18. Surgical diseases of the pylorus and spleen. Aetiology, diagnosis and therapy. Pyloroplasty. Splenectomy.
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What is the location of the spleen?
Left side of the cranial abdominal cavity, parallel to the abdominal wall, between the abdominal wall and stomach (curvatura major).
What are the functions of the spleen?
Immunological and haematological: blood reservoir, blood filtration, IgG and cytokine synthesis, RBC maturation, platelet reservoir, removal of old platelets, and production of B and T lymphocytes and IgM.
What are the surgical diseases of the pylorus?
Stenosis
Obstruction
Neoplasia
What is the aetiology of pyloric stenosis?
Congenital in brachycephalic breeds.
Acquired in response to infection
What are clinical signs of pyloric stenosis?
Vomiting several hours after eating
How is pyloric stenosis diagnosed?
X-ray with contrast, endoscopy, biopsy (to exclude neoplasia)
What is the treatment for pyloric stenosis?
Surgical (pyloroplasty)
Medical treatment of oesophagitis, acid-base abnormalities and dehydration should be instituted before surgery
What are examples of pyloric neoplasia?
Benign: adenoma
Malignant (more common): lymphoma (cats), adenocarcinoma, leiomyosarcoma
What are indications for a pyloropasty?
Recurrent gastric dilatation
Neoplasia
Hepatic or pancreatic abscesses
Specific inflammatory processes
Gastroduodenal ulcers
Congenital pyloric stenosis with hypertrophy of pyloric musculature
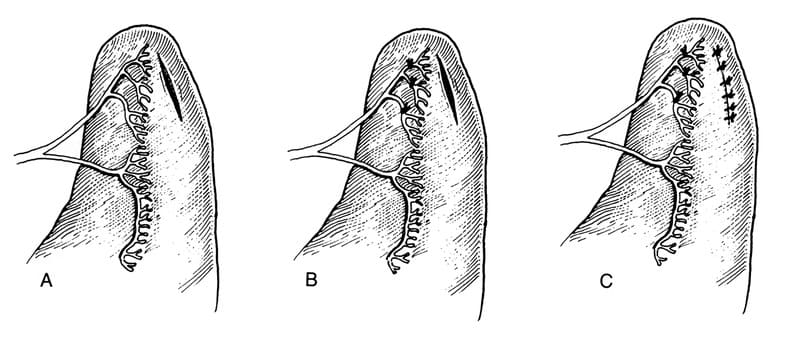
What are three common methods of pyloroplasty?
Fredet-Ramstedt pyloromyotomy
Y-U shaped
Heineke-Mikulicz.
What is the Fredet-Ramstedt pyloroplasty?
Performed by making longitudinal incision through serosa & muscularis of ventral pylorus. Only the serosa and muscularis should be incised, not mucosa (partial thickness incision)
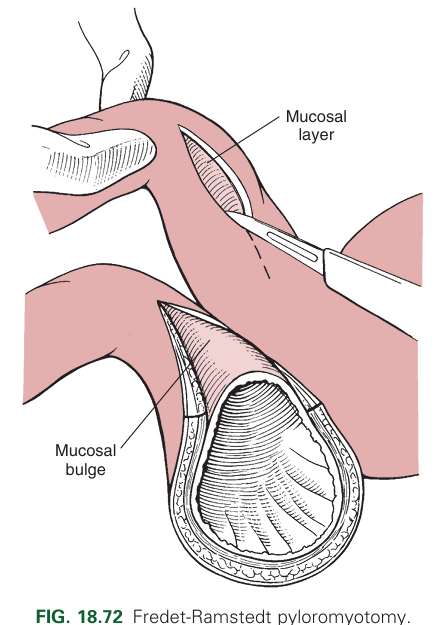
What is a limitation of the Fredet-Ramstedt pyloroplasty?
Limited visualisation into the lumen.
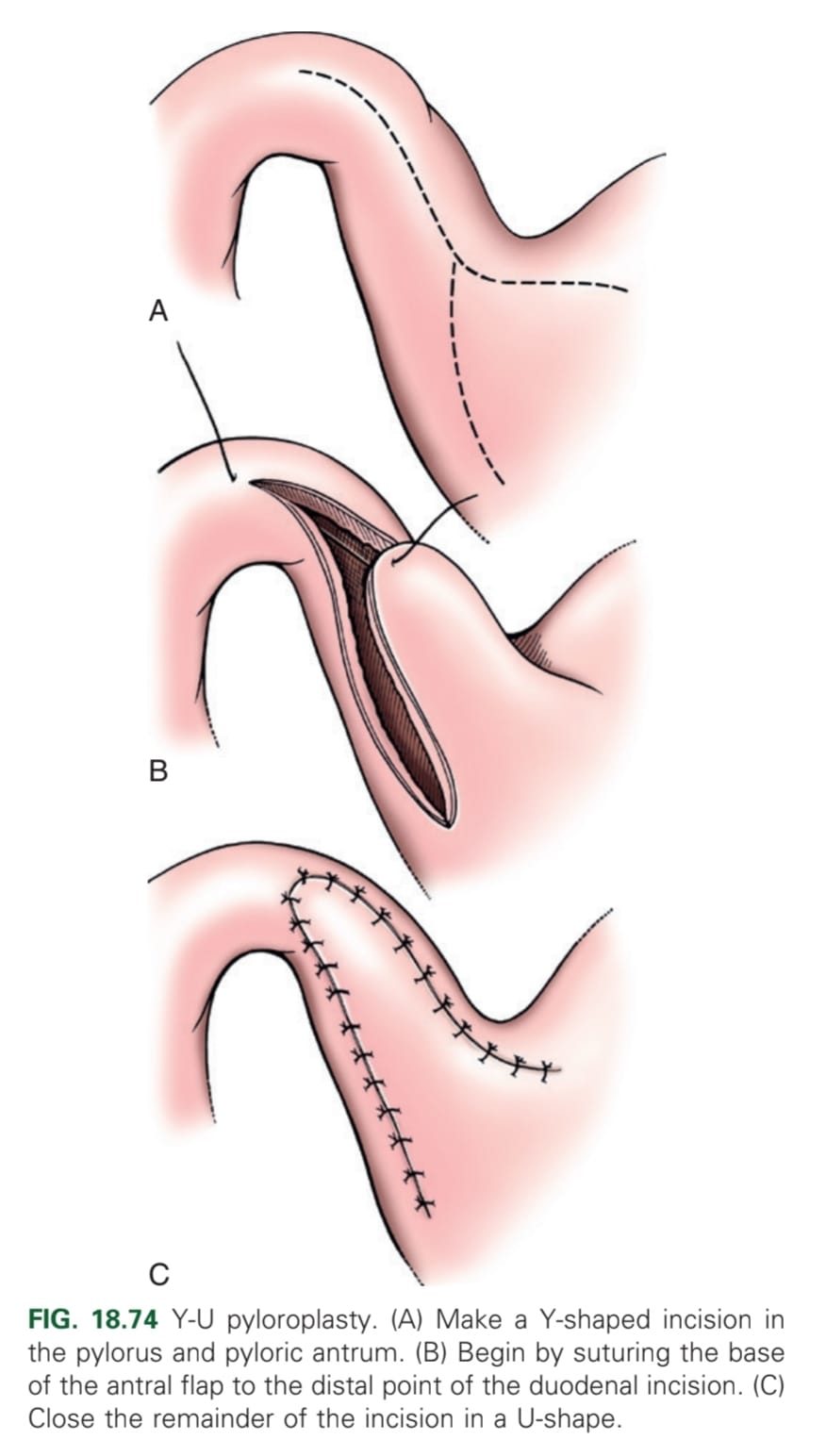
What is the Y-U shaped pyloroplasty?
Making a full-thickness Y-shaped incision
Y-base: antimesenteric aspect of the duodenum and pyloric sphincter
Y-arms: pyloric antrum
Advancing the U-shaped flap and suture to the base of the Y.
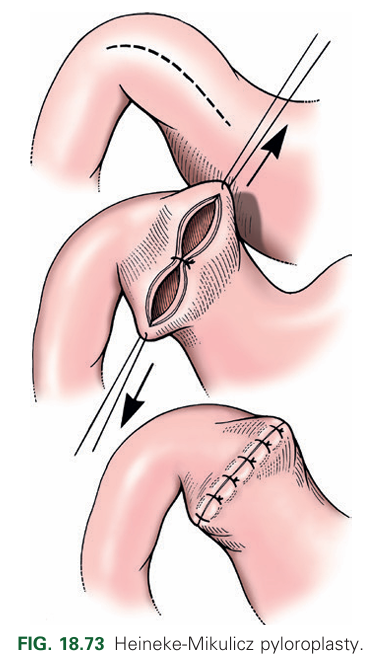
What is the Heineke-Mikulicz pyloroplasty?
A full-thickness longitudinal incision of the ventral pylorus closed transversely with an appositional interrupted pattern.
What are surgeries for when pyloric outflow obstruction cannot be treated with a routine pyloroplasty?
Billroth I: Pylorectomy with end-to-end gastroduodenostomy
Billroth II: Resection of pylorus, antrum, and proximal duodenum with anastomosis of proximal jejunum and stomach
What are the surgical diseases of the spleen?
Torsion
Rupture/trauma
Neoplasia.
What are the clinical signs of splenic torsion?
Abdominal pain, vomiting, abdominal distension, inappetence, PU/PD.
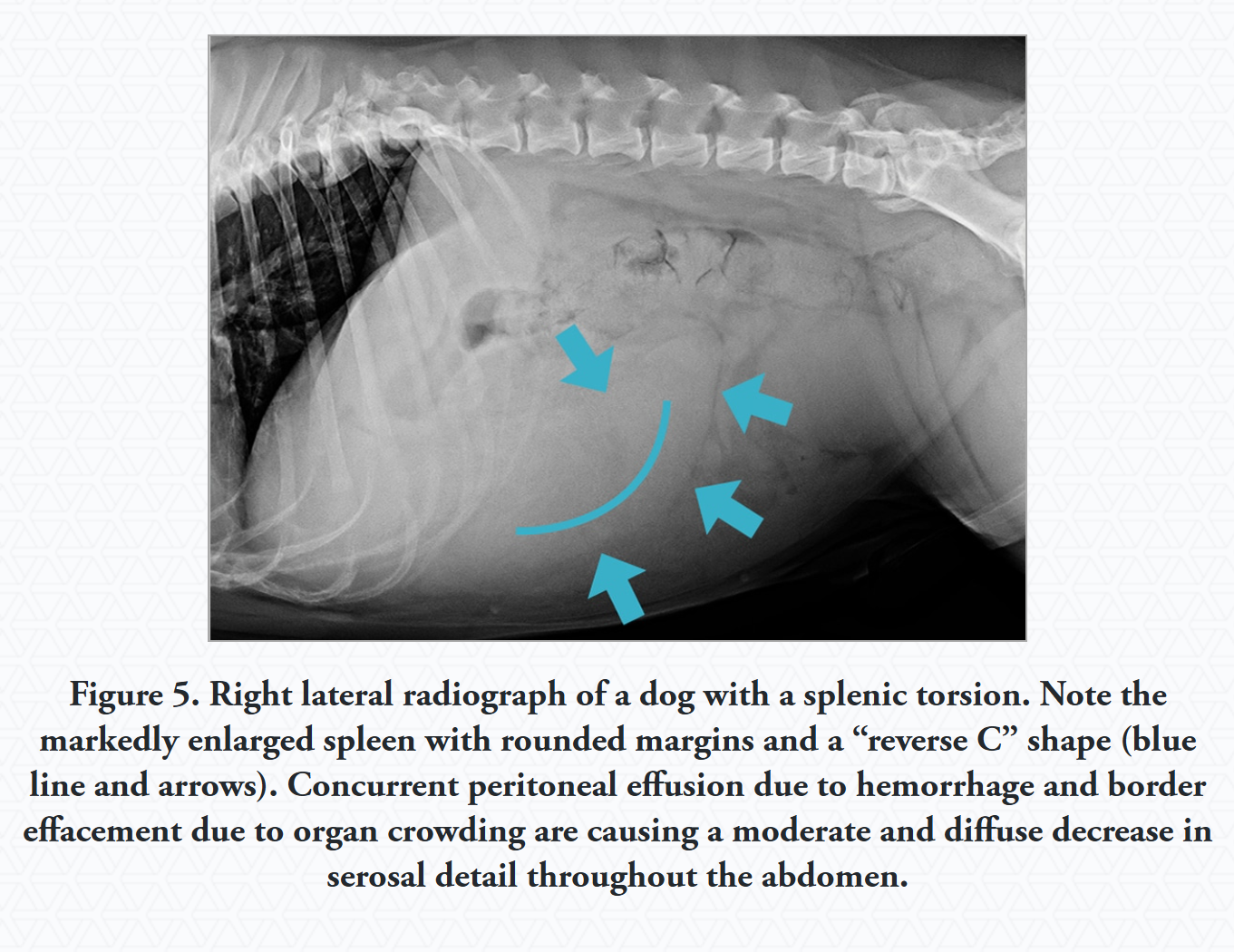
What is the most useful diagnostic tool for splenic torsion?
USG (detects splenomegaly and a lacy pattern).
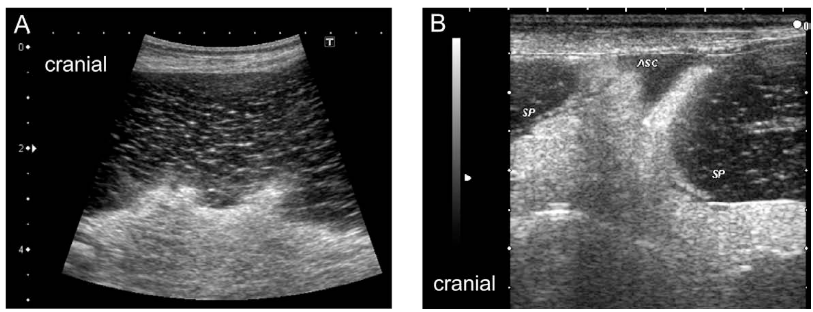
How is splenic torsion treated?
Supportive therapy
Total splenectomy
Prophylactic gastropexy with partial splenectomy.
What are the clinical signs of splenic rupture/trauma?
Haemorrhage into the abdominal cavity, distended abdomen, pale mucous membranes, hypotension, acute abdomen, depression, and enlarged spleen.
Small bleedings may stop spontaneously. Large bleeding may lead to haemorrhagic shock.
How is splenic neoplasia treated?
Patient stabilisation, total or partial splenectomy followed by chemotherapy.
What are examples of splenic surgical interventions?
Splenorrhaphy
Splenectomy
What is splenorrhaphy?
Surgical repair of small splenic lacerations or punctations with interrupted pattern.
What are indications for splenectomy?
Haemangiosarcoma, GDV, splenic torsion, severe trauma, generalised infiltrative disease
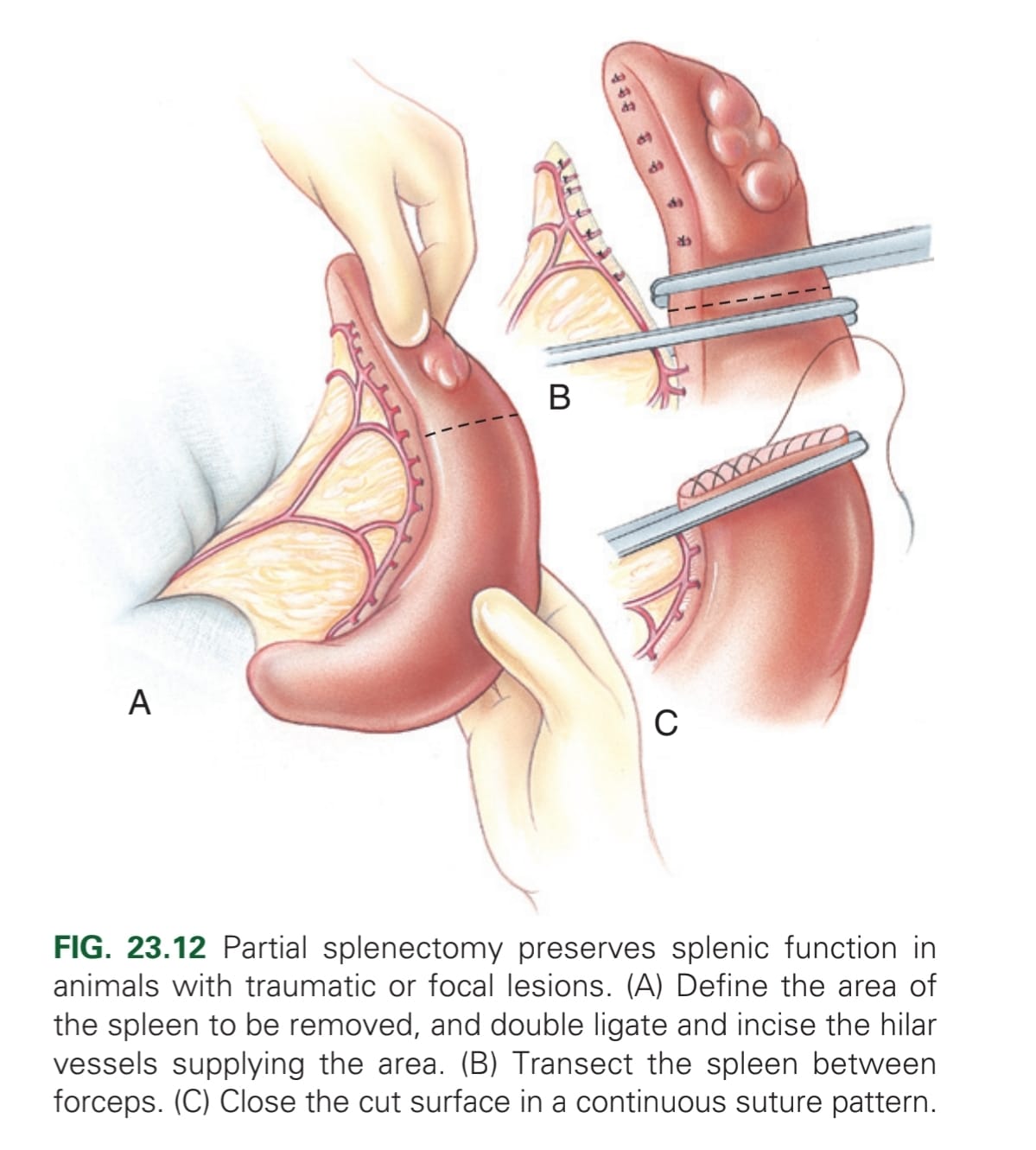
What is the method for a partial splenectomy?
Elevate spleen from abdomen → Ligate or seal hilar vessels in area → may use automatic stapling device to separating parenchyma, or digital pressure (not to destroy capsule) → haemostatic clamp across separated parenchyma & second clamp 1-2 cm distally, & transect midway between clamps → Appose capsule w/ continuous absorbable material. A second line of continuous or interrupted mattress may be used to gain a more haemostatic effect.
What is the surgical approach for total splenectomy?
Midline celiotomy from xiphoid to pubis.
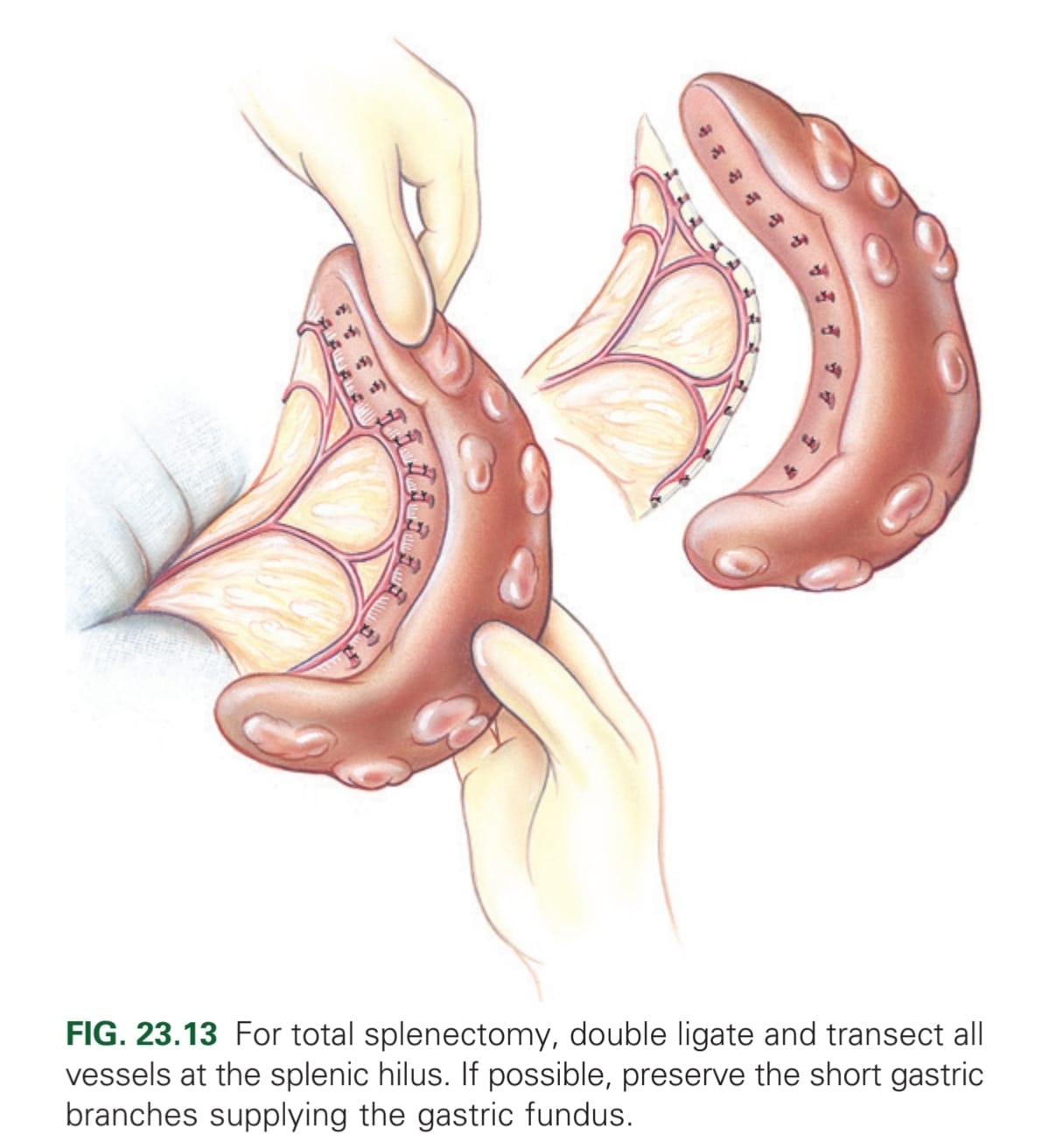
What is the method for a total splenectomy?
Elevate by gentle manipulation out of abdomen → double ligation of each vessel that remains in abdomen (if possible, preserve the short gastric branches supplying the gastric fundus) → Resect spleen. If spleen has ruptured at the time of surgery, lavage the abdominal cavity to prevent neoplastic cells entering.
How can an animal be tested to see if pyloroplasty is indicated?
When contrast agent is not evacuated from the stomach 12-24 hours after administration
Which breeds are more predisposed to requiring pyloroplasty?
Miniature and brachycephalic breeds
Which vessels are ligated in a complete splenectomy?
All vessels at splenic hilus (or splenic artery distal to the branches supplying left limb of the pancreas; pancreatic artery)