Preparation of Amines
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are the two main methods for preparing amines?
Nucleophilic substitution of halogenoalkanes with ammonia.
Reduction of nitriles.
What type of amine is produced from the reaction of a halogenoalkane with ammonia?
A primary amine.
What is a major disadvantage of preparing amines by nucleophilic substitution?
It produces a mixture of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines unless a large excess of ammonia is used.
Why is excess ammonia used in the nucleophilic substitution method?
To prevent further substitution of the primary amine product into secondary and tertiary amines.
What type of amine is produced from the reduction of a nitrile?
A primary amine.
What is the key advantage of preparing an amine via a nitrile?
It produces a pure primary amine without the mixture of products.
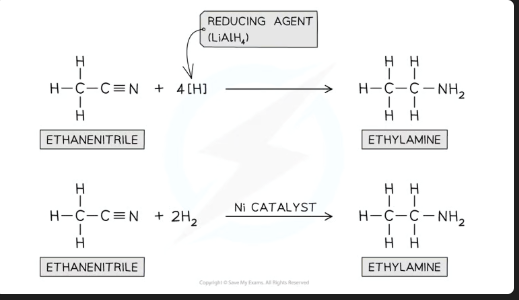
Name two different reagents that can be used to reduce a nitrile to an amine
LiAlH₄ in dry ether and dilute HCl
H₂ with a Ni catalyst
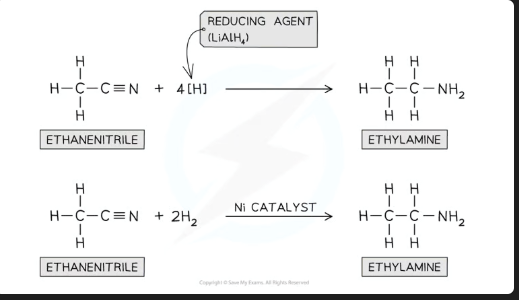
Write the general formulas for the reduction of a nitrile (R-CN) to a primary amine (R-CH₂-NH₂) using:
a) LiAlH₄
b) H₂ with a Ni catalyst
a) Using LiAlH₄:
Reagents: R-CN + LiAlH₄
Conditions: In dry ether, followed by dilute HCl acid work-up.
Equation:
R-CN + 4[H] → R-CH₂-NH₂
(The [H] comes from the LiAlH₄ + acid)
b) Using H₂ with Ni catalyst:
Reagents: R-CN + 2H₂
Conditions: High pressure of H₂ gas, Nickel catalyst.
Equation:
R-CN + 2H₂ → R-CH₂-NH₂
![<p><strong>a) Using LiAlH₄:</strong></p><ul><li><p class="ds-markdown-paragraph"><strong>Reagents:</strong> R-CN + LiAlH₄</p></li><li><p class="ds-markdown-paragraph"><strong>Conditions:</strong> In <strong>dry ether</strong>, followed by <strong>dilute HCl acid</strong> work-up.</p></li><li><p class="ds-markdown-paragraph"><strong>Equation:</strong><br><strong>R-CN + 4[H] → R-CH₂-NH₂</strong><br><em>(The [H] comes from the LiAlH₄ + acid)</em></p></li></ul><p class="ds-markdown-paragraph"><strong>b) Using H₂ with Ni catalyst:</strong></p><ul><li><p class="ds-markdown-paragraph"><strong>Reagents:</strong> R-CN + 2H₂</p></li><li><p class="ds-markdown-paragraph"><strong>Conditions:</strong> High pressure of <strong>H₂ gas</strong>, <strong>Nickel catalyst</strong>.</p></li><li><p class="ds-markdown-paragraph"><strong>Equation:</strong><br><strong>R-CN + 2H₂ → R-CH₂-NH₂</strong></p></li></ul><p><br></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/04bdc4a2-bbe9-4d0c-b178-eafb30b13e42.png)
What is the name of the reaction and mechanism for adding a nitro group to benzene?
Nitration, via Electrophilic Substitution.
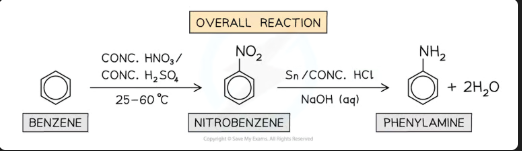
What are the reagents and temperature for the nitration of benzene?
Reagents: Concentrated HNO₃ and concentrated H₂SO₄.
Temperature: 50°C.
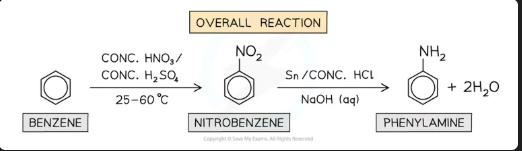
What is the organic product of benzene's nitration?
Nitrobenzene (C₆H₅NO₂).
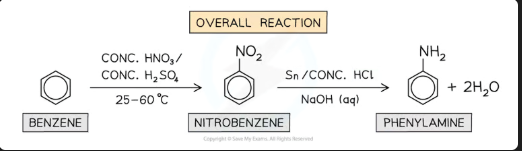
Why is the nitration reaction so important industrially?
Because the nitro group can be reduced to an amino group (-NH₂), forming phenylamine, which is a key starting material for many products.
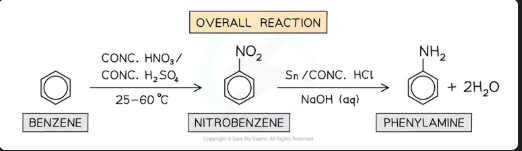
How is nitrobenzene reduced to phenylamine? Give one set of reagents.
Reagents: Tin (Sn) and concentrated HCl (this produces an intermediate with the formula C6H5NH3+, followed by NaOH.
OR: H₂ gas with a Nickel catalyst.
Conditions: Under reflux, and steam distillation after NaOH to separate
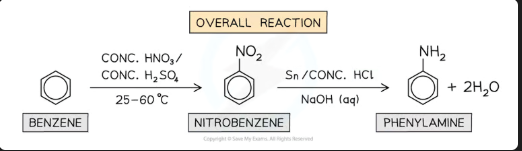
Write the overall balanced equation for the reduction of nitrobenzene to phenylamine (including the reagents Sn/HCl and NaOH).
C₆H₅NO₂ + 7[H] → C₆H₅NH₂ + 2H₂O
*(The [H] comes from: Sn + 2HCl → SnCl₂ + 2[H], and the NaOH neutralizes the acid)*