2.2 Organisational structure
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Organizational structure
The formal interrelationships + hierarchical arrangements of HR in a business
What does the organizational structures arrange employees to show?
Job titles
Accountability
Responsibility
Accountability
Extent to which person is held responsible for a specific job
Its success / failure
Allows senior managers to have better control over the running of their organisations
Responsibility
Who is in charge of whom + in what role + capacity
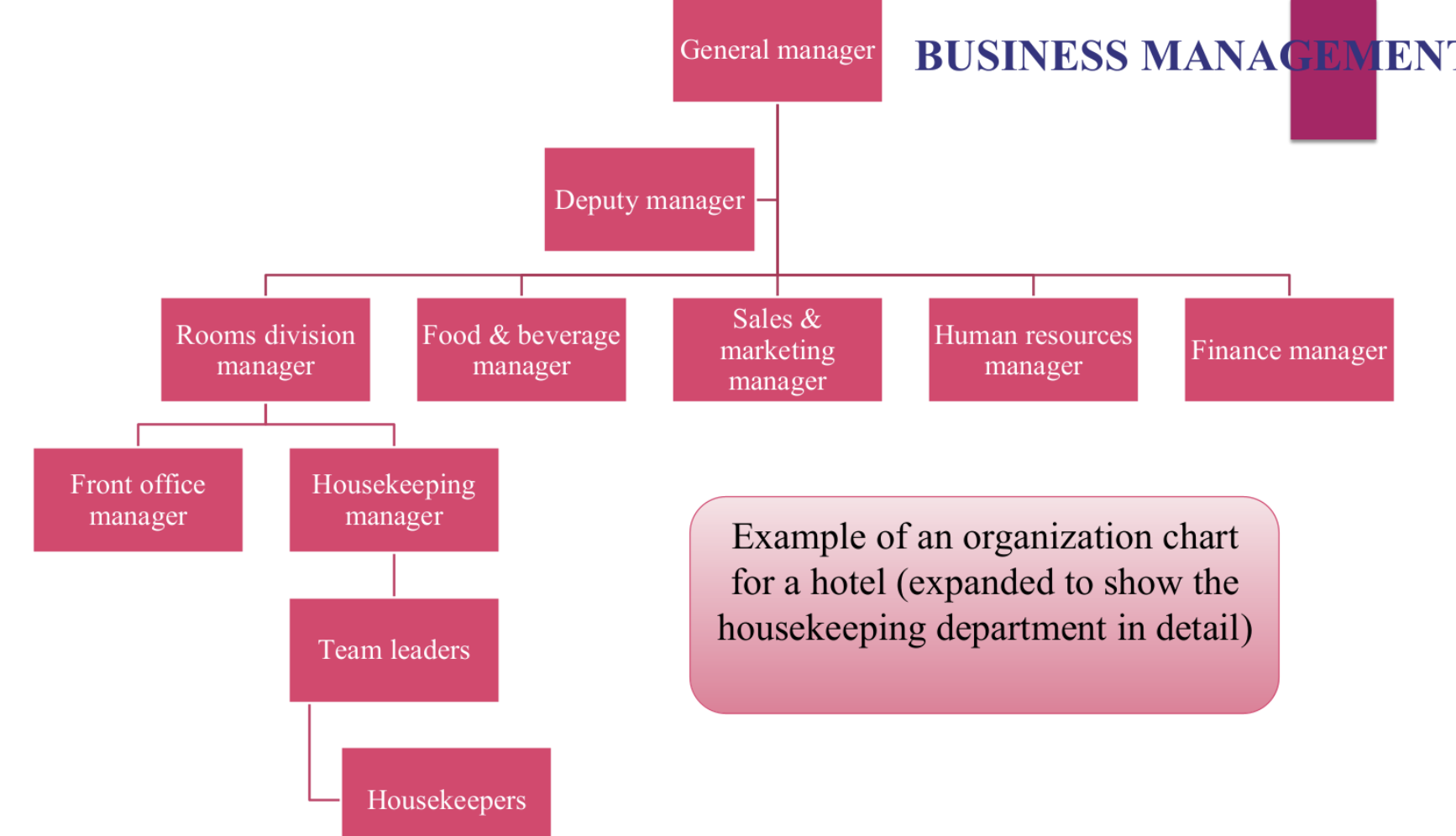
Organisation chart
Diagram
Shows firm’s formal structure of HR
Delegation
Managers pass on control + decision-making authority to subordinates
But retain responsibility for the task
Pros of delegation
Motivates employees (lower in OS). Feel trusted
Manager = less tasks = saves time. More time for strategic, core work.
Cons of delegation
Training costs- train employees for new responsibilities
Risk of error if inexperienced employees make mistakes
Manager hesitate to delegate- fears loss od control
SMARTER delegation
Specific- clearly define tasks
Measurable- quantifiable results to measure success
Agreed- to avoid misunderstandings, eg deadlines
Realistic
Time-bouind
Ethical- delegate boring work = demotivating
Recorded- can credit staff for accomplishments
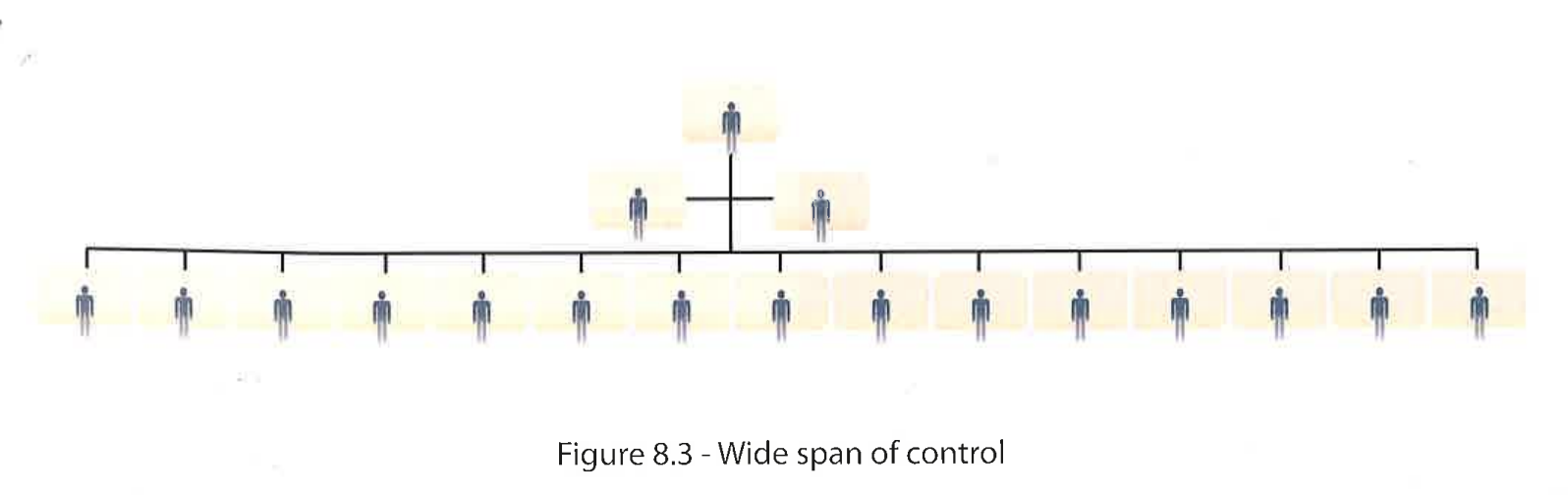
Span of control
No. of subordinates overseen by a manager,
Directly accountable to the manager
Greater seniority of manager =
greater SOC
Wide SOC
More subordinates per manager
Encourages autonomy but may overwhelm managers
Pro of wide SOC
Fewer layers needed in the OS = fewer managers = cost control
Narrow SOC
Fewer subordinates per manager
Allows for close supervision but higher management costs
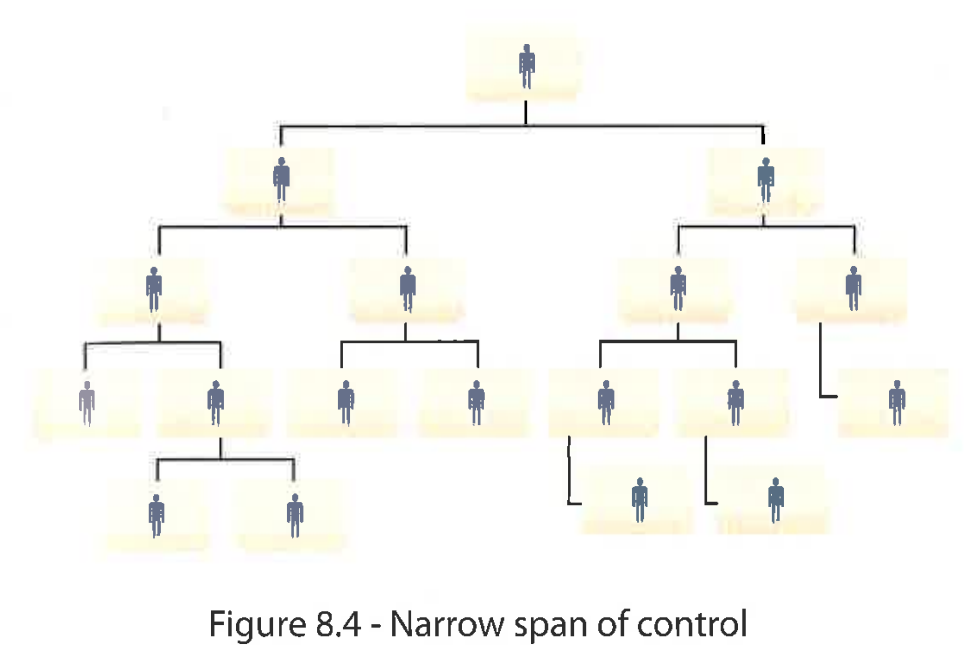
Pros of narrow SOC
Easier to communicate + control
Small teams = more productive, better team spirit, less conflict
Factors affecting the degree of control given to managers (MOST)
Manager
More skilled + experienced = wider SOC
Organisational culture
Democratic culture, tend to delegate more = wider SOC
Subordinates
High skilled staff work in smaller teams = wider SOC
Task
Complex, urgent task = narrow SOC (communication is imp)
Mass produced products, less supervision, simple tasks = wider SOC
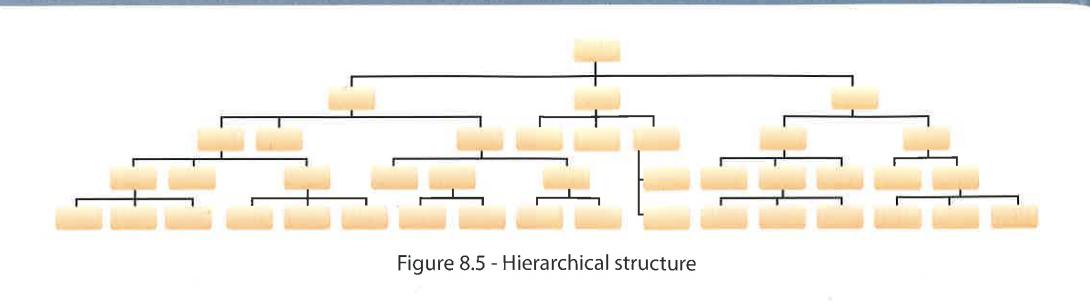
Hierarchy
Organizational structure based on a ranking system
Each level = diff rank w diff degree of authority + responsibility
Most skilled / senior employees at the top
Levels of hierarchy
The no. of layers of formal authority in an organization
No. of levels shown in organization chart
Line managers
The person directly above an employee in the organizational structure
Manager
Responsible for the day-to-day running of the business / department within the organization
Pros of using hierarchal structures
Shows clear lines of authority in the firm → improves coordination + productivity of workers
Establishes teams → sense of belonging in workplace → motivating
Cons of using hierarchal structures
Departments → works isolated from official teams
Inflexible. Issue when changes in external environment need flexible structural changes in firm
Chain of command
The formal line of authority, thru which formal communications + orders are passed down
Shown on OC
Short vs long chain of command
Short = firm w few levels of hierarchy
Long = firm w many levels of hierarchy
Bureaucracy
Execution of tasks that are governed by official administrative + formal rules. Govern business activity
Includes: prescribed rules + policies, standardized procedures, formal hierarchical structures.
Why can bureaucracy be a source of inefficiency + frustration?
Due to:
Must fill out excessive paperwork often
Long official chains of command
Managers w duplicate roles + responsibilities
Staff working in multiple departments → need to report to several managers
SO SLOWS DOWN DECISION MAKING + LESS CREATIVITY
Why can bureaucracy be a source of efficency?
Div of labour for administrative tasks
Characteristics of a bureaucratic organisation (complete, pg 115)
Continuity- follows official rules, n
Rules
Hierarchal structure
Accountibility
Centralisation
When the majority of decision making is done by a v small no of people who hold decision-making authority + responsibility
Usually the senior leadership team
Don’t consult others
Pros of centralisation
Rapid decision-making
Better control
Better sense of direction
Efficiency
Cons of centralisation
Added stress for senior staff
Inflexibility
Possible delays in decision making
Demotivating
Decentralisation
When decision-making authority + responsibility are shared w a large no. of ppl in the organisation
Pros of decentralisation
Input from the workforce
Quicker decision-making
Improved morale
Improved accountability
Teamwork
Cons of decentralisation
Expensive
Inefficiencies
Greater chances of mistakes
Loss of control
Communication issues
Factors affecting if a firm should be centralised or decentralised
Size of organisation
Importance of decision
Risk level
Corporate culture
Management attitudes + competences
ICT usage
Factors affecting if a firm should be centralised or decentralised: Size of organisation
Larger firm = decentralised
Factors affecting if a firm should be centralised or decentralised: Importance of decision / risk level
Imp / high-cost decisions / high risk = centralised
Delayering
Process of removing levels in the hierarchy to flatten the organizational structure
→ Widens the span of control in the hierarchy
Purpose of delayering
Widen the SOC at each level
Shorten the chain of command
Pros of delayering
Reduces costs
Improves communication speed
Encourages delegation + empowerment
Cons of delayering
Creates anxiety
Increases workloads
Slower decision-making
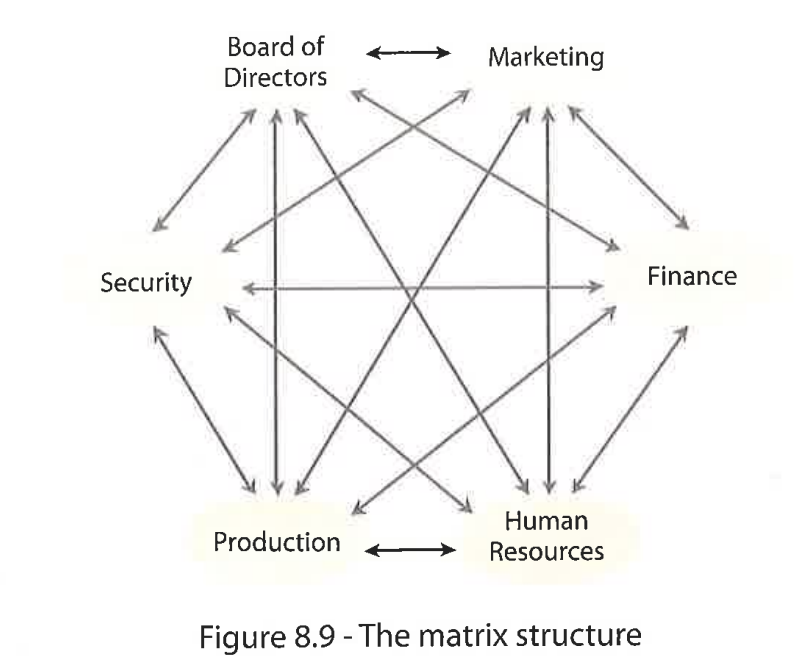
Matrix structure
Employees from diff departments temporarily work tog on a specific project
Flexible organisational structure
Which 2 managers is each member of the matrix organisation held accountable to?
Department / line manager
Project manager (from the matrix)
Pros of the matrix structure
Improved communications
Maximises skills set of the workforce
Cost-effective
Cons of the matrix structure
Added workloads
Difficult to coordinate
Time consuming
Organization charts
Shows firm's formal structure of human resources on a diagram
5 types of organisation charts
Flat/horizontal
Tall/vertical
By product
By function
By region
5 features organizational charts show
Functional department
Chain of command
Span of control\
Channels of communication
Levels of hierarchy
Flat / horizontal organisational structure
Only a few layers in the formal hierarchy
→ managers have a wide SOC
Pros of flat / horizontal organizational structures
Delegation is imp → more opportunities for career development for subordinates
Improved communication bc fewer layers
Cheaper to operate bc fewer managers
Reduces power distance betw
senior + junior staff.
What type of work cultures would flat organizational structures be in?
Creative
Innovation
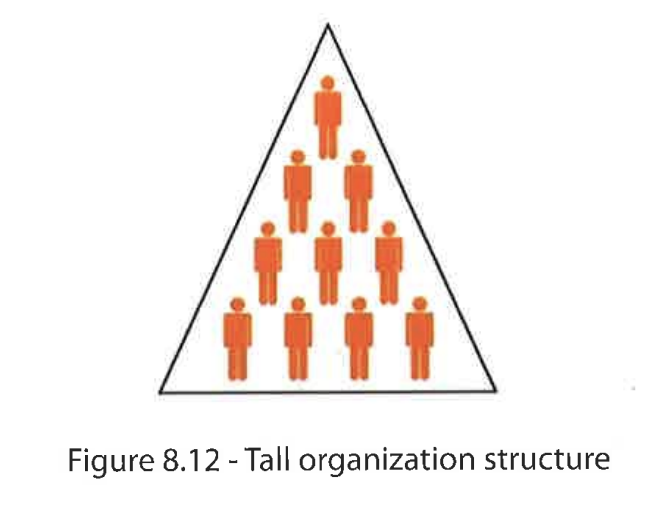
Tall / vertical organization structure
Many layers in the hierarchy
→ managers have a narrow SOC
Pros of tall / vertical organizational structures
Smaller teams → quicker communication
Smaller teams → easier to control
Greater div of labour → increase efficency + productivity.
Managers spend less time monitoring their teams
More opportunities for promotion → motivating
Bc more levels in hierarchy
Pros of tall structures = cons of horizontal
Pros of horizontal = cons of vertical
Organization by product
Structuring a workforce based on g/s produced or sold.
Each department focuses on a diff product within the organization's overall product portfolio.
Organization by function
Structuring a workforce based on business functions
Eg roles / tasks
Marketing / finance
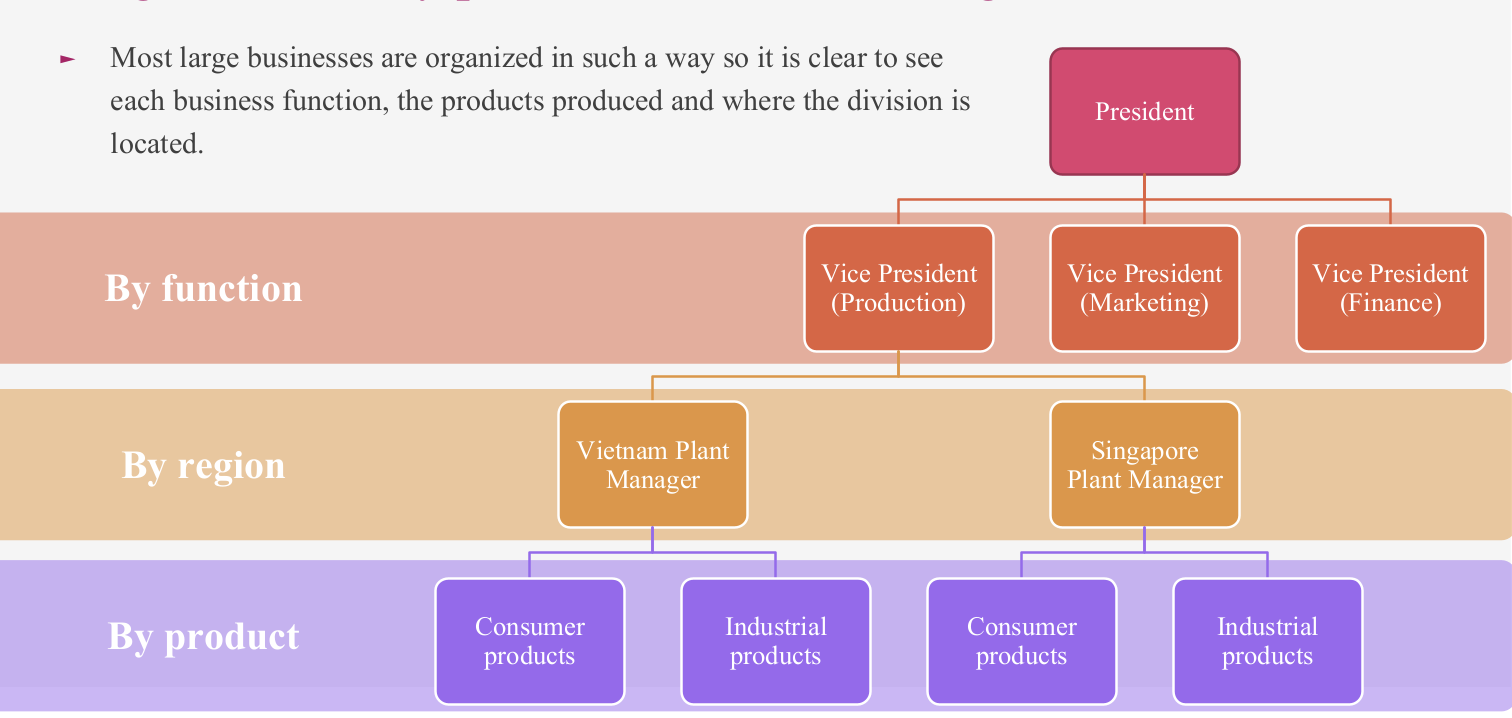
Organization by region
Structuring a workforce based on diff geographical areas
Based on where the firm's operations are
Organization restructuring
Reorganizing of human resources of a firm into a new organizational structure
General reason for organization restructuring
Need for change to remain competitive in a changing business external environment
Flexible structure → adapt to changes in internal + external business environment
Reasons for restructuring a firm
Incorporate new job roles + eliminate redundant roles
Reduce costs/debt
Concentrate on key business activities
Incorporate new technology
Ensure skills + expertise of employees are used effectively
Sell a part of the firm’s business activities
Merge with another company
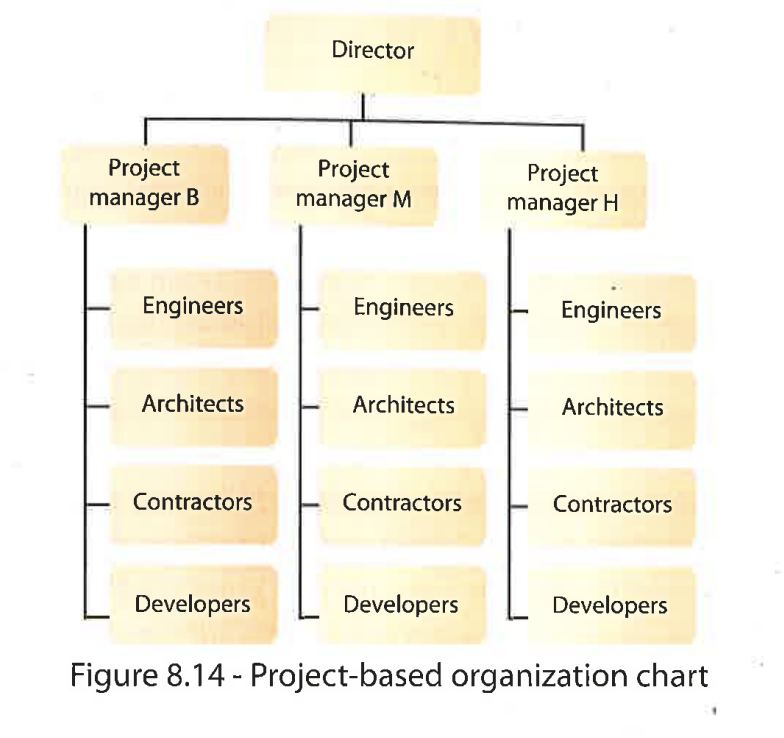
Project based organization
Arranges HR around particular projects, each led by a project manager
Purpose of the project based organization structure
Increased flexibility to:
Adjust quickly to market changes
Adopt rapid innovations
Examples of industries that use PBO organization structure
Construction
Software engineering
Entertainment
Aerospace
Oil exploration
Pros of PBO
Flexibility
Productivity
Efficiency
Motivational
Cons of PBO
Discontinuity
Isolation
Inefficiencies
Conflicting interest + priorities

Shamrock Organization
Handy's model:
Organizations are increasingly made up of core staff who are supported by peripheral + outsourced workers
(consisting of consultants and contractors)
How did Handy propose human resources should be organized?
(3 groups of workers in the Shamrock Organization)
Core staff
Peripheral workers
Outsourced workers
Core workers / professional core
Full-time specialists (professionals) who are vital for the organization's operations + survival
Purpose of core works
Contributes to firms operation, growth survival
Handle daily operations of
the business
Peripheral workers
Contingent workers
Includes part-time + temporary staff hired by the organization to provide greater flexibility
Purpose of peripheral workers
Provide greater flexibility to the firm → to adapt to changes in the external environment
Employed when needed (short time periods) → reduces overall labour costs
Contract / outsourced workers
Individuals / organizations hired on a contract basis to carry out specific but non-core roles
Purpose of hiring contract workers
So firm can focus on their core activities
Pros of Shamrock Organisation
Core workers = imp → well-paid, remunerated → job security → motivated + productive
Peripheral workers provide flexibility
Cons of Shamrock Organisation
Peripheral workers → lack of job security → harms morale
Outsourced workers = experts = expensive