Orgo 1 Unit 4 Reactions
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
NaCrO7
CrO3
NaOCl(excess)

NaOCl/TEMPO
Na2Cr2O7
CrO3

PCC
NaOCl (1 equiv.)

1. LiAlH4,THF
NaBH4
2. H3O+

1. LiAlH4,THF
NaBH4
2.H3O+
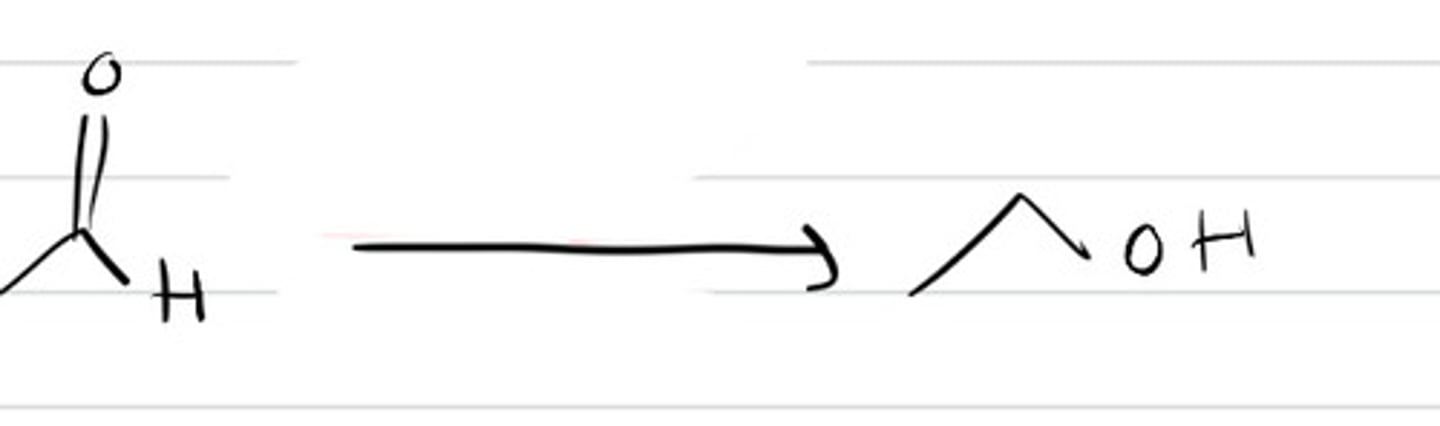

1.RLi
RMgBr
2. H3O+
1. RLi
RMgBr
2. H30+

NaNH3

H2,Pt/Ni/Pd

H2, Lindlar's catalyst
HX

HBr in ROOR
H3O+ in H2O

1. BH3-THF
2. H2O2 / H2O + NaOH

X2

X2 and H2O
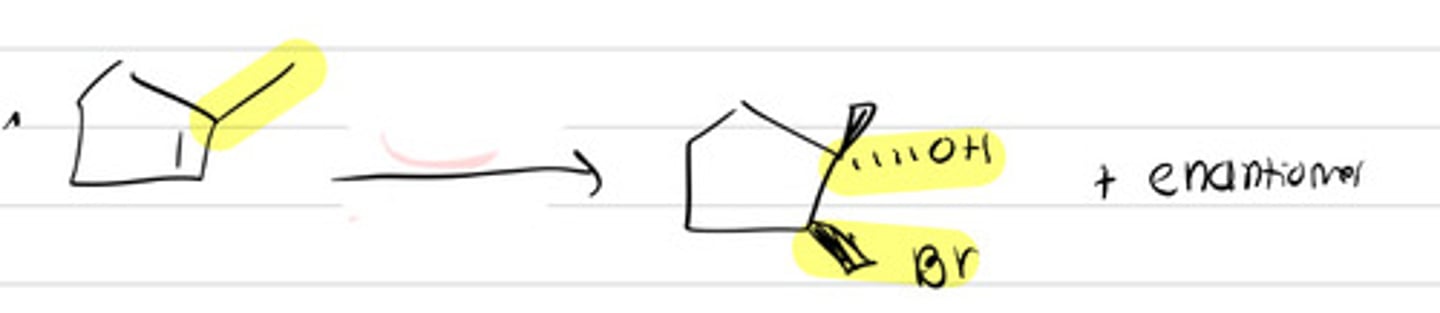
RCO3H or MCPBA
Makes epoxidation ring
RCO3H
In H3O+ and H2O

OsO4, H2O2
Or
KMnO4, HO-, cold

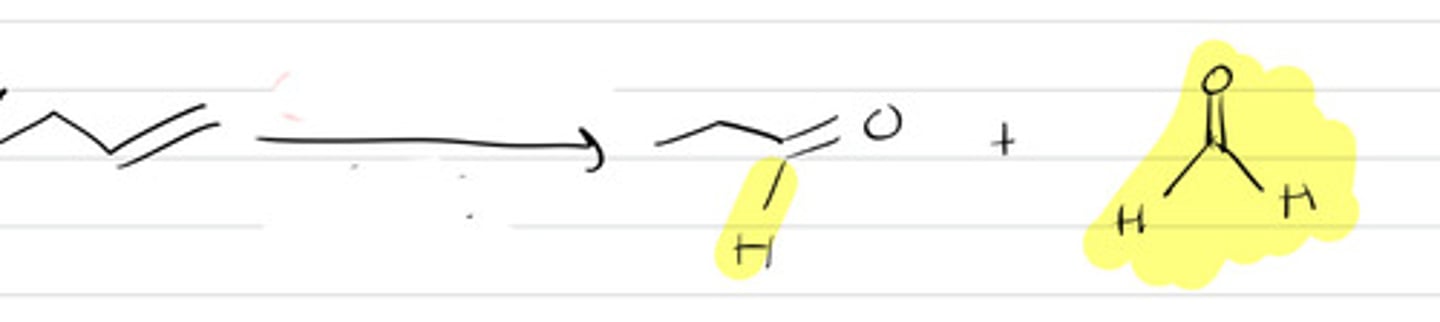
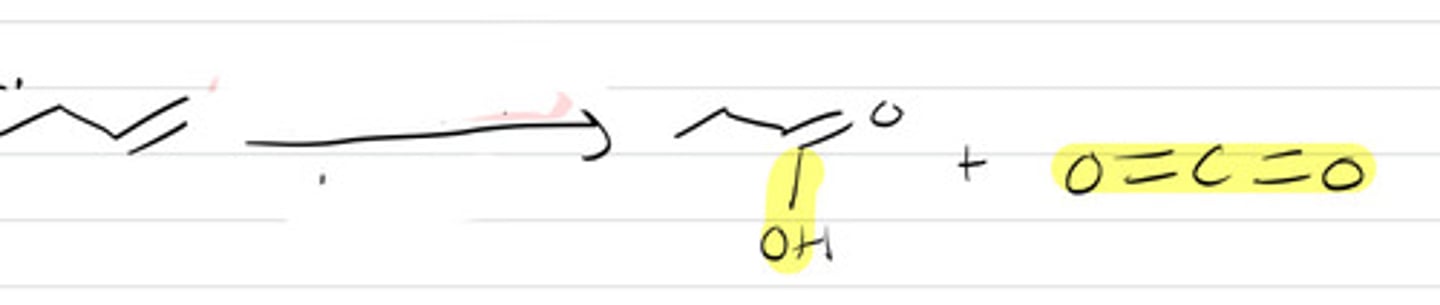
O3, -78C 2.DMS
KMnO4, H+, warm
- H becomes OH or O depending on stability
H30, H20

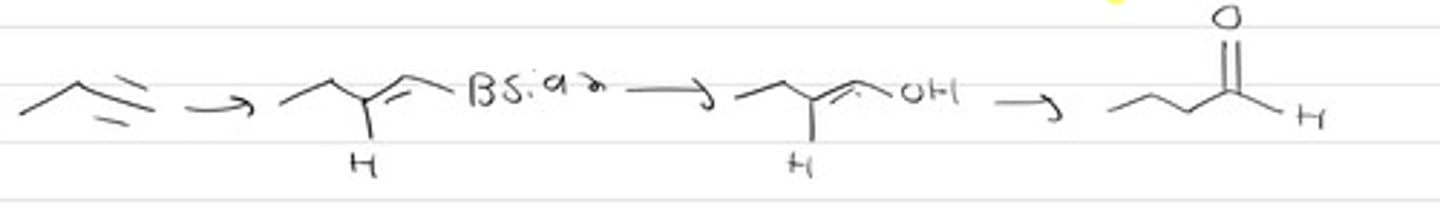
1. Sia2BH-THF
2. H2O2 / NaOH, H2O
3. Basic conditions
Hydride reagents mechanism
LiAlH4-THF and NaBH4
1. The Hydrogen attacks the carbonyl carbon
2. The double bond breaks and donates electrons to the O, which is now negatively charged
3. Proton transfer occurs, O steals H from H20
4. Final products include an alcohol and OH-
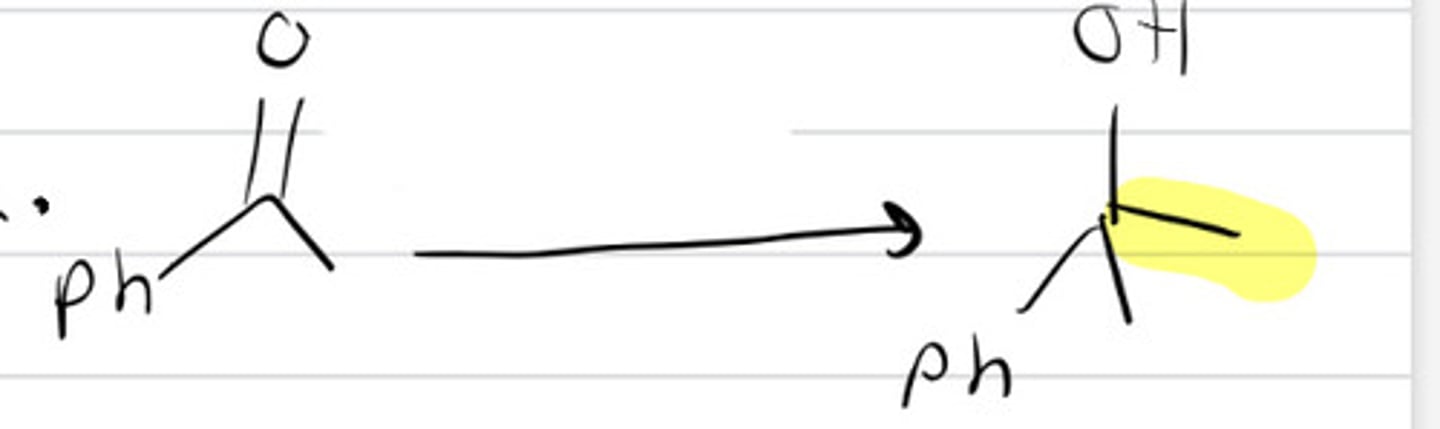
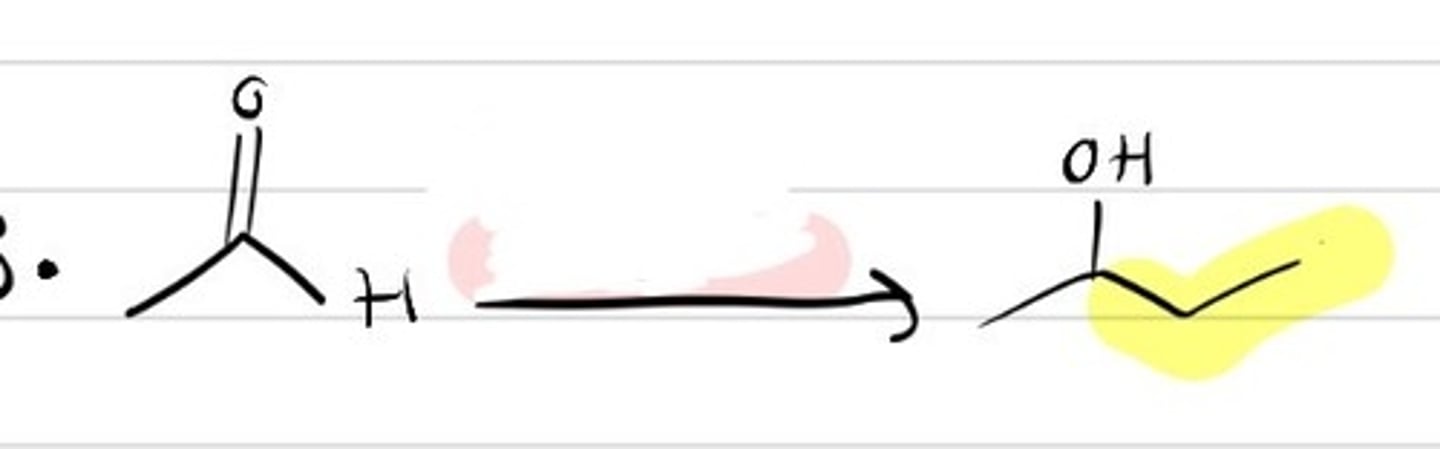
Organometallic Reagents mechanism
RMgBr and RLi
1. The R group (CH3 variant) attacks the carbonyl carbon
2. Double bond breaks and donates electrons to O, which is now negatively charged.
3. Proton transfer occurs, O steals H from H2O
4. Final products include an alcohol with the R group attached, OH-
Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes mechanism
HX
1. Alkene attacks the Hydrogen, X leaves, H attaches to less sub carbon
2. This creates a carbocation on the more substitited carbon
3. Bromine attacks the carbocation and attaches
4.
Stereochemistry of hydrohalogenation
On an unsymmetrical carbon with stereocenters, H and Br can add cis both ways or trans both ways, so there are 4 possible isomers.
Anti-Markovnikov
Br attaches to less subsititued
Needs HBr and ROOR
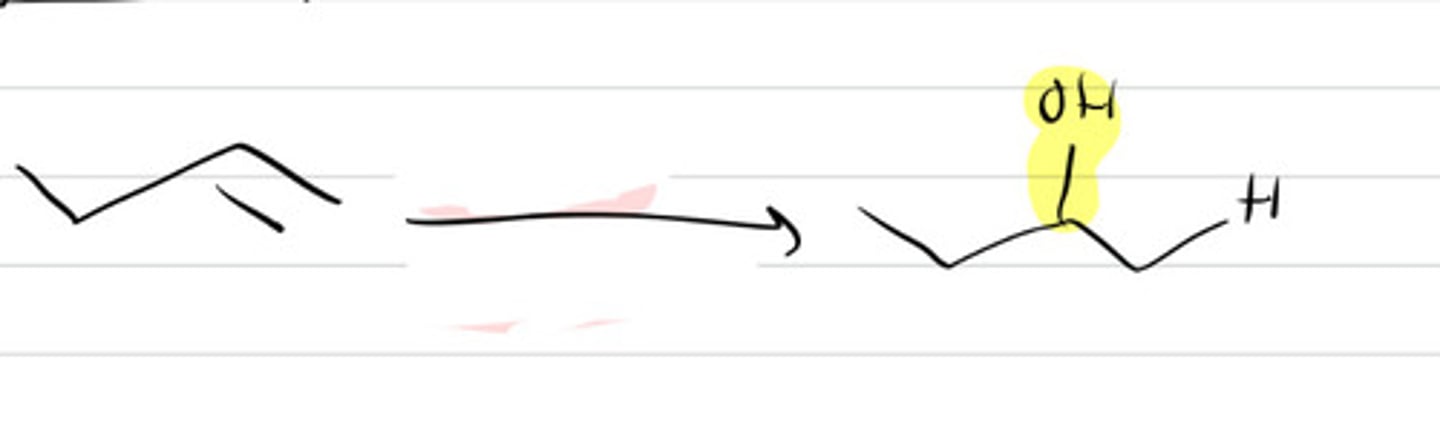
Alkene Hydration Mechanism
H3O+ in H2O
1. The alkene attacks the H in H3O+, OH2 leaves. H attaches to least sub carbon
2. Carbocation forms on the more substituted carbon
3. The lone pair on O of H2O attacks the carbocation and attaches
4. PT with H2O
5. Final products include alcohol and H3O+
Anti Markovnikov alkene hydration stereo/regiochemistry
- H and BH are CIS, only 2 stereoisomers and 1 regioisomer
Alkene Halogenation mechanism
Br2
1. Alkene attacks a Br. The Br attacks back. The other Br leaves
2. A triangle shape forms with the Br. The other Br attacks the more substituted carbon.
3. Final product is two trans bromines attached where the alkene was
Halohydrin Formation mechanism
Br2 H2O
1. Alkene attacks Br. Br attacks back and the other Br leaves.
2. H2O attacks the more substituted Bromine. That Br leaves.
3. The ring opens and PT occurs with H2O to another H2O
Epoxidation
RCO3H
1. Alkene attacks O, O-O sigm bond attacks the O-C sigma bond, the double bond to O attacks the H, the sigma bond of H attacks the more substituted carbon of the alkene
2. Results in cis O and RCO2H-
Anti Dihydration mechanism
RCO3H, H3O+, H2O
1. Alkene attacks O, O-O sigm bond attacks the O-C sigma bond, the double bond to O attacks the H, the sigma bond of H attacks the more substituted carbon of the alkene
2. Ring structure with O is formed, the lone pair on O attacks the H on H3O+, OH2 leaves. O is now OH
3. H2O attacks and attaches anti to OH
4. PT with H2O and another H2O
5. Forms anti with two OH attached and H3O+
Electrophilic addition of HX to Alkyne mechanism
HBr
1. Alkyne attacks H, Br leaves
2. Br attacks carbocation on most substituted carbon
3. Alkene attacks H, Br leaves
4. Br attacks carbocation on the same carbon as the other Br
5. Product is two Brs on one carbon
Alkyne hydration mechanism
H3O+ and H2O
1. Alkyne attacks H, OH2 leaves
2. H2O attacks carbocation on substituted carbon next to alkene
3. PT with H and another H2O
4. Lone pair on OH attacks sigma bond, alkene attacks H on H2O, OH2 leaves
5. H2O attcks H on OH, O is now neutral
6. Final product is carbonyl and H3O+
base catalyzed tautomerization mechanism
OH-
1. O in OH- attacks H on OH, O is now negative
2. Lone pair on O attacks sigma bond, alkene attacks H, OH leaves
3. Forms the carbonyl with double bond to oxygen and OH-
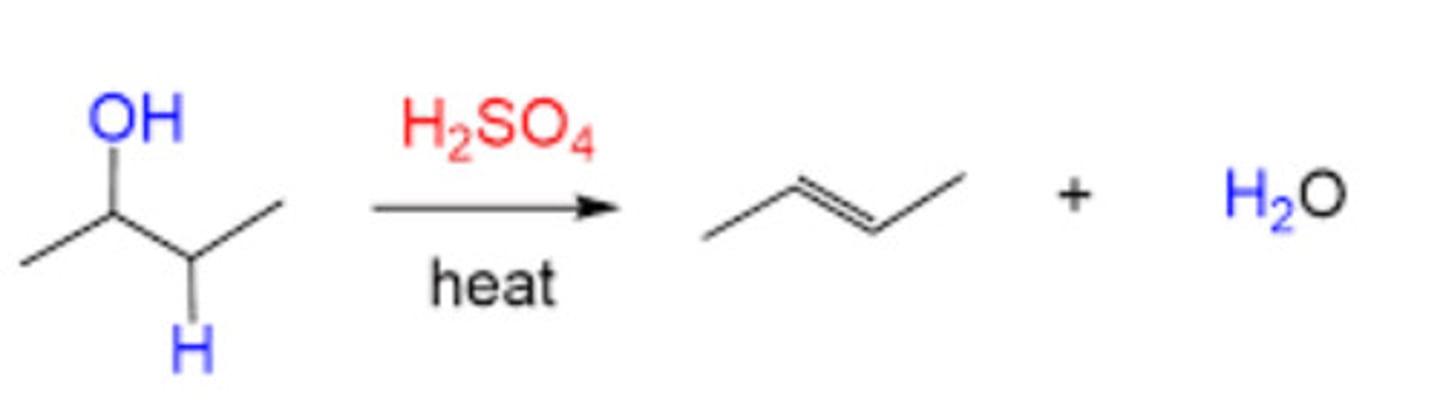
H2SO4
Alcohol dehydration