ch 25 (urinary system)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Kidney Functions
• Regulating total water volume and total solute concentration in water
• Regulating ECF ion concentrations
• Ensuring long-term acid-base balance
• Removal of metabolic wastes, toxins, drugs
Endocrine functions
Renin - regulation of blood pressure
• Erythropoietin - regulation of RBC production
-Activation of vitamin D
Kidneys cleanse blood; adjust its composition → rich blood supply
• Renal arteries deliver ~ ¼ (1200 ml) of cardiac output to kidneys each minute!!
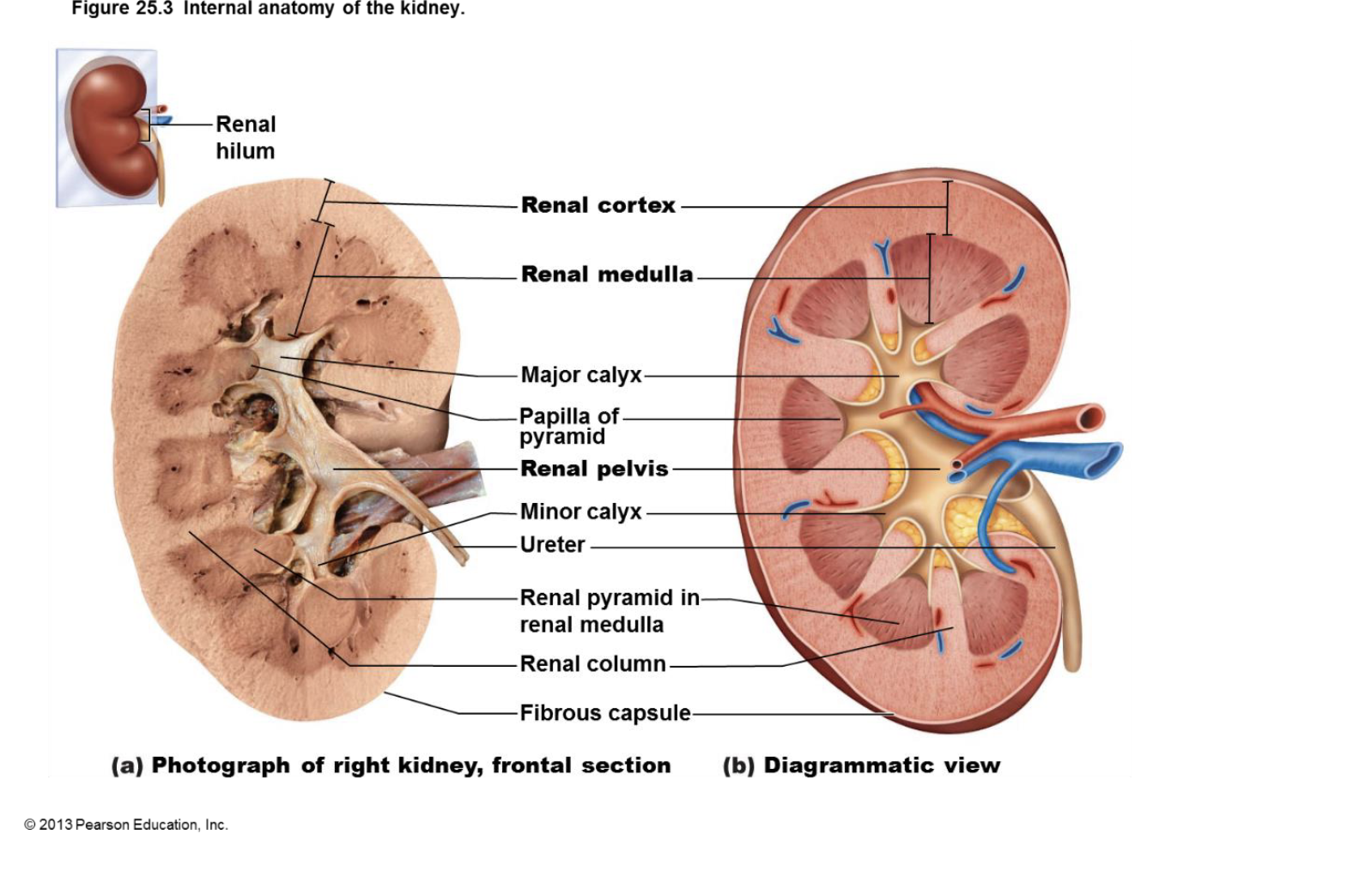
internal anatomy of the kidneys
nephron associated blood vessels
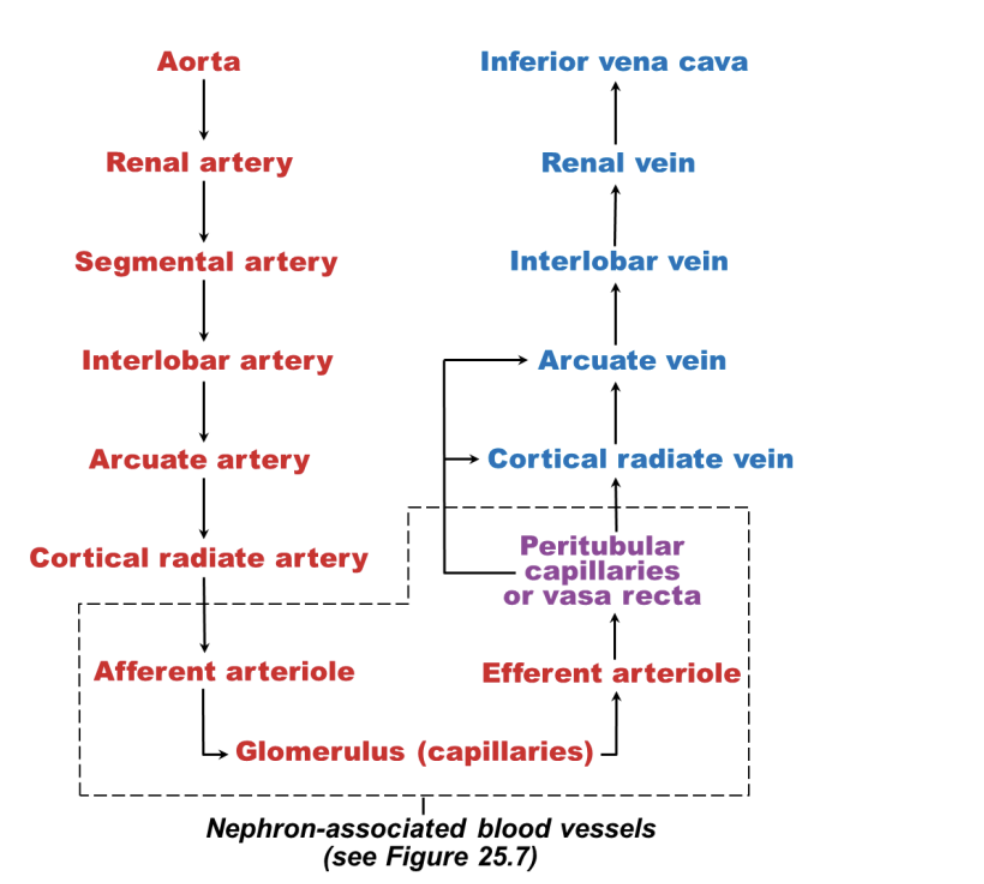
Glomerulus
- specialized for filtration (note: all glomeruli are in the cortex of kidney!)
• Different from other capillary beds – fed and drained by arteriole
– Afferent arteriole → glomerulus → efferent arteriole
• Blood pressure in glomerulus high because
– Afferent arterioles larger in diameter than efferent arterioles
– Arterioles are high-resistance vessel
Peritubular capillaries
– Low-pressure, porous capillaries adapted for absorption of water and solutes
– Arise from efferent arterioles
– Cling to adjacent renal tubules in cortex
Vasa recta
– Long, thin-walled vessels parallel to long nephron loops of juxtamedullary nephrons >>
countercurrent exchange
– Arise from efferent arterioles serving juxtamedullary nephrons
• Instead of peritubular capillaries
– Function in formation of concentrated urine
Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC)
– Distal portion of ascending limb of nephron loop
– Afferent (sometimes efferent) arteriole
Macula densa
Tall, closely packed cells of ascending limb
– Chemoreceptors; sense NaCl content of filtrate>>More NaCl=increased GFR and vice
versa
Granular cells (juxtaglomerular, or JG cells)
Enlarged, smooth muscle cells of arteriole
Ch 25 review sheet BIO163
– Secretory granules contain enzyme renin
– Mechanoreceptors; sense blood pressure in afferent arteriole
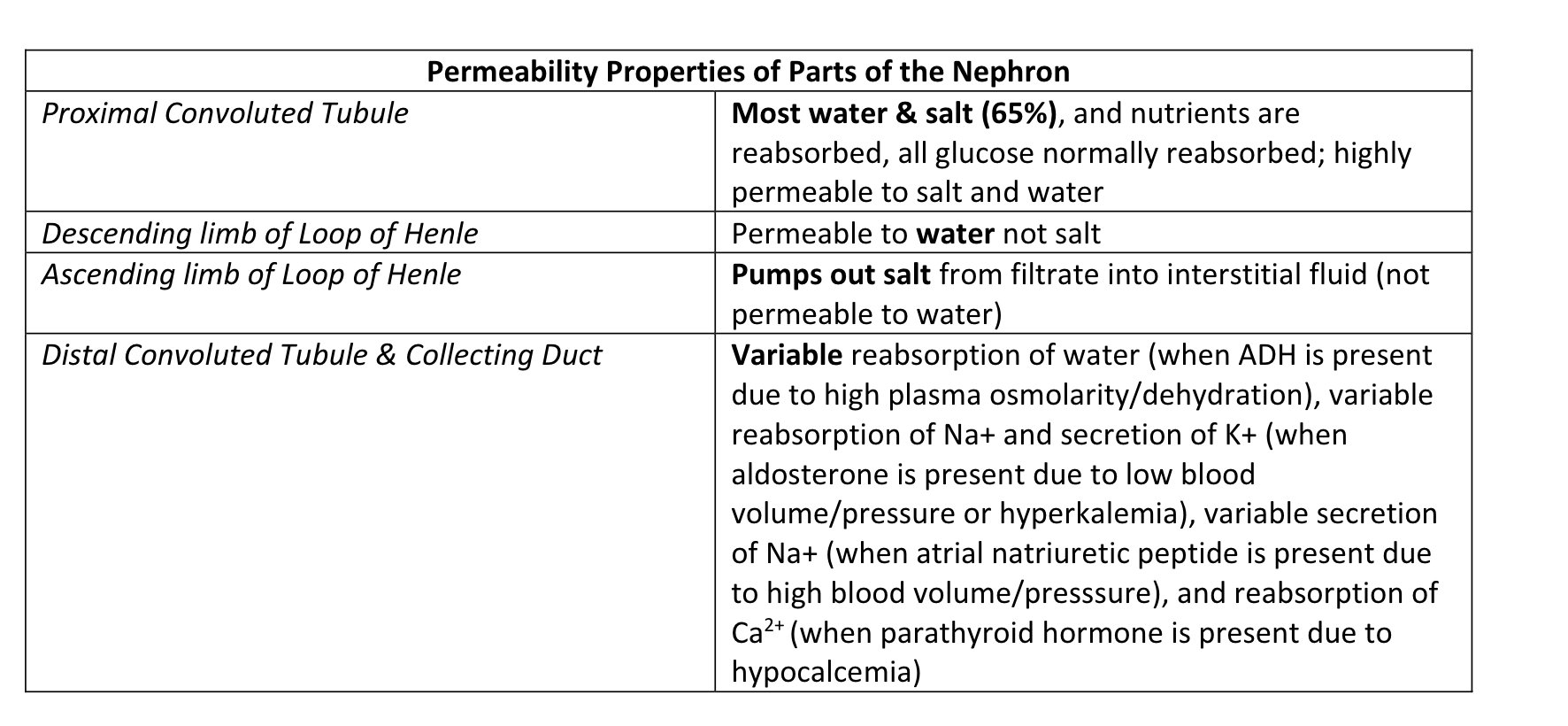
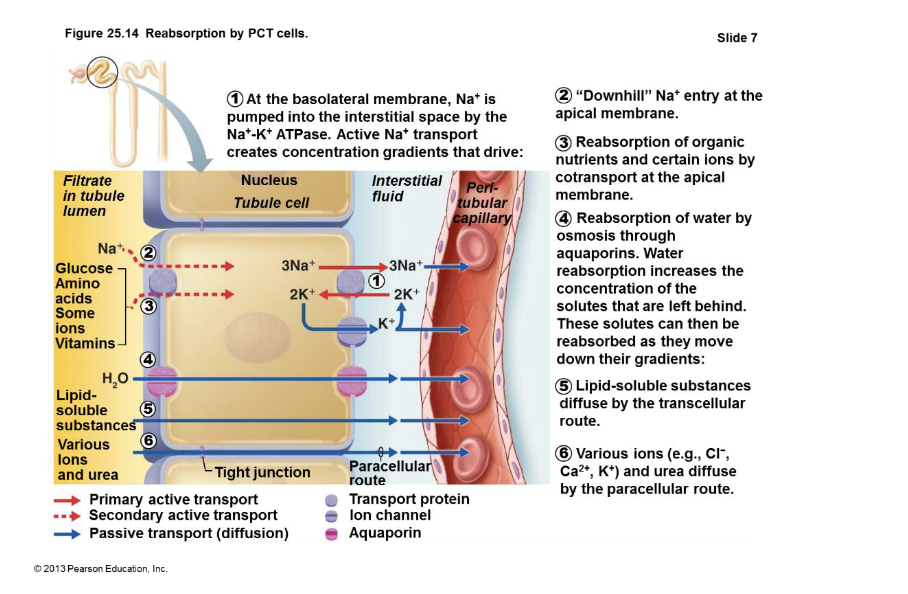
Permeability Properties of Parts of the Nephron
how much fluid is processed in kidney?
180 L fluid processed daily; only 1.5 L → urine (99% is reabsorbed)
Filtration membrane includes..
. Fenestrated endothelium of glomerular capillary
2. Basement membrane
3. Podocytes of epithelium
These filtration membrena structures allow all components of blood to normally pass
through into the tubule except:
1. cells
2. protein
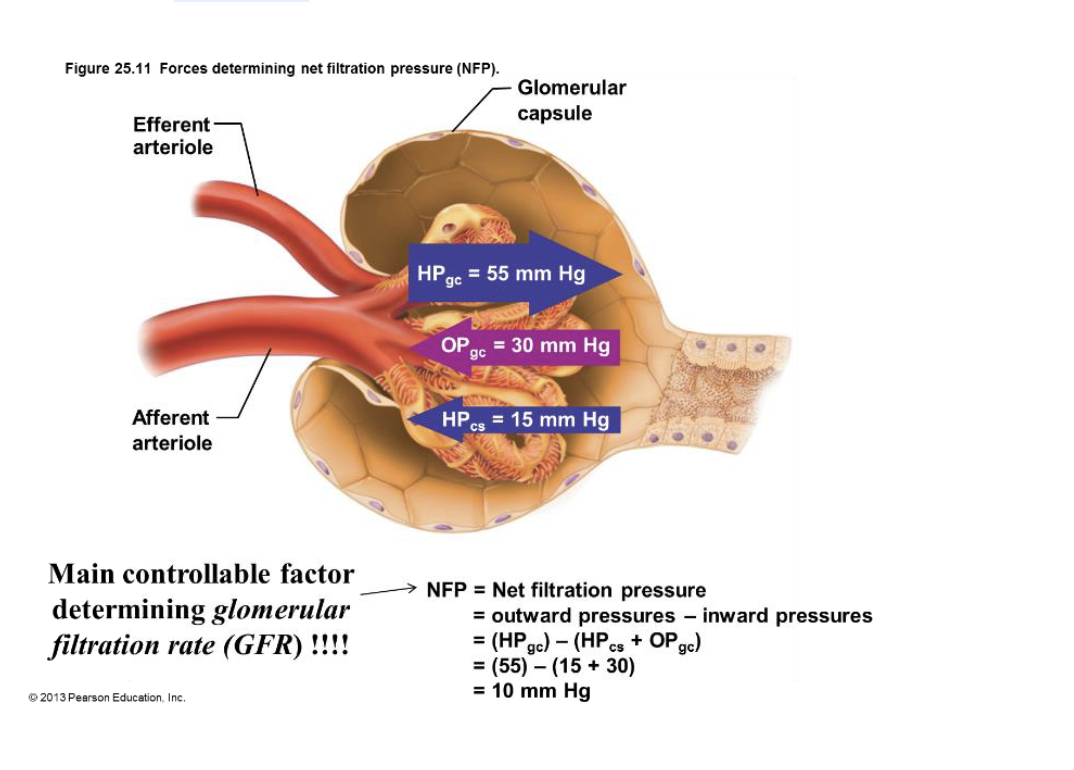
forces determining net filtration pressure
kidney physiology: mechanisms of urine formation
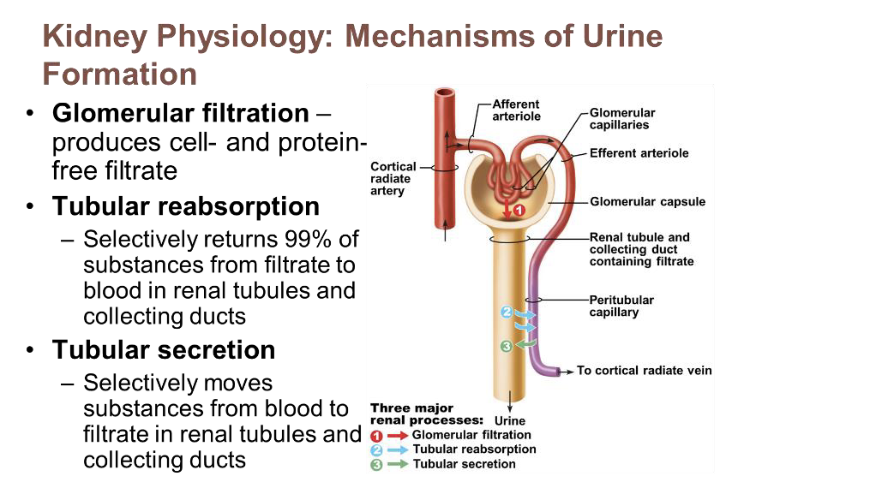
glomerular filtration
produces cell and protein free filtrate
tubular reabsorption
selectively returns 99% of substances from filtrate to blood in renal tubules and collecting ducts
tubular secretion
selectively moves substances from blood to filtrate in renal tubules and collecting ducts
Regulation of Glomerular Filtration
• Intrinsic controls (renal autoregulation)
– Act locally from within kidney to maintain GFR at a level high enough to filter waste
from the blood but low enough the reabsorb nutrients, salts, and fluid needed from
filtrate, typically around 125 ml/min
– Myogenic Mechanism
• ↑ BP → constriction of afferent arterioles = decreases GFR back to 125 ml/min
• ↓ BP → dilation of afferent arterioles = increases GFR back to 125 ml/min
– Tubuloglomerular feedback
• Macula densa measures Na+ content in distal convoluted tubule
• Na+ (due to high GFR) → constriction of afferent arterioles = decreases GFR
back to 125 ml/min
• Na+ (due to low GFR) → dilation of afferent arterioles = increases GFR back to
125 ml/min
Extrinsic controls
– Nervous and endocrine mechanisms from outside the kidney that maintain blood
pressure; can negatively affect kidney function… only concern is maintaining systemic blood pressure!!
– Take precedence over intrinsic controls if systemic BP < 80 or > 180 mm Hg
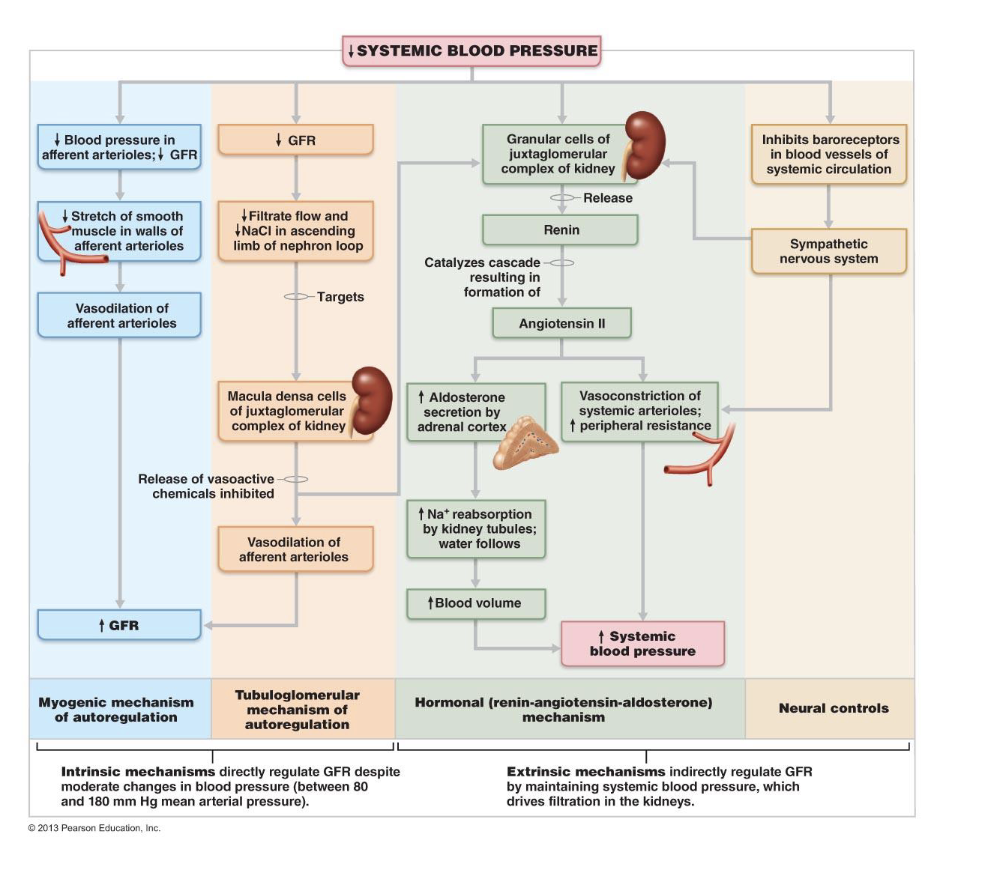
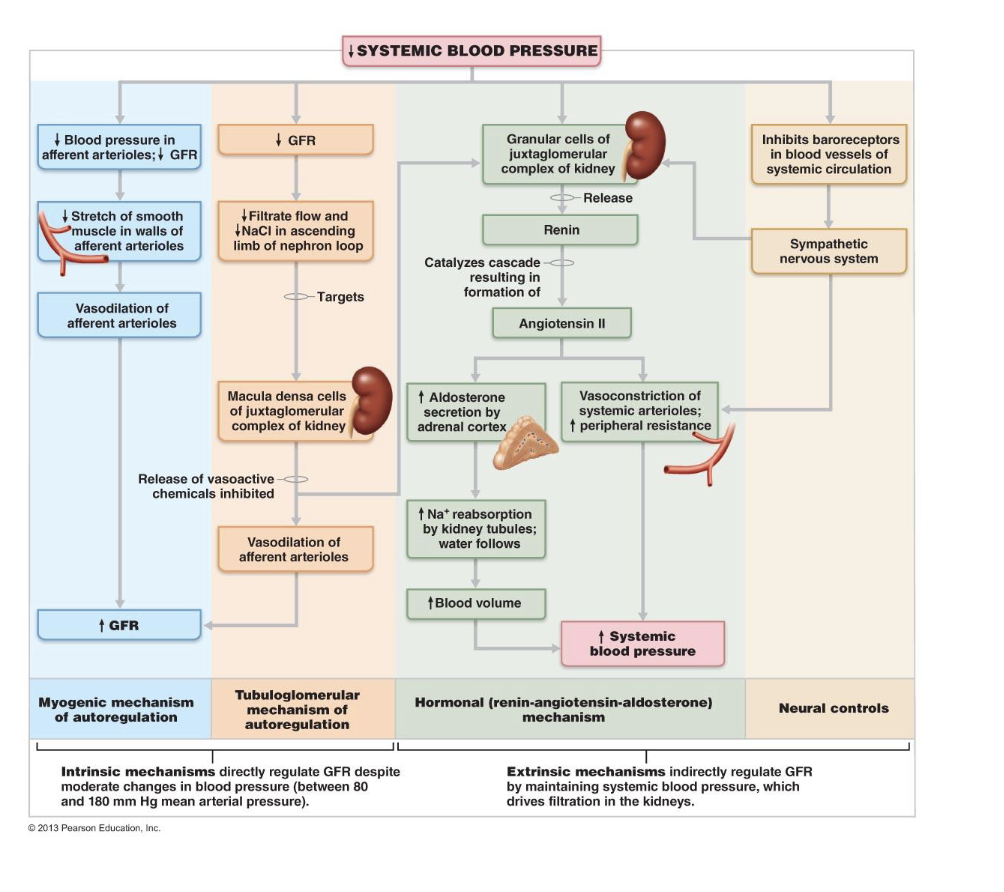
– Sympathetic Nervous System
• Trigger: Low blood pressure
• Response: Norepinephrine released by sympathetic nervous system;
epinephrine released by adrenal medulla
• Systemic vasoconstriction → increased blood pressure
• Constriction of afferent arterioles → ↓ GFR → increased blood volume and
pressure
Renin-Angiotensin- Aldosterone Mechanism
• Three pathways to renin release by granular cells
• Direct stimulation of granular cells by sympathetic nervous system
Ch 25 review sheet BIO163
• Stimulation by activated macula densa cells when filtrate NaCl concentration
low
• Reduced stretch of granular cells
• See below for effects!! >> raises blood volume and pressure
systemic bp chart explained
reabsorption of PCT cells chart
Transport maximum (Tm)
for ~ every reabsorbed substance; reflects number of carriers
in renal tubules available
– When carriers saturated, excess excreted in urine
• E.g., hyperglycemia → high blood glucose levels exceed Tm → glucose in urine
Kidneys maintain osmolality of plasma at ~300 mOsm by regulating urine concentration and volume
hormones that affect urine production and properties
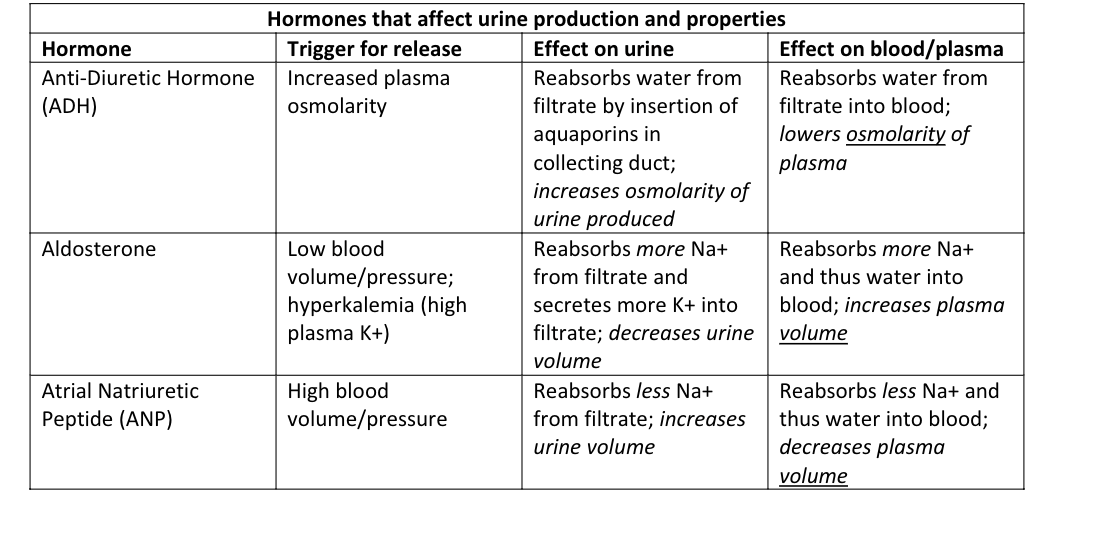
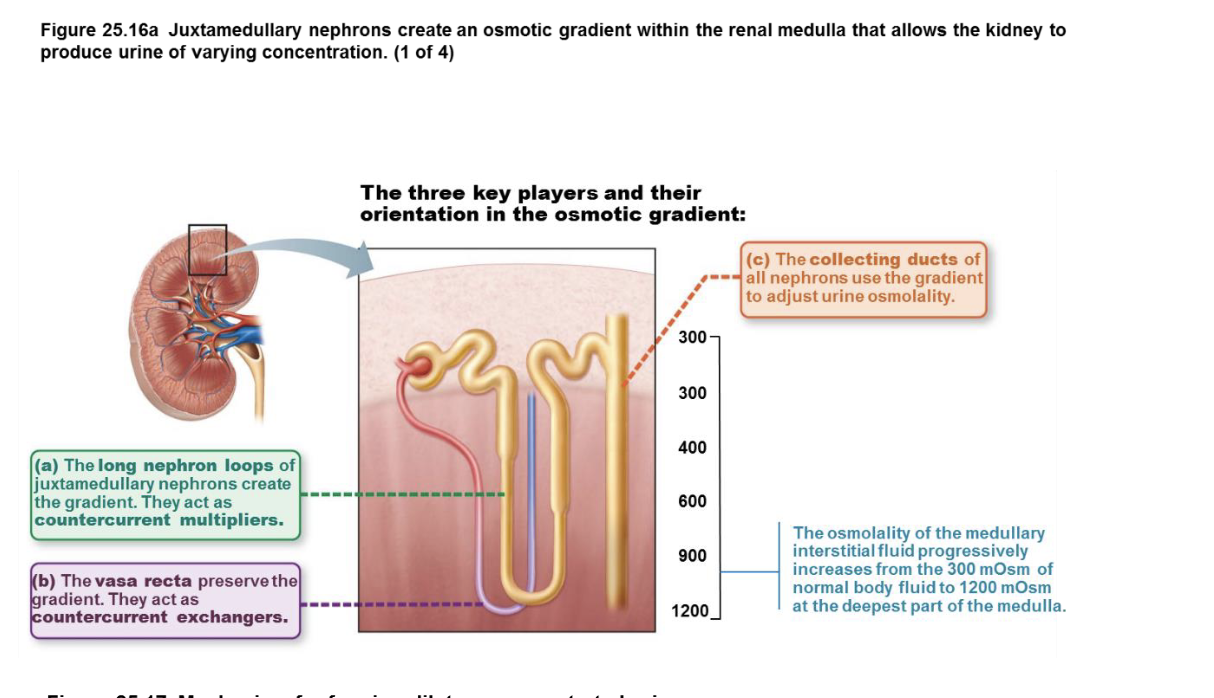
Counter current multiplication
due to the permeability properties and anatomy of the loop of Henle/nephron loop
establishes the medullary salt gradient, while countercurrent exchange due to shape of the vasa recta helps maintains it from being washed away.
key players & orientation in the osmotic gradient
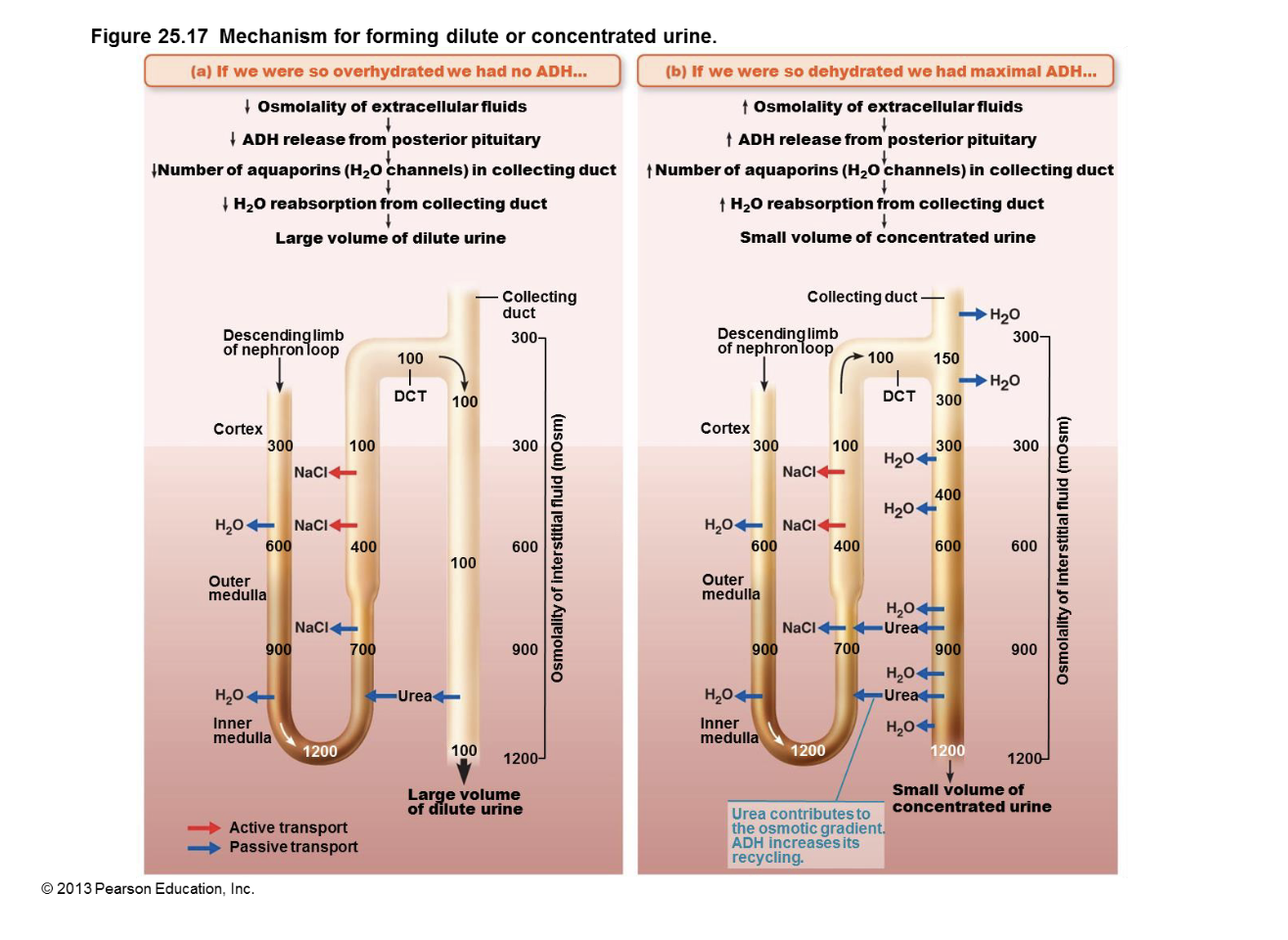
mechanisms for forming dilute or concentrated urine
diuretics
Chemicals that enhance urinary output
I. ADH inhibitors, e.g., alcohol
II. Na+ reabsorption inhibitors (and resultant H2O reabsorption), e.g., caffeine, drugs for
hypertension or edema
III. Loop diuretics inhibit medullary gradient formation
IV. Osmotic diuretics - substance not reabsorbed so water remains in urine, e.g., high
glucose of diabetic patient
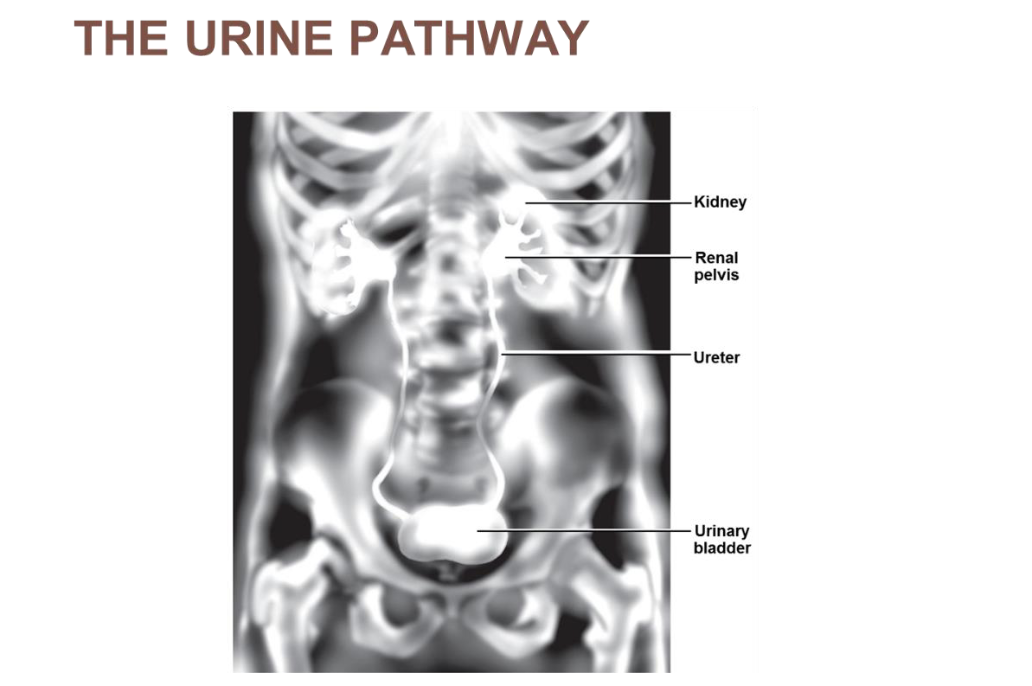
the urine pathway
urinary bladder
muscular sac for temporary storage of urine
urethra
Muscular tube draining urinary bladder (shorter in females>> more UTI’s)
sphincters
Internal urethral sphincter
• Involuntary (smooth muscle) at bladder-urethra junction
• Contracts to open
– External urethral sphincter
• Voluntary (skeletal) muscle surrounding urethra as it passes through pelvic floor
• relaxes to open
incontinence
aka peeing when you don’t want to
– Stress incontinence
• Increased intra-abdominal pressure forces urine through external sphincter
– Ex. pregnancy
– Overflow incontinence
• Urine dribbles when bladder overfills, usually because it can’t be emptied
effectively
– Ex. Blockage of the urethra by enlarged prostate
Urinary retention
– Bladder unable to expel urine
– Common after general anesthesia
– Hypertrophy of prostate
– Treatment – medication or removal of enlarged portion of prostate
Renal Calculi “Kidney Stone”
• a solid crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine
– Crystallized calcium, magnesium, or uric acid salts
• typically leave the body by passage in the urine stream (ie. “passing a kidney stone”)
• Large stones block ureter → pressure >> pain!!
• Dehydration from low fluid intake is a major factor in stone formation
• May be due to chronic bacterial infection, urine retention, Ca2+ in blood, pH of urine
• Treatment - shock wave lithotripsy – noninvasive; shock waves shatter calculi
Chronic renal disease
GFR < 60 ml/min for 3 months
– E.g., in diabetes mellitus; hypertension; glomerulonephritis
Renal failure
GFR < 15 ml/min
– Causes uremia syndrome – ionic and hormonal imbalances; metabolic abnormalities;
toxic molecule accumulation
– Treated with hemodialysis or transplant
Hemodialysis
• a process for removing waste and excess water from the blood
• used primarily as an artificial replacement for lost kidney function in people with renal failure