Pre-Calc FInal
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:41 AM on 12/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
1
New cards
How do you point out a function?
When there is one output value for every x-value
2
New cards
How to determine the domain of a function?
set denominator of action equal to zero
3
New cards
2 RULES
1. anything divided by zero is undefined
2. negative in a square root
4
New cards
when writing parentheses
the lower number always goes first!
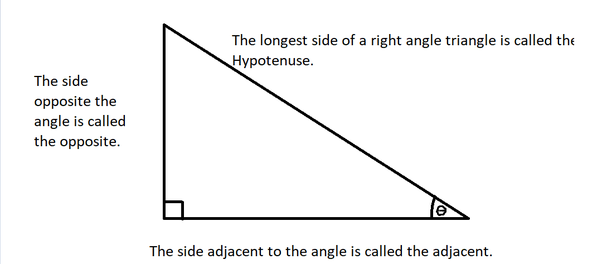
5
New cards
cosine
adjacent/hypotenuse
6
New cards
Sine
opposite/hypotenuse
7
New cards
Tangent
Oppisite/ adjacent
8
New cards
csc
hyp/op
9
New cards
Secant
hyp/adjacent
10
New cards
Cotangent
adjacent/oppisite
11
New cards
Isosceles Triangle
12
New cards
When finding angles on Unit Circle CSC, SEC, COT
csc→1/Y
sec→ 1/x
Cot→ x/y
(x,y)→ are your coordinates!!
sec→ 1/x
Cot→ x/y
(x,y)→ are your coordinates!!
13
New cards
a^2+b^2=c^2
c^2 is always your hypotenuse
14
New cards
Remember !!
no square roots on denominator!
15
New cards
Compound Interest Formula!
A=P(1+r/n)^rn
\
\
P=Principe balence
r= interest rate
n= number of times interest applied per time period
t= number of time periods elapsed
\
\
\
P=Principe balence
r= interest rate
n= number of times interest applied per time period
t= number of time periods elapsed
\
16
New cards
What do you do for a Quadratic Function
\-Add to middle
\-Multiply to end
\-Multiply to end
17
New cards
Slope Intercept form
y=mx+b
m=slope
x=variable
b=y-intercept
y=variable
m=slope
x=variable
b=y-intercept
y=variable
18
New cards
Slope
rise/run
* y2-y2/x2-x1
* y2-y2/x2-x1
19
New cards
Quadrents
numbered counter-clock wise area contained by the x &y axis
20
New cards
x&y plane
plane they form at intersection
21
New cards
Cordinate axis’s
2 fixed coordinate lines that form the cordinate plane
\
\
22
New cards
origin
2 lines point of intersection
23
New cards
Quadrents
Counter clock wise
\
2 1
34
\
2 1
34
24
New cards
Distance Formula
√\[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²\].
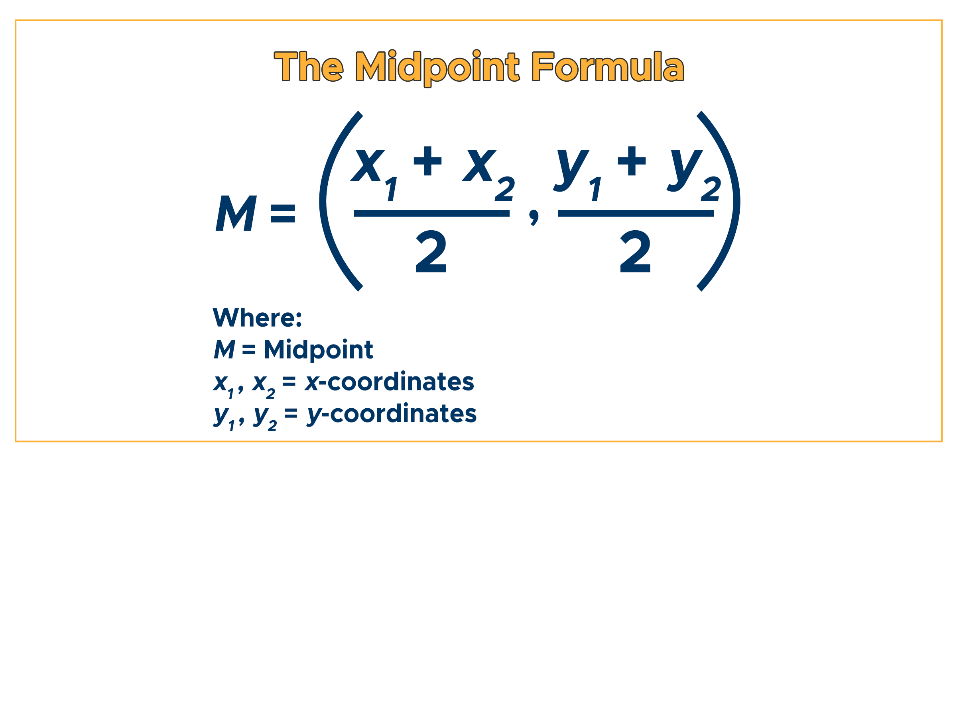
25
New cards
Mid Point Formula
26
New cards
f (x)
F is a machine creating y out of X
27
New cards
Functions →
can only have One output value for every input value!
28
New cards
When Square root is already present in a function
only one version is necessary
29
New cards
When using square root as a solving technique
both + and -
30
New cards
Bracket \[=
included
31
New cards
Parenthesis (=
Excluded
32
New cards
IDENTITY FUNCTION y=-f(x)
x-axis reflection making y-negative
33
New cards
IDENTITY FUNCTION y=f(-x)
y-axis reflection
\-making x negative
\-making x negative
34
New cards
Notation→ (fog)(x)
F(g(x)
\
“f of g of x”
\
“f of g of x”
35
New cards
if you have 2 x-values
you do the domain for both
36
New cards
Quadratic Function standard form
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
→ a cannot equal 0
→ b, c can be anything!!
→ a cannot equal 0
→ b, c can be anything!!
37
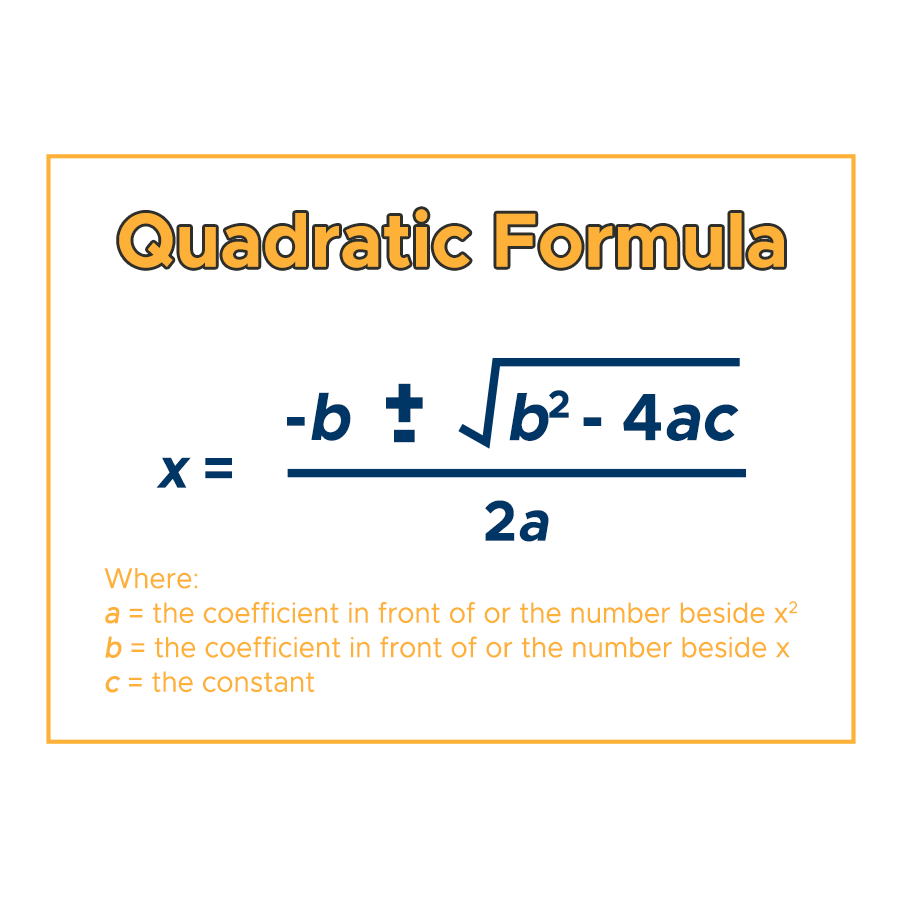
New cards
Quadratic Formula for x-intercepts
38
New cards
How to solve for vertex?
x=-b/2a
39
New cards
if in standard form and leading coefficient is postive=
opens up
\
\
40
New cards
If leading coefficient is negative and in standard form =
opens down
41
New cards
Steps in solving a Quadratic Equation
1. Opens up/down
2. X-intercepts set equation = to zero
3. Y-intercept , set x=0
4. Factoring
42
New cards
Exponents both (+) or (-)
→ touches (Bounces)
43
New cards
Opposite
crosses x-axis
44
New cards
x-intercepts
where x=o
45
New cards
Multiplicity even→
graph bounces off x-axis
46
New cards
Multiplicity odd→
graph crosses x-axis
47
New cards
huge/tiny=
normal/tiny=
normal/tiny=
HUGE
48
New cards
normal/huge=
Still really tiny
49
New cards
tiny/tiny
could be tiny, normal or huge
50
New cards
Whats an asymptote?
a line or a curve that a function goes close to and might NEVER touch
51
New cards
Aysmptotes do NOT ..
X-axis
52
New cards
Rational Functions
a function defined as the quotient (division) of two polynomials
53
New cards
Asmpytotes may..
never be touched or be crossed by a function
54
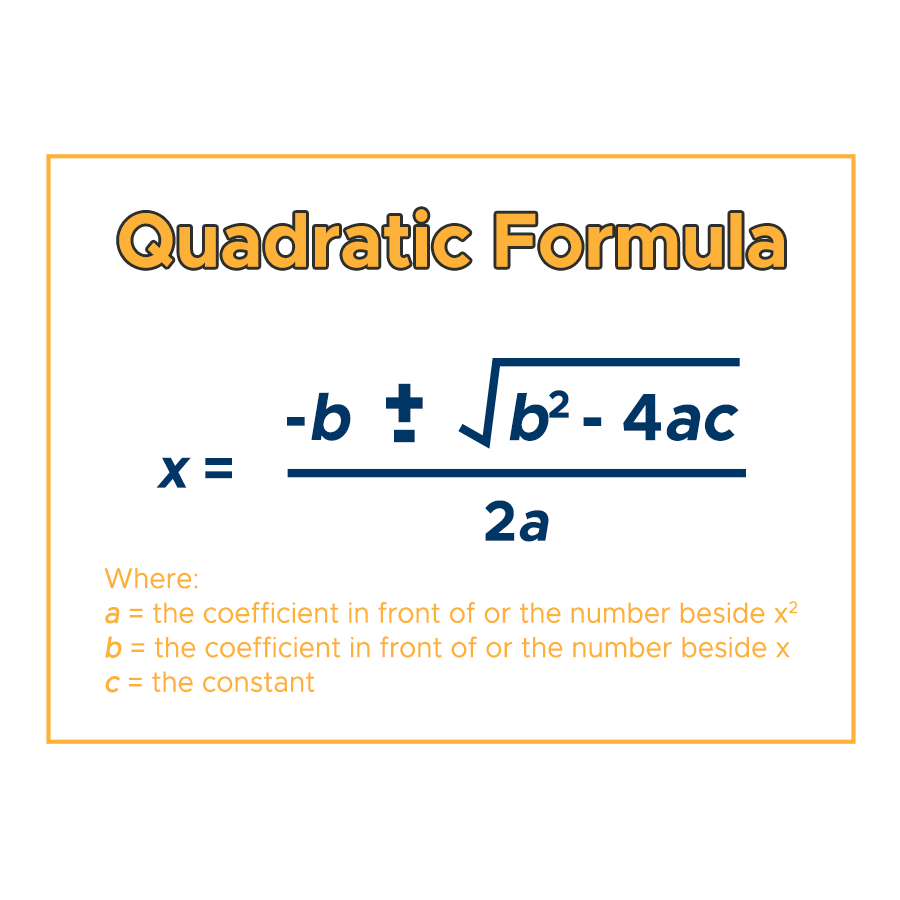
New cards
Asymptotes of Polynomials
standard form
55
New cards
In order to solve for vertical asymptotes
set denominator equal to zero
56
New cards
How do you get a hole!
cancels out completely
57
New cards
How to find horizontal asymptotes
1. if top is heavy there is no horizontal asymptote
2. If the exponents are the same then divide both number
3. If bottom is heavy then it is zero
58
New cards
Rational functions.
x- intercept →numerator
domain→ denominator
domain→ denominator
59
New cards
Orignial formula (Continious compounding interest formula)
P(t)=Pe^rt
p=principal
e= e on calculator
r= rate of interest
t=time in years
p=principal
e= e on calculator
r= rate of interest
t=time in years
60
New cards
y=log a ^x
form
61
New cards
Exponential Form
base^exponent= result
\
a^t=R
\
a^t=R
62
New cards
Logarithmic form
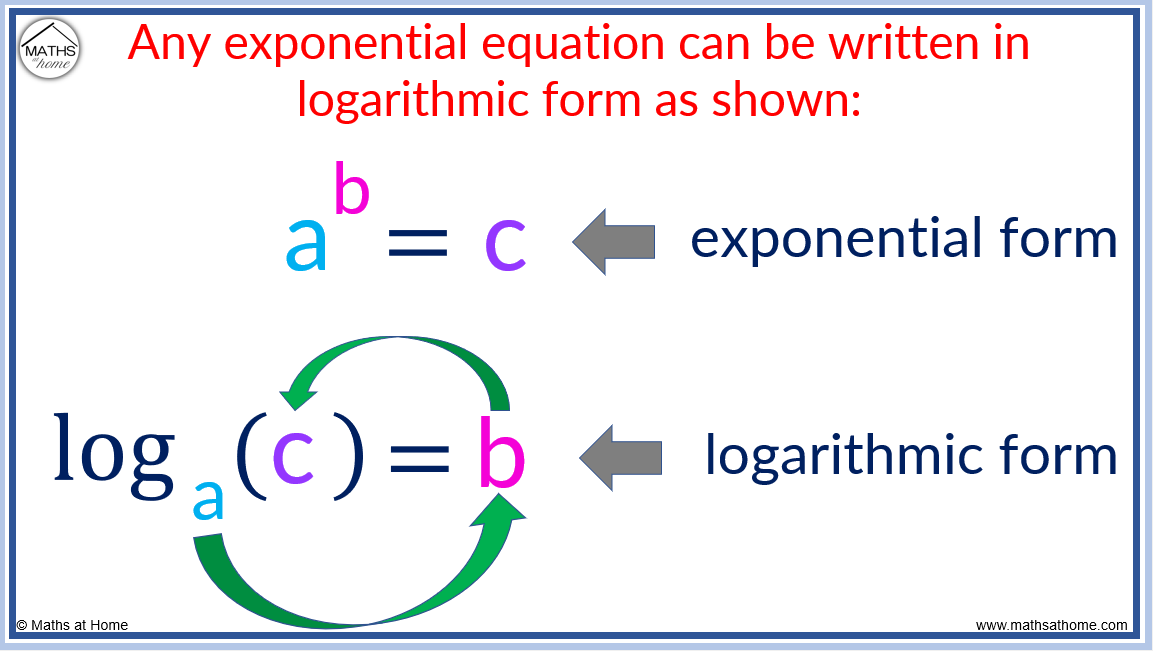
63
New cards
Degree to radians →
x pie/180
64
New cards
Radioans to Pie→
x 180/pie
65
New cards
For a Rational Function. intruder to find x-intercepts
set numerator equal to zero