lecture 8 microbial metabolism
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
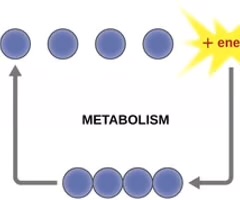
Metabolism
All the chemical reactions that take place inside a cell.
Exergonic reactions
Reactions that are spontaneous and release energy.
Endergonic reactions
Reactions that require energy to proceed.
Anabolism
Endergonic metabolic pathways involved in biosynthesis, converting simple molecular building blocks into more complex molecules, and fueled using cellular energy.
Catabolism
Exergonic pathways that break down complex molecules into simpler ones.
Autotrophs
Organisms that convert inorganic carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic carbon compounds.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that rely on organic molecules for energy, growth, and reproduction.
Oxidation-reduction reactions
Reactions that are important in metabolism for energy transfer.
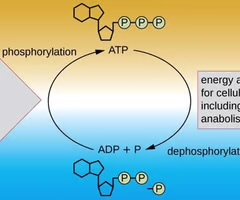
ATP
A high-energy molecule used to drive anabolic pathways.
FAD
A coenzyme involved in redox reactions in metabolism.
NAD+
A coenzyme that plays a key role in redox reactions.
NADP+
A coenzyme that is involved in anabolic reactions.
Enzyme structure
The structural components of an enzyme that facilitate biochemical reactions.
Competitive enzyme inhibitors
Molecules that compete with substrate for binding to the active site of an enzyme.
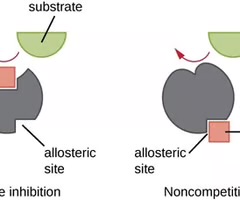
Noncompetitive enzyme inhibitors
Molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, reducing its activity.
Glycolysis
A metabolic pathway that is not oxygen dependent and yields three-carbon molecules, ATP, and NADH.
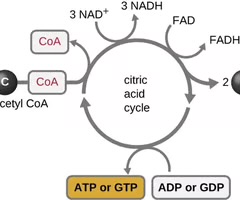
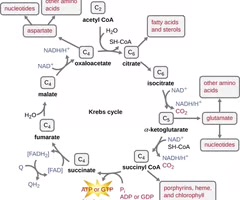
Krebs cycle
A metabolic pathway that yields CO2, GTP/ATP, FADH2, and NADH.
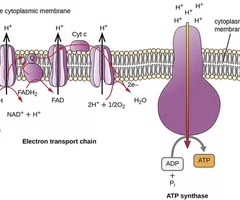
Electron transport system
A system that functions in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells for ATP production.
Substrate-level phosphorylation
A method of producing ATP by directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP.
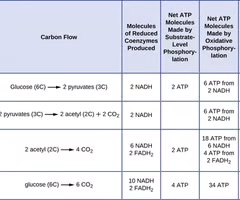
Oxidative phosphorylation
A method of producing ATP that involves the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Chemiosmosis
The process by which ATP is produced using the proton motive force.
ATP synthase
An enzyme that synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Aerobic respiration
A metabolic process that requires oxygen to produce ATP.
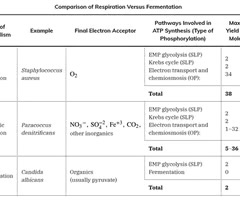
Anaerobic respiration
A metabolic process that does not require oxygen to produce ATP.
Fermentation
A metabolic process that does not require oxygen and involves the conversion of sugars to acids, gases, or alcohol.
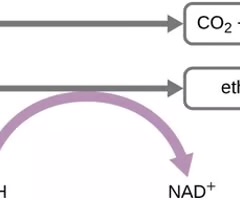
Fermentation pathways
Metabolic routes that lead to the production of end products like alcohol or acids.
Lipid catabolism
The breakdown of lipids to generate energy and identify microbes.
Protein catabolism
The breakdown of proteins to generate energy and identify bacteria.
Examples of Heterotrophs
Many organisms, ranging from humans to many prokaryotes, including the well-studied Escherichia coli, are heterotrophic.
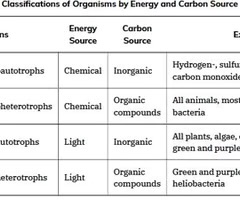
Energy Source Classification
Organisms can also be identified by the energy source they use.
Electron Transfer
All energy is derived from the transfer of electrons, but the source of electrons differs between various types of organisms.
Photo-
The prefix photo- refers to the energy sources that various organisms use, specifically light.
Chemo-
The prefix chemo- refers to the energy sources that various organisms use, specifically chemicals.
Phototrophs
Those that get their energy for electron transfer from light are phototrophs.
Chemotrophs
Chemotrophs obtain energy for electron transfer by breaking chemical bonds.
Organotrophs
Organotrophs, including humans, fungi, and many prokaryotes, are chemotrophs that obtain energy from organic compounds.
Lithotrophs
Lithotrophs are chemotrophs that get energy from inorganic compounds, including hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and reduced iron.
Lithotrophy
Lithotrophy is unique to the microbial world.
Chemoheterotrophs
Most organisms are chemoheterotrophs because they use organic molecules as both their electron and carbon sources.
Oxidation Reactions
Reactions that remove electrons from donor molecules, leaving them oxidized, are oxidation reactions.
Reduction Reactions
Reactions that add electrons to acceptor molecules, leaving them reduced, are reduction reactions.
Redox Reactions
Oxidation and reduction occur in tandem, and these pairs of reactions are called oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions.
Energy Carriers
The energy released from the breakdown of the chemical bonds within nutrients can be stored either through the reduction of electron carriers or in the bonds of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Mobile Electron Carriers
In living systems, a small class of compounds functions as mobile electron carriers, molecules that bind to and shuttle high-energy electrons between compounds in pathways.
Principal Electron Carriers
The principal electron carriers we will consider originate from the B vitamin group and are derivatives of nucleotides; they are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate, and flavin adenine dinucleotide.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
ATP is often called the 'energy currency' of the cell.
Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP)
At the heart of ATP is a molecule of adenosine monophosphate (AMP), which is composed of an adenine molecule bonded to a ribose molecule and a single phosphate group.
Ribose
Ribose is a five-carbon sugar found in RNA, and AMP is one of the nucleotides in RNA.
Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP)
The addition of a second phosphate group to AMP results in the formation of adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
Dephosphorylation of ATP
The energy released from dephosphorylation of ATP is used to drive cellular work, including anabolic pathways.
Phosphorylation
ATP is regenerated through phosphorylation, harnessing the energy found in chemicals or from sunlight.
High-energy phosphate bonds
The bonds between phosphate groups in ADP and ATP that are inherently unstable due to repulsion.
Dephosphorylation
The process of breaking high-energy bonds to release inorganic phosphate (Pi) or pyrophosphate (PPi) from ATP, releasing energy.
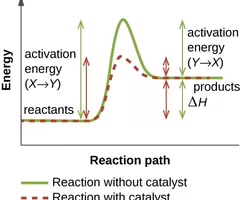
Catalyst
A substance that helps speed up a chemical reaction and is reusable because it is not used or changed during the reaction.
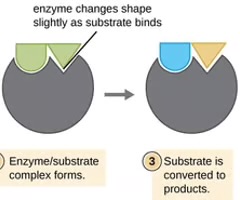
Enzymes
Proteins that serve as catalysts for biochemical reactions inside cells by lowering the activation energy.
Activation energy
The energy needed to form or break chemical bonds and convert reactants to products.
Substrates
The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds.
Active site
The location within the enzyme where the substrate binds.
Induced fit
The active-site modification in the presence of substrate, along with the formation of the transition state.
Cofactors
Inorganic ions such as iron (Fe2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) that help stabilize enzyme conformation and function.
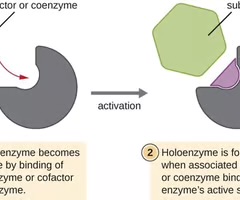
Coenzymes
Organic helper molecules required for enzyme action, which are not consumed and are reusable.
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that requires a bound zinc ion (Zn2+) as a cofactor to function.
Coenzyme A (CoA)
A coenzyme that often binds to the enzyme's active site, aiding in the chemistry of the transition of a substrate to a product.
Apoenzyme
An enzyme lacking a necessary cofactor or coenzyme and is inactive.
Holoenzyme
An enzyme with the necessary associated cofactor or coenzyme and is active.
NADH
A commonly used coenzyme that provides high-energy electrons.
Competitive Inhibitor
A molecule similar enough to a substrate that it can compete for binding to the active site.
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
An inhibitor that binds to the enzyme at an allosteric site and blocks substrate binding by inducing a conformational change.
Allosteric Inhibitor
A noncompetitive inhibitor that binds to a site other than the active site.
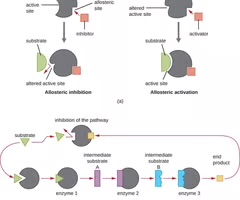
Allosteric Activator
A molecule that binds to locations on an enzyme away from the active site, increasing the affinity of the enzyme's active site for its substrate.
Feedback Inhibition
The use of a pathway product to regulate its own further production.
Chemoheterotrophic Organisms
Organisms that obtain energy by breaking down organic compounds.
Catabolism of Carbohydrates
Extensive enzyme pathways exist for breaking down carbohydrates to capture energy in ATP bonds.
Anabolic Reactions
Metabolic processes that build larger molecules from smaller ones.
Catabolic Reactions
Metabolic processes that break down larger molecules into smaller ones.
Conformational Change
A change in the shape of an enzyme that can affect its activity.
Enzyme Regulation
The process by which enzyme activity is increased or decreased by various molecules.
Ionic Bonds
Chemical bonds formed through the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds formed between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom.
Covalent Bonds
Strong bonds formed when atoms share electrons.
Intermediate Molecules
Molecules produced during catabolic pathways that can also serve as building blocks for anabolism.
Escherichia coli
A bacterium used to study metabolism due to its ease of manipulation.
Catabolic pathways
Pathways that produce intermediate molecules used as building blocks for anabolism.
Carbohydrate catabolism
The typical example used to introduce concepts of metabolism to students.
Amylase
An enzyme that breaks down glycogen or starch.
Cellulases
Enzymes that break down cellulose.
Hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds
The process that releases glucose for further catabolism.
Energy production in glycolysis
Glycolysis produces energy, reduced electron carriers, and precursor molecules for cellular metabolism.
Oxygen in glycolysis
The process does not use oxygen but can be coupled with aerobic or anaerobic processes.
Location of glycolysis
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Pyruvate
A three-carbon sugar that glycolysis ends with, which may be further broken down for energy.
Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) pathway
The type of glycolysis found in animals and most common in microbes.
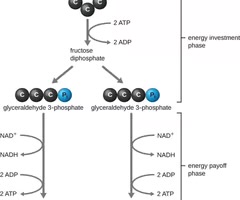
Energy investment phase
The first part of the EMP pathway that uses energy from two ATP molecules to modify glucose.
Energy payoff phase
The second part of the EMP pathway that oxidizes G3P to pyruvate, producing four ATP molecules and reducing NAD+ to NADH.
Net gain from glycolysis
The breakdown of a single glucose molecule yields 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 Pyruvate.
Entner-Doudoroff (ED) pathway
An alternative glycolytic pathway used by some prokaryotes, named after its discoverers.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
A gram-negative pathogen that contains only the ED pathway for glycolysis.
E. coli
A bacterium that can use either the ED pathway or the EMP pathway for glycolysis.
Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)
A third type of glycolytic pathway that occurs in all cells and is different from the EMP and ED pathways.
Biosynthesis of nucleotides and amino acids
The intermediates from the PPP are used for this purpose.