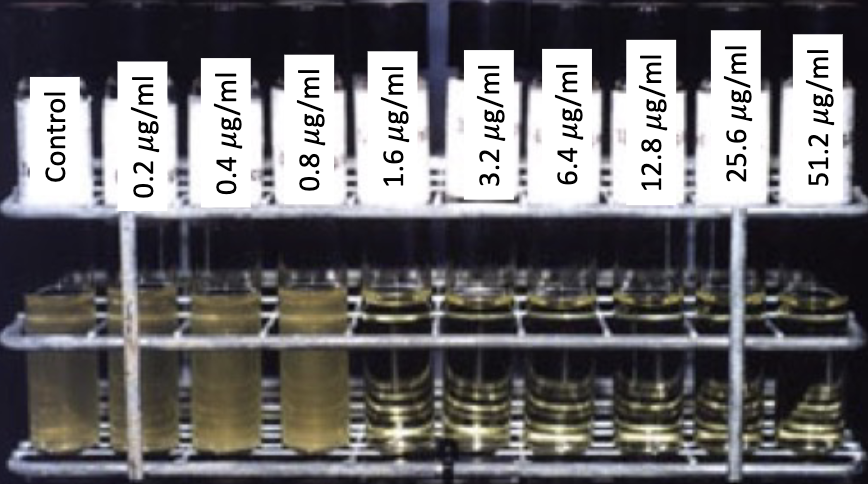
dilution susceptibility tests
MIC and MLC values can be determined be serially diluting the drug and adding consistent number of bacteria
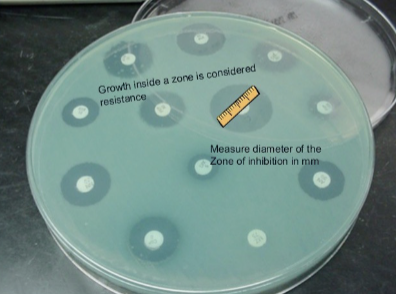
Disc diffusion assay
Able to monitor for resistance or susceptibility to multiple antibiotics, includes zone of inhibition

E-Test
Determine MIC on one test, strip has increasing concentrations of antibiotics
A challenge to develop new antibiotics is finding bacterial _____ or _____ not already targeted
structures or processes
The most selective antibiotics are those that interfere with _______ synthesis
bacterial cell wall
The most crucial feature of the penicillin molecule is _____ ?
B-lactam ring (beta lactam ring)
Transpeptidase
enzyme that forms peptidoglycan cross-links to add new units to a growing bacterial cell wall
What part of penicillin’s structure resembles the amino acids at the end of the peptidoglycan units side chain, D-alanyl-D-alanine? Hint: it is the terminal end of the penicillin molecule.
B-lactam ring
How does the B-lactam ring work to block bacterial cell wall formation ?
It’s structural similarity to D-alanyl-D-alanine, the terminal structure of peptidoglycan peptide chains, causes it to bind to transpeptidase blocking cell wall formation
What does PBP stand for?
Pencillin-binding proteins
What occurs after penicillin blocks cell wall formation?
Osmotic lysis.
True or False: Penicillins act only on growing bacteria
True: penicillin act on peptidoglycan synthesis, and therefore are only affective on bacteria actively synthesizing new peptidoglycan
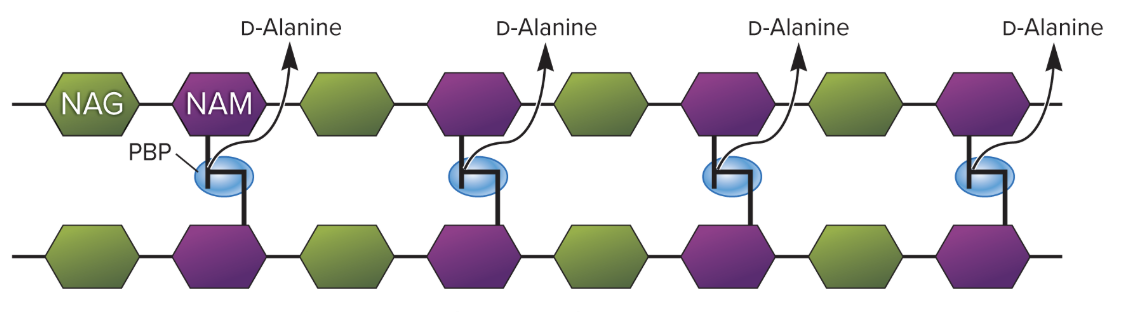
What does this diagram show?
Transpeptidase (aka PBP) forming peptide bonds/cross-links between parallal strands of peptidoglycan subunits
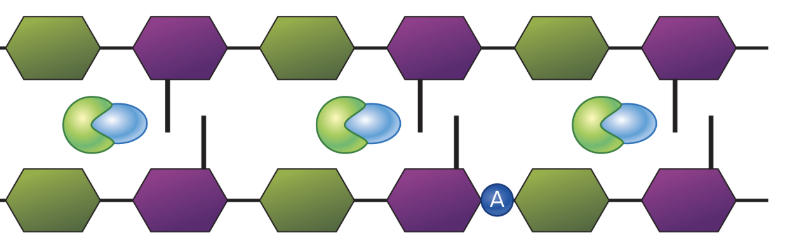
What is the function of the light green molecule that is engulfing the blue enzyme? Hint: the blue enzyme is a PBP
The light green represents penicillin’s B-lactam ring preventing transpeptidation and cell wall synthesis
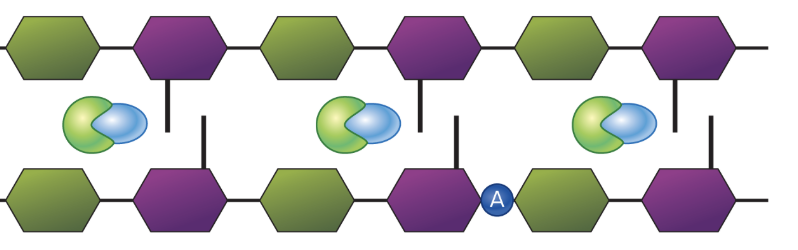
What does the dark blue A represent?
The A is bacterial autolysins (B-lactam rings increase the activity of bacterial autolysins which contribute to peptidoglycan degredation)
Penicillinase
enzymes produced by penicillin resistant bacteria
How do penicillinase work to inactivate penicillin?
They hydrolyze a bond in the B-lactam ring
What three consequences to bacterial cells are associated with Penicillin?
Inhibition of cell wall production
Disruption of transpeptidase
Swelling and eventually lysis of cell
What kind of inhibition is demonstrated with penicillin’s B-lactam ring and transpeptidase (PBP) D-alanyl-D-alanine end?
Competitive inhibition
What is B-lactam on peptidase similar in structure to? Hint: what does it competitively inhibit?
D-alanyl-D-alanine, terminal structure on peptide chains
vancomycin
glycopeptide antibiotic produced by bacterium streptomyces orientalis
How is vancomycin blocking peptidoglycan synthesis different than penicllin?
Instead of binding to PBPs like B-lactam antibiotics, vancomycin binds to the enzyme’s substrate itself
True or False: vancomycin is bacteriacidal only for Gram-negative bacteria
False: Vancomycin is only effective against Gram-positive bacteria because it cannot penetrate the Gram-negative outer membrane
what does vancomycin bind to?
D-alanyl-d-alanine terminal sequence
protein synthesis inhibitors
inhibition of protein synthesis by binding bacterial ribosomal proteins or rRNA
what are two examples of cell wall synthesis inhibitors
Penicillin and vancomycin
aminoglycosides
bind to 30s ribosomal subunit and stops peptide bond formation
tetracyclines
four-ring structure with a variety of side chains attached
Tetracyclines and Aminglycosides target the ___ subunit of the ribosome
30 S
True or False: Tetracyclines are broad spectrum and bacteriostatic
True: tetracyclines are effective against most bacteria, but do not kill them (only inhibit growth)
True or False: Aminoglycosides, like Tetracyclines, are bacteriostatic antibiotics
False: Aminoglycosides are bacteriocidal, which means that bacterial cells are killed not just inhibited
Aminoglycosides treat Gram _______ bacterial cells
Negative
Metabolic antagonists
drugs act as antimetabolites, as they block the functioning of metabolic pathways as they are structural analogs of the substrates for enzymes in the pathways (competitive inhibition)
Metabolic antagonists are (broad or narrow) spectrum?
They are broad spectrum and can prevent metabolic activity across various bacteria
Sulfa drugs (sulfonamides)
used for bacteria that make their own folic acid, these antibiotics prevents the synthesis of purines in bacteria that use PABA to make folic acid (competitive inhibition, drug is structural analog to PABA)
what enzymes does nucleic acid synthesis inhibition target?
Inhibition of DNA polymerase, topoisomerases, RNA polymerases
What enzyme(s) specifically do Fluoroquinolones inhibit?
Dna polymerase and topoisomerase
What enzyme(s) specifically do Rifamycin target?
RNA polymerase
Why are drugs that work to inhibit nucleic acid synthesis not as selectively toxic as other antibiotics?
Bacteria and eukaryotes do not differ greatly with respect to nucleic acid synthesis
How do most antiviral drugs work?
inhibiting virus-specific enzymes and virus replication cycle processes
What are the two types of drug resistance methods?
Intrinsic and Acquired
Intrinsic resistance
resistance due to a property bacteria already possesses, example: resistanve to B-lactam antibiotics due to lacking a cell wall
Acquired resistance
Change in the genome of a bacterium that converts it to one that is resistant to an antibiotic, example” acquiring mutations or genetic material
drug-tolerant bacteria
lack mechanisms for anti-biotic resistance and therefore “ignore” the presence of antibiotics
Acquired drug resistance mechanisms (5)
destroying the antibiotic
adding modifying groups to the antibiotic
modifying target so it no longer bind antibiotic
pumps antibiotic out of the cell
using alternative biochemical reactions
How does drug resistance develop?
due to flexibility of genomes, mutations can occur and resistance genes can transfer
what is the function of effux pumps?
pumping the drug out of the cell after it has entered, usually drug/proton antiporters
What are we doing to contribute to antibiotic resistance? (3)
Overprescribing antibiotics
Not taking the correct dosage of antibiotics
Overusing antibiotics in agriculture
How can we fight against antibiotic resistance?
Co-administering drugs
Synergy between antibiotics of different classes
Developing faster and better diagnostics
New strategies to fight/prevent infections
What is the difference between an E-test and the Kirby-Bauer assay? (i-clicker question)
An E-test can determine the concentration of antibiotic needed to inhibit growth