Lecture 1 - Bonding and Water
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is a covalent bond?
The sharing of valence electrons.
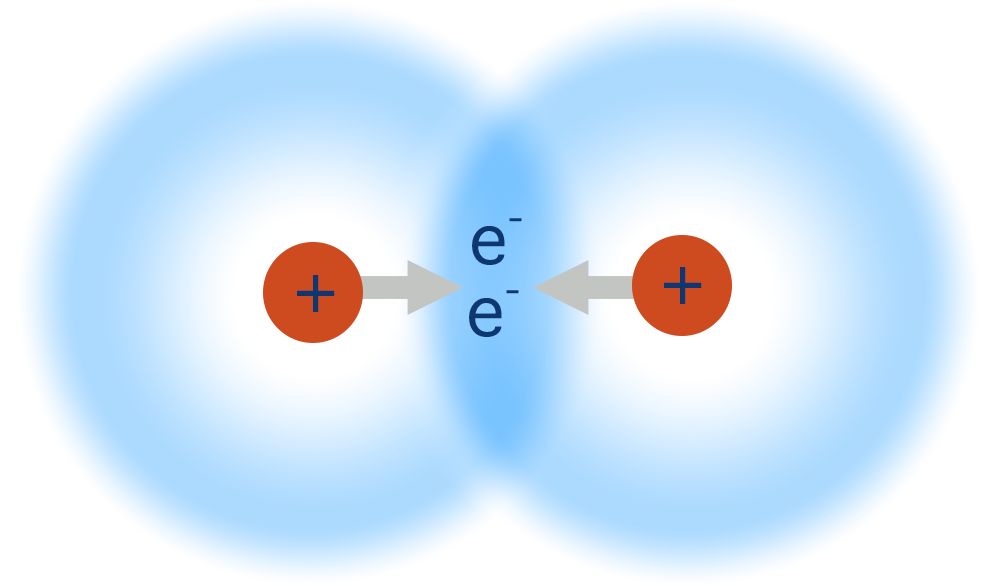
What is permanent dipole?
Covalent bond between two atoms with different electronegativities
Is water polar or non-polar?
Polar
What is a hydrogen bond?
Intermolecular attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom (like Oxygen, Nitrogen, or Fluorine) and another nearby electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons

What are the requirements for a hydrogen bond?
Hydrogen donor and acceptor.
What is a hydrogen donor?
Hydrogen bonded to an electronegative atom
What is a hydrogen acceptor?
A lone pair of electrons associated with an electronegative atom.
How many hydrogen bonds can each water molecule form?
Four
How many does a water molecule form on average?
Three
What are the van der Waals forces?
Dipole-dipole interactions (between charged atoms)
London dispersion forces (exist for every atom)
Is a hydrogen bond considered a dipole-dipole interaction?
Yes
What is hydrophobic effect?
The tendency of water molecules to minimize interactions with non-polar molecules in a solution, which causes non-polar compound to be forcefully associated with each other,
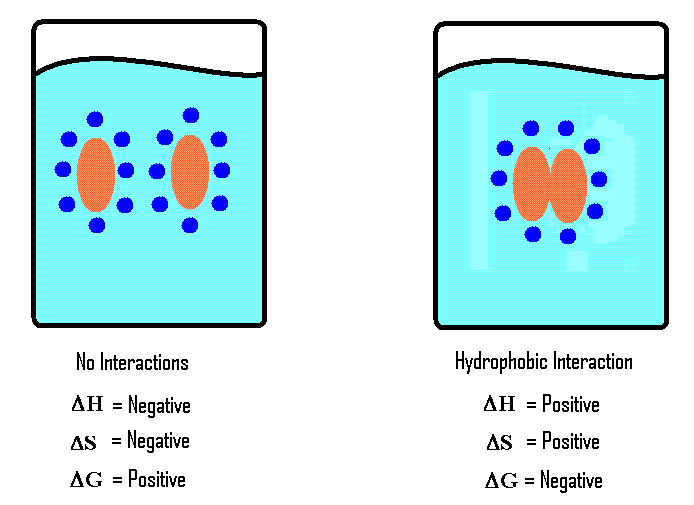
What is the benefit of hydrophobic effect?
A higher entropy (nature's tendency toward disorder, randomness, and energy dispersal). The clumped nature of the Nonpolar solvents decreases surface area therefore less hydrogen atoms have to surround the non-polar substances.
What is an amphipathic/amphiphilic molecule?
A molecule which experiences both hydrophilic interactions and hydrophobic effect
What is an example of an amphiphilic/amphipathic molecule?
Micelle