PTA 250 Final (Chapters 6, 10, & 12)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
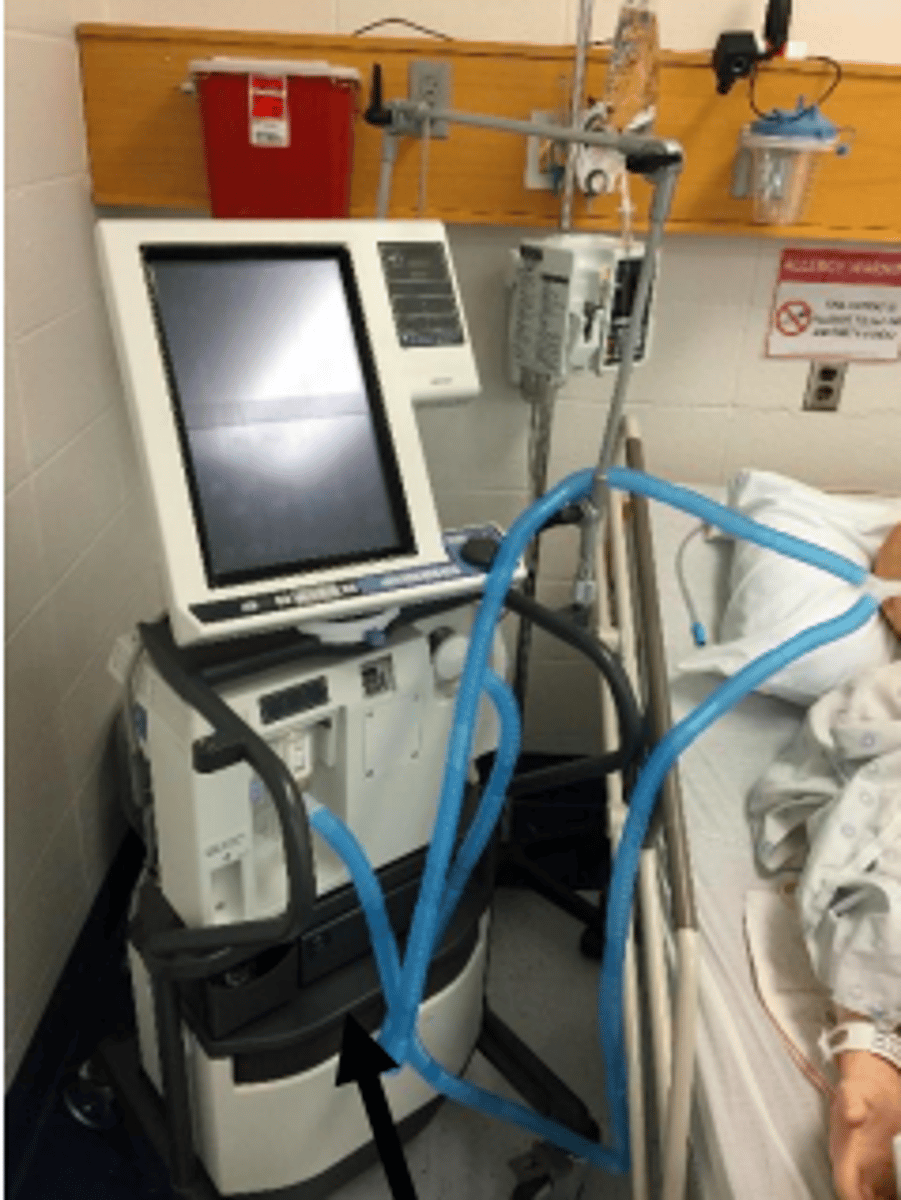
ventilator
- keeps pt. alive & breathing
- don't adjust settings, pull tube, or turn machine off, let nurse deal with it
- connects to pt. through nose or mouth
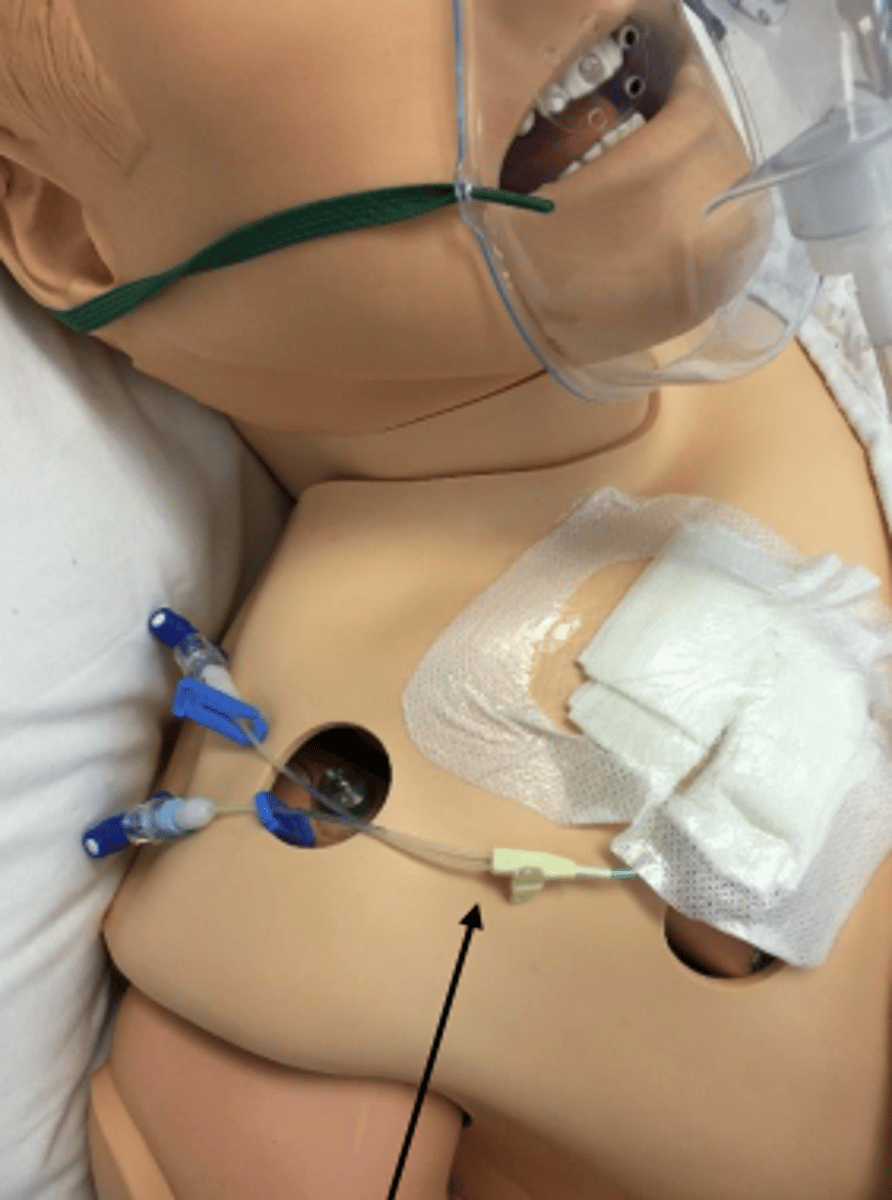
central venous pressure catheter
plastic IV tube used to measure pressure in right atrium or superior vena cava
- gives most accurate blood pressure
- surgically inserted
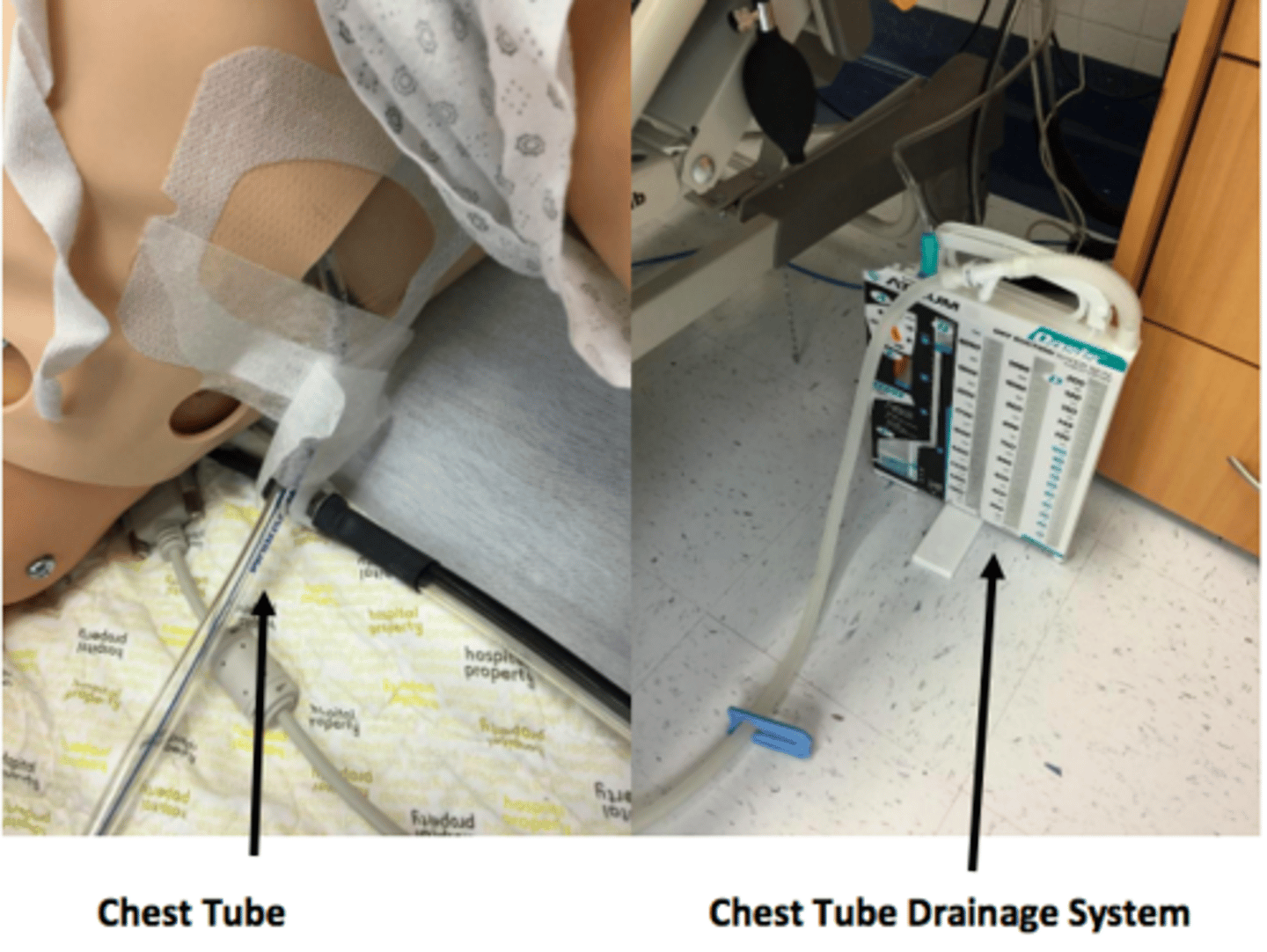
chest tube drainage system
- surgically inserted into lateral side of ribs
- drains excess fluid, air, blood, drainage
- can operate off of gravity or pump
- don't pull/kink/dislodge tubes, don't kick over collection container
Gastric Tube (G tube)/PEG
- feeding tube surgically inserted into middle of pt.'s stomach
- pt. is not allowed to have any food by mouth
- can administer medications and liquid food through it
- place gait belt above tube
- pt. cannot be in supine, needs to be at least 35-40 degrees elevated
- long term
colostomy bag
- surgical opening created to allow elimination of feces
- external collection bag
- be aware pt. has it and consider gait belt position
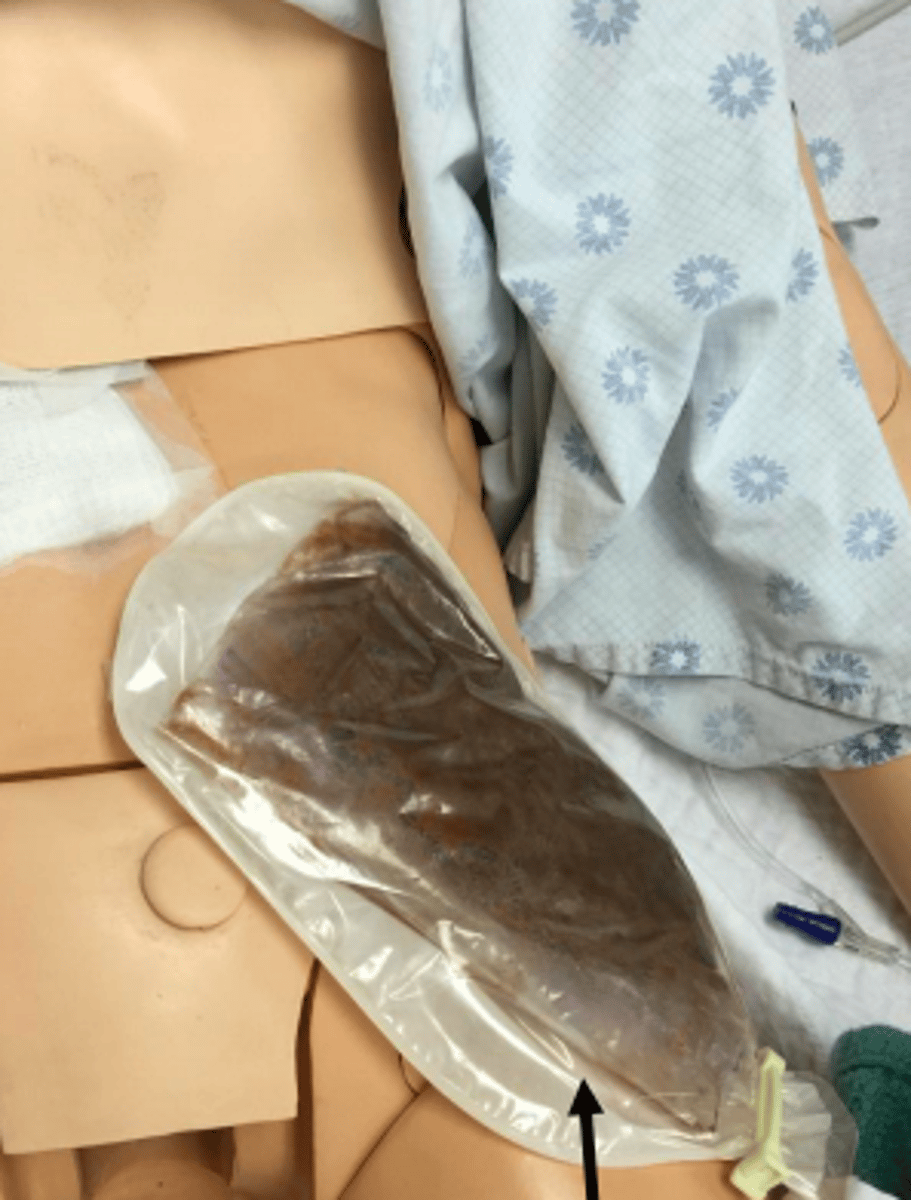

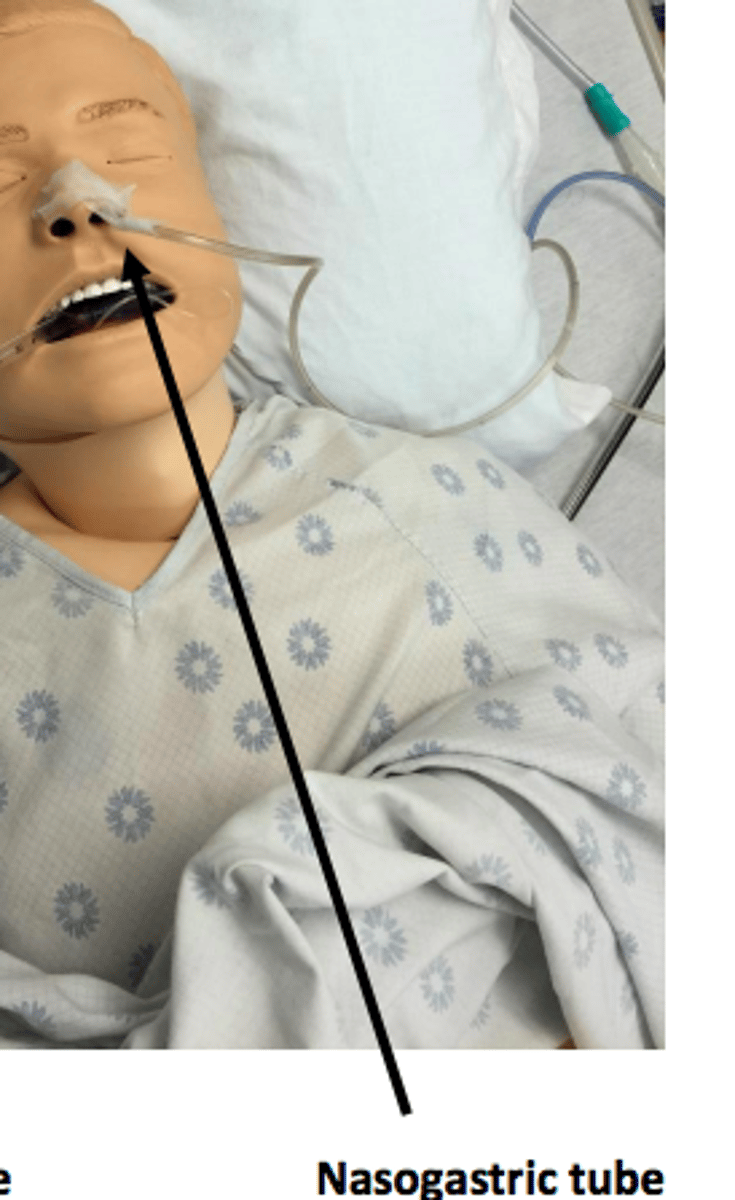
nasograstric tube
feeding tube inserted in nose that goes down into pt.'s stomach
- can remove fluid, gas, content from stomach through this tube, can also administer medication
- pt. cannot have anything by mouth
- short term
- pt. should not flex head or bend forward
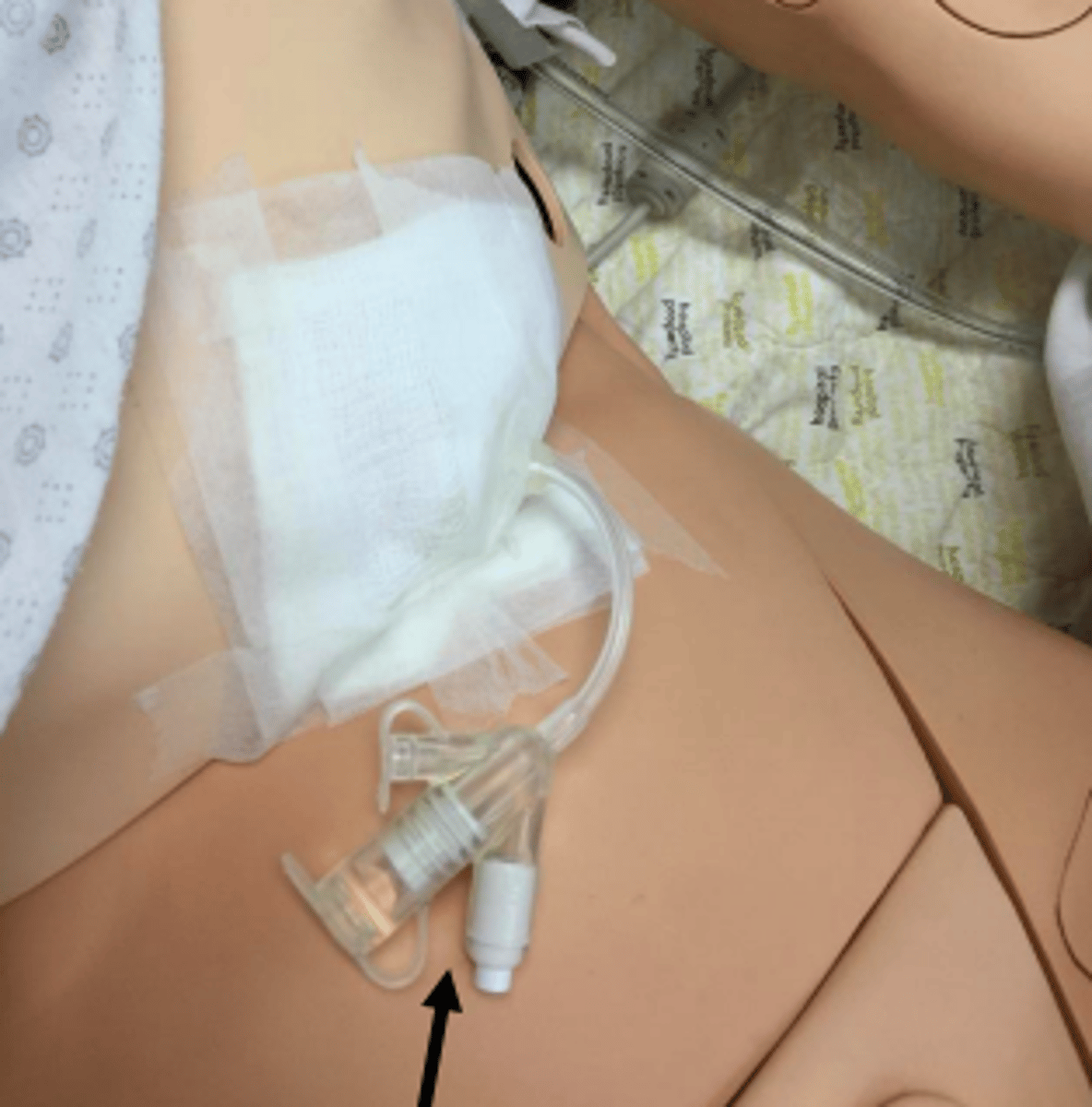
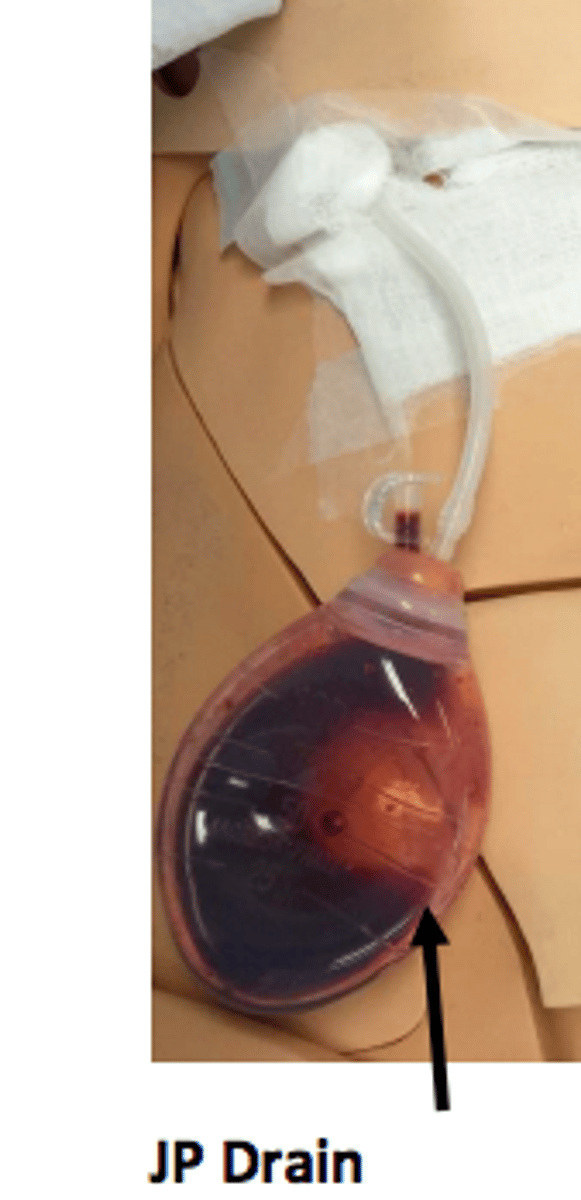
JP drain
drain inserted into body, soft collection canister where blood/fluid/drainage collect
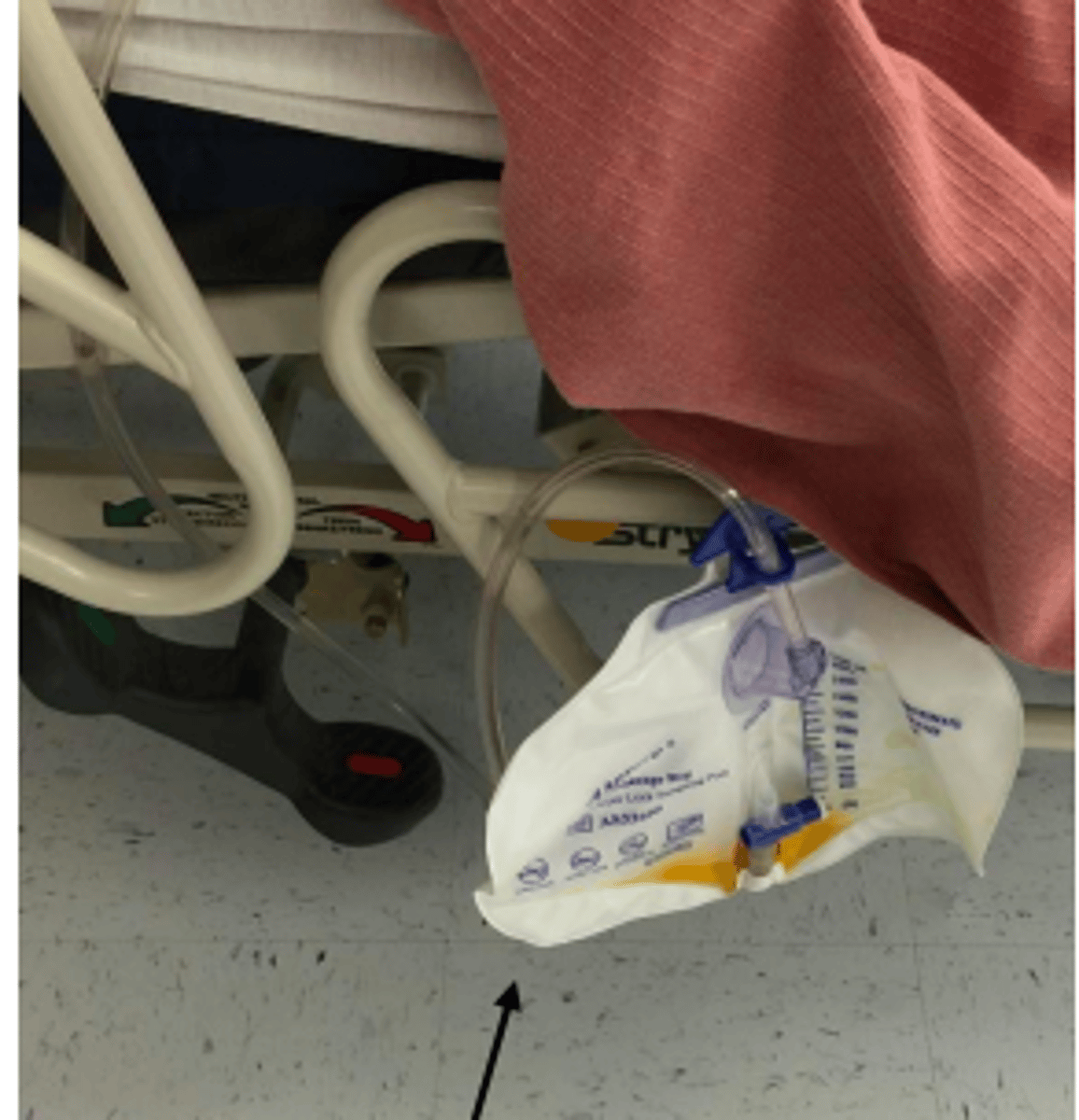
urinary catheter
inserted into bladder to remove urine from bladder
- be careful not to pull, move, or kink tube
- foley, external, suprapubic
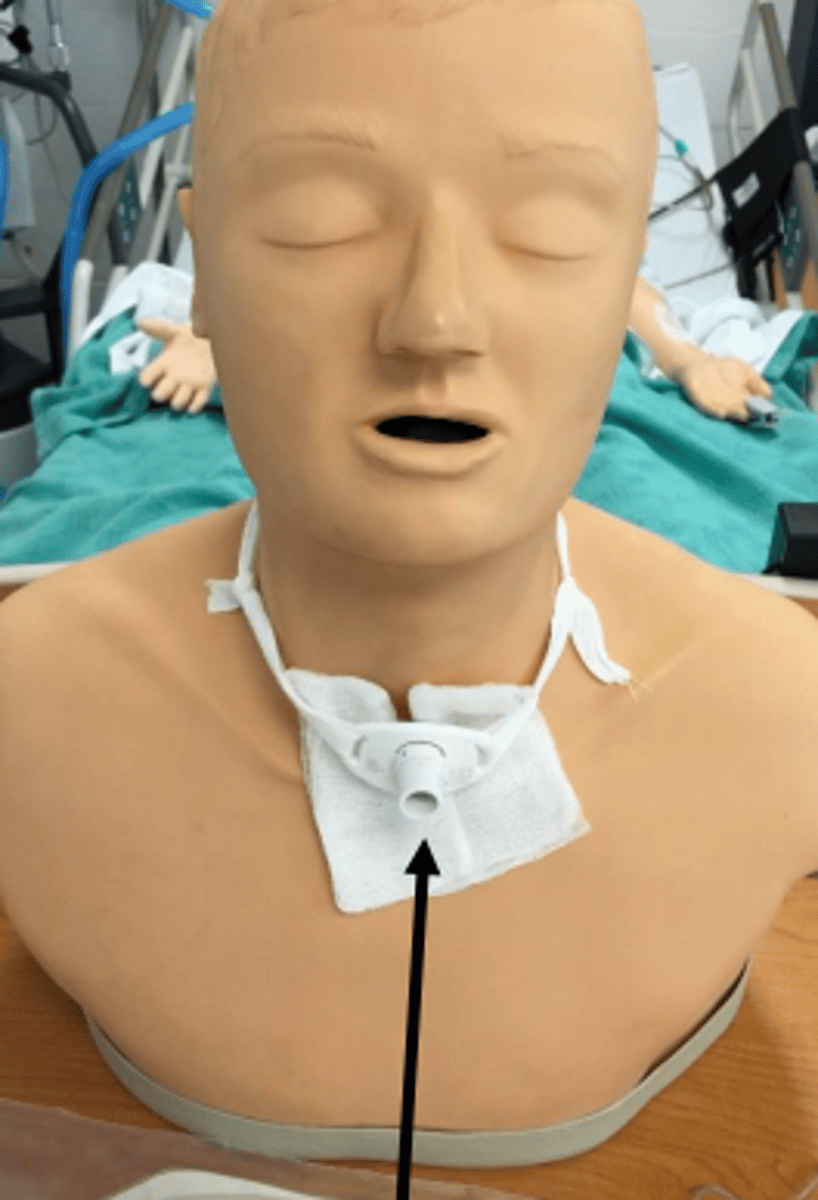
tracheostomy
breathing tube directly inserted into trachea
- be mindful of neck flexion/rotation
intercranial pressure monitor
measures pressure in pt.'s head (pressure against skull and brain tissue)
- normal intercranial pressure: 4-15 mm mercury
- avoid prone position, isometric exercise, head flexion, hip flexion more than 90 degrees and valsalva maneuver
- head of bed should be 15 degrees elevated

benefits of passive exercise
preserves & maintains ROM
minimizes contracture formation
minimizes adhesion formation
maintains mechanical elasticity of muscke
promotes & maintains local circulation
promotes awareness of joint motion
evaluates joint integrity and motion
enhances cartilage nutrition and stimulates movement of synovial fluid
inhibits or reduces pain
PROM
passive range of motion
- taking joint through full range of motion until end feel is met
end feel
the feel of resistance of the tissue at the end of the range
circular bandage pattern
the bandage is applied in a series of overlapping circular turns around a body part to anchor the bandage initially or terminally.
spiral bandage pattern
the bandage is applied in a series of overlapping diagonal turns (up or down) around a body part
open spiral or oblique bandage pattern
series of diagonal turns that do not overlap and have an open space between each turn
recurrent bandage pattern
series of lengthwise layers applied to the anterior-posterior surfaces of an extremity or digit. used to cover the most distal aspect.
figure-of-eight pattern
series of spiral turns applied in alternate directions. the first turn progresses in an inferior-to-superior and the second turn progresses in an superior-to-inferior direction
standard hospital bed
can be adjusted in many ways, has controls and rails
Volume cycled ventilator
long term use
Pressure cycled ventilators
short term use
Vital Signs Monitor
Includes blood pressure, heart rate/cardiac patterns, temperature, respiration rate, oxygen saturation
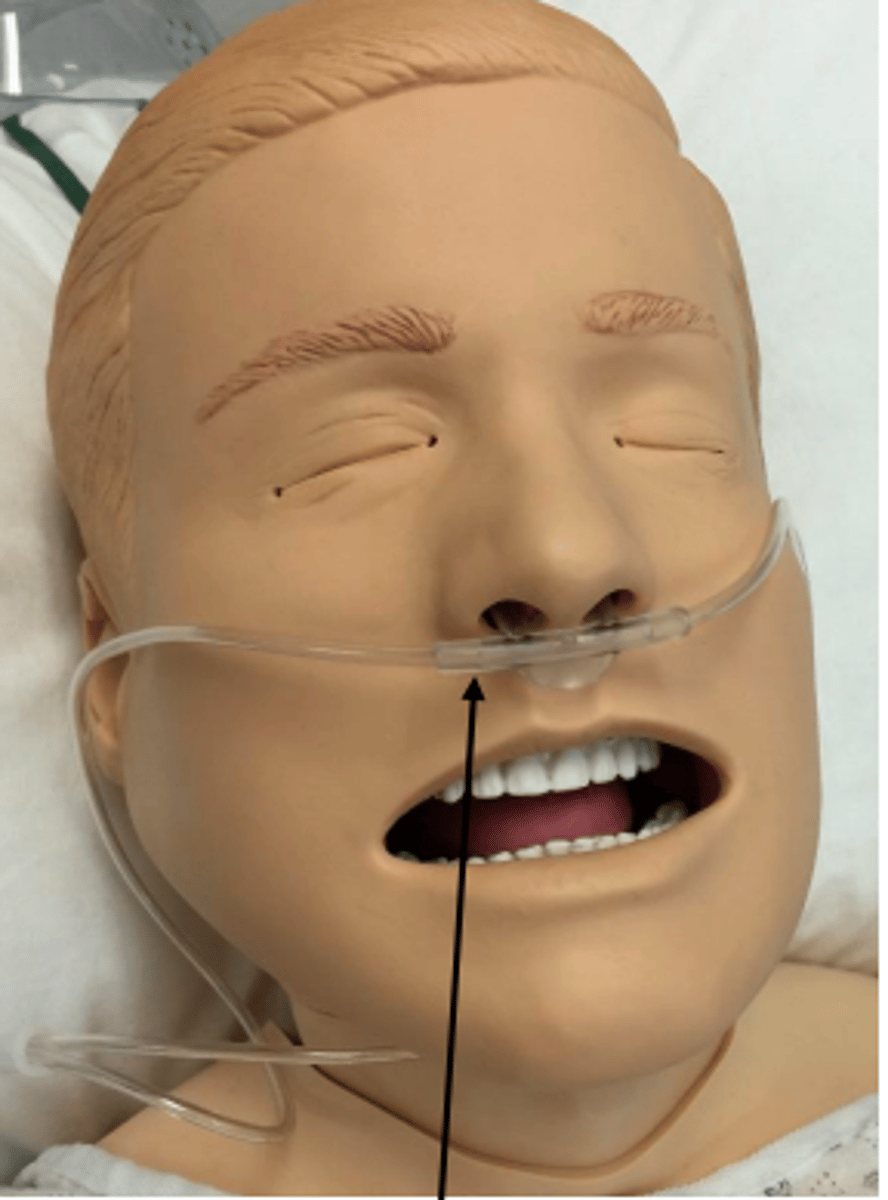
Nasal Cannula
A common oxygen-delivery device in which oxygen flows through two small, tubelike prongs that fit into the patient's nostrils
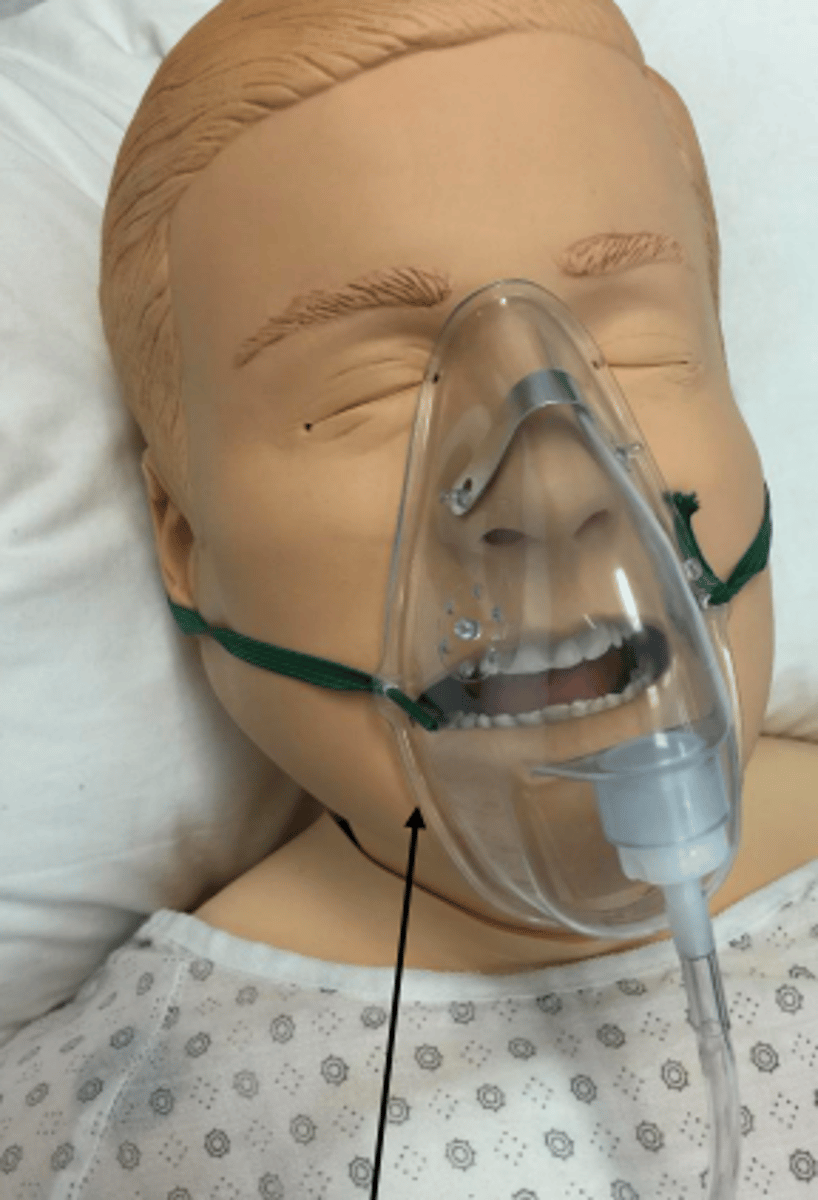
Oronasal mask
Soft plastic mask that goes over the nose and mouth
- Used if pt.'s need more oxygen than nasal cannula can supply
Endotracheal (ETT) Tube
tube in mouth or nose that connects ventilator to patient through their airway
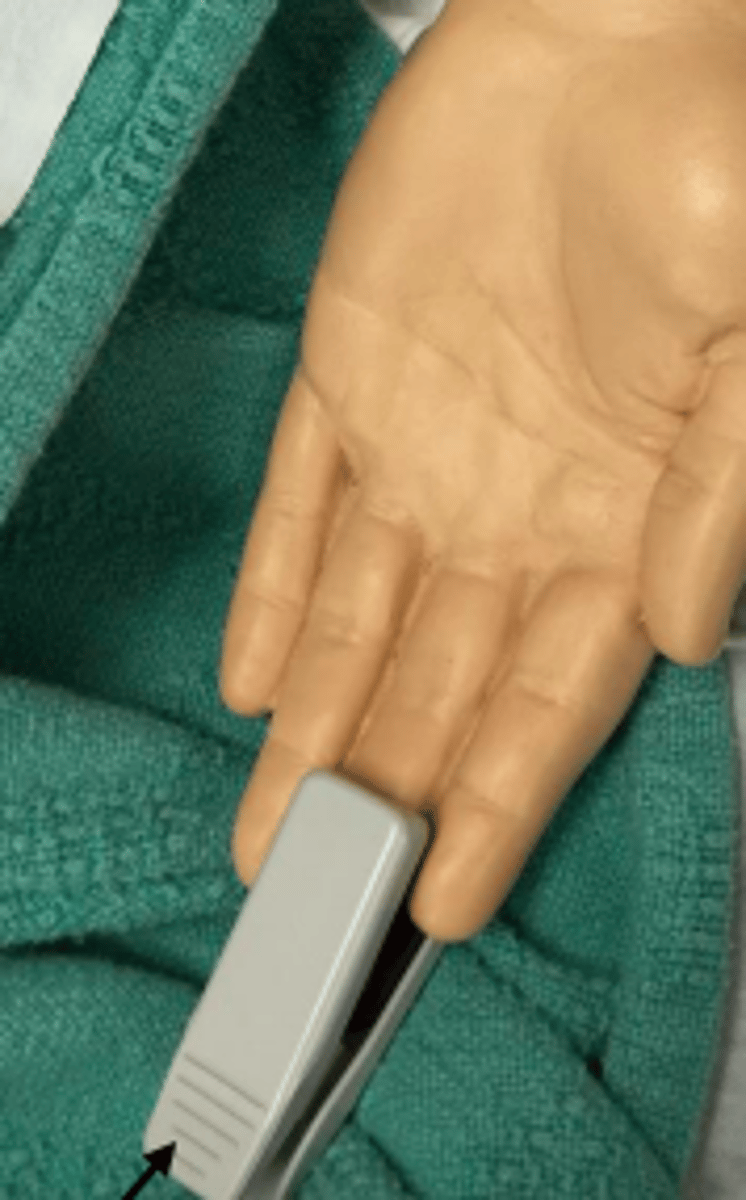
Pulse oximeter
Measures oxygen saturation in blood
Less than 90 is low

pulmonary artery catheter
long plastic IV tube that is inserted into the jugular or femoral vein, measures PAP
- do not allow hip flexion greater than 30 degrees or abduction (if inserted in femoral vein) and shoulder motion (if inserted in subclavian vein)
arterial (A) line
placed in artery (radial, dorsal pedal, axillary, brachial, femoral)
-measures blood pressure, can draw blood
Hickman catheter
inserted in cephalic or internal jugular vein
- measures central venous pressure, can administer medications or remove blood through it
lab values
- levels of troponin/creatine kinase are elevated - heart attack
- 90% of oxygen saturation should be maintained during exercise
- patients with Hgb less than 8 g/dl should not participate in physical activity
- patients who are on anticoagulants:
INR less than 4.0: can participate in therapy
INR between 4.0 and 5.0: light exercise permitted
INR greater than 5.0: no exercise allowed
INR 6.0 or higher: bed rest
intravenous infusion (IV) lines
- used to draw blood, and/or infuse fluids/nutrients/medications
- don't take blood pressure in that arm, make sure infusion bag stays above where IV is placed
- avoid elbow flexion if IV is in elbow
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA)
delivery system that allows patients to self-administer a predetermined dose of pain medications on demand
dialysis
replaces or assists in normal kidney function
shock symptoms
pale, moist, cool skin
shallow/irregular breathing
dilated pupils
weak/rapid pulse
diaphoresis
dizziness/nausea
syncope
orthostatic hypotension
low blood pressure that occurs upon standing up
allergic reactions
be aware of equipment you are using/anything that can cause a reaction with your patient
- identify what causes the reaction and remove it from patient
falls
common occurrences
- educate patient on how to recover
fracture
swelling, bruising, deformity, pain in bone
- protect site, prevent further injury/infection, never try to realign fracture
burns
red/blistered skin
- prevent wound contamination
seizures
protect the person from injury by moving nearby objects away, protect their modesty/privacy, position person on side/safe area
heat exhaustion
- least threatening
- pt. experiences: profuse sweating, nausea, headache, shallow or rapid breathing, weak or rapid pulse, pale color, elevated temperature, exhaustion, unconsciousness, muscle cramos
heat stroke
- most threatening
- pt. experiences: nausea, headache, dry skin, labored breathing, strong/rapid pulse, flushed/gray color, very elevated temperature, unconsciousness, pupils contracting & dilating
insulin-related illness
objective is to restore the pt. to a normal insulin-glucose state
hypoglycemia - caused by too much insulin, pt. should be treated with sugary substance
hyperglycemia - caused by too little insulin, pt. should be treated with insulin injection, don't give them sugar
stroke
signs: face drooping, arm weakness, speech difficulty,
- time is crucial
- 3rd leading cause of death
- call 911
what does PROM not do
increase ROM
prevent muscle atrophy
reduce adipose tissue
build muscle strength
vertebral artery occlusion test
- performed before cervical PROM to ensure circulation to the brain won't be interrupted
procedure:
- position pt. in supine
- fully extend head, flex head, and laterally flex the neck to the R for 30 seconds then back to neutral
- full extend the head, neck, and laterally flex the neck to the L for 30 seconds then back to neutral
- ask about dizziness/fainting and look at eyes for darting