Animal Nervous Systems Overview
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Nervous System
Allows animals to sense and respond to environment.
Neuron
Basic functional unit of the nervous system.
Peripheral Nervous System
Includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central Nervous System
Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
Sensory Receptors
Detect stimuli through changes in membrane potential.
Brain
Integrates information from various sensory sources.
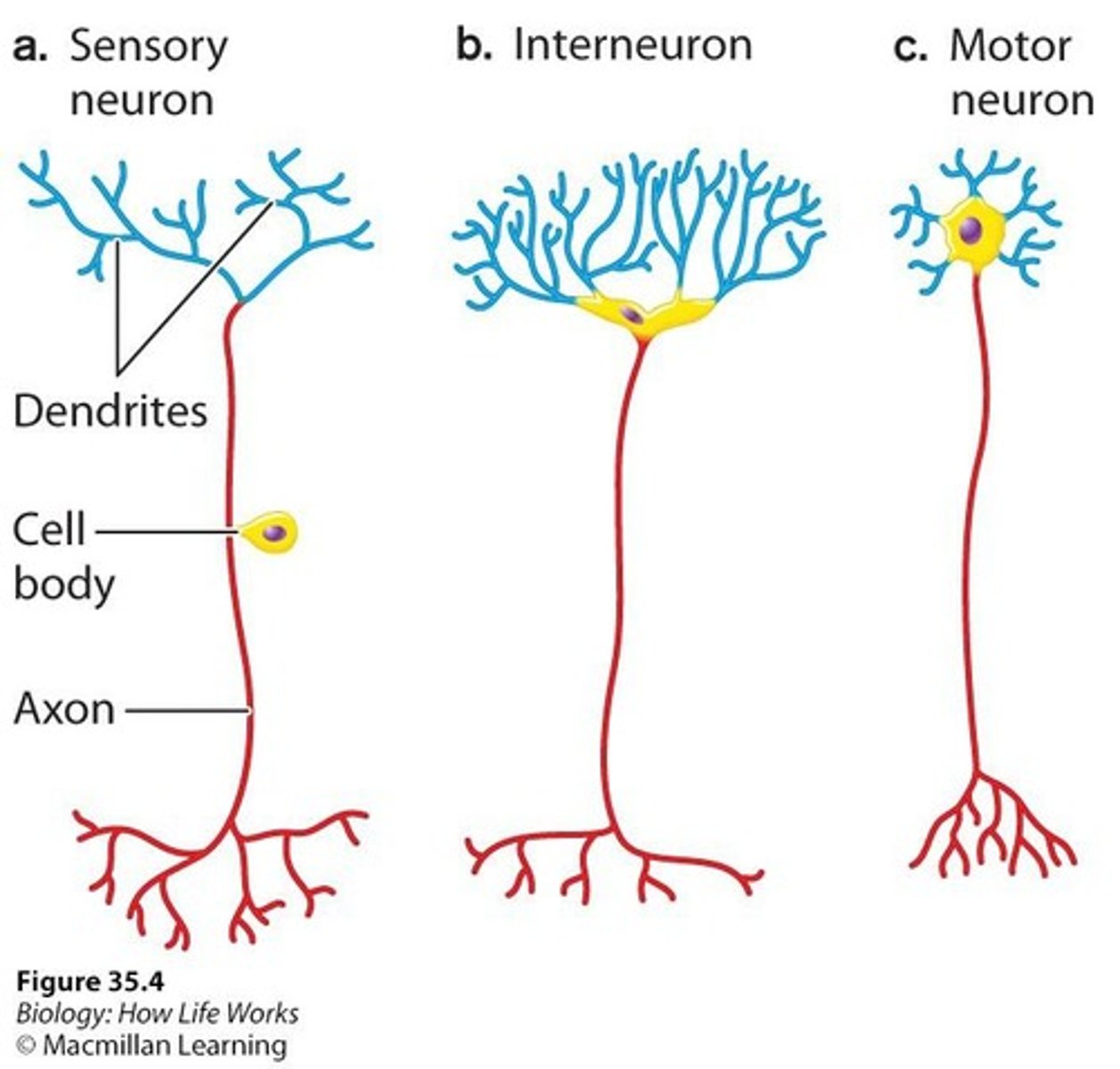
Dendrites
Receive signals from other neurons.
Cell Body
Contains the nucleus and organelles of a neuron.
Axon
Transmits electrical signals away from the cell body.
Sensory Neurons
Send information about external and internal environments.
Interneurons
Process information and transmit it to other regions.
Motor Neurons
Produce motor responses based on received information.
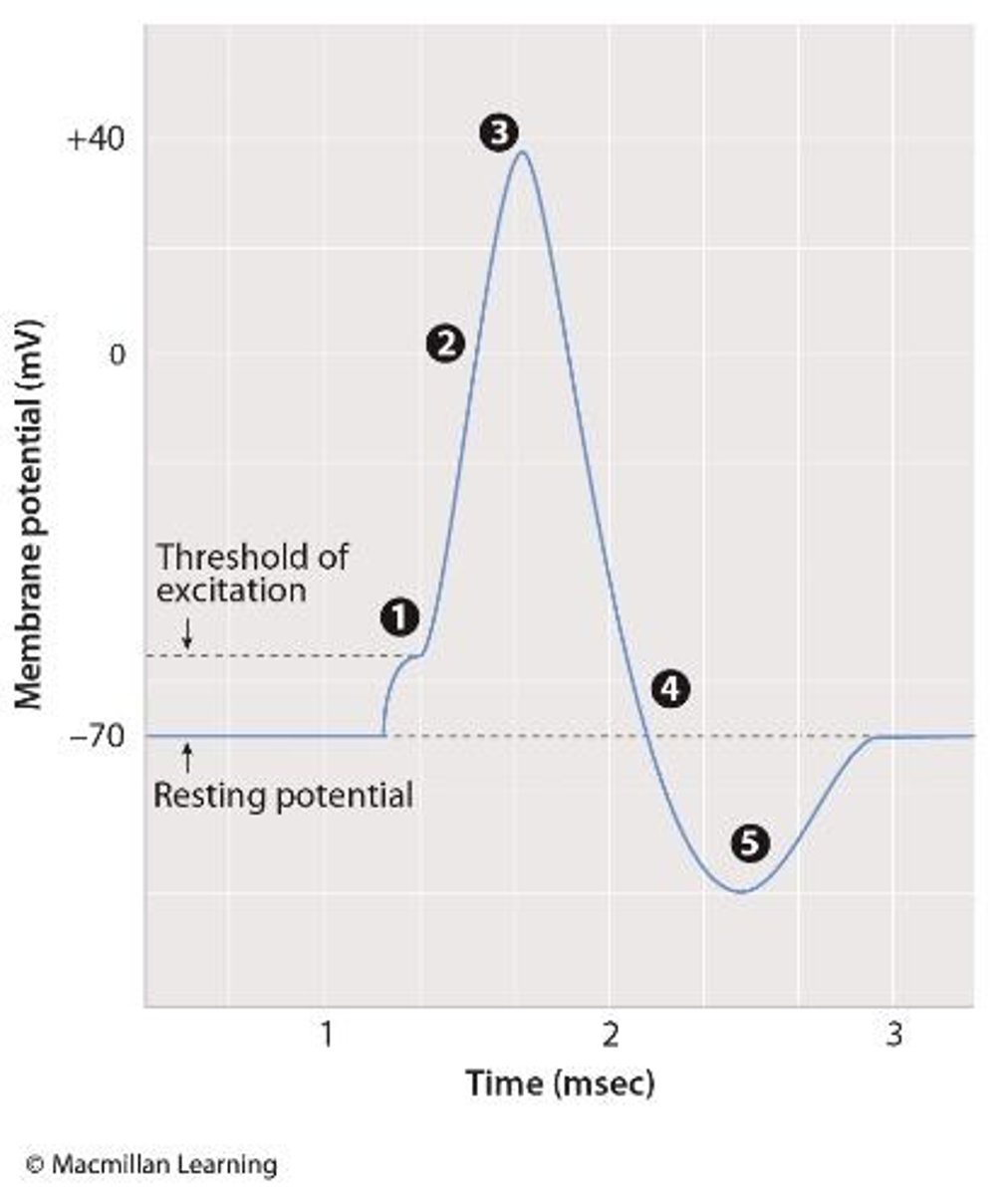
Action Potential
Brief electrical signal transmitted along axon branches.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical signals used for neuron communication.
Membrane Potential
Charge difference across a neuron's plasma membrane.
Resting Membrane Potential
Negative voltage across the membrane at rest.
Na+/K+ Pump
Maintains resting membrane potential by ion movement.
Depolarization
Membrane becomes less negative during excitation.
Threshold Potential
Membrane potential needed to trigger an action potential.
All-or-None Principle
Action potentials do not vary in strength.
Frequency Coding
Information is coded by action potential frequency.
Glial Cells
Support neurons without transmitting electrical signals.
Action Potential Propagation
Travels unidirectionally towards axon terminals.
Saltatory propagation
Fast transmission of action potentials along axons.
Hodgkin & Huxley
Researchers who studied action potentials in squid axons.
Synapse
Junction where neurons communicate via chemical signals.
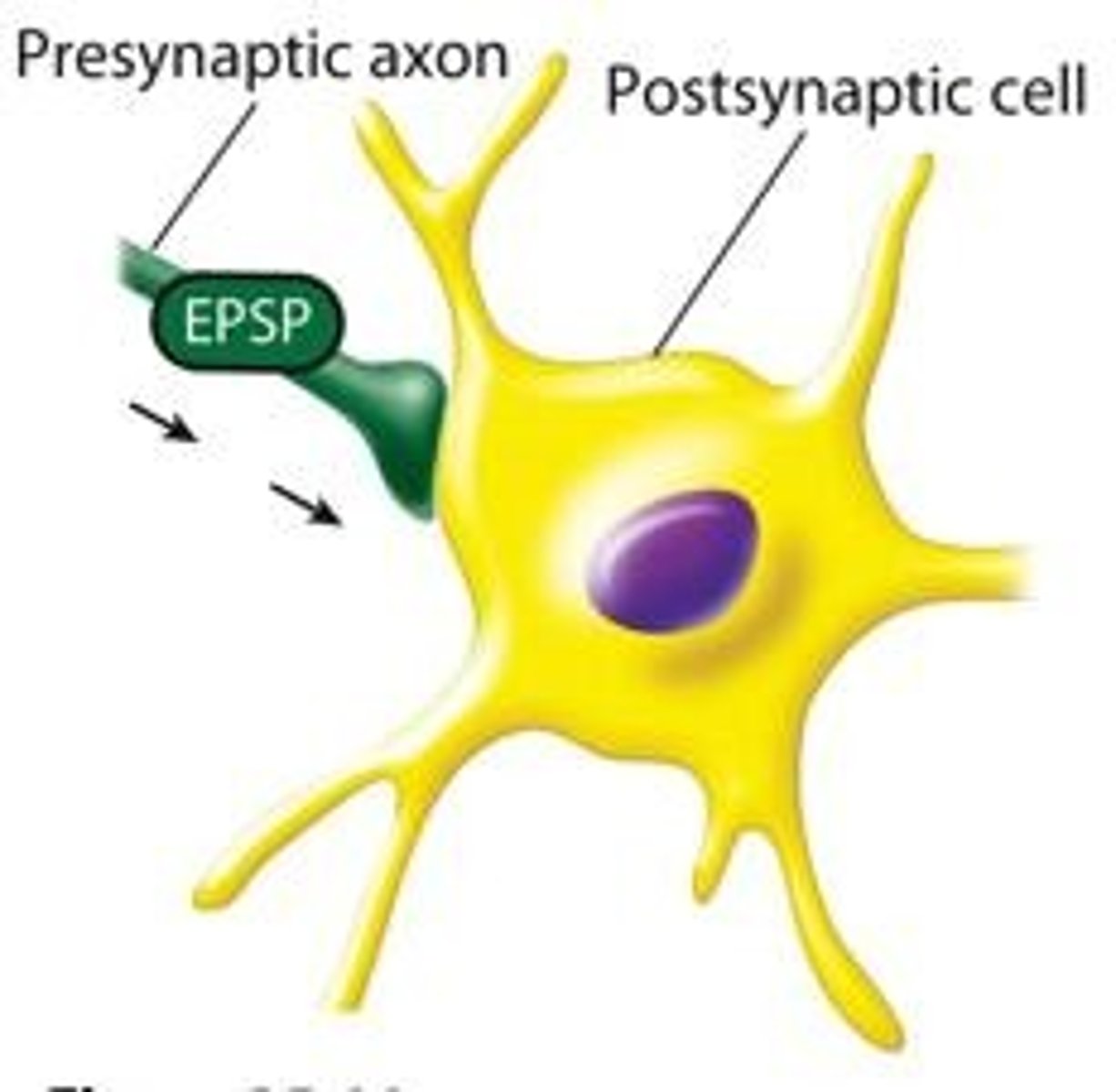
Postsynaptic membrane
Membrane receiving signals from neurotransmitters.
Voltage-gated Na+ channels
Channels that open during action potential depolarization.
Excitatory synapses
Transmit relevant information between nerve cells.
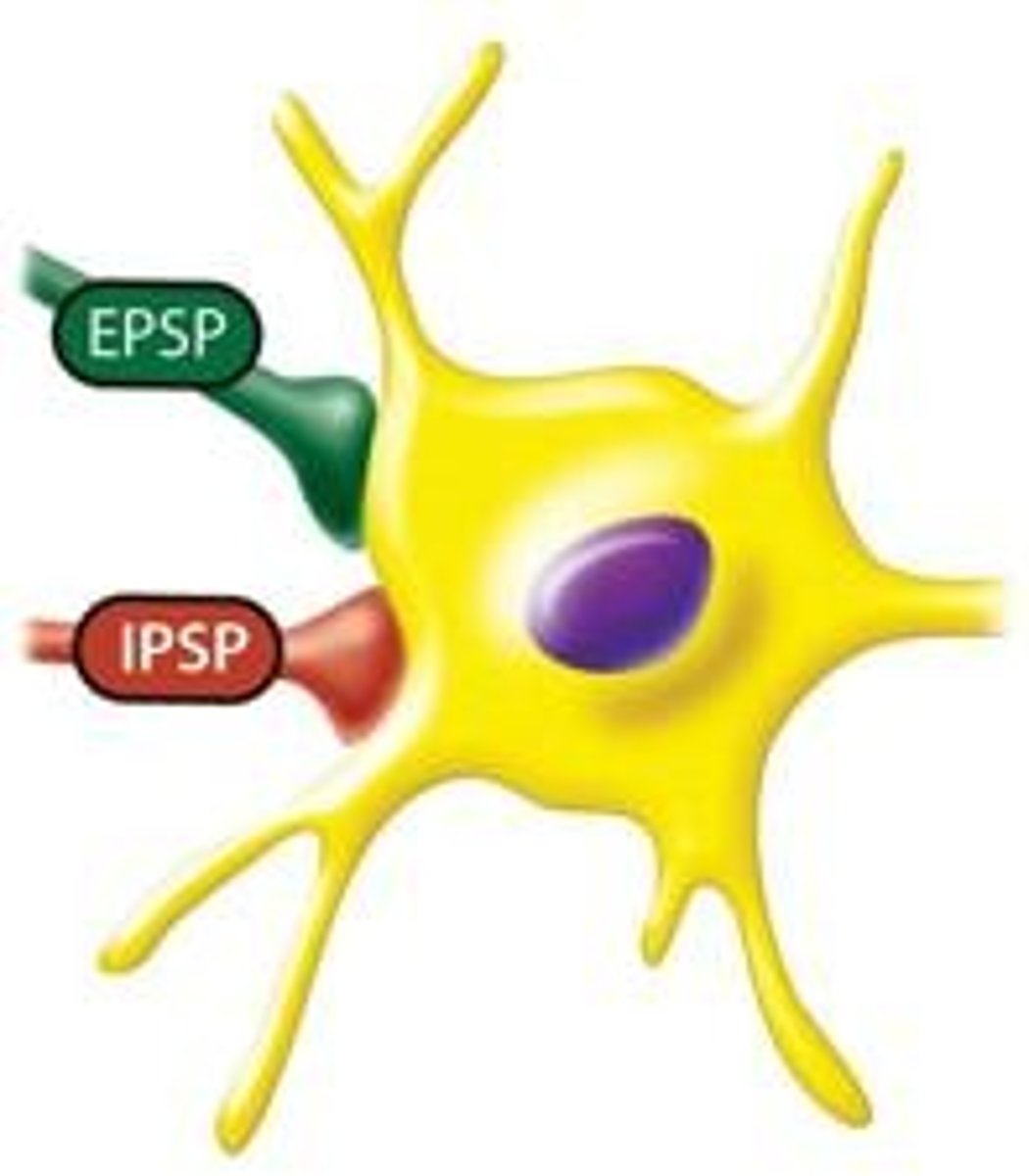
Inhibitory synapses
Filter out unimportant information between neurons.
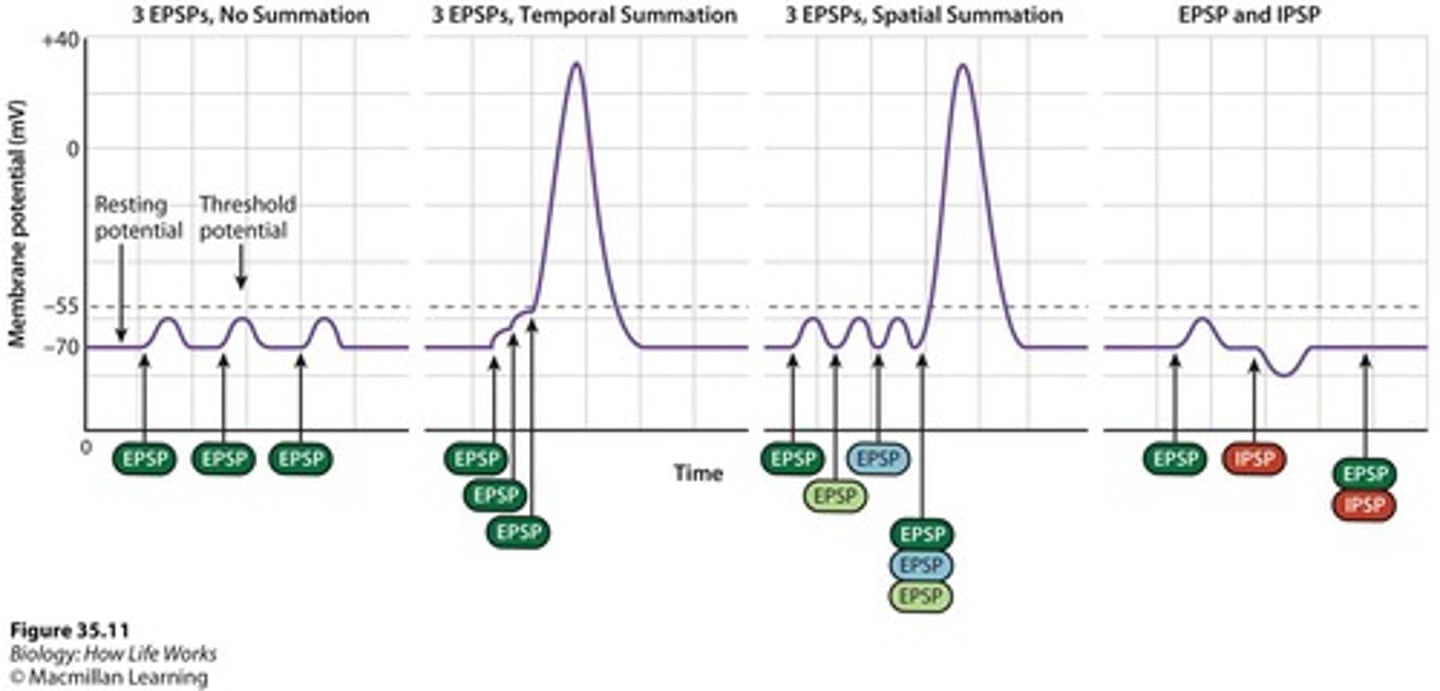
EPSP
Excitatory Post-Synaptic Potential, increases membrane potential.
IPSP
Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential, decreases membrane potential.
Temporal summation
Summation of EPSPs/IPSPs over time.
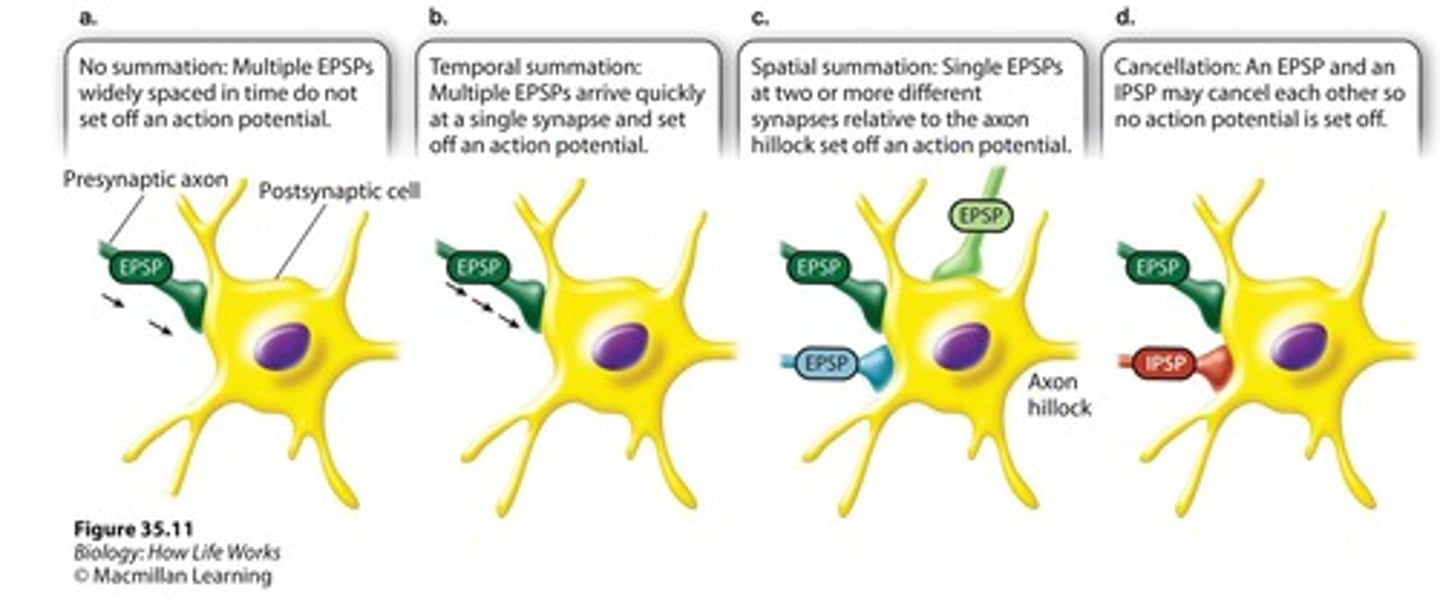
Spatial summation
Summation of EPSPs/IPSPs across different locations.
Nervous system organization
Structure coordinating responses to sensory information.
Central Nervous System
Includes brain and spinal cord.
Cerebral cortex
Region governing advanced cognitive functions.
Frontal lobe
Responsible for decision-making and planning.
Parietal lobe
Involved in body awareness and spatial orientation.
Temporal lobe
Processes auditory information and sound.
Occipital lobe
Responsible for processing visual information.
Gray matter
Superficial layer of cortex with densely packed neurons.
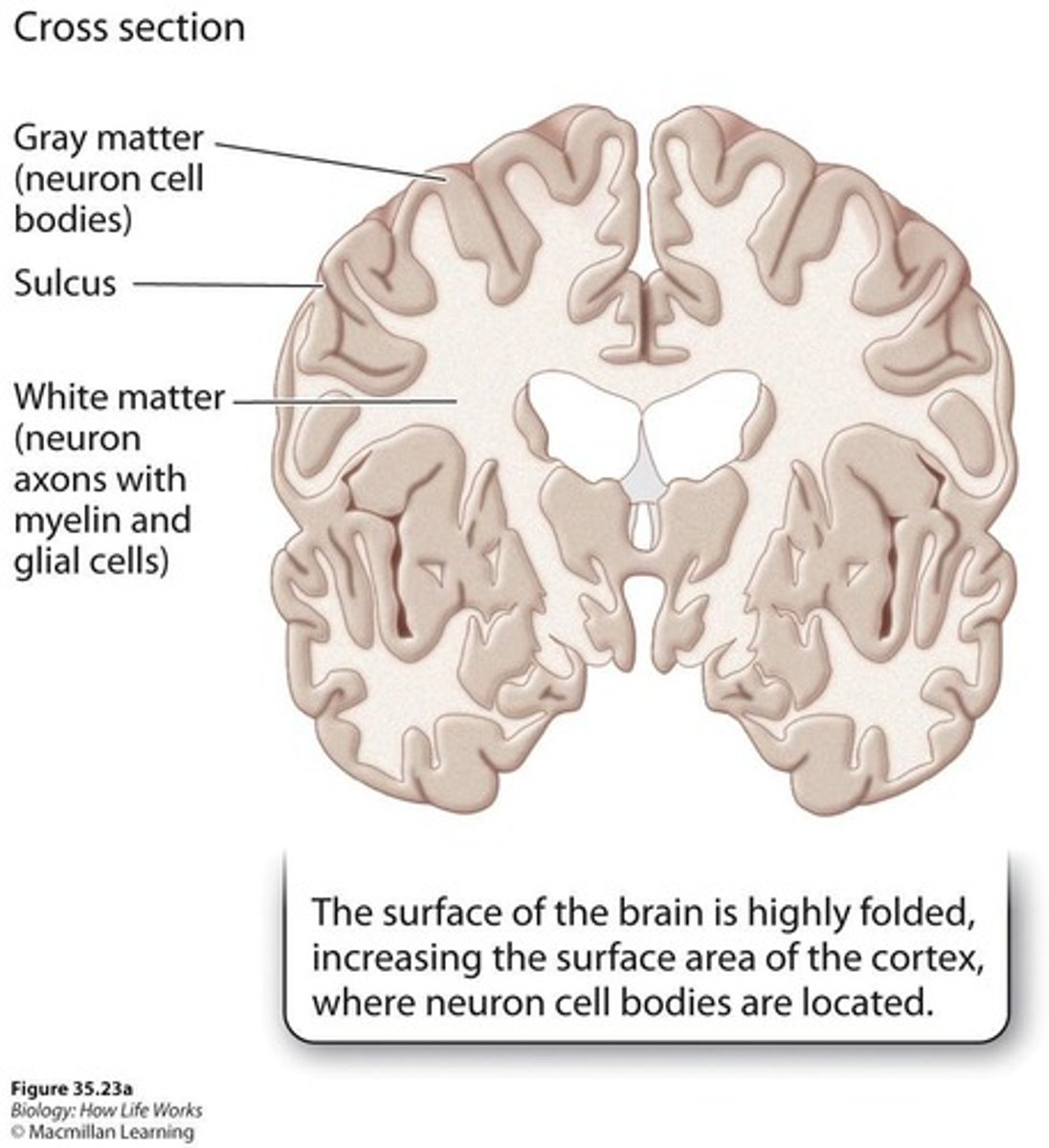
Neuronal surface area
Highly folded cortex increases neuron capacity.
Neurotransmitter-filled vesicles
Fuse with postsynaptic membrane during signal transmission.
Cerebral cortex
Outer layer of the brain, involved in complex functions.
White matter
Myelin-covered axons facilitating communication in the brain.
Thalamus
Relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex.
Hypothalamus
Regulates autonomic nervous system and endocrine functions.
Cerebellum
Coordinates complex motor tasks and integrates sensory information.
Peripheral Nervous System
Connects the central nervous system to limbs and organs.
Somatic division
Controls voluntary movements and external stimuli responses.
Autonomic division
Regulates involuntary bodily functions without conscious awareness.
Sympathetic nervous system
Prepares body for 'fight or flight' response.
Parasympathetic nervous system
Promotes 'rest and digest' functions.
Sensory receptors
Detect environmental stimuli and convert them to signals.
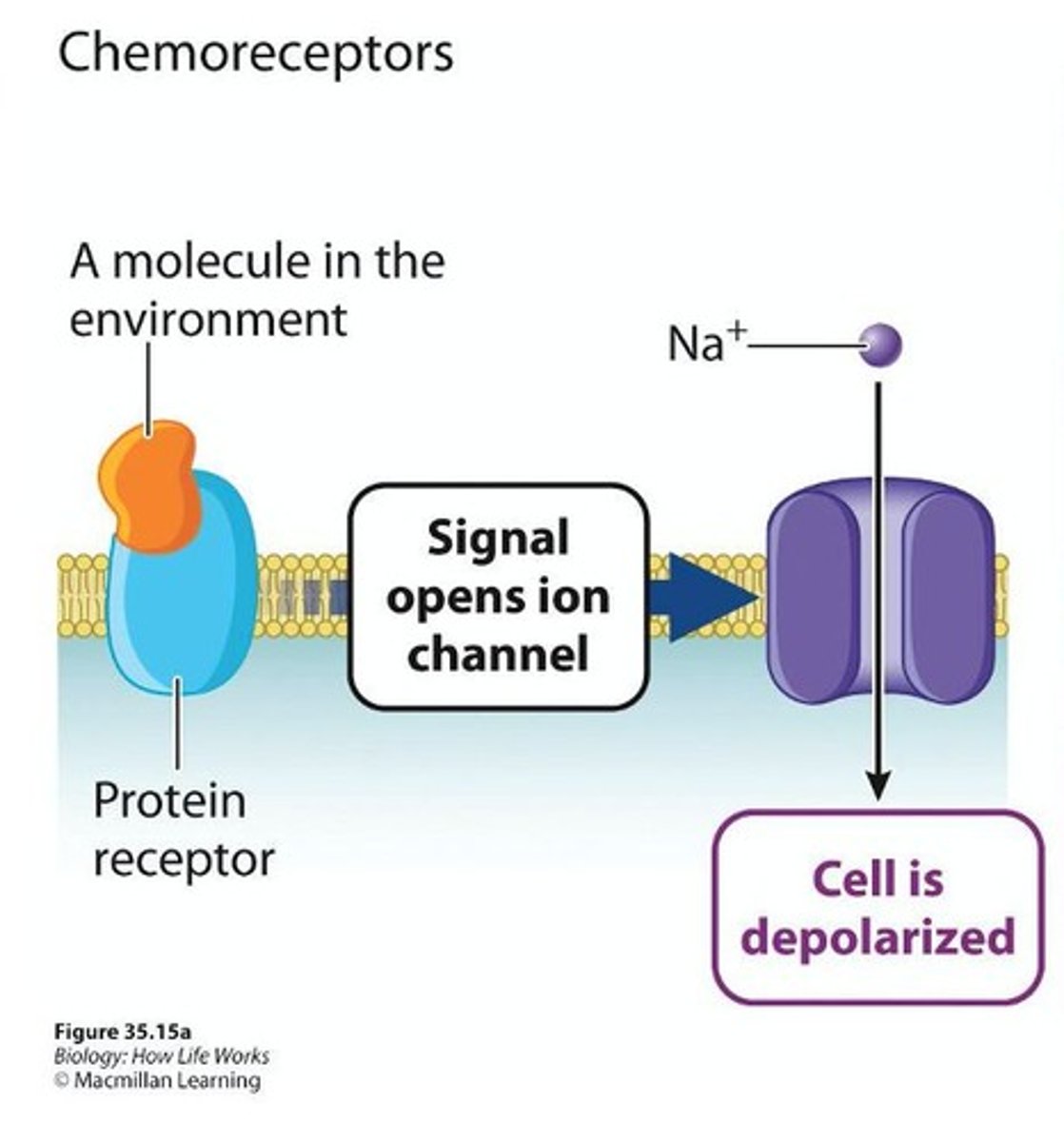
Chemoreceptors
Detect chemical stimuli and cause cell depolarization.
Mechanoreceptors
Respond to physical forces and open ion channels.
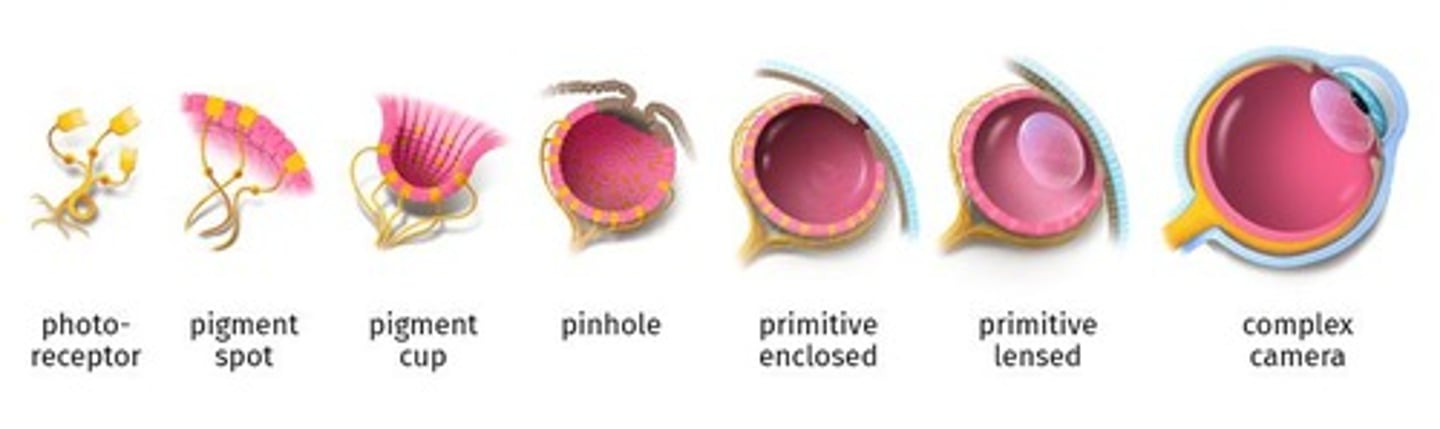
Photoreceptors
Convert light energy into electrical signals in the eye.
Gustatory cells
Taste receptors responding to chemicals in saliva.
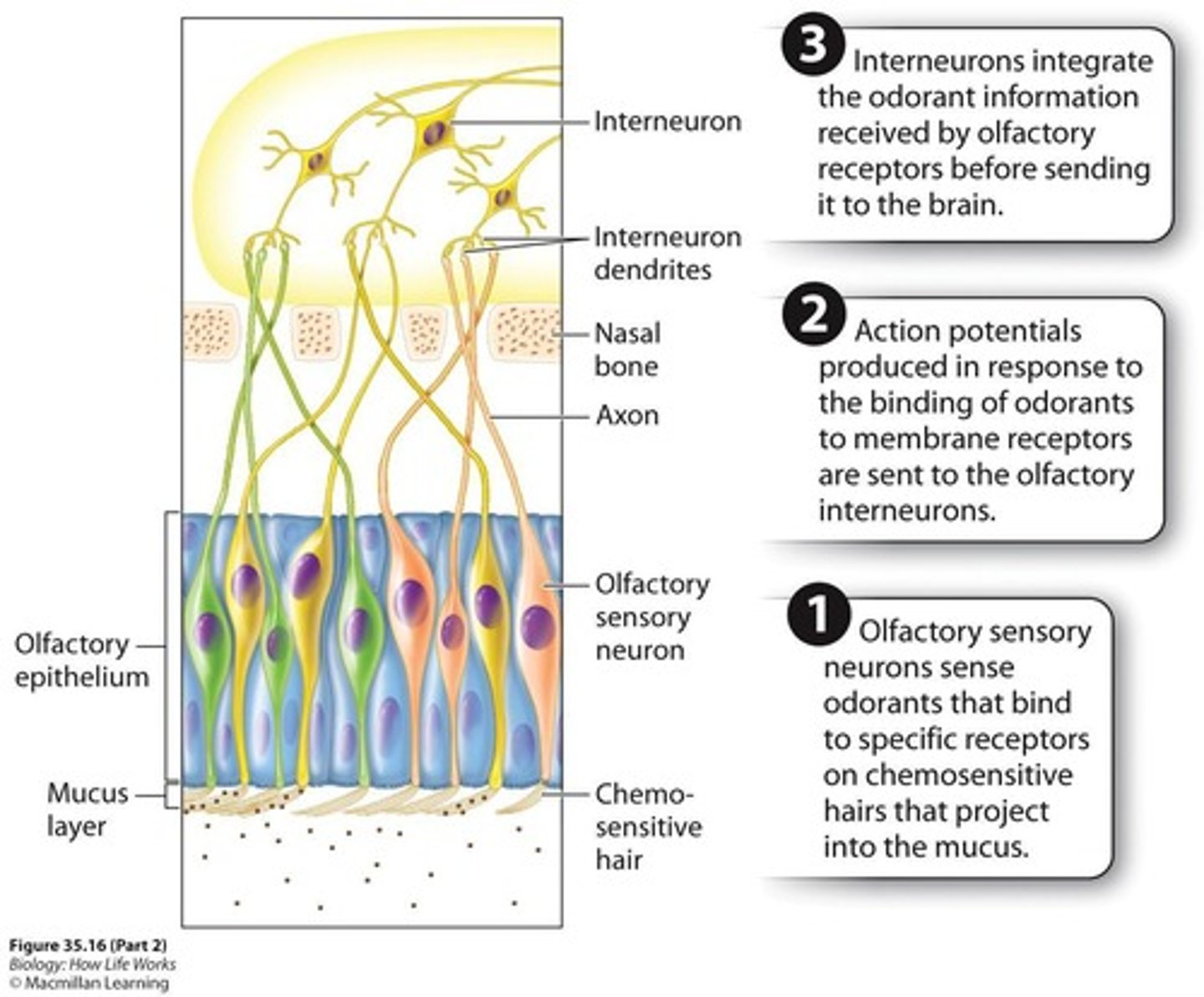
Olfactory cells
Smell receptors responding to chemical odors.
Rods
Photoreceptors for low-light vision, detect shades of gray.
Cones
Photoreceptors for color vision, sensitive to light wavelengths.
Single-lens eyes
Provide sharp images by focusing light on photoreceptors.

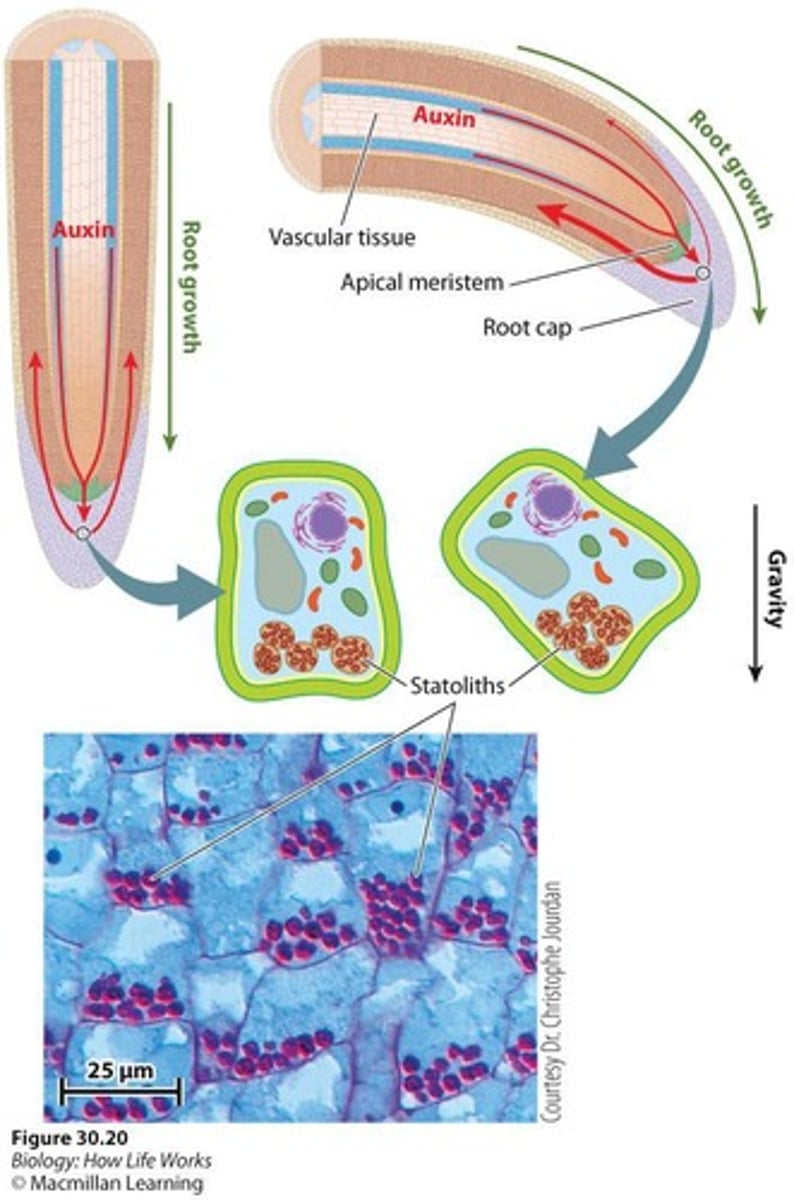
Statoliths
Starch-filled organelles aiding plant gravity orientation.
Sensory transduction
Conversion of physical stimuli into action potentials.
Action potential
Electrical signal generated by neuron response to stimuli.
Eye comparison
Differences in visual systems among various species.
Inhibitory synapses
Filter out unimportant information from signals.
EPSP
Excitatory Post-Synaptic Potential.
IPSP
Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential.
Temporal summation
Summation of signals over time.
Spatial summation
Summation of signals over space.
Nervous system organization
Includes central and peripheral components.
Central Nervous System
Comprises the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System
Includes cranial and spinal nerves.
Somatic division
Voluntary control of body movements.
Autonomic division
Involuntary control of internal functions.
Sympathetic nervous system
Prepares body for 'fight-or-flight' response.
Parasympathetic nervous system
Promotes 'rest-and-digest' functions.
Cerebral cortex
Governs advanced cognitive functions.
Parietal lobe
Involved in body awareness.
Temporal lobe
Processes auditory information.
Occipital lobe
Processes visual information.
Gray matter
Densely packed neuron cell bodies.
White matter
Myelin-covered axons facilitating communication.
Thalamus
Relays sensory information to the cortex.
Hypothalamus
Regulates autonomic and endocrine functions.
Cerebellum
Coordinates complex motor tasks.
Sensory receptors
Detect environmental physical properties.
Chemoreceptors
Detect chemical stimuli in the environment.
Mechanoreceptors
Detect physical forces and pressure.
Photoreceptors
Detect light and convert it to signals.
Gustatory cells
Respond to chemicals in saliva for taste.
Olfactory cells
Respond to chemical odors for smell.
Rods
Detect light intensity; sensitive in low light.
Cones
Detect color; sensitive to specific light wavelengths.
Opsin
Light-sensitive protein in photoreceptors.
Statoliths
Provide plant roots orientation relative to gravity.