Interactions of Chemical Substances
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
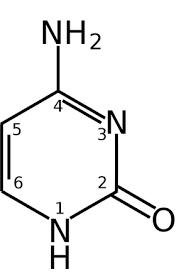
structure of cytosine:
Pyrimidine ring (six-membered ring with two nitrogens).
Key functional groups:
Amine group (-NH₂) at C4
Keto group (=O) at C2
Nitrogens at positions 1 and 3.
How does hydrogen bonding affect boiling point?
✅ Effect:
Hydrogen bonding creates strong intermolecular forces.
More energy (heat) required to break these bonds → higher boiling point.
What is Fractional Distillation?
Fractional distillation is a separation technique used to separate a mixture of liquids with different boiling points.
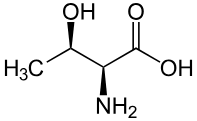
Threonine structure:
Side chain (R group): CH(OH)CH₃ (hydroxyl + methyl group)
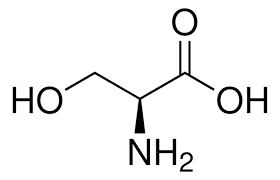
Serine structure:
"Serine is Simple" → Side chain is just –CH₂OH (simpler than threonine’s branched OH + CH₃).
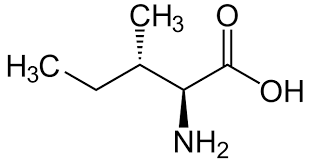
isoleucine structure:
"Iso = Isomer of Leucine" → Isoleucine is a structural isomer of leucine (same formula, different arrangement).
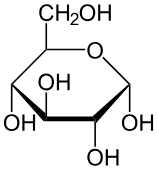
structure of glucose:
Aldehyde group (–CHO) at carbon 1 → makes glucose an aldose.
6 carbons with hydroxyl (–OH) and hydrogen (–H) groups in specific orientation.
Why is fluorine a stronger electron-withdrawing group than chlorine?
"F is Fierce (pure EWG), Cl is Compromise (EWG + resonance)."
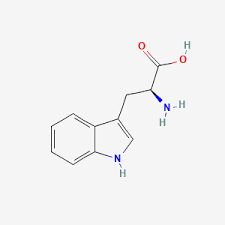
Tryptophan structure:
Side chain (R group): CH₂ connected to an indole ring (aromatic).
How is pH related to hydronium ion concentration?
pH = –log[H₃O⁺]
[H₃O⁺] = 10^(–pH)
Lower pH → higher [H₃O⁺] (acidic).
Higher pH → lower [H₃O⁺] (basic)
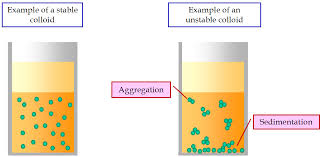
What is a Colloid?
A colloid is a mixture where small particles (1–1000 nm) are dispersed throughout another substance, but they do not settle out or separate upon standing.
Ionic Solids and Electrolytes:
Ionic solids (e.g., NaCl, KBr) consist of positive and negative ions held together by strong electrostatic forces.
When dissolved in water (a polar solvent), these ionic bonds break due to ion-dipole interactions, separating into free ions.
These free ions allow the solution to conduct electricity, forming an electrolyte solution.
weak vs. strong electrolyte:
Strong electrolytes: Fully dissociate (e.g., NaCl, HCl).
Weak electrolytes: Partially dissociate (e.g., CH₃COOH).
What is a Monoprotic Acid?
A monoprotic acid is an acid that can donate only one proton (H⁺) per molecule in an aqueous solution.
What are Strong Acids?
Strong acids are acids that completely dissociate (ionize) in water, releasing all of their protons (H⁺) and forming hydronium ions (H₃O⁺).
What are strong acids? Name the common ones.
Climb High in Chemistry, No Problems
(Cl: HCl, H: HBr, I: HI, C: HClO₄, N: HNO₃, P: H₂SO₄).
What are weak acids?
Weak acids are acids that partially dissociate (ionize) in water, releasing only some of their protons (H⁺).
Give examples of weak acids:
"A Funny Penguin Can Bake Cookies"
A – Acetic acid (CH₃COOH)
F – Hydrofluoric acid (HF)
P – Phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄)
C – Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃)
B – Benzoic acid (C₆H₅COOH)
C – HCN (Cyanide acid)
Is citric acid a strong or weak acid?
Citric acid is a weak, triprotic acid (not strong)
how is pka related to ph?
When pH = pKa:
The acid is 50% dissociated (equal acid and conjugate base concentrations).
This is the buffering point.
When pH < pKa:
Solution is more acidic (protonated form HA dominates).
When pH > pKa:
Solution is more basic (deprotonated form A⁻ dominates).
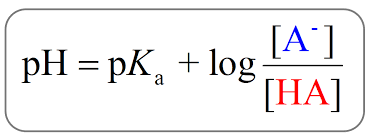
Henderson–Hasselbalch Equation:
pH = pKa+ log([HA/][A−])
Where:
pKa = acid dissociation constant (strength of acid)
[A⁻] = conjugate base concentration
[HA] = undissociated acid concentration
what does a high and low pka mean?
Low pKa → Strong acid (dissociates easily).
High pKa → Weak acid (holds onto protons).
what is pKa?
acid dissociation constant (Ka) expressed on a logarithmic scale.
determines the strength of an acid - how easily it donates a proton (H⁺). How easily is dissociates.
What is pH?
a measure of how acidic or basic (alkaline) a solution is, based on the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺)/ hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) in the solution.
What is a Buffer?
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid (H⁺) or base (OH⁻) are added.
How Does a Buffer Work?
Buffers are usually made of:
A weak acid (HA) and
Its conjugate base (A⁻).
The weak acid neutralizes added base, and the conjugate base neutralizes added acid, keeping pH stable.
why does a triprotic acid have three pkas?
A triprotic acid has three pKa values because it can donate three protons (H⁺), each at a different stage of dissociation.
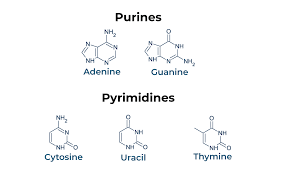
Which nucleotides are purines and which are pyrimidines?
Purines:
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
→ Two-ring structures
Pyrimidines:
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T) (DNA)
Uracil (U) (RNA)
→ One-ring structures
What determines the stability of DNA and RNA folded structures?
The number of G-C (guanine–cytosine) base pairs greatly affects the stability of both DNA and RNA.
This is because G≡C has three hydrogen bonds, compared to A=T (or A=U in RNA), which has only two.
What is Tm (melting temperature) in the context of DNA/RNA structure?
Tm is the temperature at which 50% of the nucleic acid molecules are denatured (unfolded) and 50% remain folded.
It reflects the thermal stability of the molecule — higher Tm means more stable structure.
What does it mean that galactose is a C-4 epimer of glucose?
Galactose and glucose are both six-carbon aldoses (hexoses), but they differ in the configuration around carbon 4 (C-4).
That’s why galactose is a C-4 epimer of glucose.
What are oxidation and reduction in organic/biological chemistry?
Oxidation = Loss of electrons (or gain of oxygen / loss of hydrogen)
Reduction = Gain of electrons (or gain of hydrogen / loss of oxygen)
Why is adding hydrogen a reduction?
A hydrogen atom (H) consists of 1 proton and 1 electron.
When a molecule gains hydrogen, it also gains the electron that comes with it.
Gaining electrons = reduction.
What is NADH redox cycling, and why is it important?
NADH redox cycling refers to the continuous reduction and oxidation of NAD⁺/NADH in metabolic pathways:
NAD⁺ is reduced to NADH when it accepts electrons (and a proton) during catabolic reactions like glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
NADH is oxidized to NAD⁺ when it donates electrons to the electron transport chain or during fermentation.