skeletal system exam
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
What are the primary functions of the skeletal system?
Support and protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell production (hemopoiesis), and triglyceride storage.
What is hemopoiesis?
The production of red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and platelets.
What type of tissue is cartilage?
A type of connective tissue composed of collagen or elastic fibers and associated matrix materials.
What is the function of hyaline cartilage?
Provides flexibility and support, reduces friction, and absorbs shock; it forms a temporary skeleton in the fetus and covers articular surfaces of joints.
What distinguishes fibrocartilage from other types of cartilage?
Fibrocartilage is the strongest type, made up of thick bundles of collagen fibers providing strength and rigidity.
What is the primary function of elastic cartilage?
Maintains the shape of various structures while providing strength and elasticity.
What are the main components of a long bone?
Cortical bone, spongy bone, red and yellow bone marrow, and various types of connective tissue.
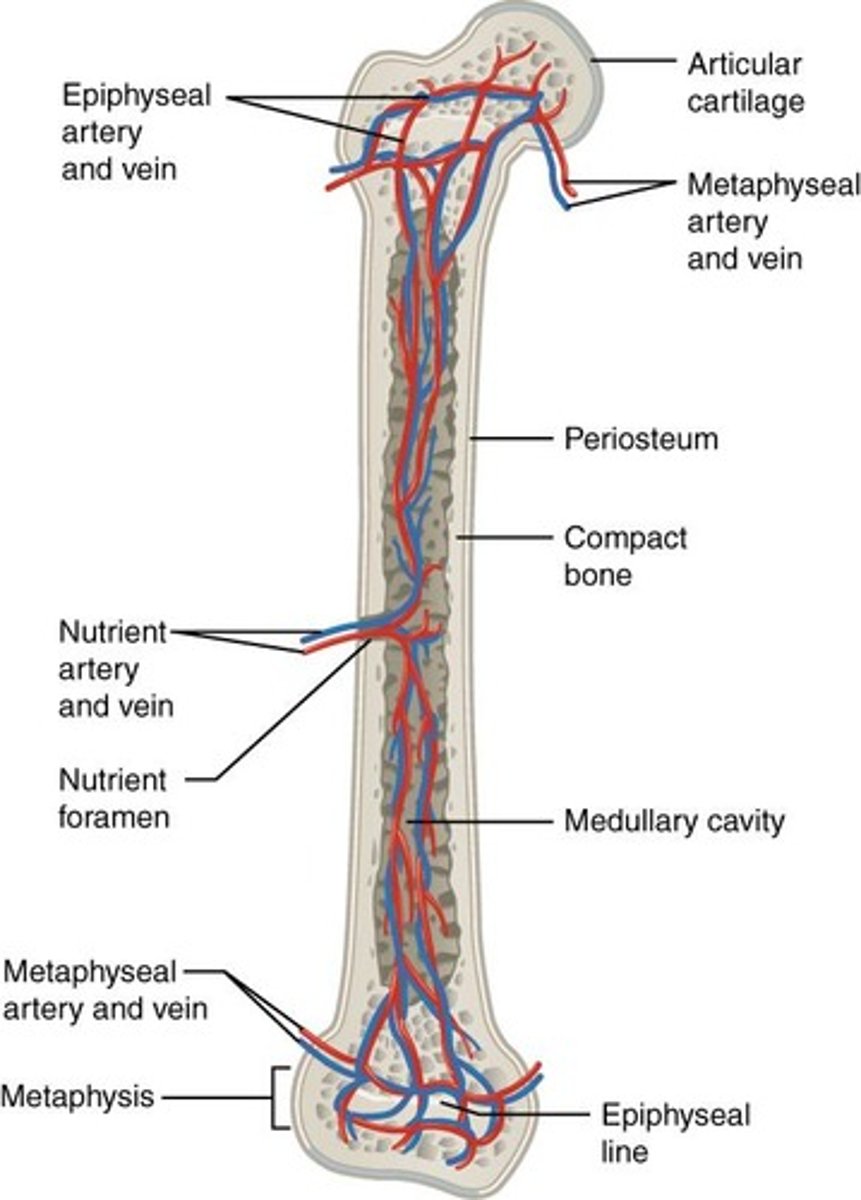
What is the diaphysis of a long bone?
The shaft of the bone, which contains a thick layer of compact bone and a hollow medullary cavity.
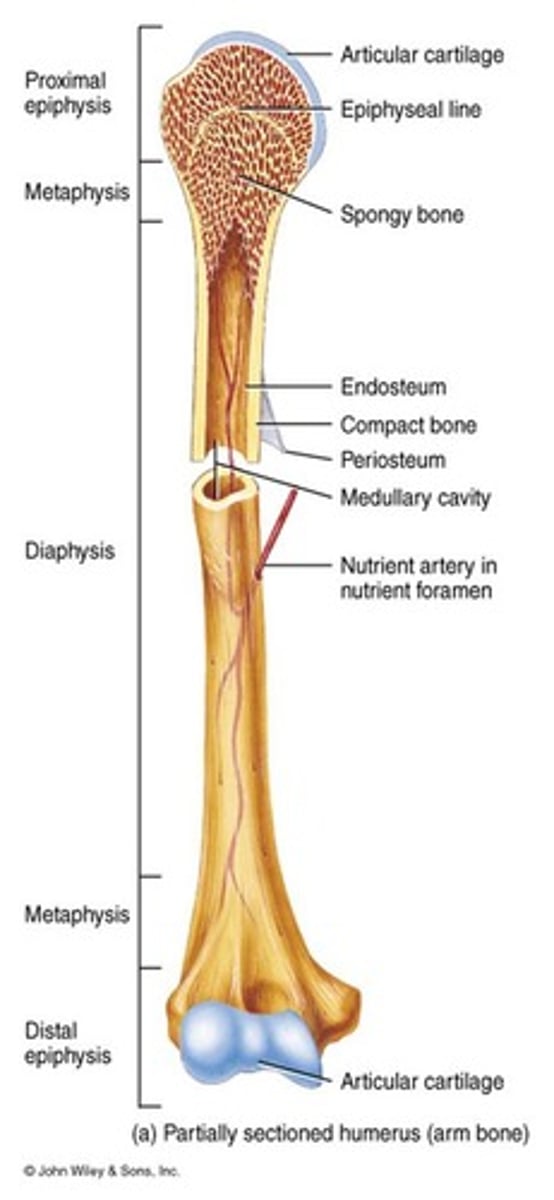
What is the role of the epiphysis in long bones?
The rounded ends of long bones filled with spongy bone containing red bone marrow, covered by compact bone.
What is the metaphysis in long bones?
The region between the diaphysis and epiphyses, containing the epiphyseal plate or line.
What is the periosteum?
A fibrous membrane covering the exterior of bones, consisting of an outer fibrous layer and an inner osteogenic layer.
What is the function of the endosteum?
Covers internal bone surfaces facing the medullary cavity and contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
What types of arteries supply the bone?
Periosteal arteries, nutrient artery, metaphyseal arteries, and epiphyseal arteries.
What is the composition of the extracellular matrix of bone tissue?
15% water, 30% collagen fibers, and 55% crystallized mineral salts, primarily calcium phosphate.
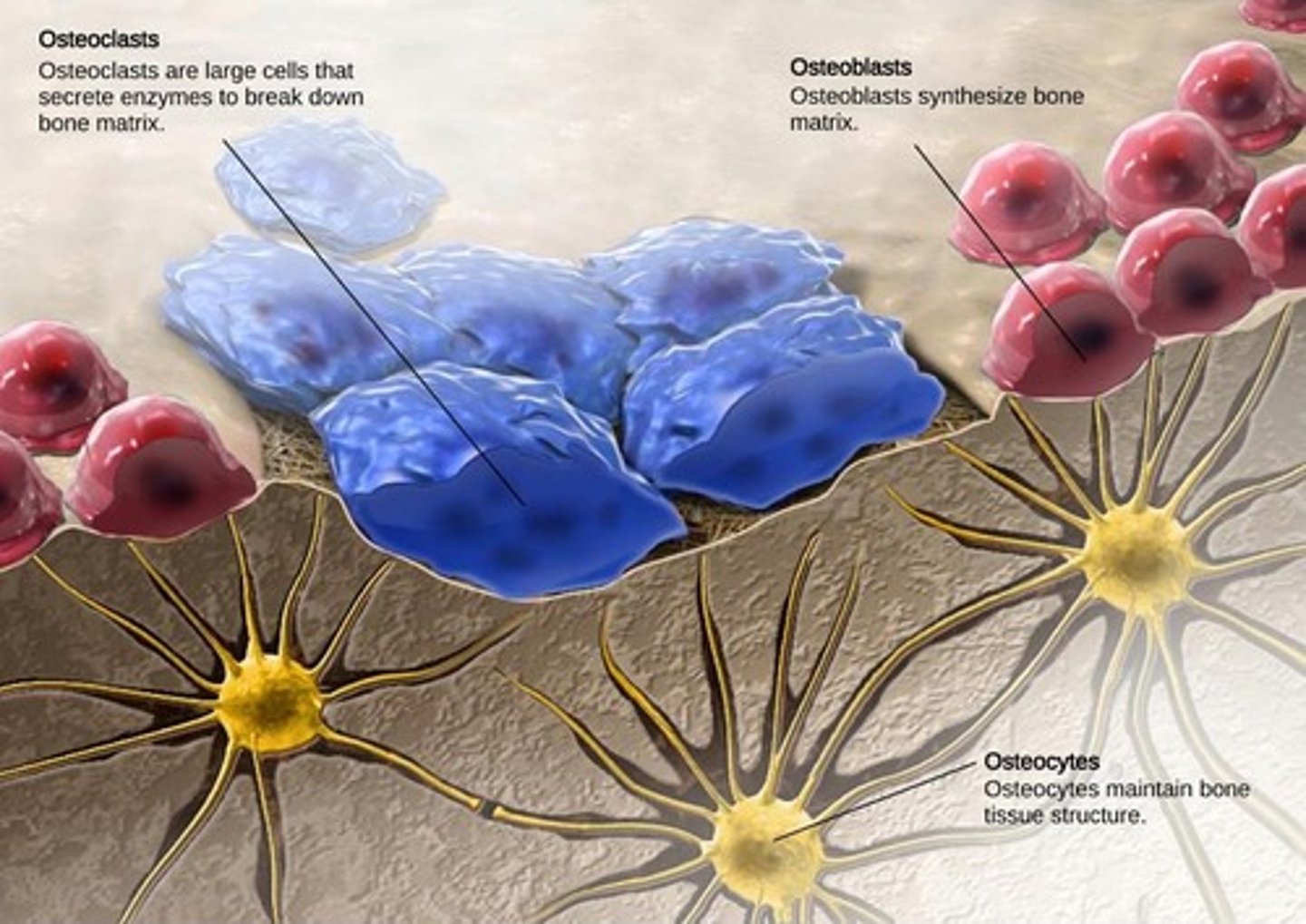
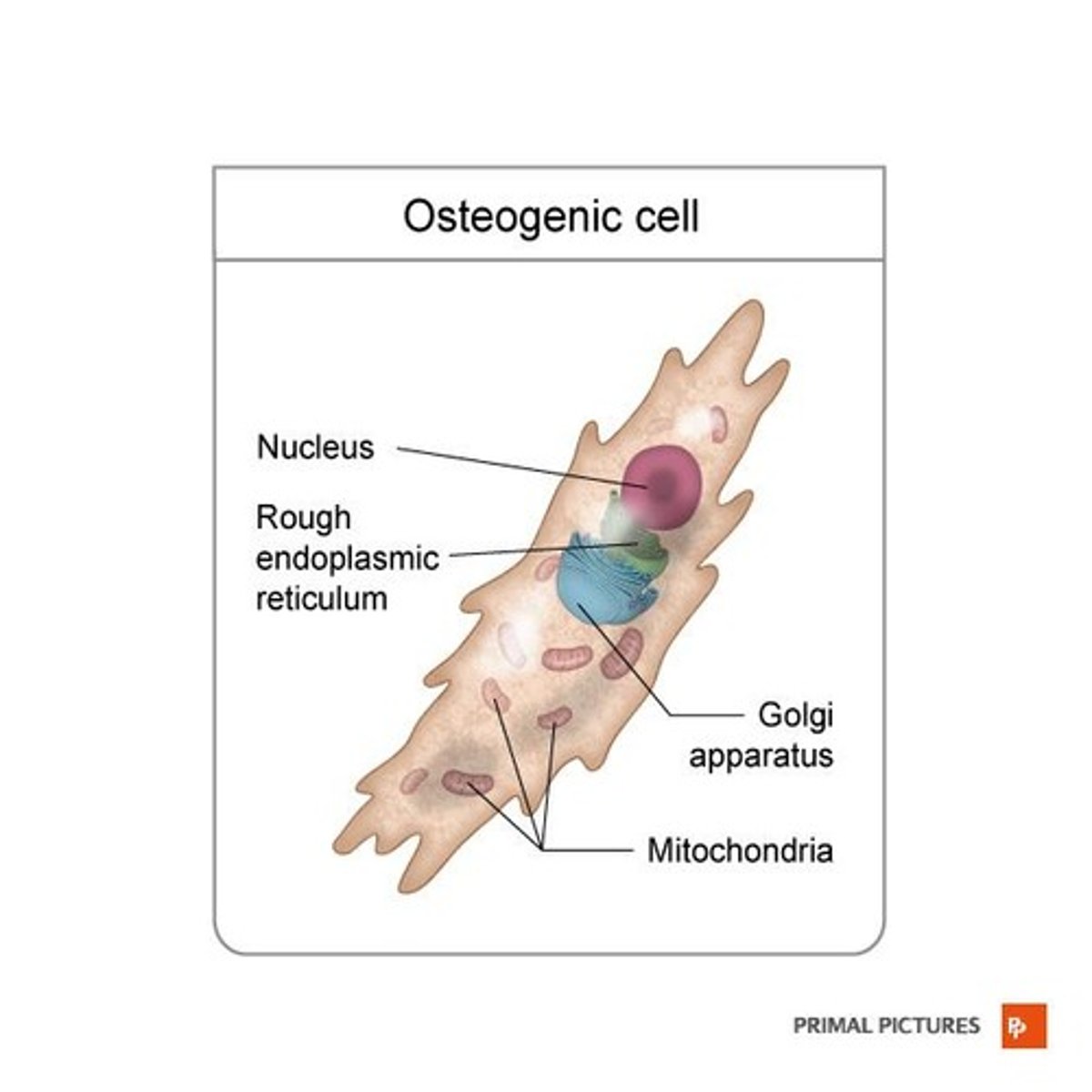
What are osteogenic cells?
Unspecialized bone stem cells derived from mesenchyme that develop into osteoblasts.
What is the role of osteoblasts?
Bone-building cells found on the surface of growing bones or during active bone remodeling.
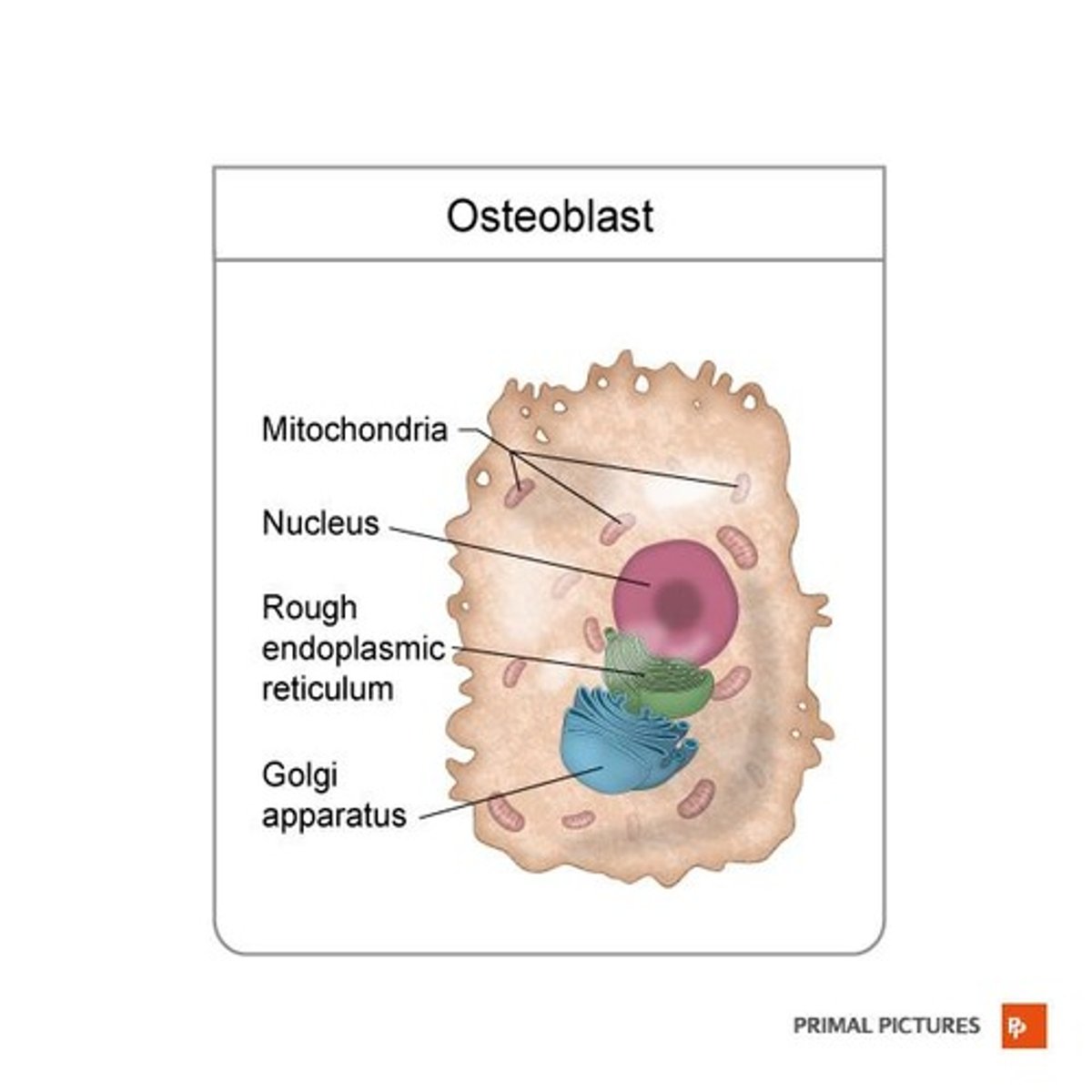
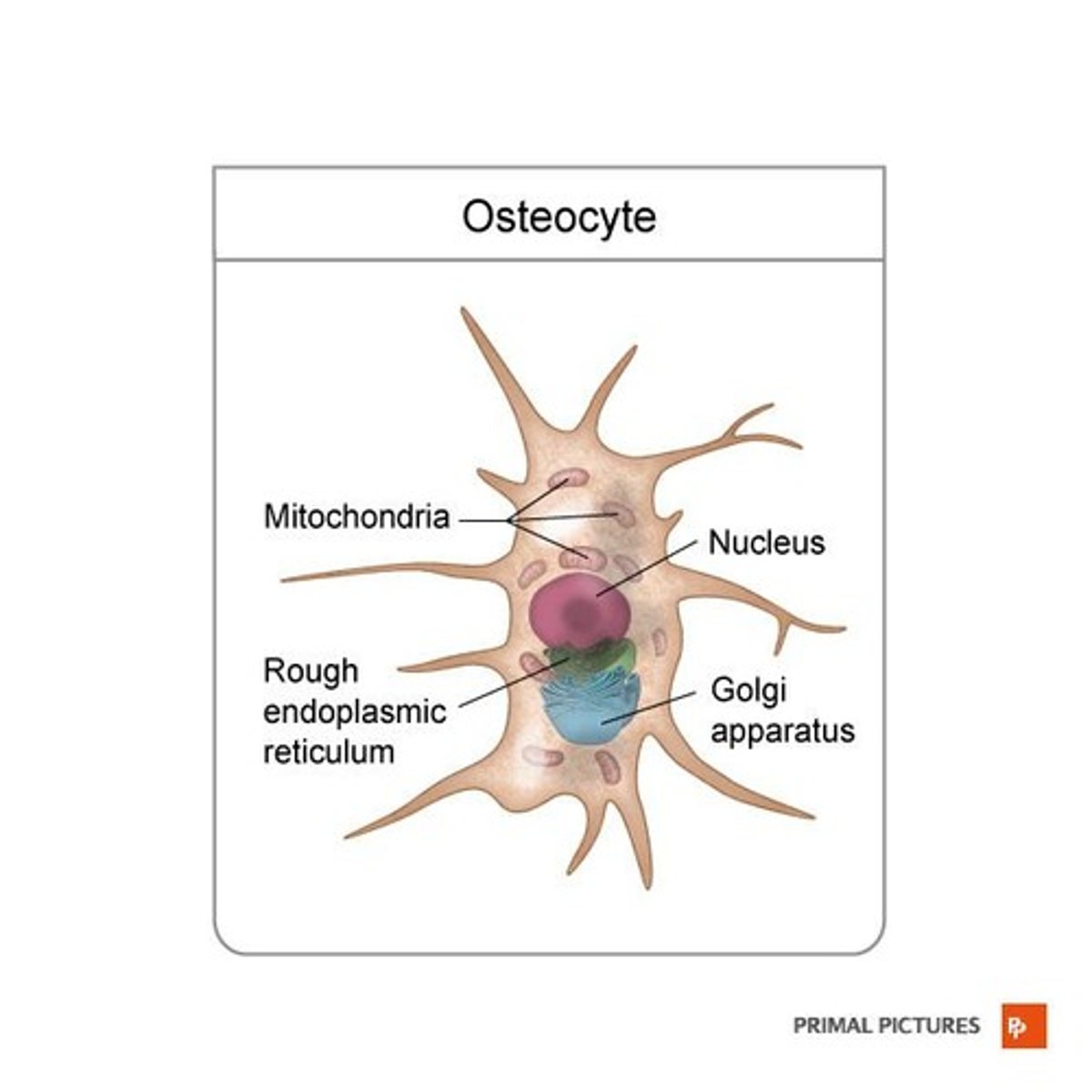
What are osteocytes?
Mature bone cells that maintain bone tissue and are found within lacunae.
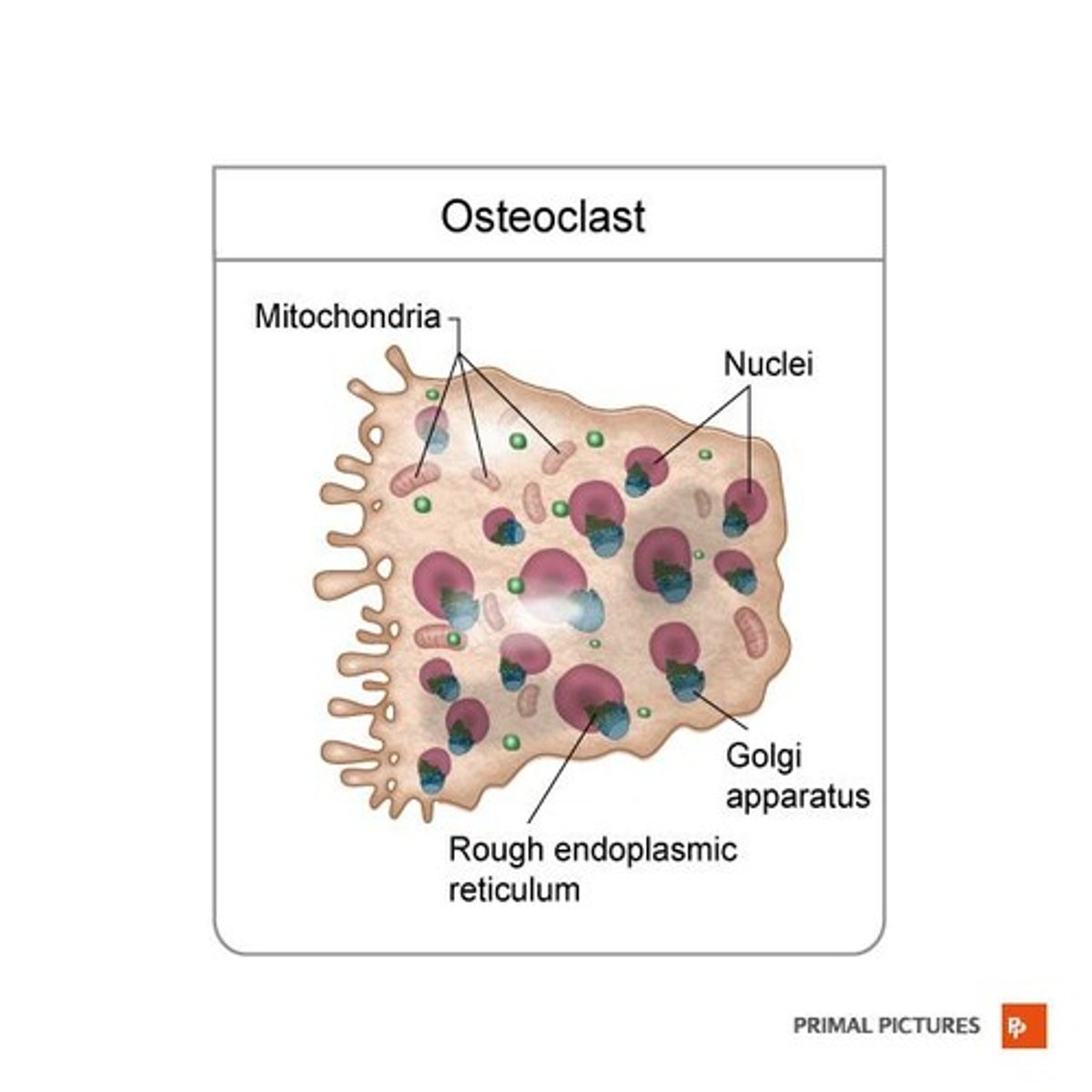
What are osteoclasts?
Bone-destroying cells that resorb bone tissue.
What is calcification in bone tissue?
The process initiated by osteoblasts where mineral salts are deposited and crystallized in the extracellular matrix.
What is the significance of the medullary cavity?
It contains yellow bone marrow and blood vessels, serving as a storage site for fat and a passage for blood supply.
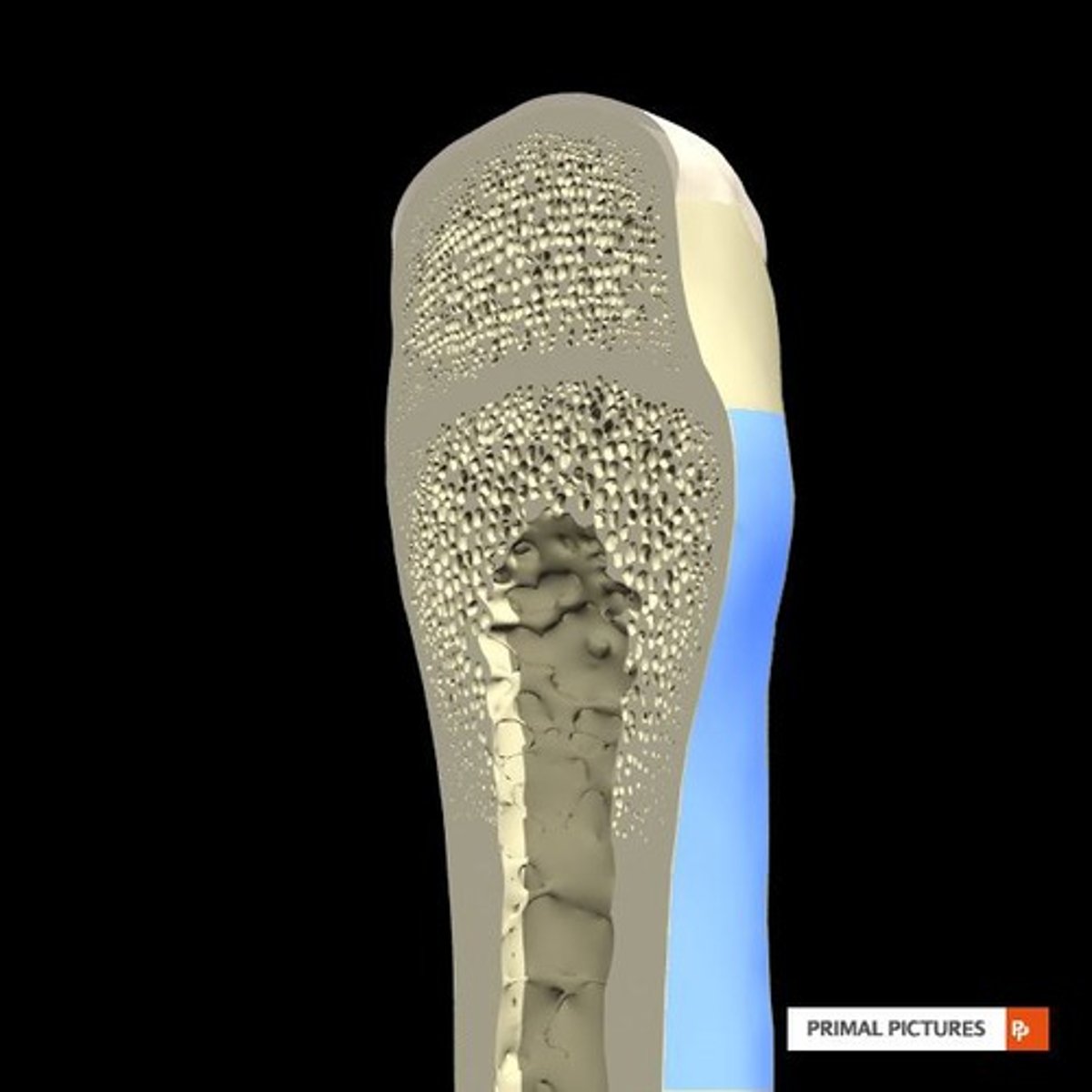
What is the structure of trabecular bone?
It consists of a network of trabeculae that contain red and yellow bone marrow.

What is the role of Sharpey's fibers?
Thick bundles of collagen fibers that attach the periosteum to the underlying bone.
What happens to bone marrow as a person ages?
Bone marrow changes from red to yellow and fills the medullary cavity.
What is the function of the nutrient artery?
It nourishes the medullary cavity and the inner two-thirds of the cortex of the bone.
What is the primary mineral salt found in bone tissue?
Calcium phosphate, which combines with hydroxyapatite to form the mineral component of bone.
What is the function of osteoblasts?
Osteoblasts synthesize and secrete collagen fibers and other organic components to build the extracellular matrix and initiate calcification.
What is the primary role of osteocytes?
Osteocytes maintain daily metabolism of bone tissue and facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste with blood.
What are osteoclasts and their function?
Osteoclasts are large cells with 15-20 nuclei that digest protein and mineral components of the bone matrix using powerful lysosomal enzymes.
What is the difference between compact and spongy bone?
Compact bone is dense and provides strength, while spongy bone has open spaces and supports weight distribution.
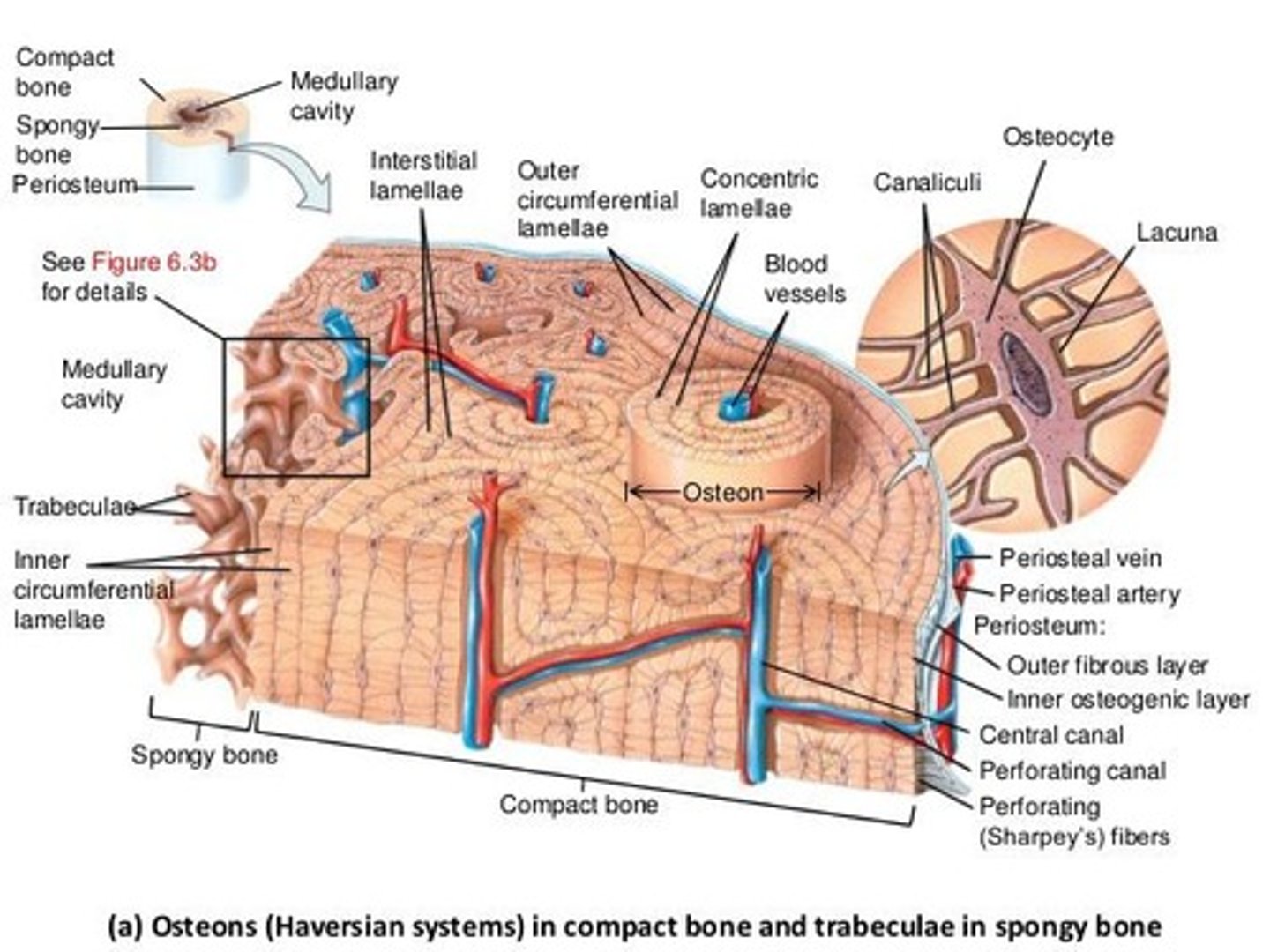
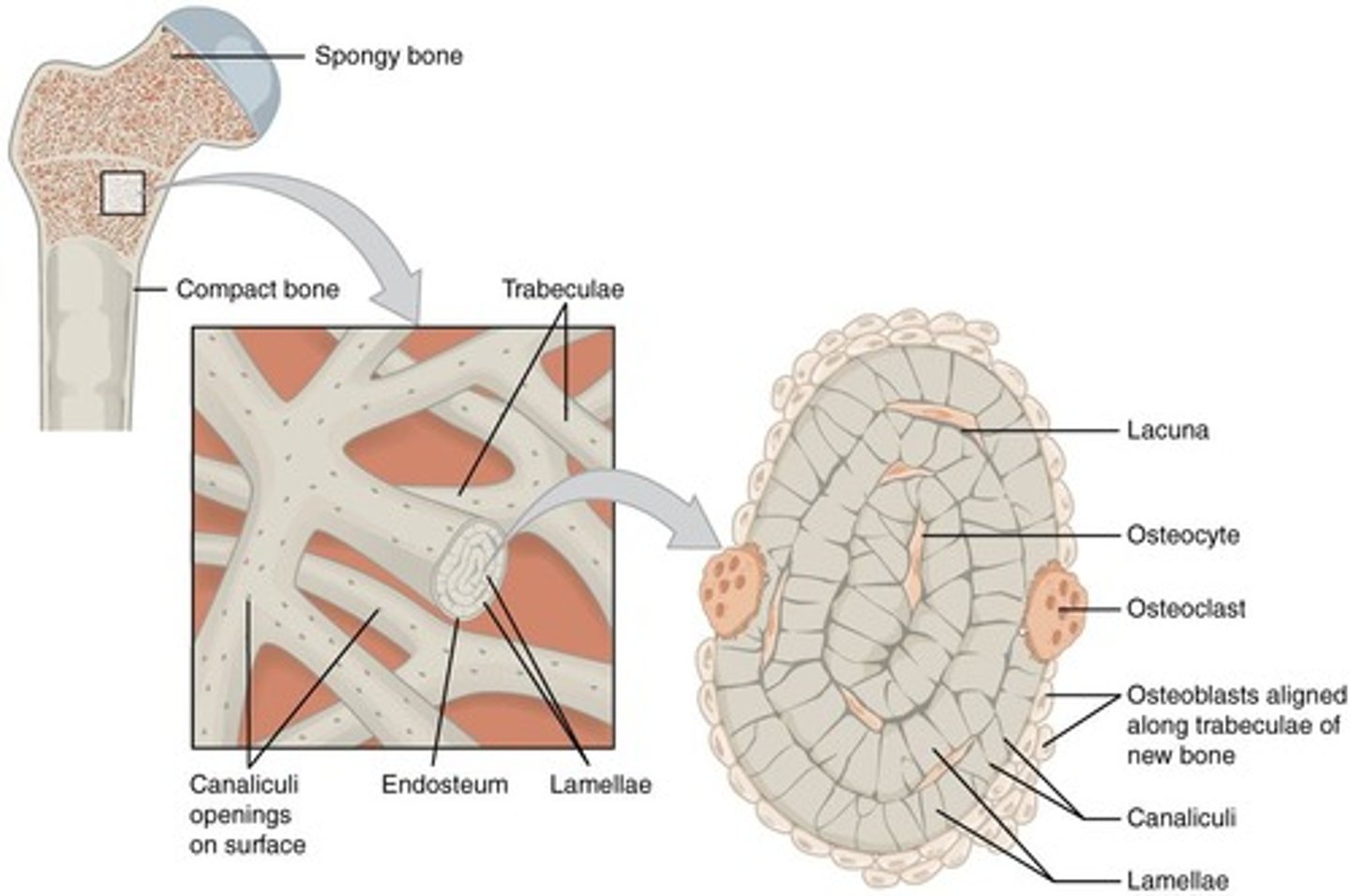
What is the structure of compact bone?
Compact bone is organized into osteons (Haversian systems), which consist of concentric rings of lamellae surrounding a central canal.
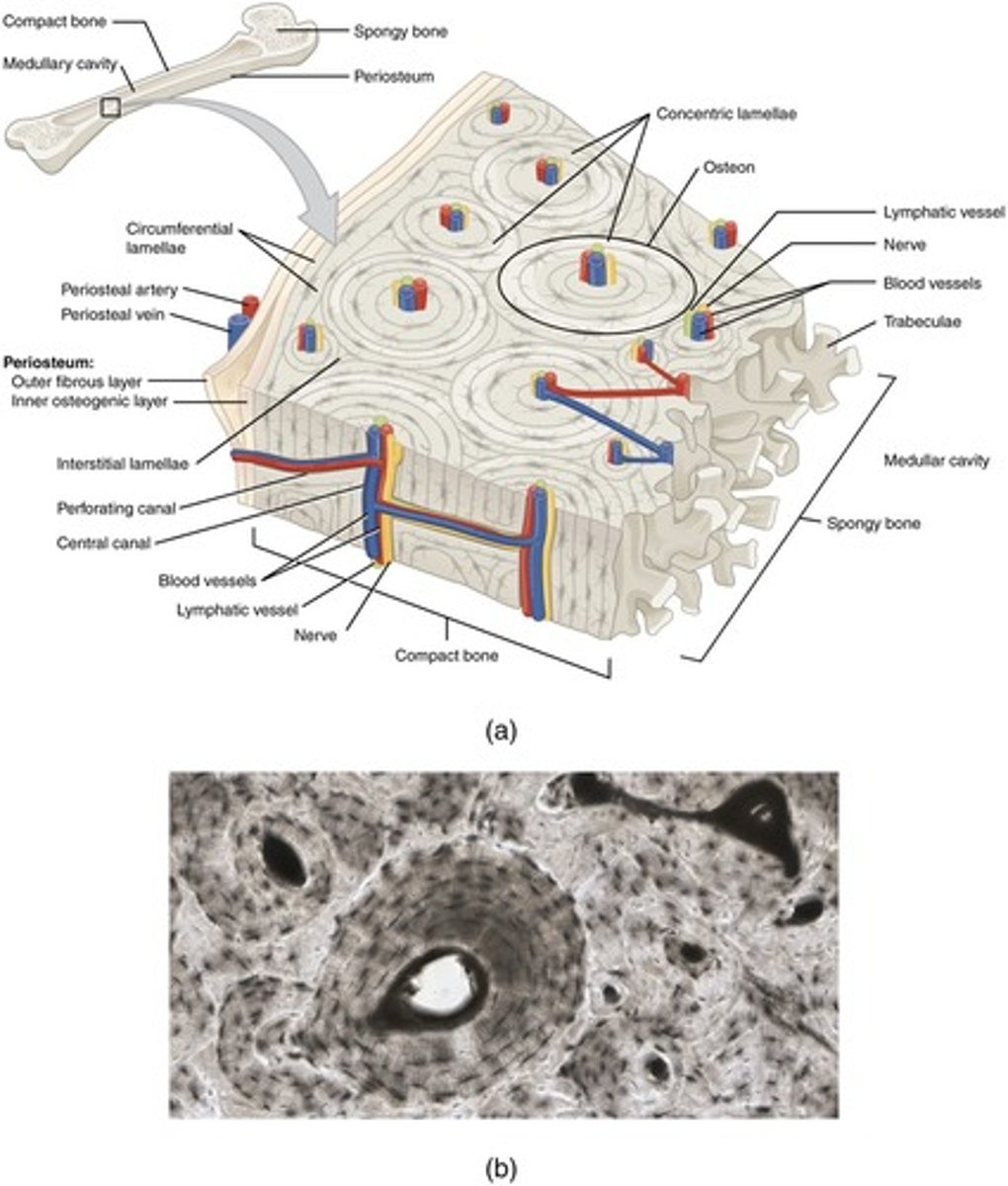
What is the central canal in compact bone?
The central canal (Haversian canal) runs longitudinally through each osteon and contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels.
What are Volkmann's canals?
Transverse channels that connect the blood and nerve supply of the periosteum with the central canals and medullary cavity.
What is the composition of bone matrix?
Bone matrix consists of organic components like osteoid, collagen fibers, and inorganic components such as hydroxyapatite mineral.
What is the role of trabeculae in spongy bone?
Trabeculae are lattice-like networks that provide strength to spongy bone and are arranged along lines of stress.
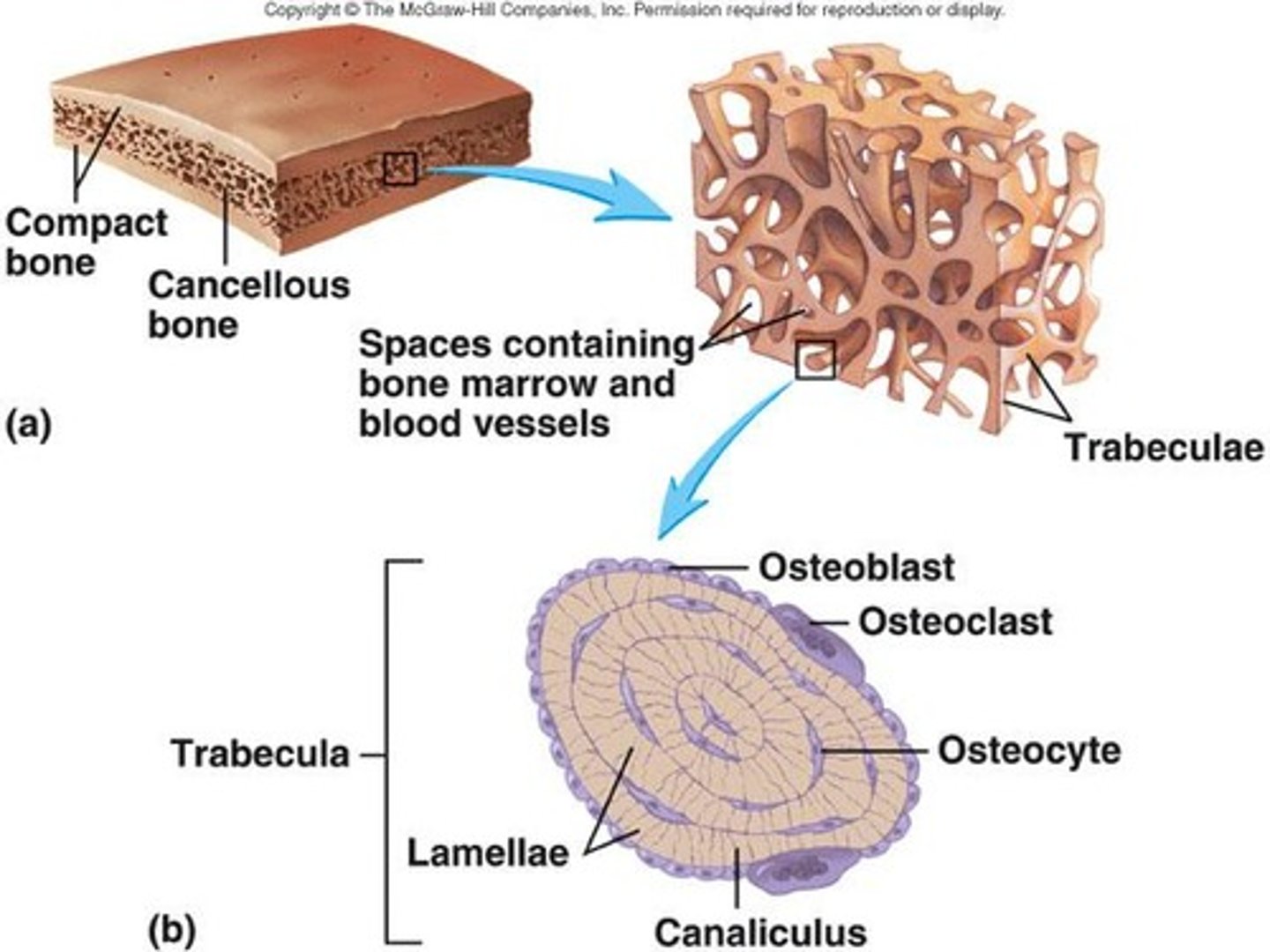
Where is spongy bone primarily found?
Spongy bone is found in the epiphyses of long bones and the interior of short, flat, and irregularly shaped bones.
What is the purpose of lacunae in bone tissue?
Lacunae are tiny cavities that house osteocytes and are located between lamellae.
What are canaliculi?
Canaliculi are hair-like canals that connect lacunae to each other, allowing for nutrient transport and waste removal.
What is ossification?
Ossification is the process of bone formation, occurring during embryonic development, growth, and remodeling.
What is the difference between interstitial and circumferential lamellae?
Interstitial lamellae are remnants of old osteons, while circumferential lamellae line the inner and outer surfaces of compact bone.
What is the significance of the arrangement of collagen fibers in lamellae?
The alternating direction of collagen fibers in adjacent lamellae allows the bone to withstand torsion pressures.
What is the role of red bone marrow in spongy bone?
Red bone marrow is involved in hematopoiesis, the production of blood cells, and is found in the spaces of spongy bone.
What is the main characteristic of spongy bone compared to compact bone?
Spongy bone is lighter and has a less dense structure, providing balance to the heavier compact bone.
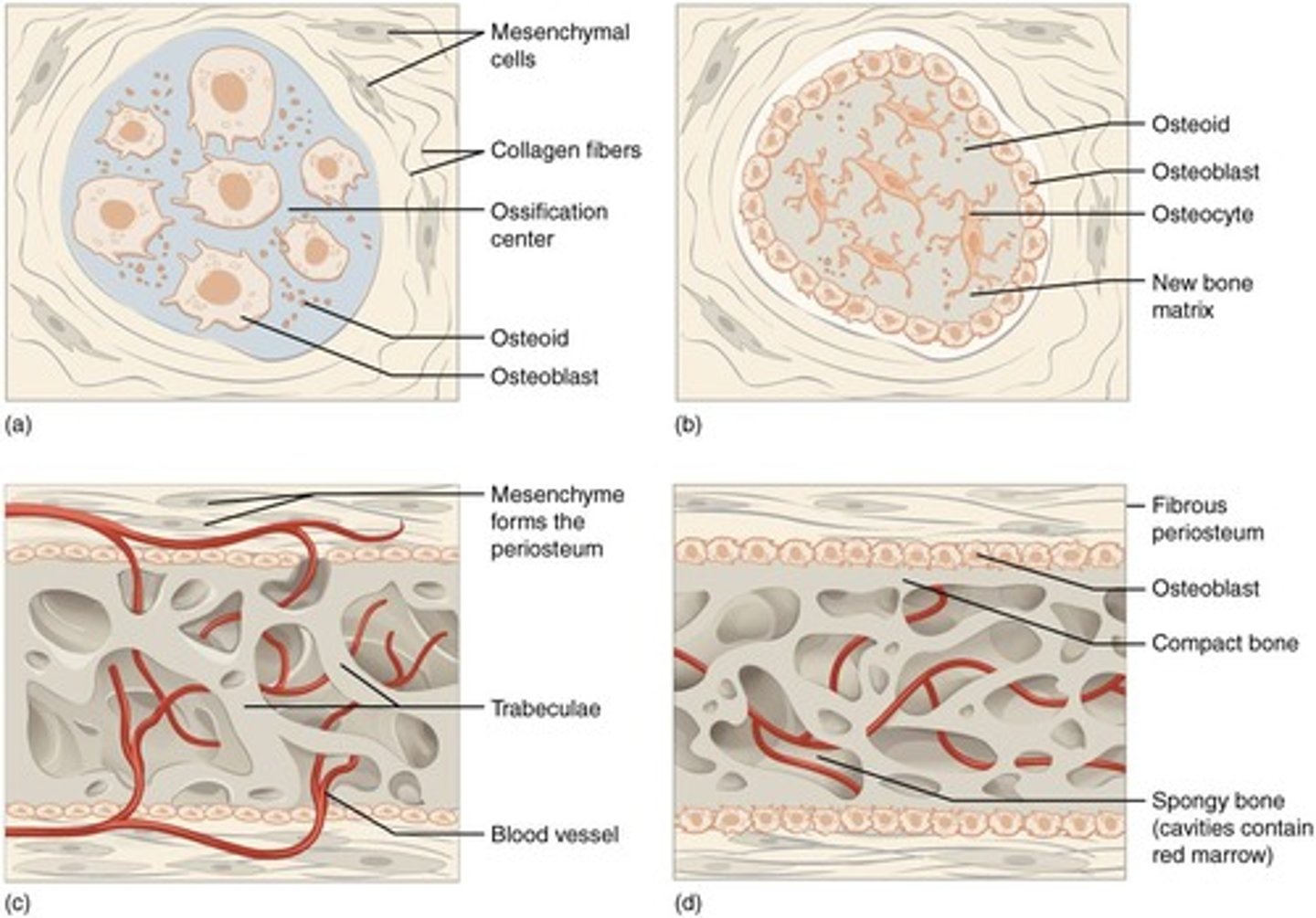
What is intramembranous ossification?
Formation of bone directly from mesenchymal cells, occurring in flat bones of the face, cranial bones, mandible, and clavicles.
What is endochondral ossification?
Formation of bone within hyaline cartilage that develops from mesenchyme.
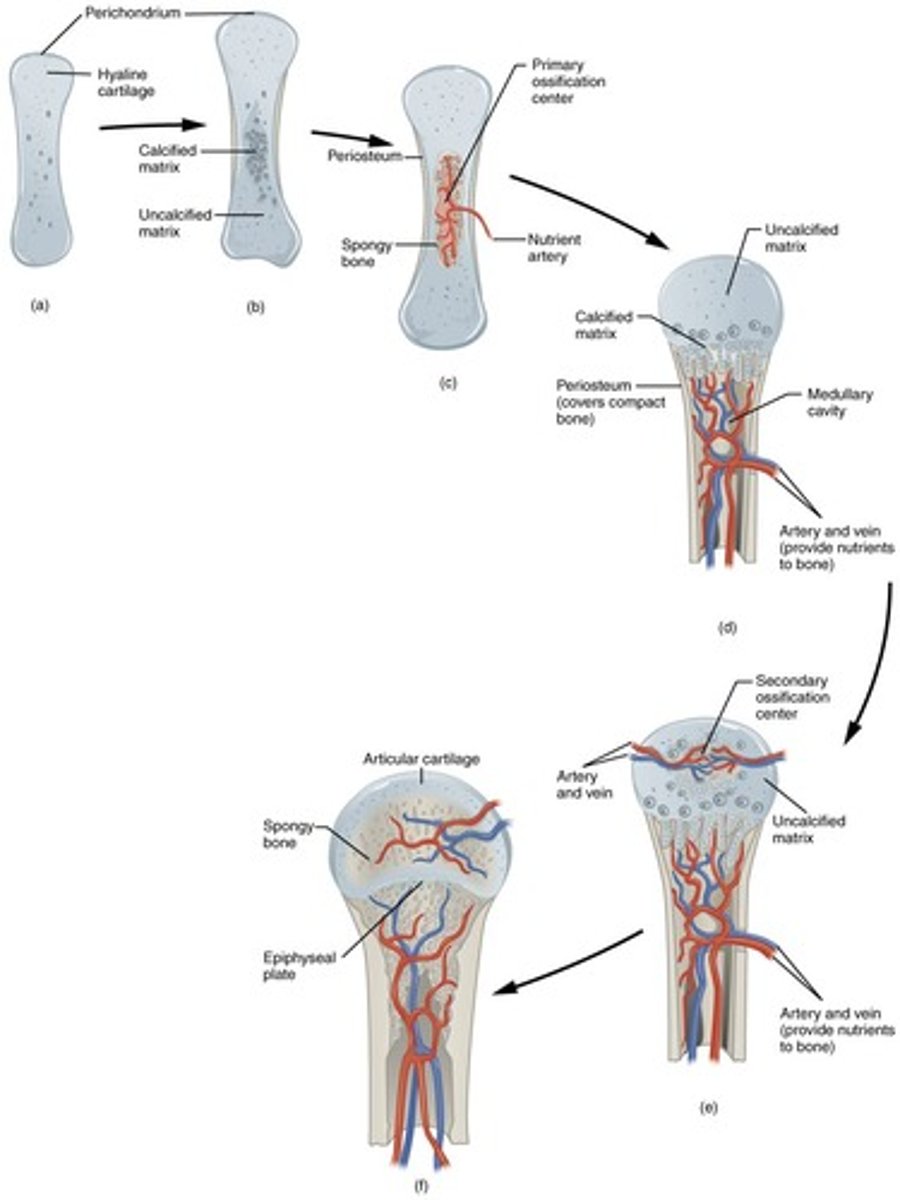
What are the key steps in intramembranous ossification?
Development of ossification center, calcification of matrix, formation of trabeculae, and development of periosteum.
What initiates the ossification center during intramembranous ossification?
Chemical messages cause mesenchymal cells to cluster and differentiate into osteoblasts.
What happens during the calcification of the matrix in intramembranous ossification?
Osteoblasts stop secreting extracellular matrix and become osteocytes, which lie in lacunae.
What is the role of osteoclasts in bone development?
Osteoclasts break down newly formed spongy bone, creating a medullary cavity.
What are the stages of endochondral ossification?
Development of cartilage model, growth of cartilage model, development of primary ossification center, development of medullary cavity, and secondary ossification centers.
How does cartilage grow during endochondral ossification?
Cartilage grows through interstitial growth (length) and appositional growth (width).
What is the epiphyseal plate and its significance?
A growth plate where cartilage is replaced by bone, allowing for the lengthening of long bones.
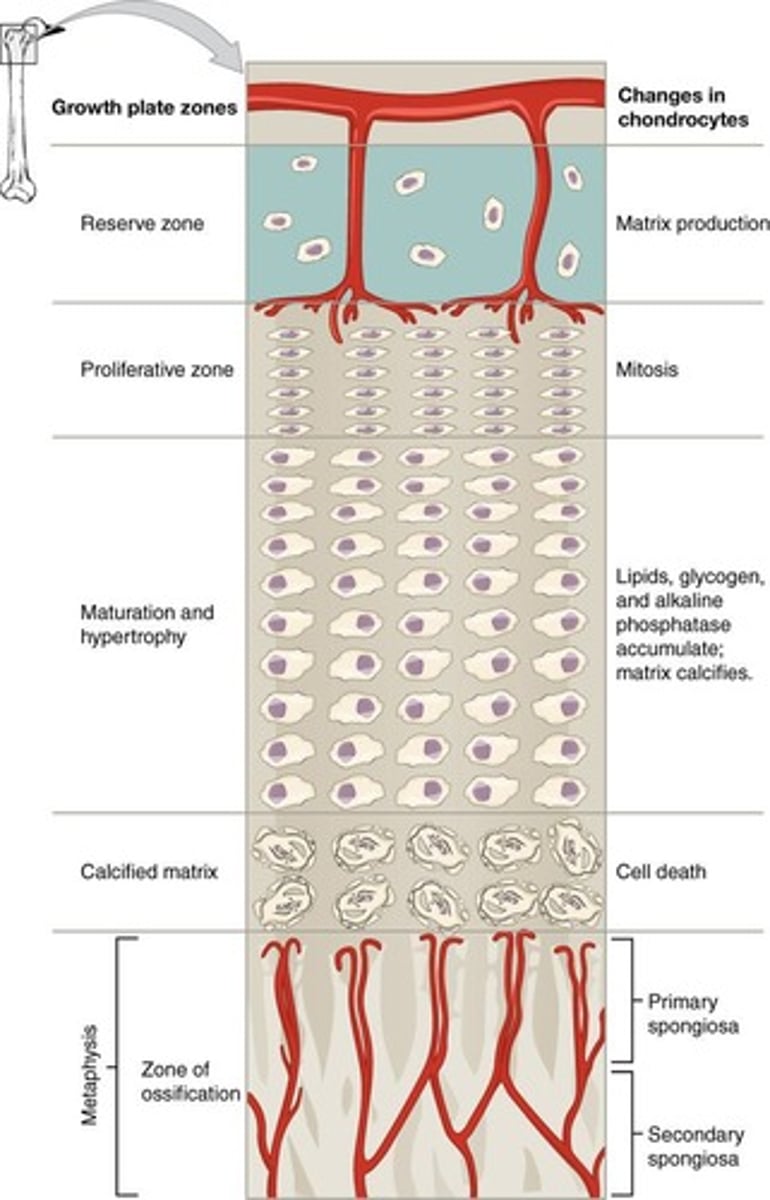
What are the zones of growth in the epiphyseal plate?
Zone of resting cartilage, proliferating cartilage, hypertrophic cartilage, and calcified cartilage.
What occurs in the zone of proliferating cartilage?
Rapid cell division of larger chondrocytes arranged in stacked coins.
What is the effect of hormones on bone growth?
Hormones like insulin-like growth factor and hGH promote cell division at the epiphyseal plate.
What is osteoporosis?
A condition characterized by decreased bone mass and increased porosity, leading to fragile bones.
What factors affect bone growth?
Nutrition (calcium, vitamins), hormones (hGH, thyroid hormones), and mechanical stress from exercise.
What is the difference between hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia?
Hypercalcemia is when blood calcium levels are too high, while hypocalcemia is when they are too low.
What is the role of calcitonin in calcium homeostasis?
Calcitonin decreases blood calcium levels by stimulating osteoblast activity and reducing calcium reabsorption in the kidneys.
What happens during hypocalcemia?
The parathyroid gland releases parathyroid hormone (PTH), increasing osteoclastic activity and calcium levels in the blood.
What is the impact of aging on bone tissue?
Aging leads to demineralization, decreased protein synthesis, and increased brittleness of bones.
What is the significance of vitamin D for bone health?
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and plays a critical role in bone remodeling.
What are the effects of hormonal abnormalities on bone growth?
Over secretion of hGH causes gigantism, while under secretion leads to short stature.
What is the role of mechanical stress in bone health?
Mechanical stress from exercise increases mineral deposition and collagen production, while lack of stress leads to bone loss.
What dietary sources provide calcium?
Dairy products, green leafy vegetables, nuts, beans, and fish with soft bones.
What is osteomalacia?
A condition where new adult bone fails to ossify properly, often leading to hip fractures.
What is rickets?
A childhood condition where calcium salts are not deposited properly, resulting in soft bones and deformities.
What is the peak height velocity?
The maximum rate of growth in height during puberty.
What is appositional growth?
Growth in thickness of bones occurring at the outer surface.
What is the significance of the epiphyseal line?
It marks the closure of the epiphyseal plates in adulthood, indicating that bone lengthening has stopped.
How does exercise influence bone density?
Weight-bearing exercises stimulate bone formation and increase bone density.
Axial Skeleton
Consists of the bones that lie around the longitudinal axis of the human body.
Appendicular Skeleton
Consists of the bones of the upper and lower limbs (extremities), plus the bones forming the girdles that connect the limbs to the axial skeleton.
Long Bones
Greater length than width; slightly curved for strength; compact bone in diaphysis & spongy bone in epiphyses.
Short Bones
Cube shaped; equal in length and width; spongy bone with compact on outer surface.
Flat Bones
Thin, composed of two nearly parallel plates of compact bone with a layer of spongy in between; protection and muscle attachment site.
Irregular Bones
Complex shaped; vary in the amount of spongy and compact bone.
Sesamoid Bones
Develop in certain tendons where there is considerable friction, tension, and physical stress.
Bone Surface Markings
Structural features adapted for specific functions; not present at birth - develop from tension and force.
Depressions & Openings
Allow the passage of soft tissues or form joints.
Processes
Projections or outgrowths that either help form a joint or serve as attachment sites.
Fissure
Narrow slit between adjacent parts of bones through which blood vessels and nerves pass.
Foramen
Opening through which blood vessels, nerves, or ligaments pass.
Fossa
Shallow depression.
Sulcus
Furrow along bone surface that accommodates blood vessels, nerves, or tendons.
Meatus
Tube-like opening.
Condyle
Large, round protuberance with smooth articular surface at the end of the bone.
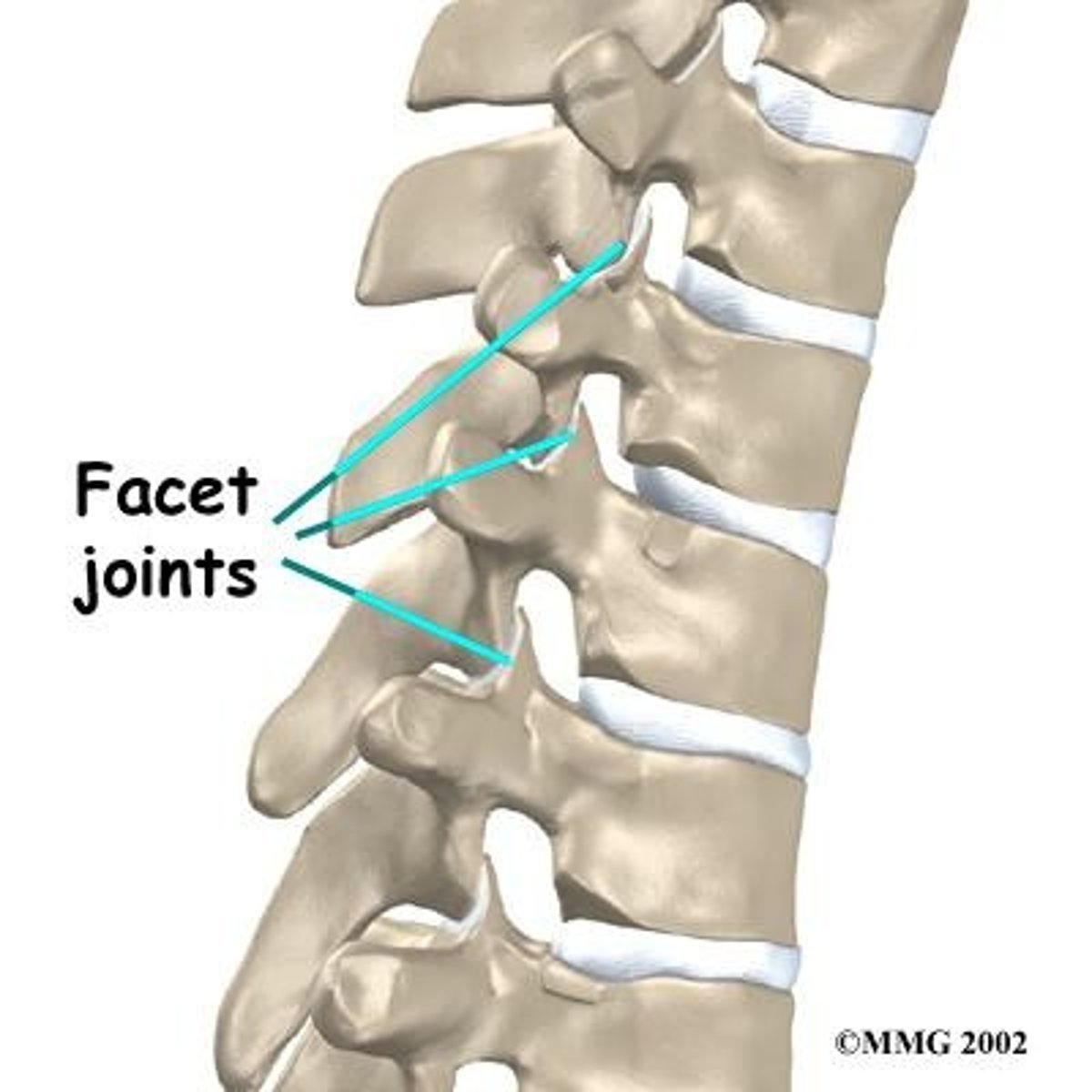
Facet
Smooth, flat, slightly concave or convex articular surface.
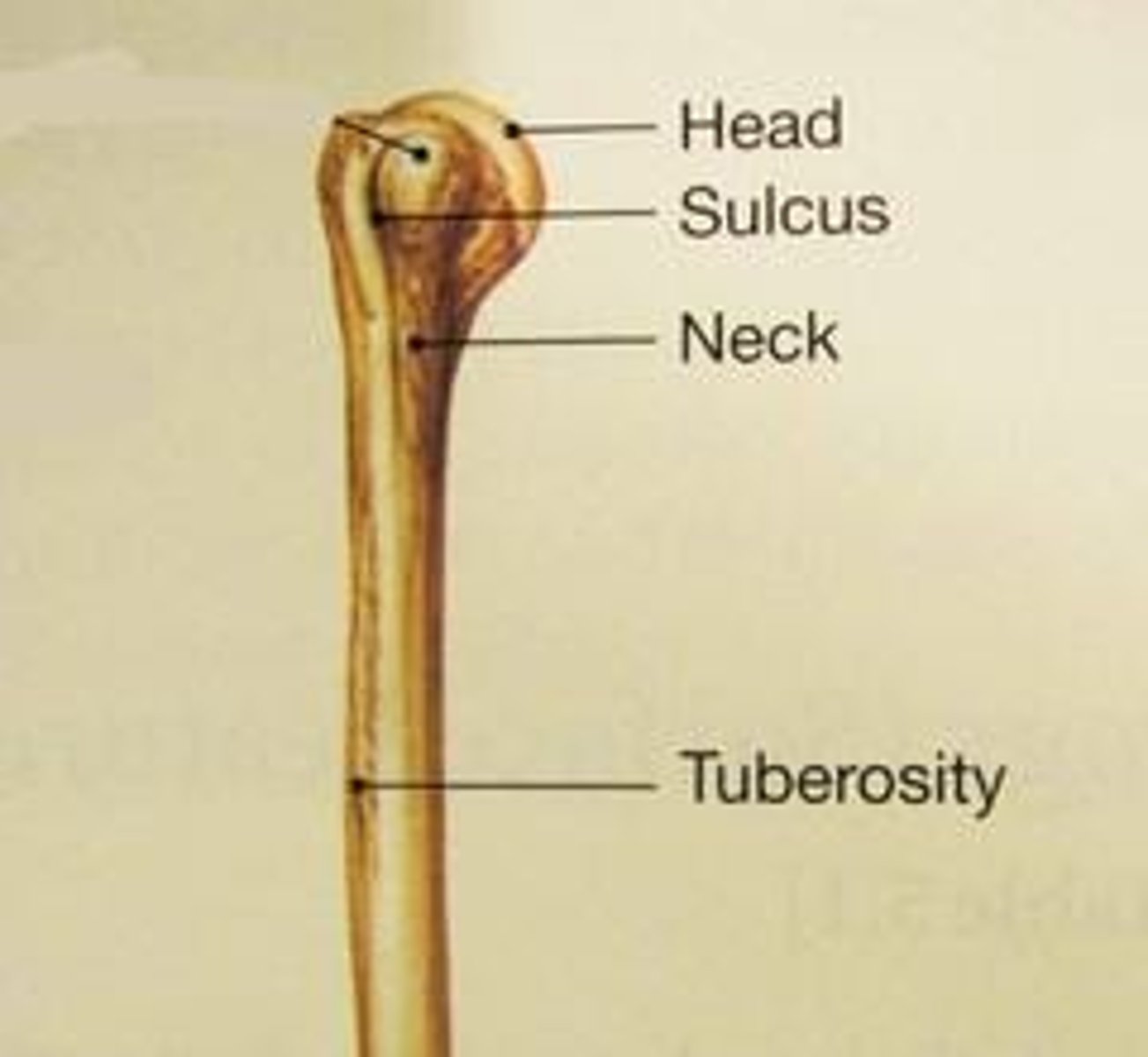
Head
Usually rounded articular projection supported on neck (constricted portion) of bone.
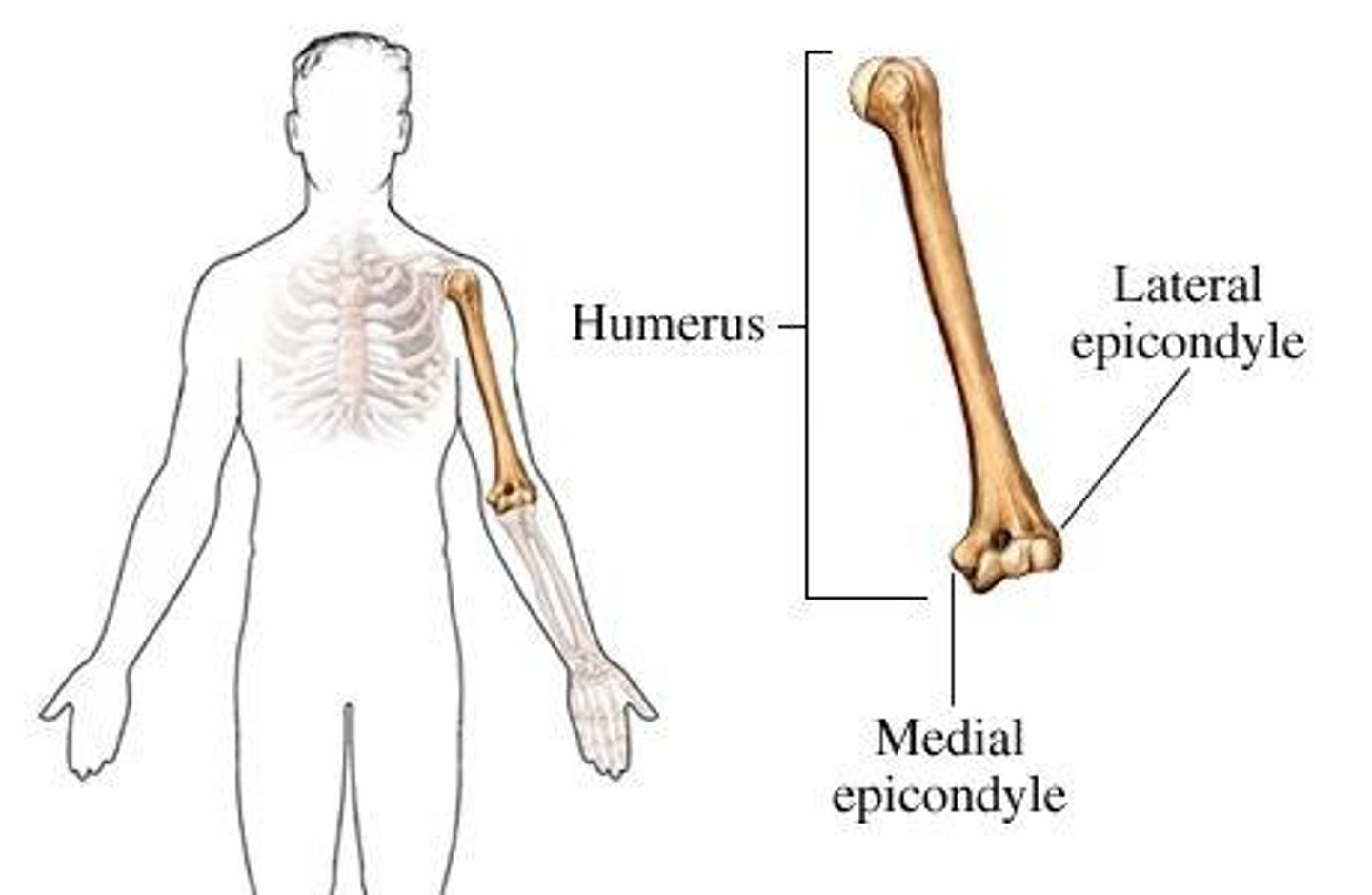
Crest
Prominent ridge or elongated projection.
Epicondyle
Typically roughened projection above condyle.
Line
Long, narrow ridge or border (less prominent than crest).
Spinous Process
Sharp, slender projection.
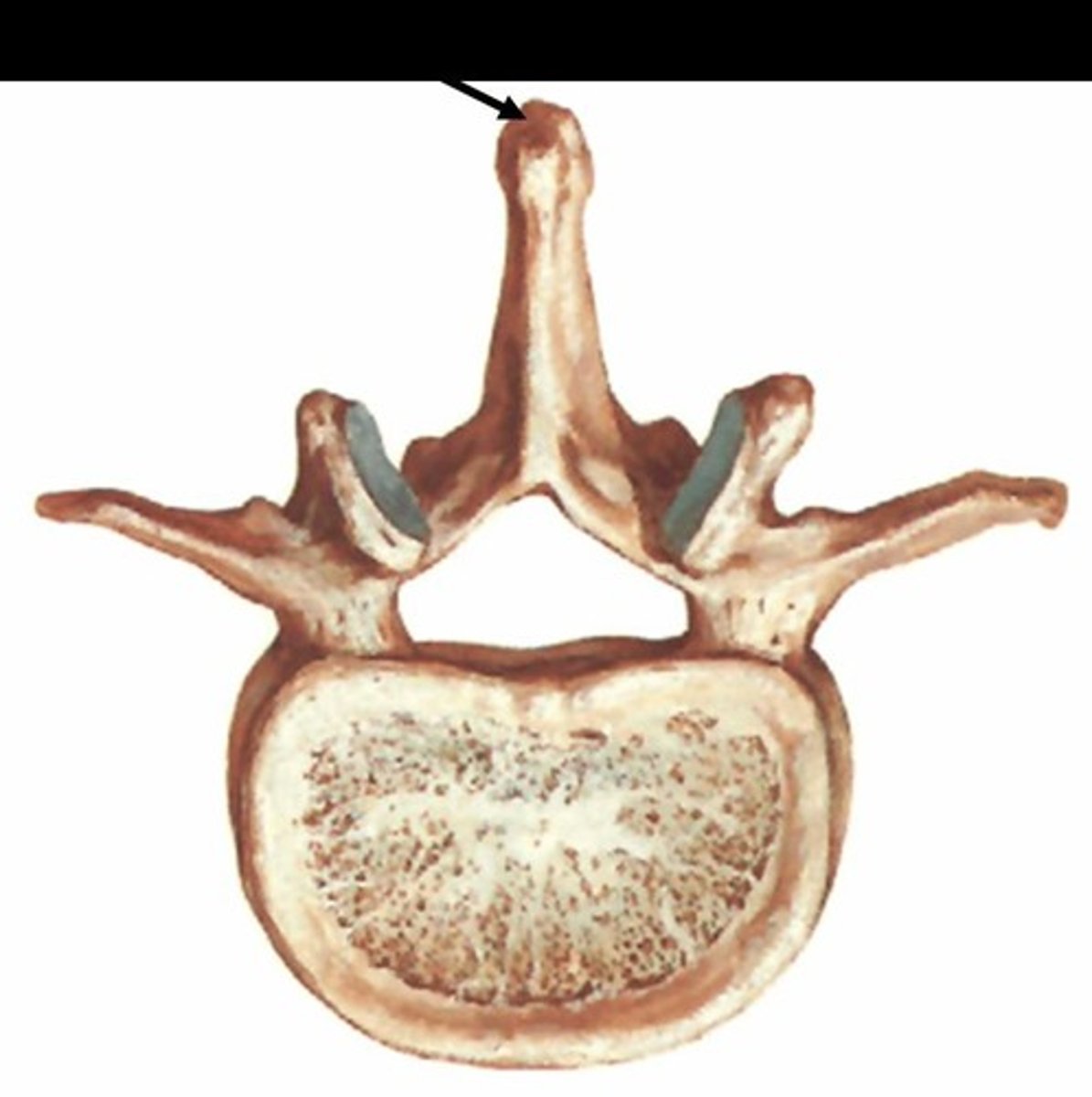
Spine
A sharp, pointed, narrow process.
Trochanter
Very large projection.
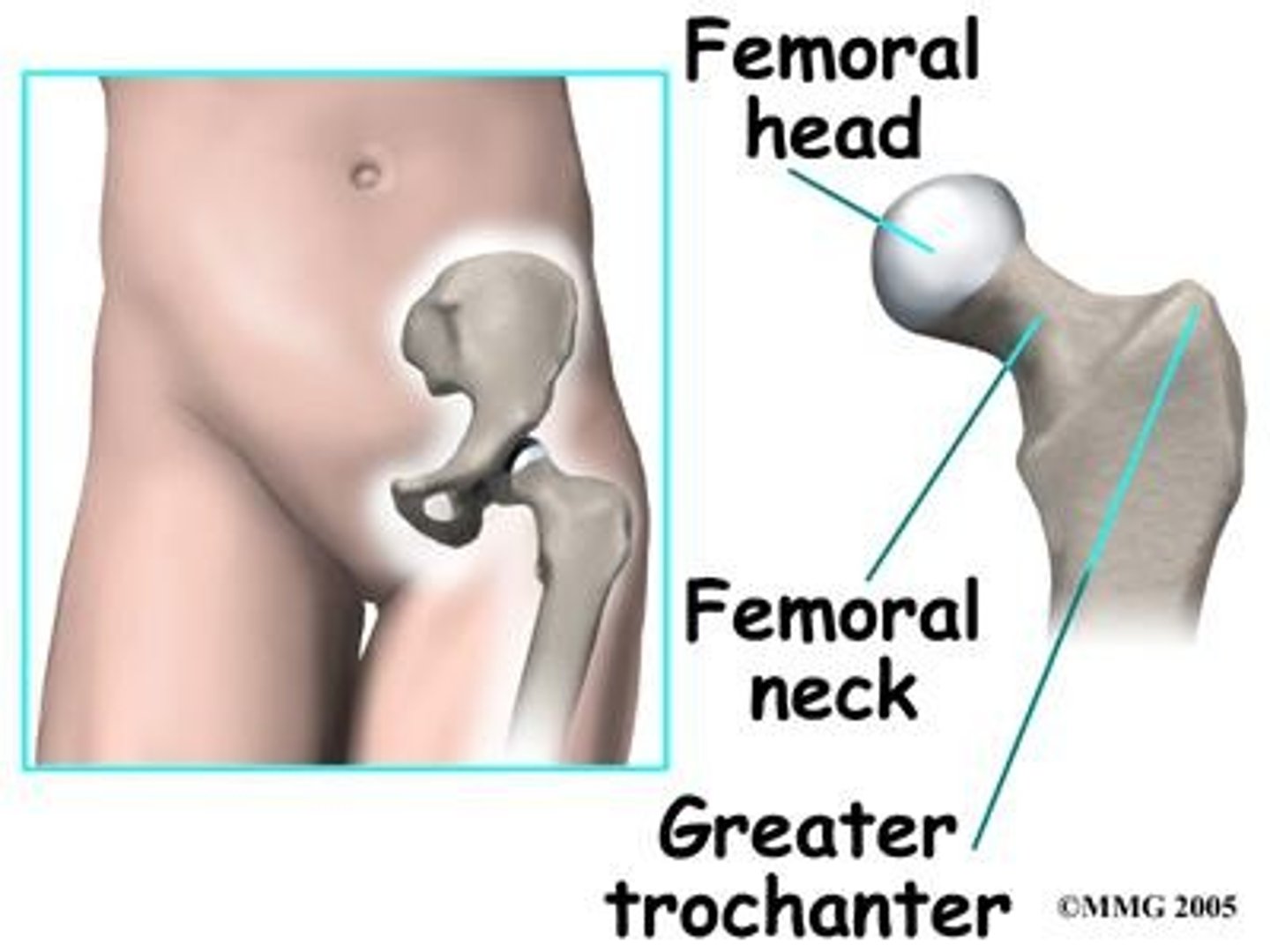
Tubercle
Variably sized rounded projection.
Tuberosity
Variable sized projection that has a rough, bumpy surface.
Joints
AKA - Articulation or arthrosis
Functional Classification
Based on the type of movement they permit
Synarthrosis
An immovable joint
Amphiarthrosis
A slightly movable joint