FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL SYSTEM
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL SYSTEM
Allows for muscle attachment therefore the bones are used as levers.
Hard framework that anchors the soft organs of the body.
Surrounds organs such as the brain and spinal cord
The bone marrow is responsible for blood cell production.
Minerals and lipids are stored within bone material.
Movement
Support
Protection
Blood Cell production
Storage
True or False: Bone surface is smooth
Reveal where ligaments, tendons, and muscles are attached as well as the passage of vessels
False
Bone Markings
Identify these bone markings
Air-filled spaces in the skull
A rounded projection that articulates with another bone
A small, nearly flat articular surface, e.g. joints between vertebrae in the spine
A hole or opening in the bone for blood vessels and nerves
A bony projection or outgrowth from a larger bone structure, essentially a bump or extension
A shallow depression in the bone’s surface
A ridge or raised border of a bone
A large, rounded, and roughened projection on a bone
A short tube-like channel extending into the bone
A prominent protrusion or elevation on a bone is commonly seen in the sacral and cochlear regions.
Any of the two bony protuberances found only in the femur
An indentation or depression in the edge of the bone, often serving as a passageway
Choices
Crest
Condyle
Facet
Foramen
Fossa
Meatus
Notch
Process
Promontory
Sinus
Trochanter
Tuberosity
Sinus
Condyle
Facet
Foramen
Process
Fossa
Crest
Tuberosity
Meatus
Promontory
Trochanter
Notch
Bone structure located in the outer layer of bone, very hard and dense ___________
Compact bones are organized in structural units called _________
Living bone cells that live in a matrix.
Compact bone
Haversian Systems
Osteocytes
Bone structure located in the ends of long bones. Many spaces that are filled with red bone marrow which produces bone cells.
Porous or spongy bone
needle-like threads of spongy bone that surround the spaces. Add strength to this portion of the bone
Trabeculae
Matrix is a firm gel with chondrocytes suspended in the matrix.
Cartilage
Classification of bone
Typically longer than wide. Have a shaft with heads at both ends and contain mostly compact bone.
Usually curved. Thin layers of compact bone around a layer of spongy bone
Generally cube-shape. Contain mostly spongy bone
Do not fit into other bone classification categories
Long bone
Flat bone
Short bone
Irregular
Parts of long bone
Diaphysis
Epiphysis
Metaphysis
Articular cartilage
Periosteum
Endosteum
Medullary cavity
Identify the parts of the long bone
Shaft. Composed of compact bone
the growing part of a long bone, located between the epiphysis and the diaphysis
contains the epiphyseal plate in children.
Ends of the bone. Composed mostly of spongy bone
Outside covering of the diaphysis. Fibrous connective tissue membrane
Covers the external surface of the epiphyses
Cavity of the shaft. Contains yellow marrow (mostly fat) in adults. Contains red marrow (for blood cell formation)
is a membrane that lines the center of your bones that contains bone marrow.
Diaphysis
Metaphysis
Metaphysis
Epiphysis
Periosteum
Articular Cartilage
Medullary Cavity
Endosteum
Secure periosteum and underlying bone
Supply bone cells with nutrients
Sharpey’s Fibers
Arteries
the intercellular substance of the bone that forms most of the mass of the bone
The matrix is composed of?
Matrix
Water 25%, collagen fibers 25%, crystalized mineral salt 50%
Seen in the periosteum and is the progenitor of bone cells. Turns into osteoblast
Secrete collagen fibers. Build a matrix and become trapped in lacunae
Once it is trapped in the lacunae, the cell from number 2 turns into __________
formed from monocytes Digest bone matrix for Normal bone turnover. releases calcium in the process
Osteogenic cells
Osteoblast
Osteocytes
Osteoclast
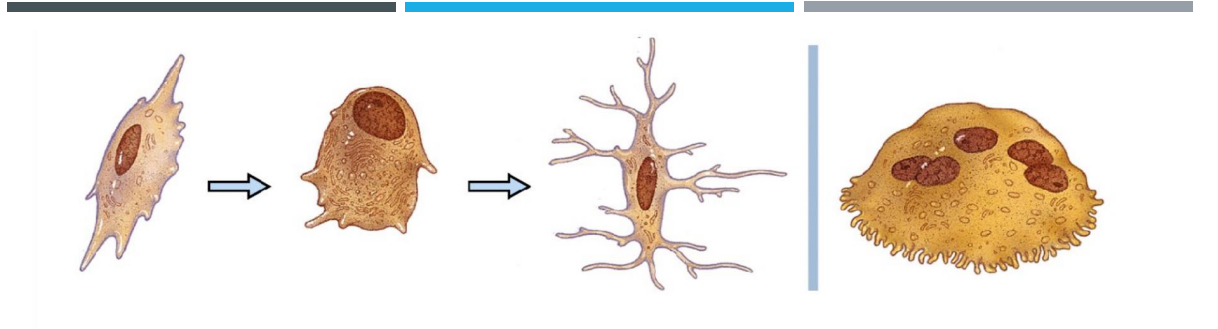
Osteogenic cell, osteoblast, osteocyte, osteoclast
concentric rings of interconnecting osteocytes surrounding a Haversian canal
Haversian system or osteon
Opening in the center of an osteon
Haversian Canal
Canal perpendicular to the central canal
Perforating Canal (Volkmann’s Canal)
Cavities containing bone cells (osteocytes)
Rings around the central canal
Tiny canals. Radiate from the central canal to lacunae. Form a transport system
Lacunae
Lamellae
Canaliculi
Changes in the Human Skeleton
When we are embryo, most of our skeleton are _________
Cartilage remains in isolated areas when we are adults. These are?
hyaline cartilage
Bridge of nose, ribs, and joints
allow for growth of long bone during childhood
True or False: Bones grow in width through periosteum
True or False: Bones do not change shape by gravity & muscle pull
Epiphyseal plates
True
False
involves the conversion of other types of connective tissue into bone.
Ossification
Ossification from a primitive connective tissue template, termed _______
Mesenchyme
Bone forms directly in mesenchyme layers (membrane like)
forms within hyaline cartilage developed from mesenchyme
Intramembranous ossification
Endochondral Ossification
What are the steps for intramembranous ossification
A. Calcification, Development of periosteum, development of ossification center, Formation of trabeculae
B. Development of ossification center, Calcification, Development of periosteum, formation of trabeculae
C. Development of ossification center, calcification, Formation of trabeculae, development of periosteum
D. Formation of trabeculae, Development of ossification center, calcification, development of periosteum
C.
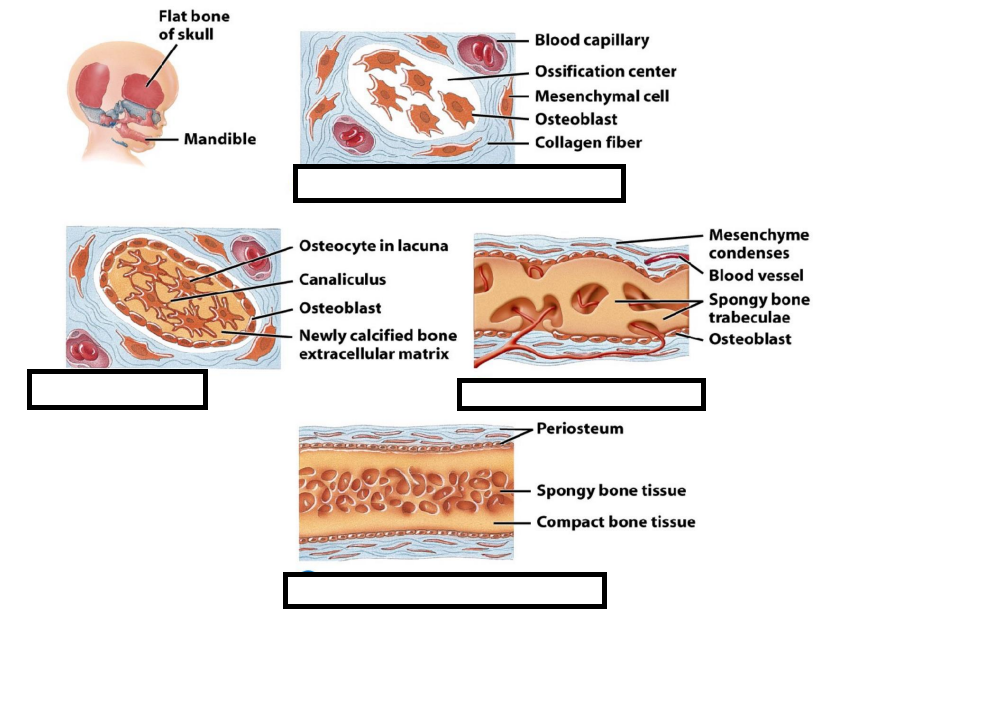
Calcification
Development of periosteum
Development of ossification center
Formation of trabeculae
Development of ossification center
Calcification
Formation of Trabeculae
Development of periosteum
What are the steps for endochondral ossification
A. Medullary Cavity development
B. Secondary ossification center
C. Cartilage model development
D. Growth of cartilage model
E. Primary ossification center
F. Articular cartilage and epiphyseal line formation
C, D, E, A, B, F
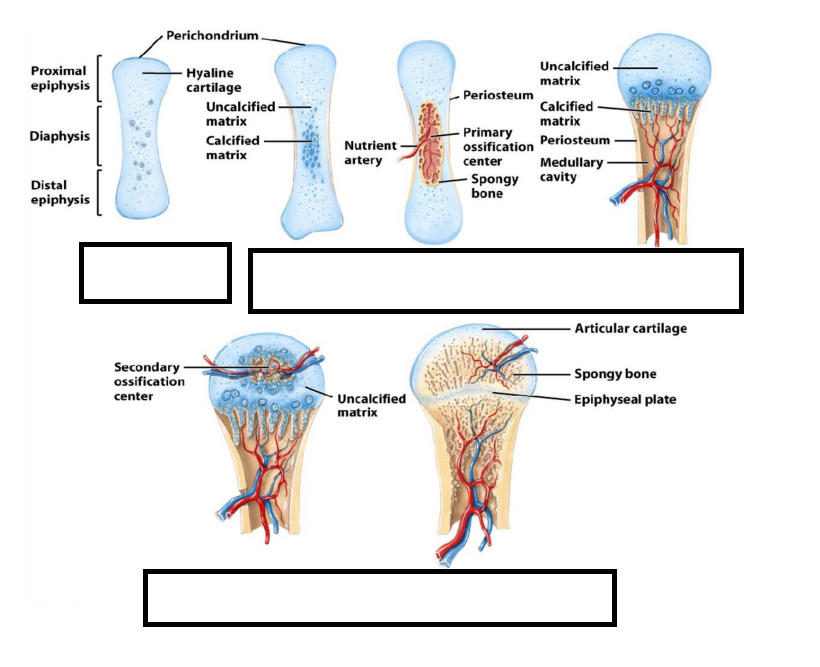
A. Medullary Cavity development
B. Secondary ossification center
C. Cartilage model development
D. Growth of cartilage model
E. Primary ossification center
F. Articular cartilage and epiphyseal line formation
Periosteum is to _____ while epiphyseal plate is to _________
Width and height
True or false: chondrocytes in the epiphyseal plate divide and increase cartilage layer
True or False: This division only stops during adolescence
True both
Types of Fracture
incomplete break (crack)
bone in two or more pieces
Not through skin
broken ends break skin
Partial fracture
Complete fracture
Closed
Open
Bone remodeling and repair
Which cells are responsible for bone resorption during the remodeling process?
A) Osteoblasts
B) Chondroblasts
C) Osteoclasts
D) Fibroblasts
What is the initial step in bone repair after a fracture?
A) Formation of a fibrocartilage callus
B) Removal of dead tissue (hematoma formation)
C) Spongy bone formation
D) Bone remodelingDuring bone repair, which type of tissue forms the temporary bridge across the fracture site?
A) Compact bone
B) Spongy bone
C) Periosteum
D) FibrocartilageWhat is the role of osteoblasts in bone remodeling and repair?
A) Breaking down bone matrix
B) Removing dead bone tissue
C) Forming new bone tissue
D) Producing fibrocartilageWhat happens to the spongy bone after the fracture site stabilizes?
A) It remains unchanged.
B) It is remodeled into compact bone.
C) It turns into fibrocartilage.
D) It gets absorbed by osteoclasts.Which cells are responsible for bone deposition during the remodeling process?
A) Osteoblasts
B) Chondroblasts
C) Osteoclasts
D) Fibroblasts
C
B.
D
C.
B.
A.
the process of deposition of minerals on the bone matrix for the development of bone.
This is typically done by the
Mineralization
Osteoblast
Factors Affecting Growth
Minerals (Ca, Mg, P)
Vitamins (A, C, D)
Hormones
Weight-bearing activity
Calcium Homeostasis is an example of what feedback?
Negative Feedback
A hormone that causes: increased osteoclast activity + decreased loss in urine
hormone made in the kidney (treats low calcium)
Hormone that decreases osteoclast activity
Parathyroid hormone
Calcitriol
Calcitonin
True or False: Bone strengthened in response to use and reabsorbed with disuse
True or False: If the bone is not used, it has less osteoclast than osteoblast and vice versa.
True
False
In ______________, connective tissue membranes are replaced by bone. This process occurs in the flat bones of the skull.
In ___________, bone tissue replaces hyaline cartilage models. Most bones are formed in this manner.
Bones grow in length at the ________ between the diaphysis and the epiphysis. It also grows in width in the ________
Bones may be classified as _________, _______, _________, or __________.
The __________ of a long bone is the central shaft. There is an _________ at each end of the diaphysis.
Intramembranous ossification.
Endochondral Ossification
Epiphyseal plate and periosteum
Long, short, flat, irregular
Diaphysis; epiphysis
In endochondral ossification, when does primary and secondary ossification occur?
Fetal Stage (first trimester) and after birth
refers to the complete process of bone formation
is a specific step within ossification where calcium salts are deposited into the bone matrix, essentially the hardening of the bone tissue
ossification
Calcification
Under the influence of hormones (especially sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone), the growth plates harden and close, a process called _______ which stops bone growth.
Epiphyseal plate fusion
What gland responds to low calcium? It releases what hormone?
Parathyroid gland, parathyroid hormone
What do you call a type of embryonic connective tissue that differentiates in to bone cells?
Mesenchyme