Biology 3rd Quarter CQA
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

48 Terms
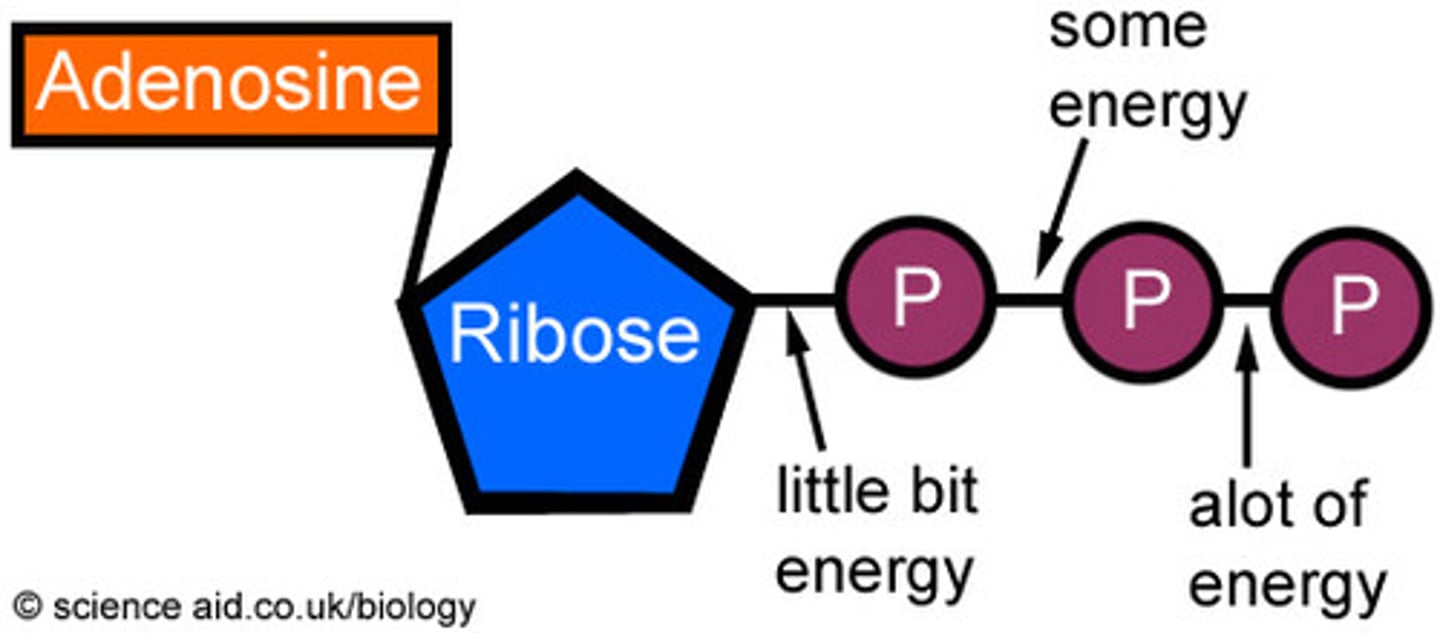
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
main energy source that cells use for most of their work, energy stored in high energy bonds between phosphates, Changes to ADP when last phosphate is lost
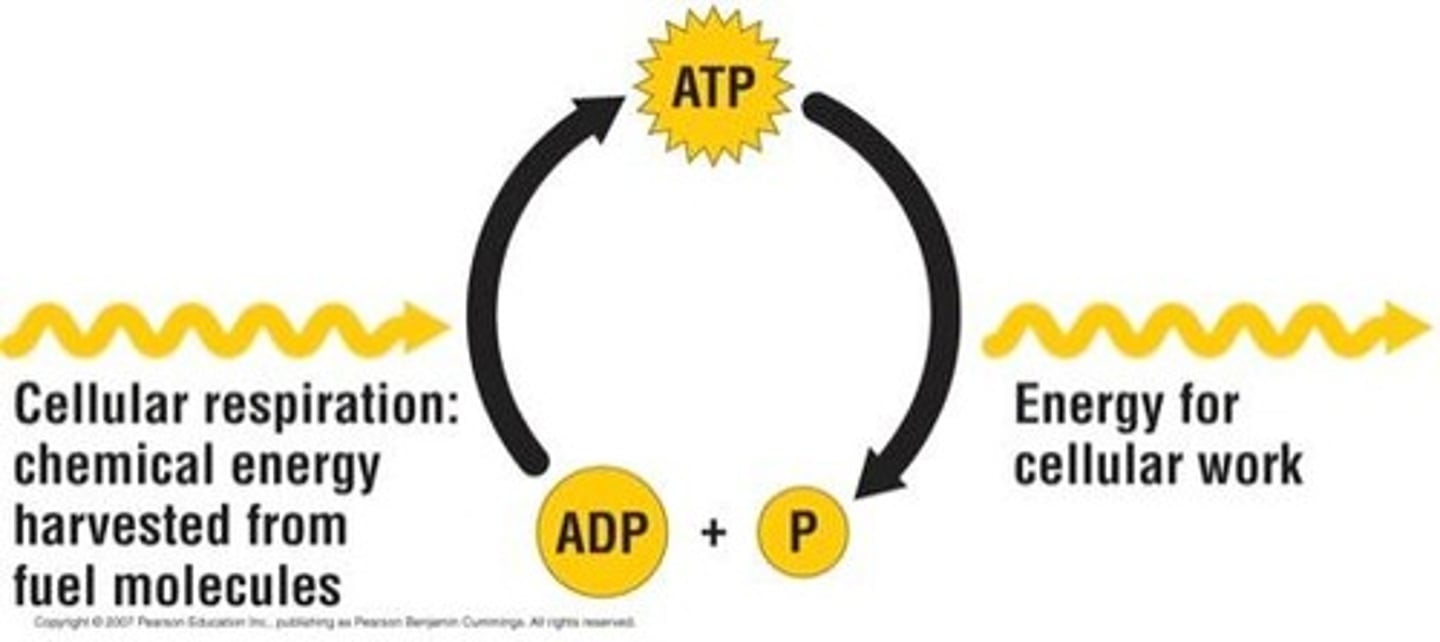
cell energy cycle
The series of metabolic processes by which living cells produce energy through the oxidation of organic substances, ADP recycled/recharged into ATP
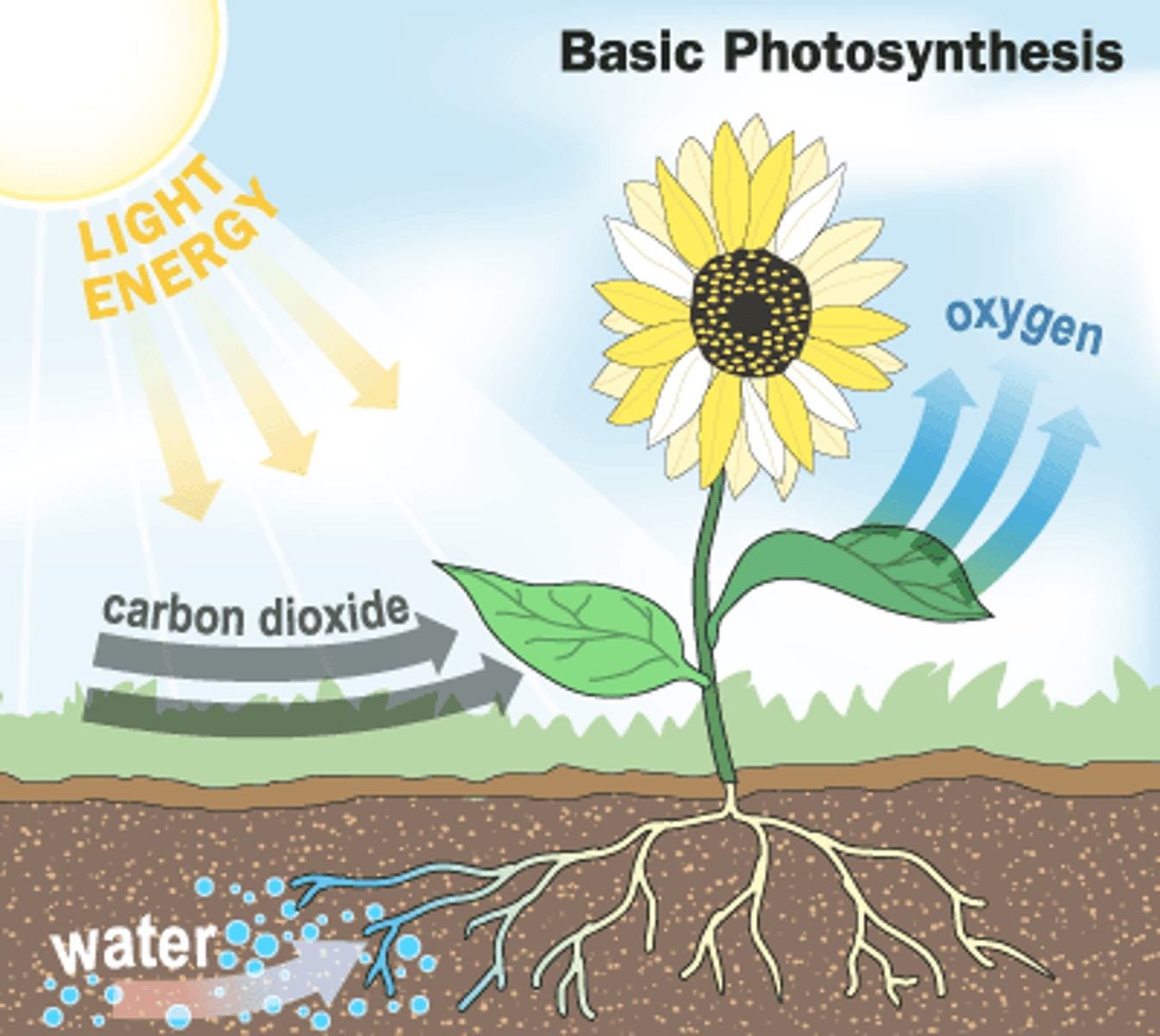
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars (glucose)
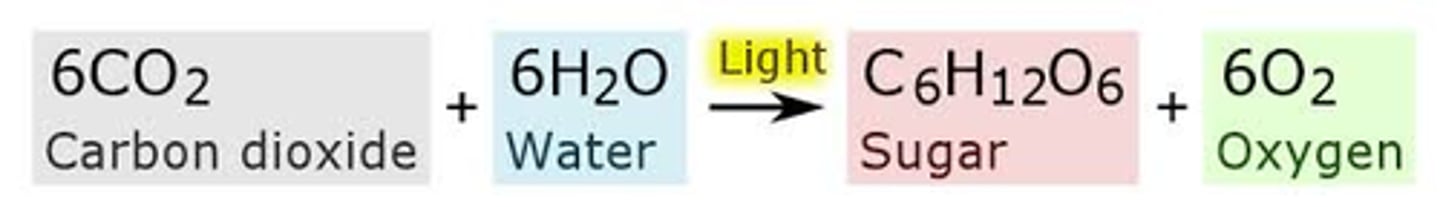
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --> light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
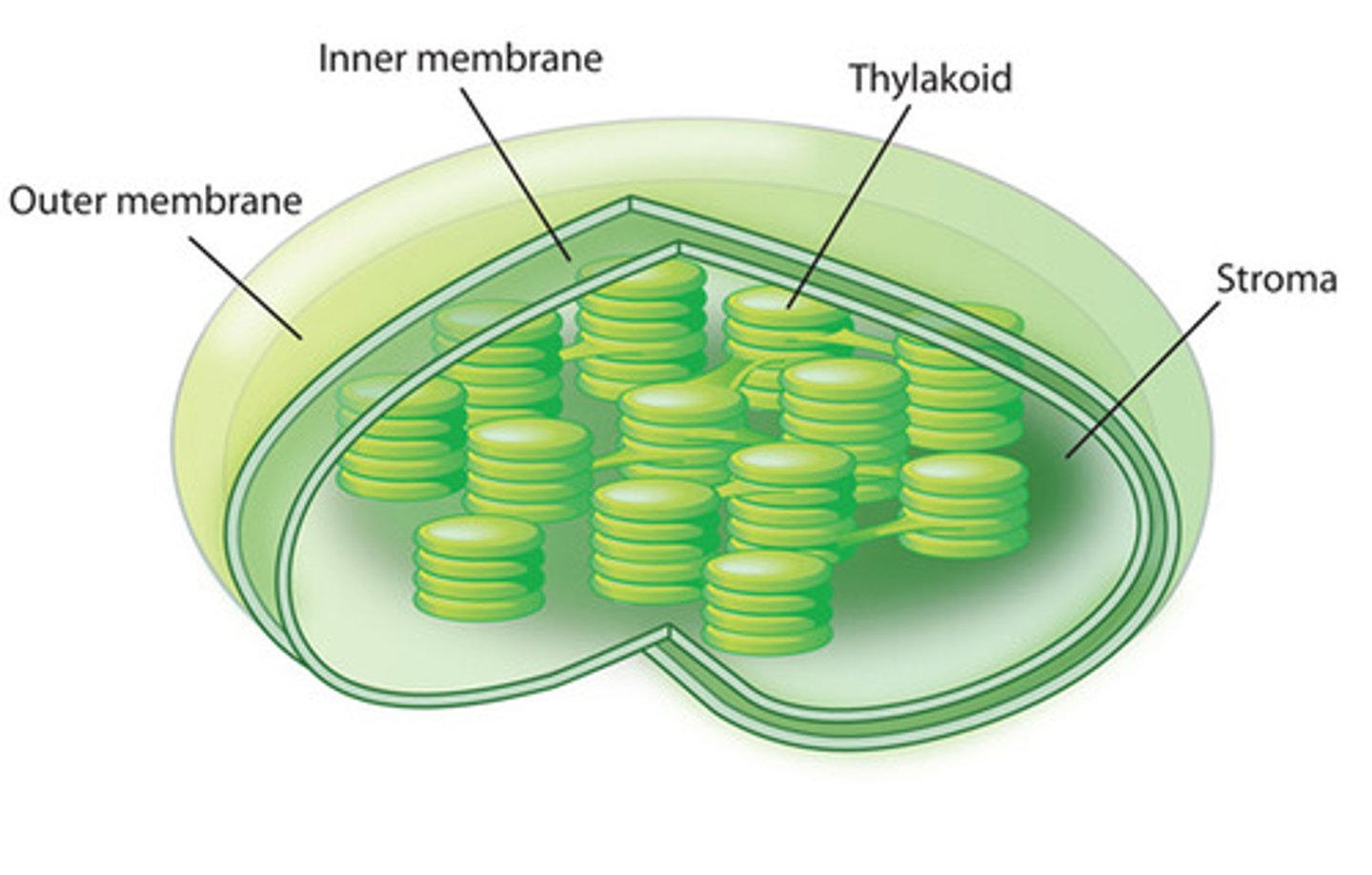
Chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
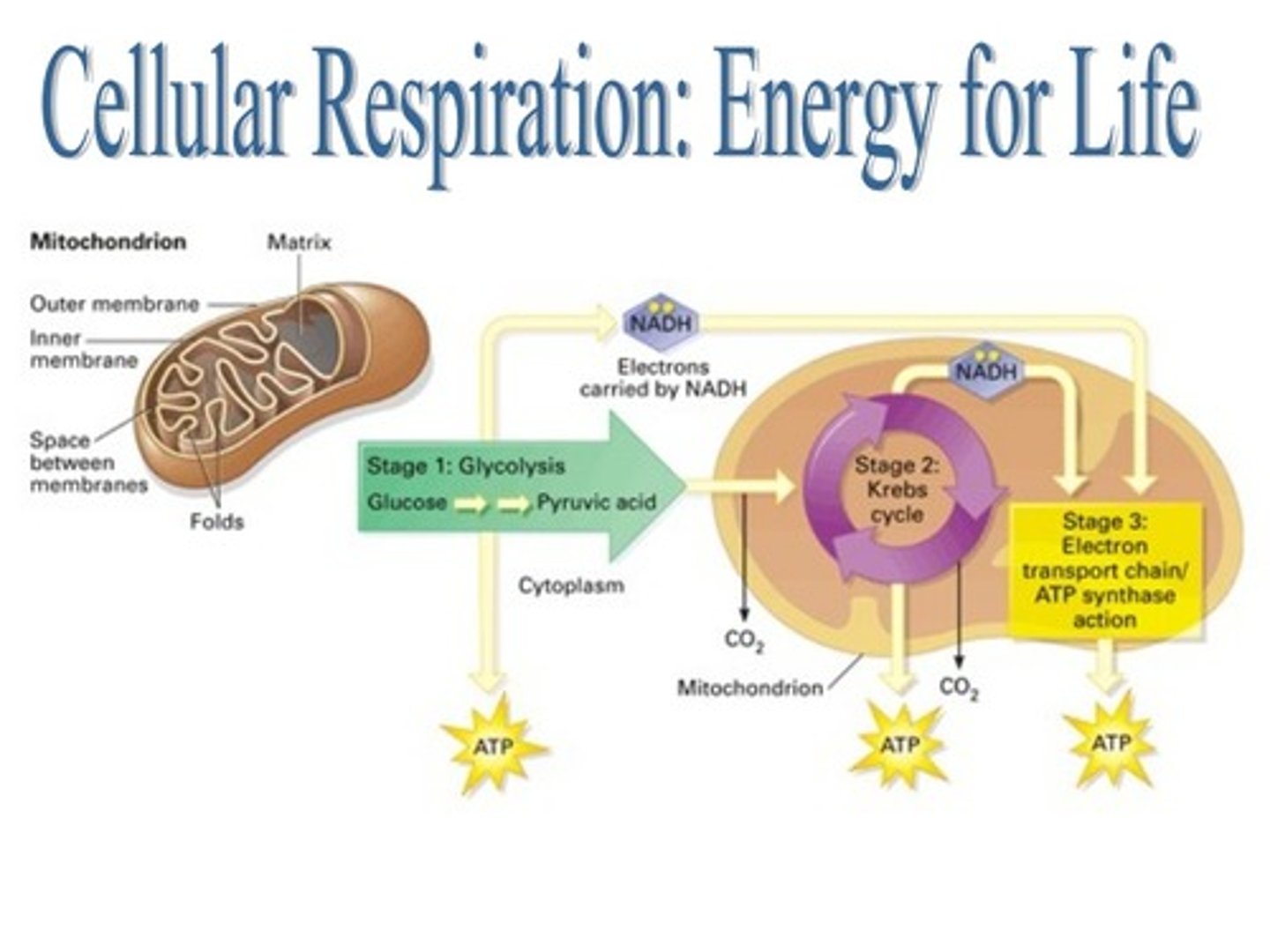
aerobic respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --→ 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (36 ATP)

anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen but makes less ATP than aerobic respiration (lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation)

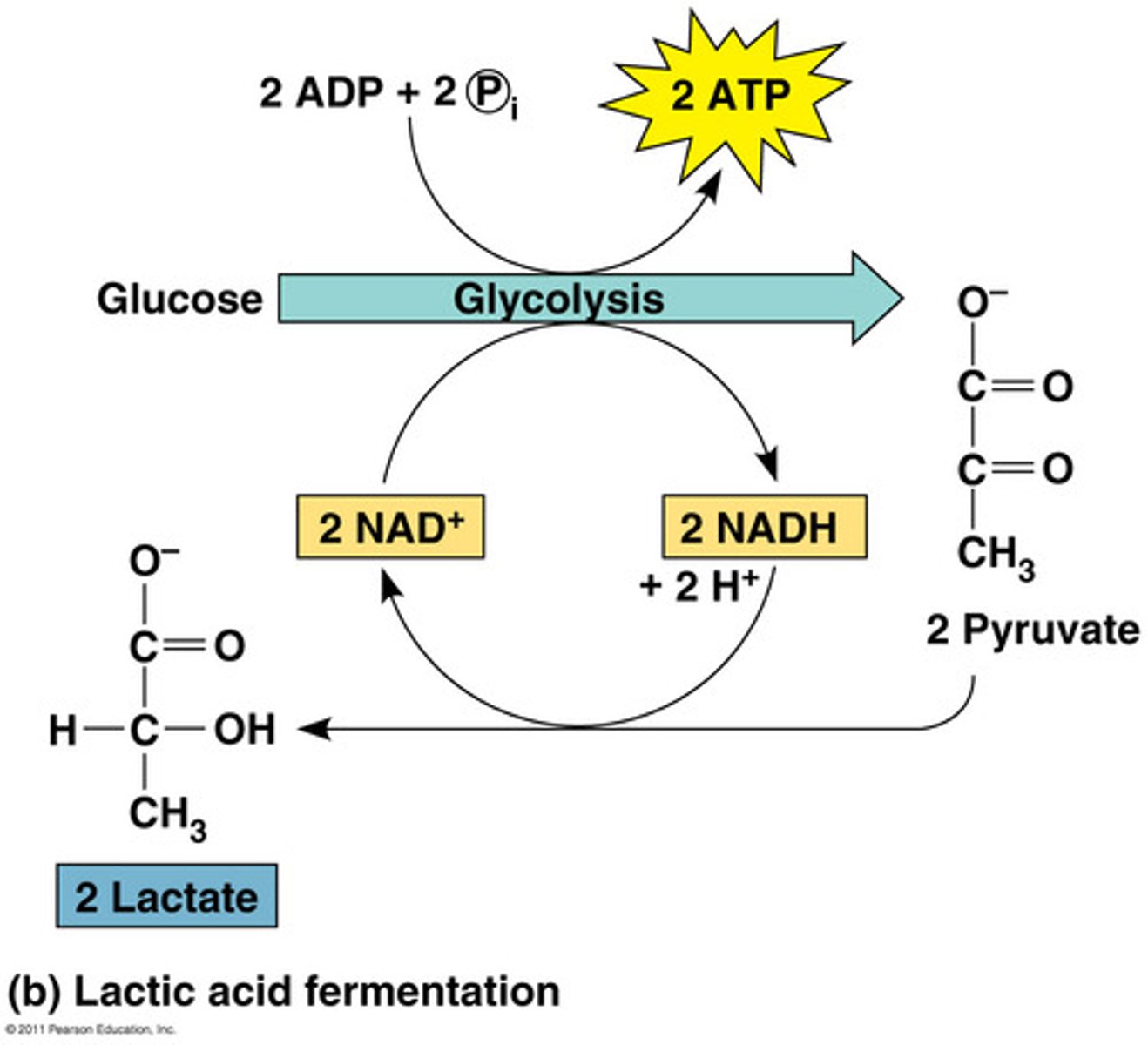
lactic acid fermentation
the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates that produces lactic acid as the main end product and 2 ATP, TYPE OF ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION
alcoholic fermentation
A process used by yeast cells and some bacteria to produce carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol, only make 2 ATP, TYPE OF ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION

light-dependent reactions
The first of two major stages in photosynthesis (preceding the Calvin cycle). These reactions, which occur on the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast converting solar energy to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH, releasing oxygen in the process.
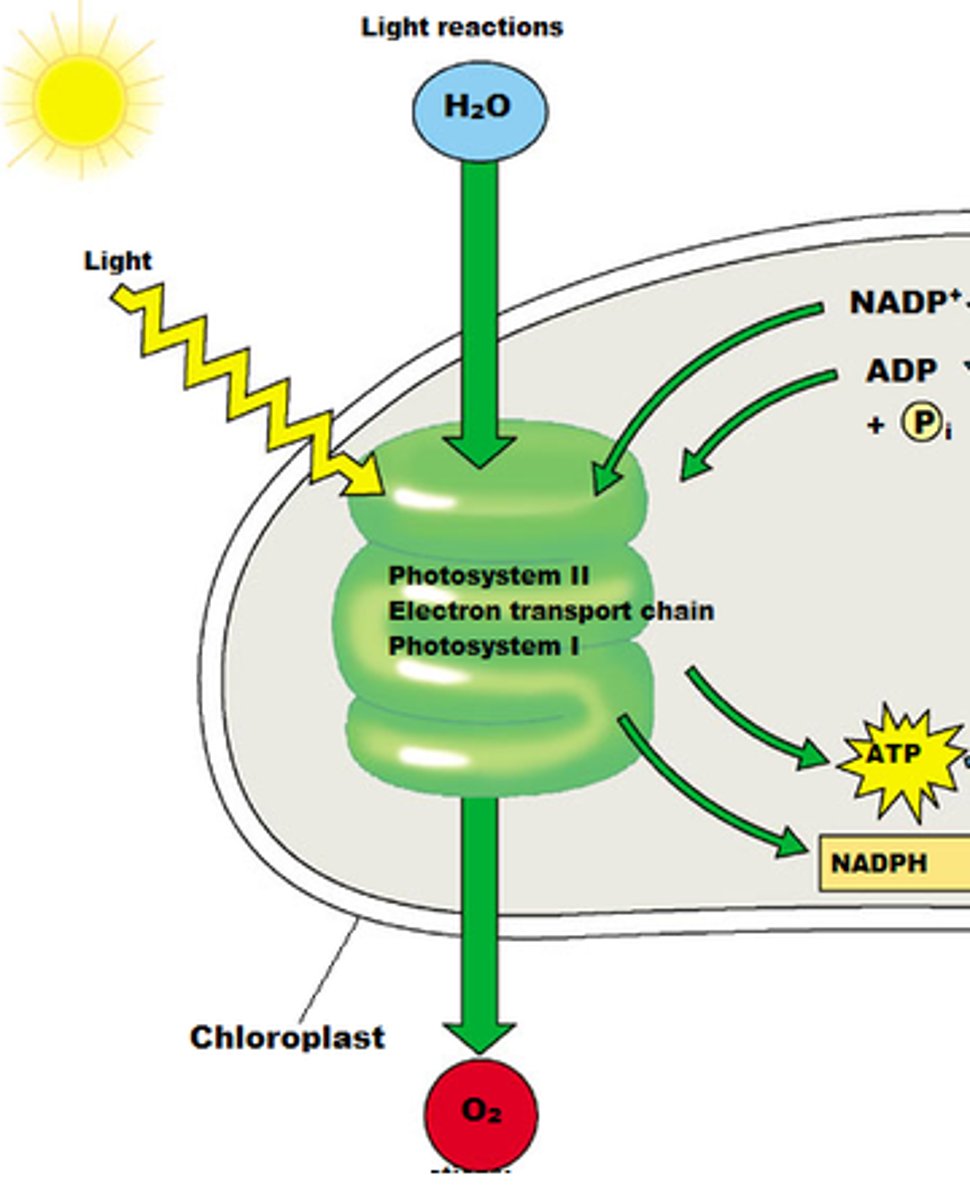
Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
set of reactions in photosynthesis that do not require light; energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar; also called the Calvin cycle
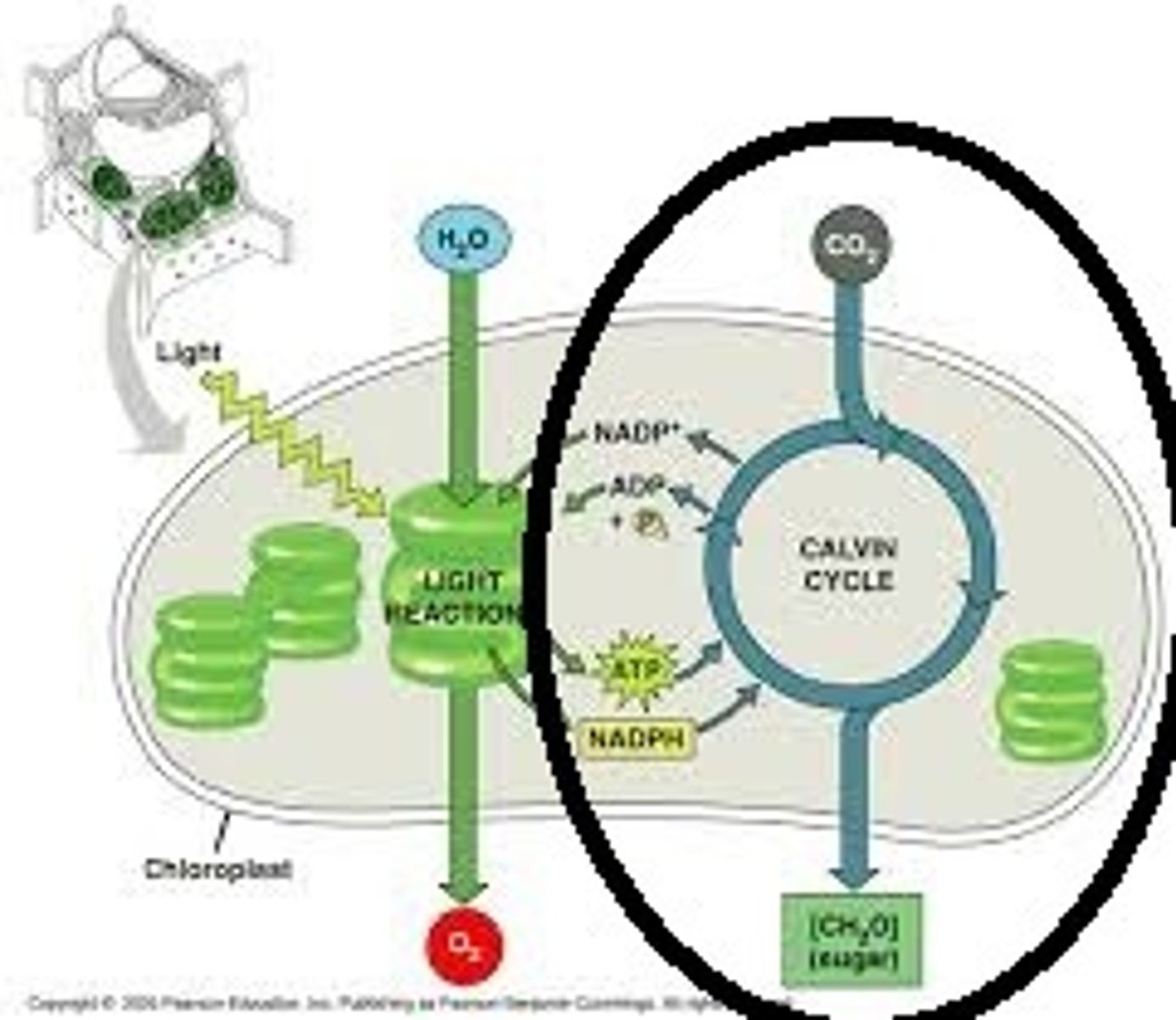
chlorophyll absorption spectrum
blue-violet and red light work best, green the worst for photosynthesis
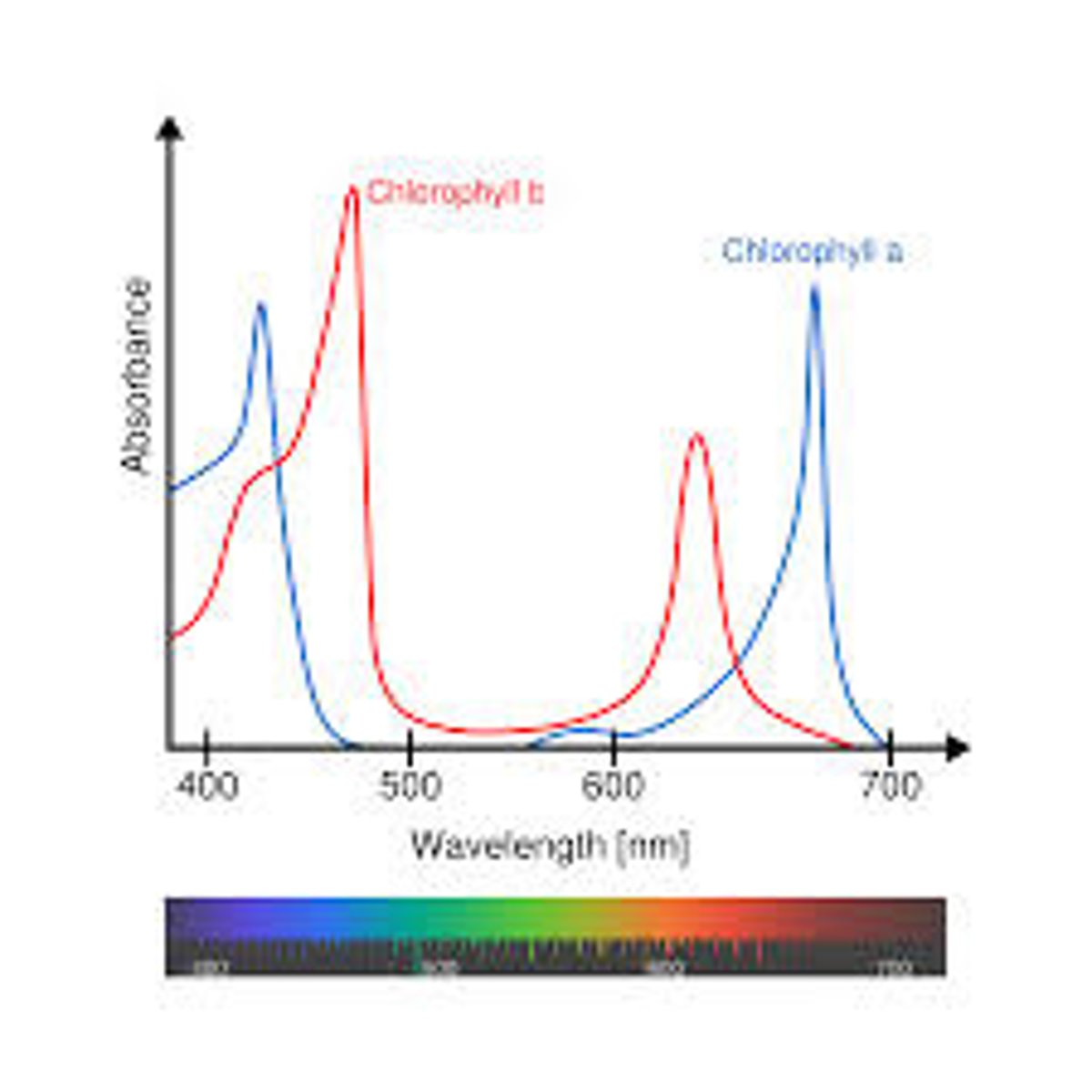
Cell size is limited by
surface area to volume ratio, large cells can't take in nutrients and remove waste products as efficiently as small cells making maintenance of homeostasis difficult
Mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes, 1 diploid (2n) cell produces 2 identical diploid (2n) daughter cells(PMAT) prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide into new cells (STUDY THIS DIAGRAM!)
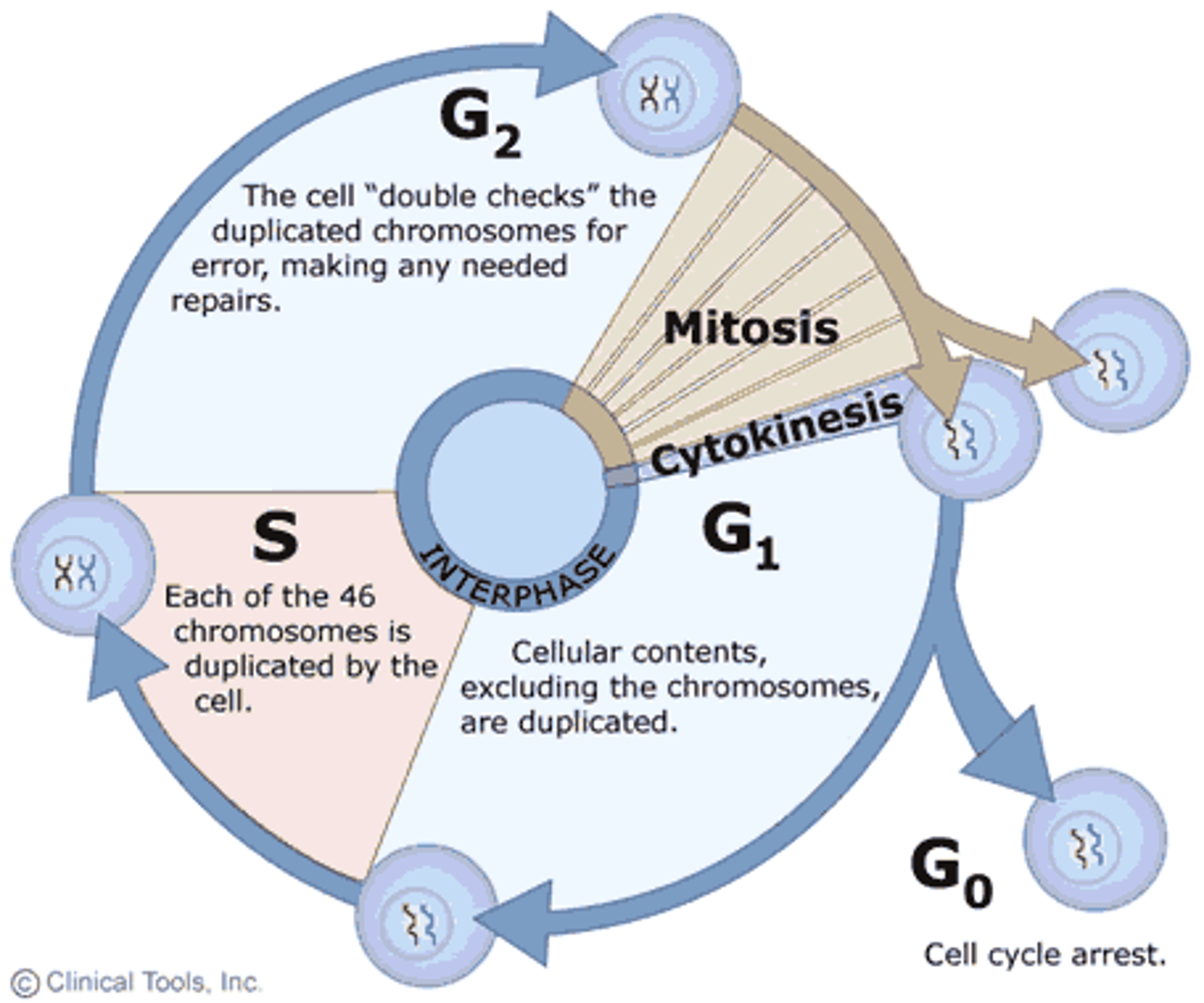
G1 phase of interphase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
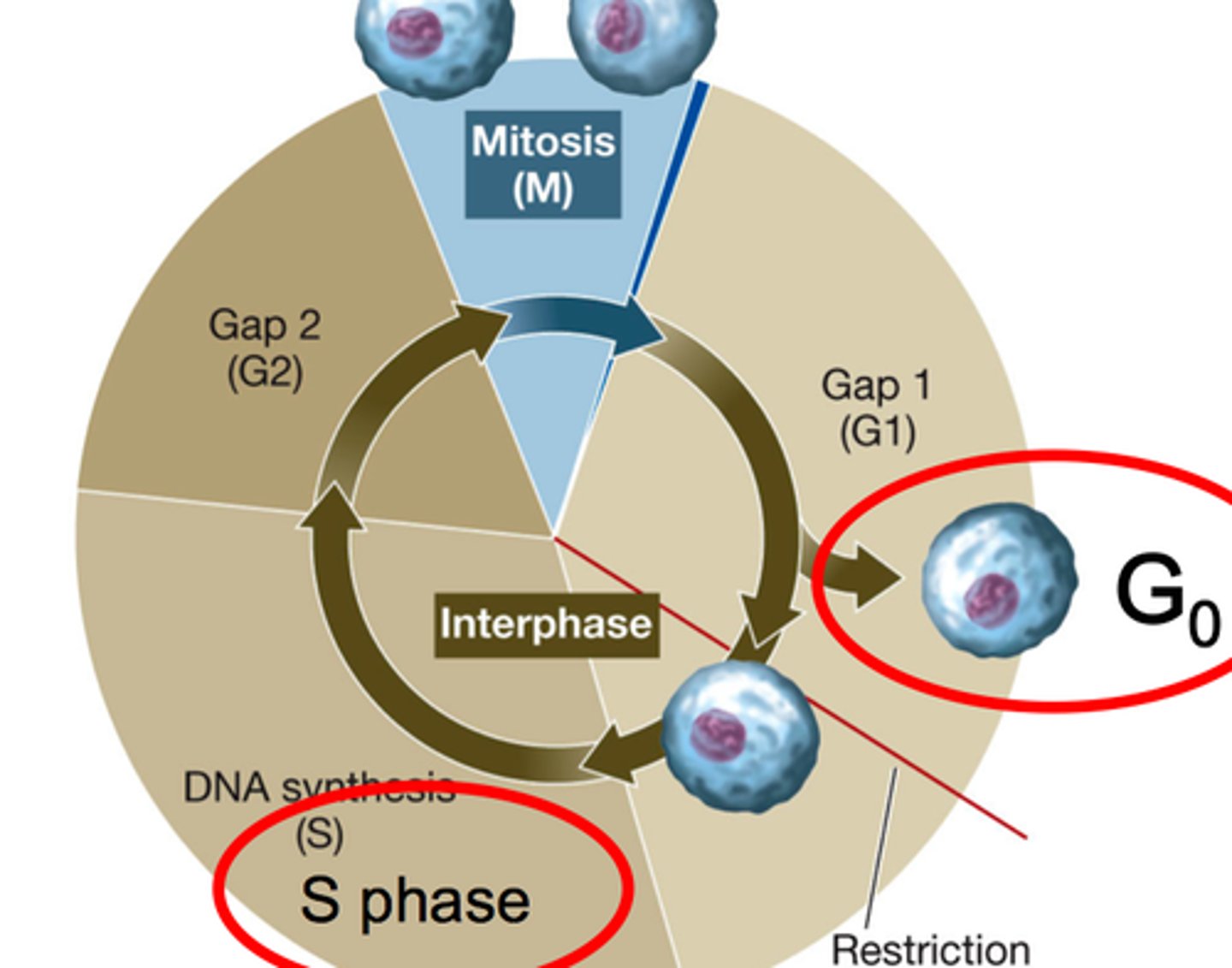
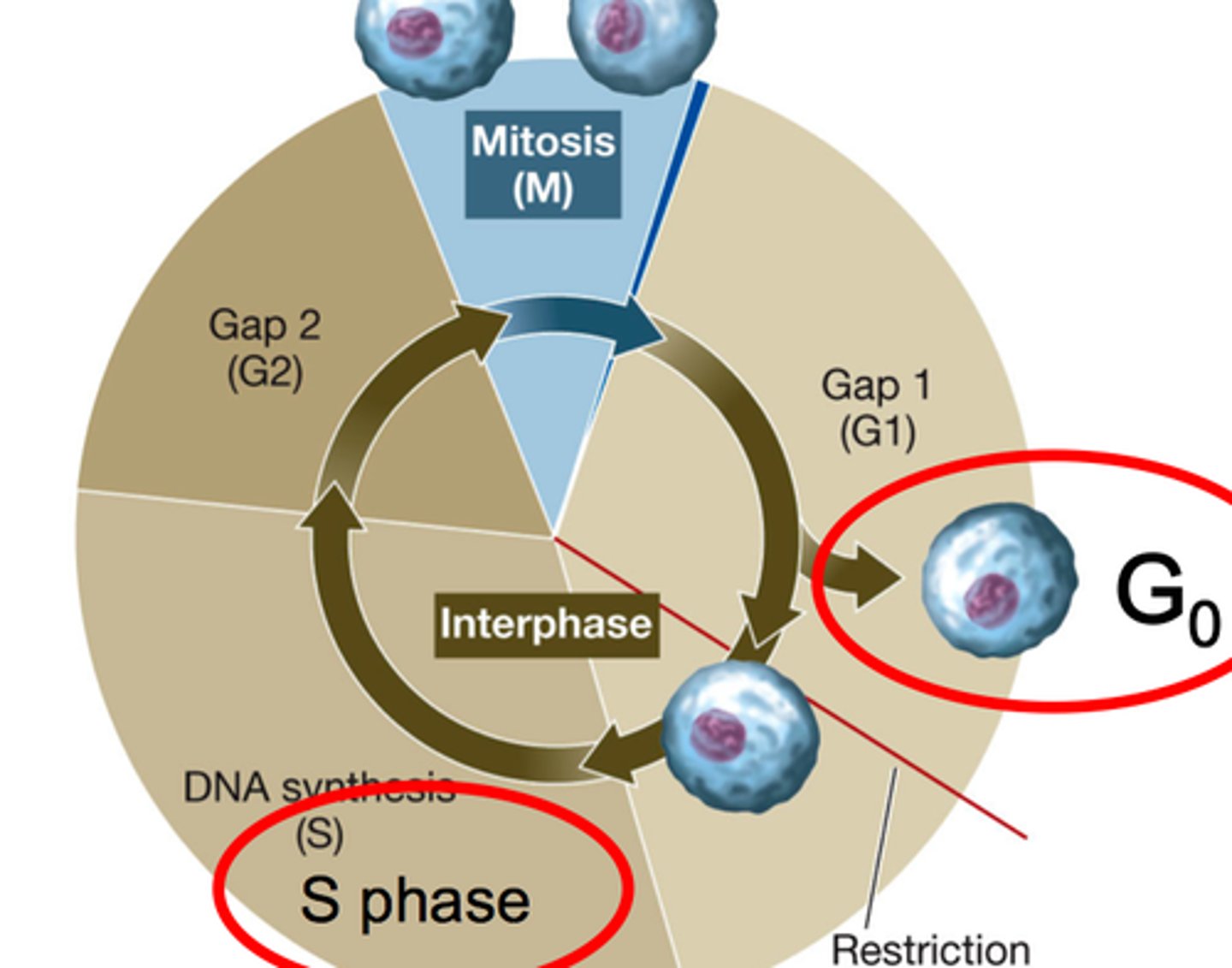
S phase of interphase
chromosome replicate and DNA synthesizes
G 2 phase of interphase
cell prepares for division
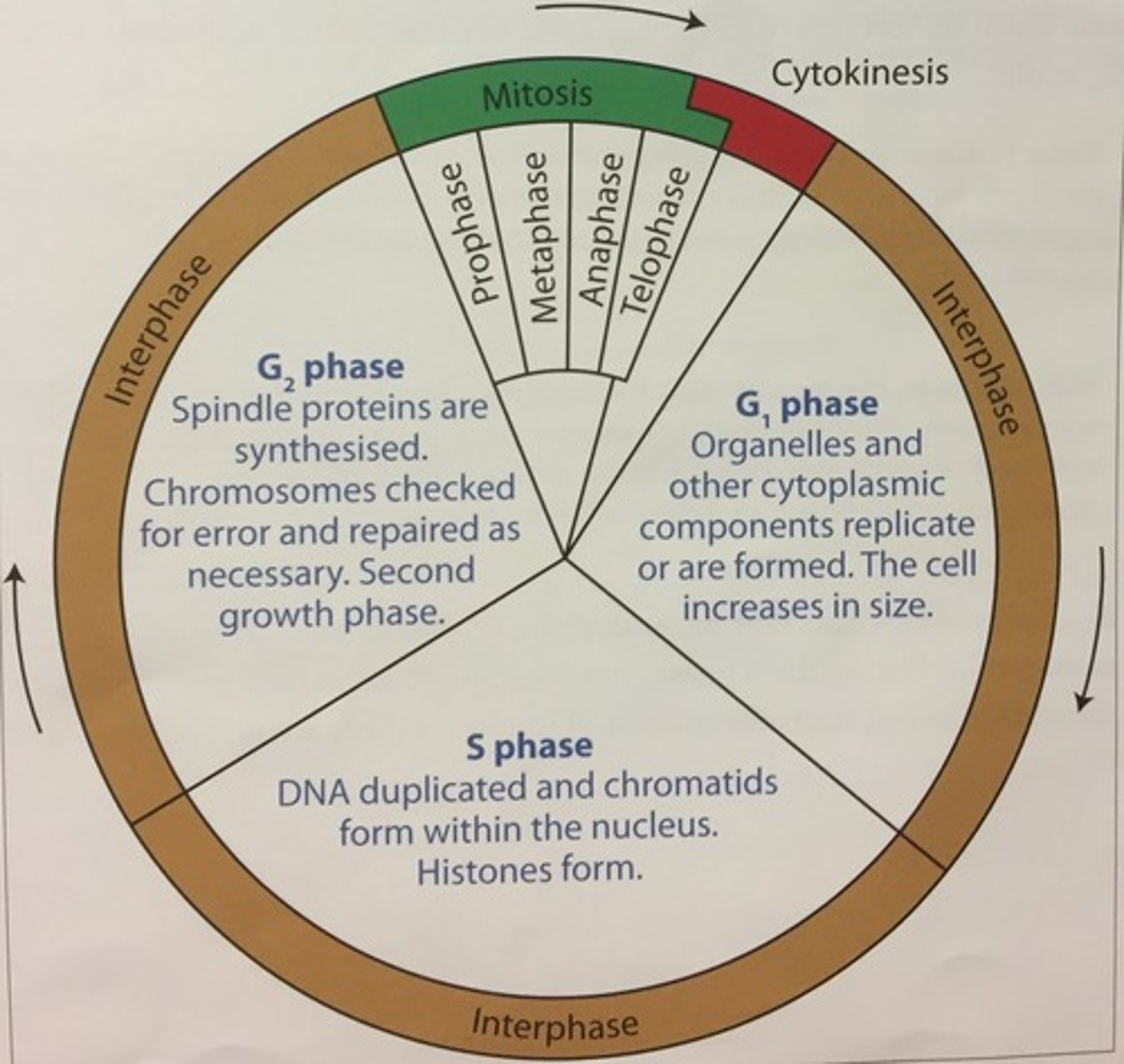
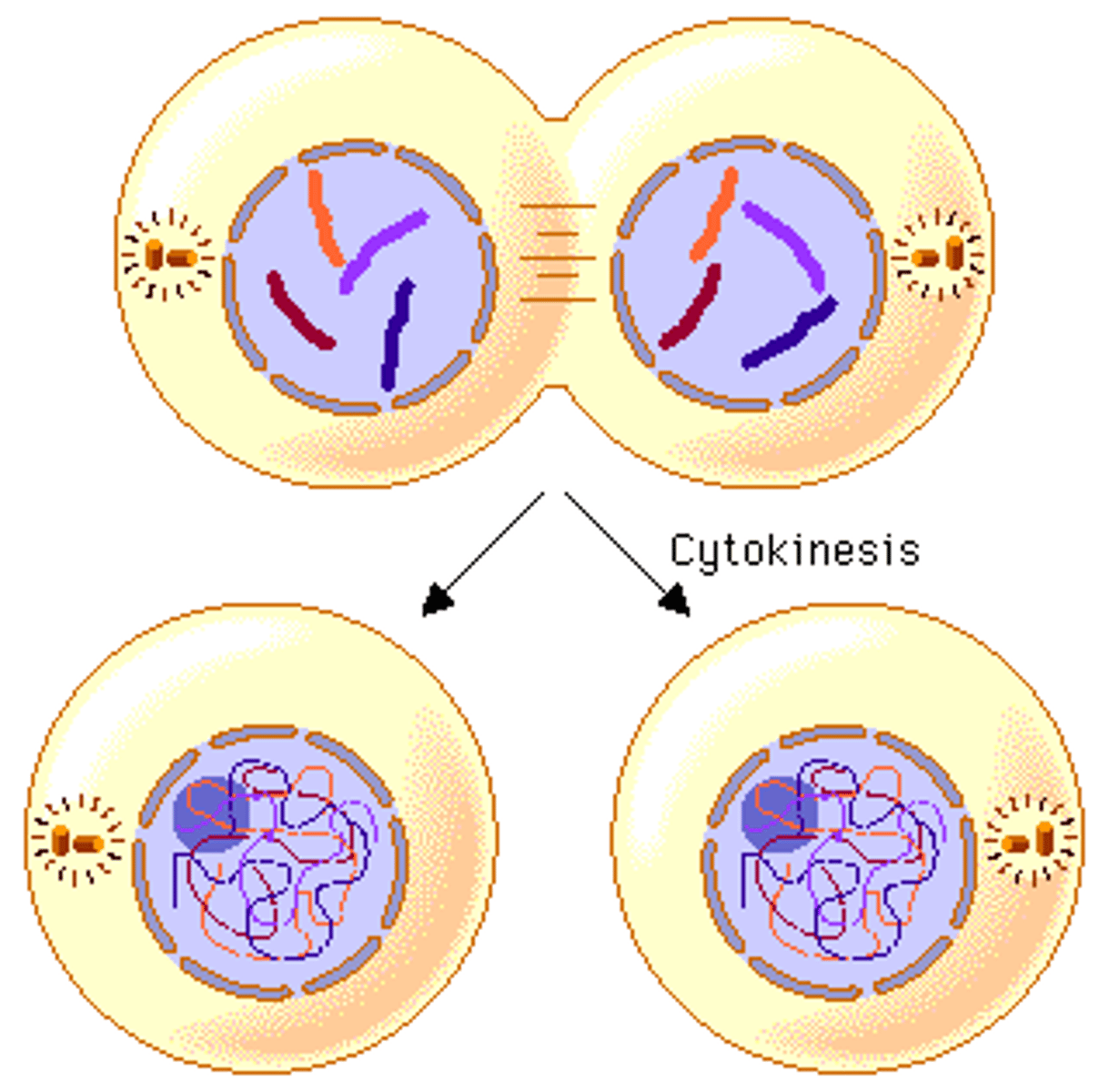
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
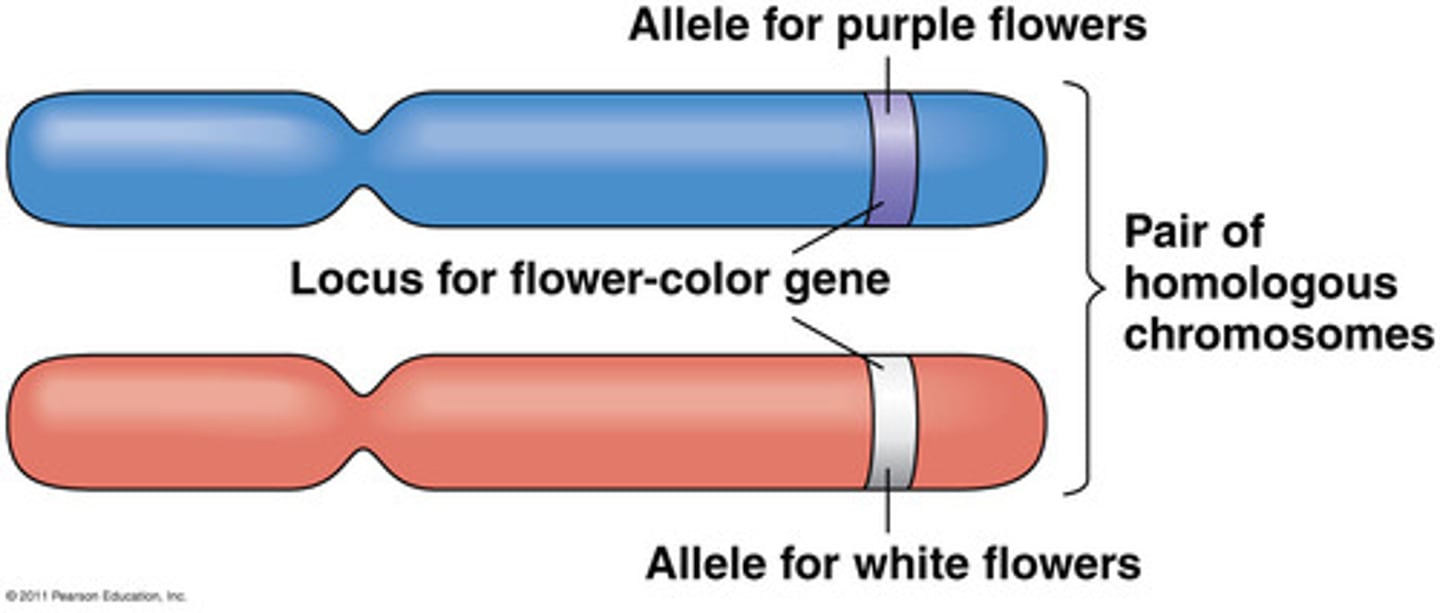
Allele
An alternative form of a gene. (A or a)
dominant allele
an allele that is fully expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygote (R)
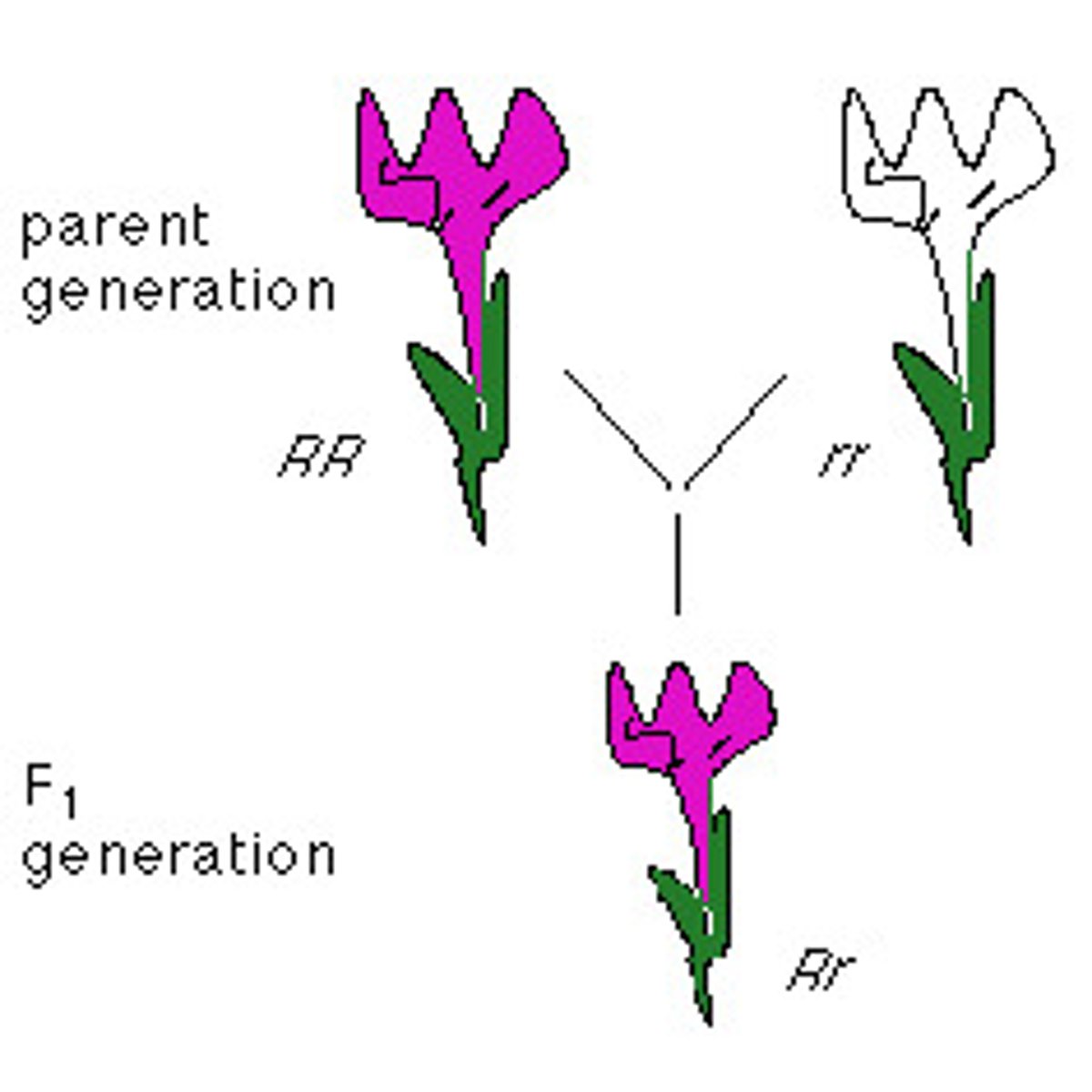
recessive allele
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present (a)

Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
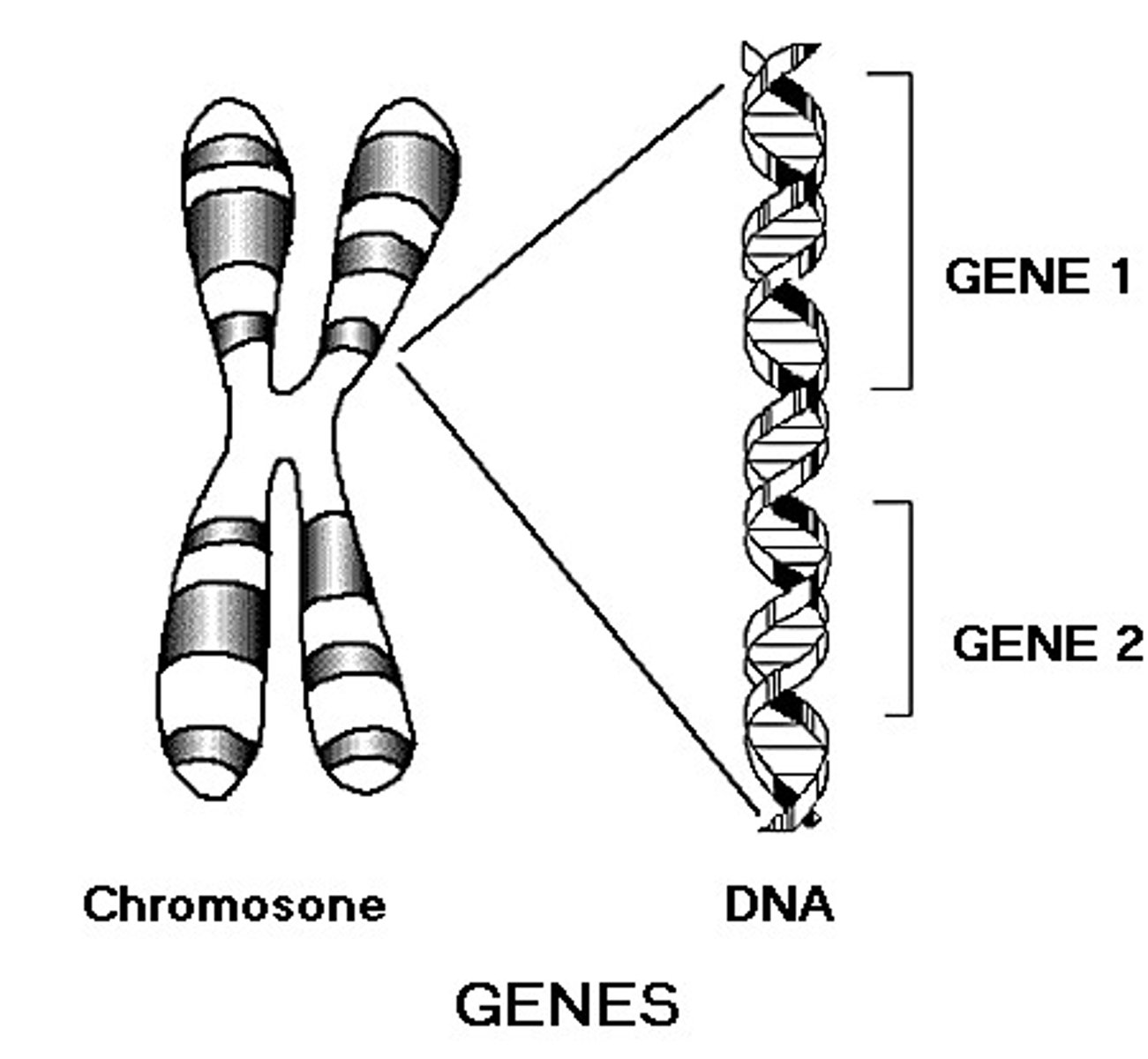
genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations. (Tt or AA or cc)
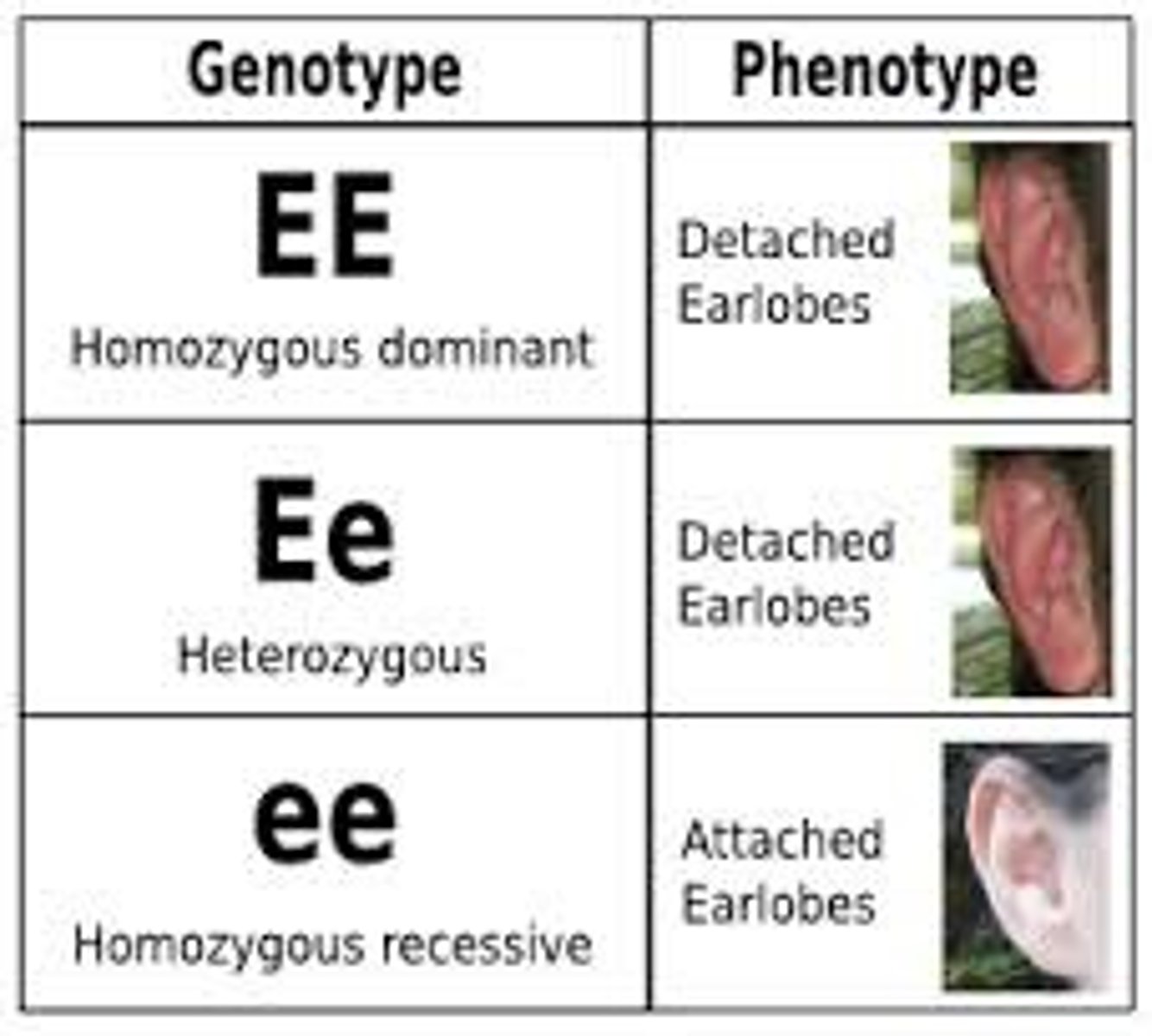
homozygous recessive
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and recessive (aa)
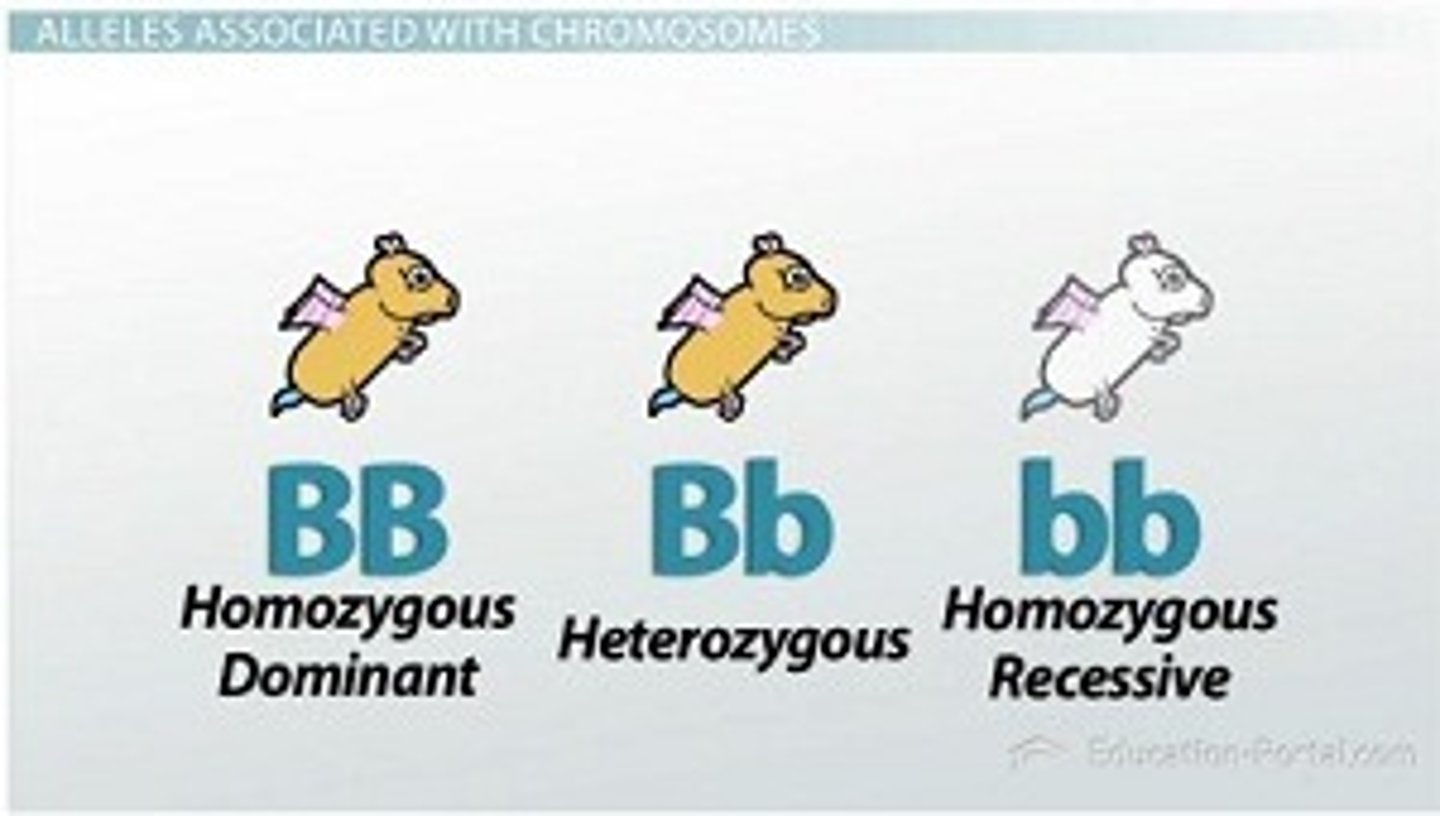
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait

homozygous dominant
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and dominant (AA)

Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.

Gametes
sex cells (egg and sperm) they are haploid (1n) and produced by meiosis

Fertilization
Process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells join to form a new cell called a zygote (1n +1n = 2n)
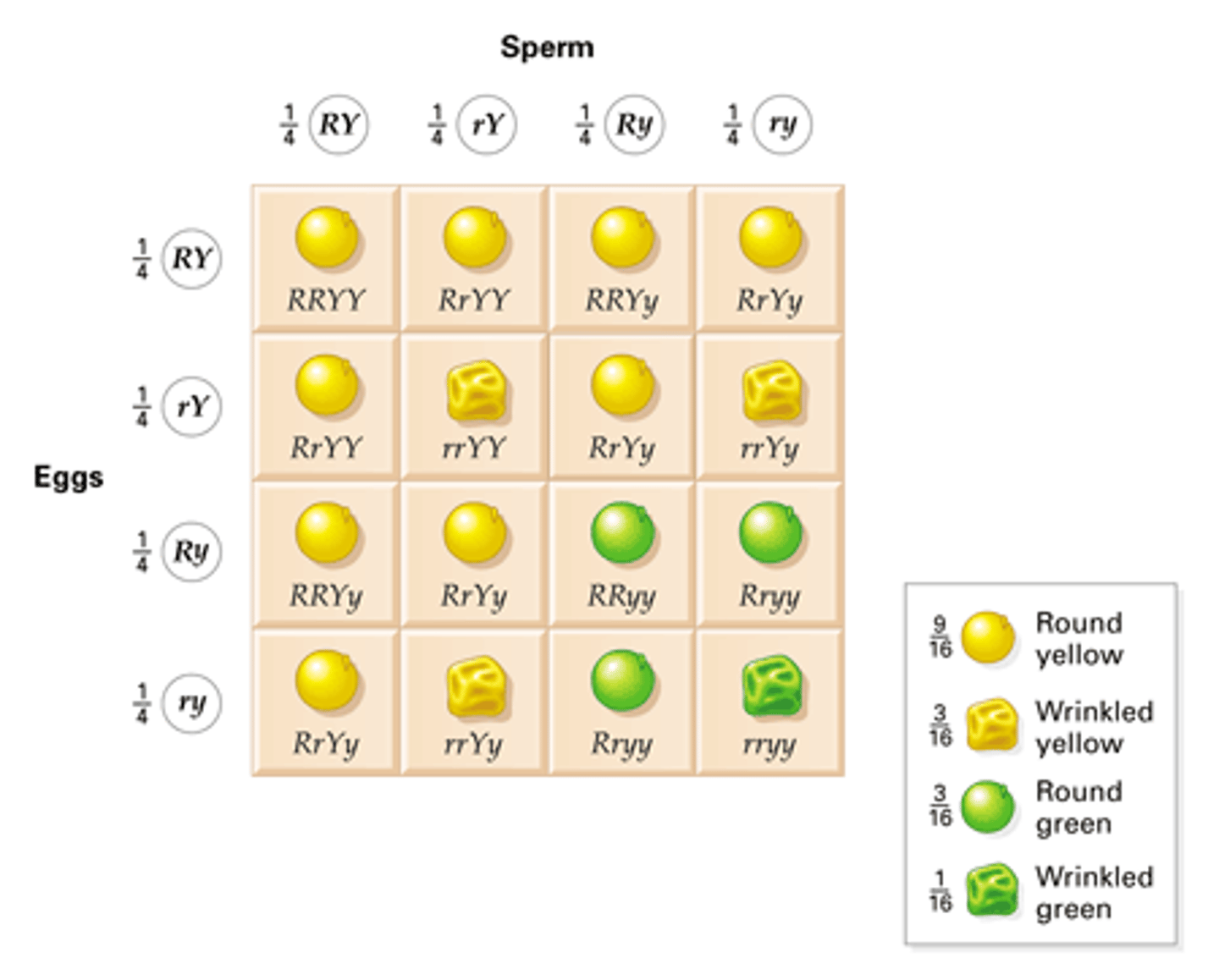
dihybrid cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
incomplete dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele

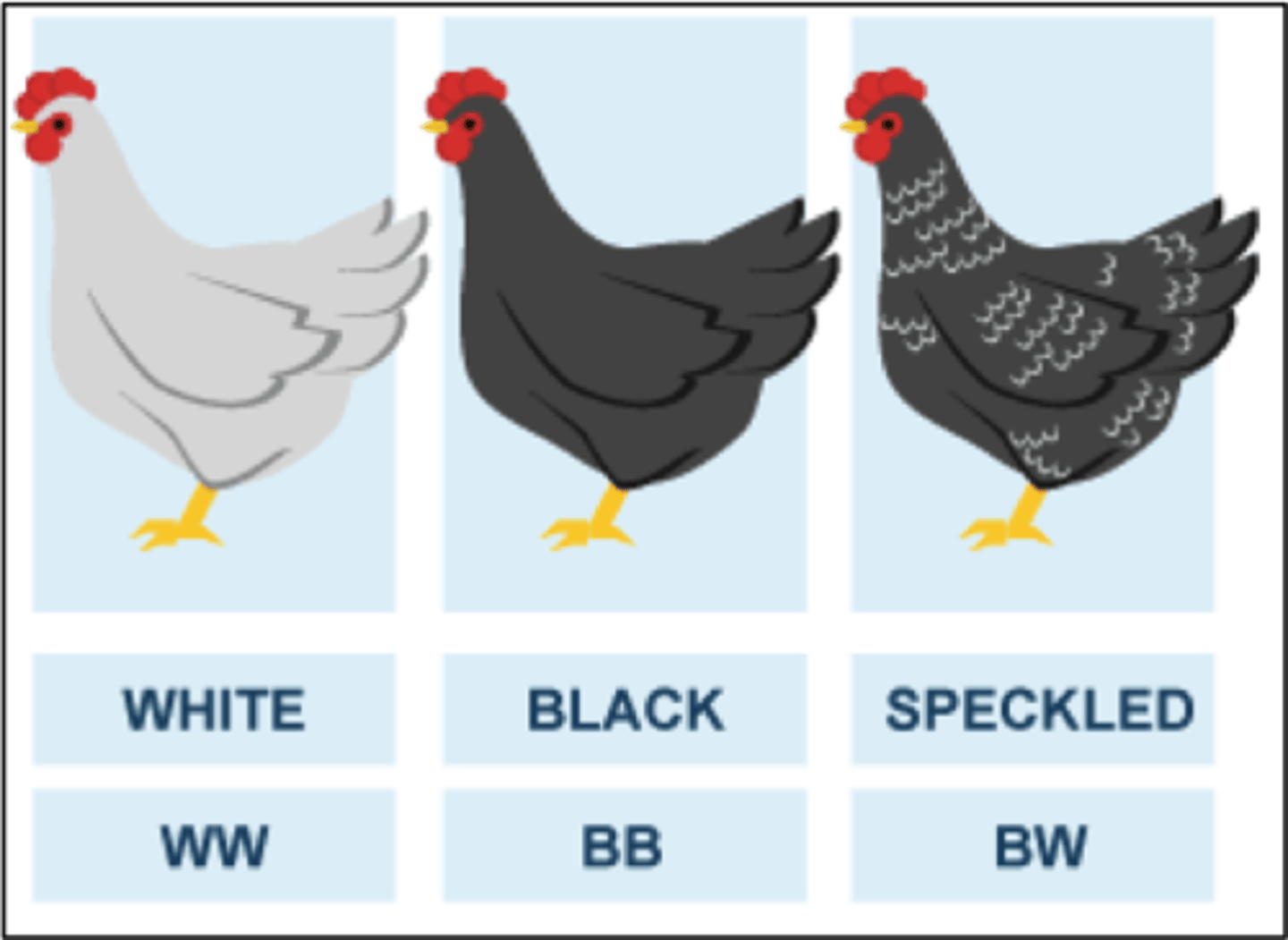
codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase.

Autosomal Dominant Pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family, NEVER skips generations
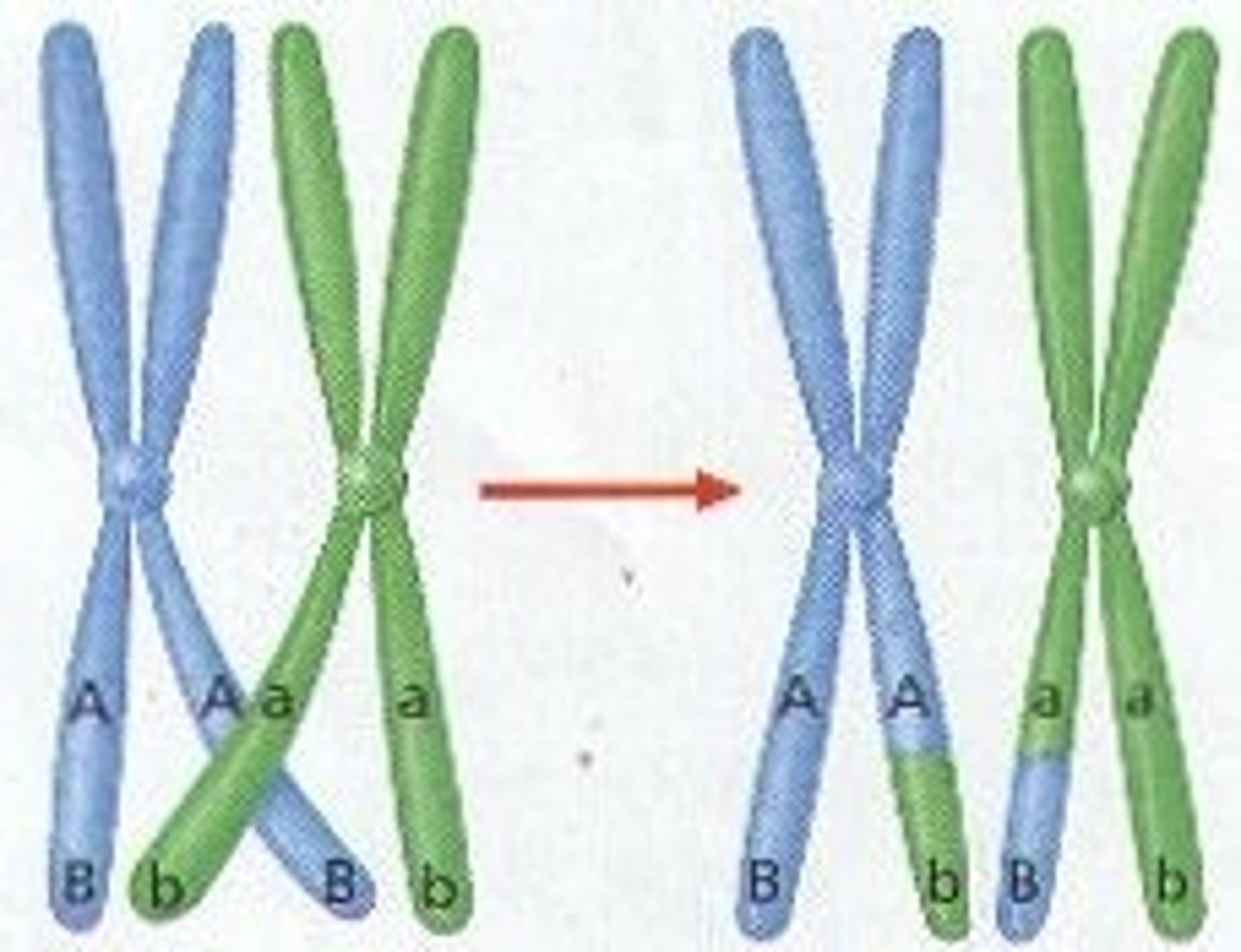
crossing over
exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis, results in more variability
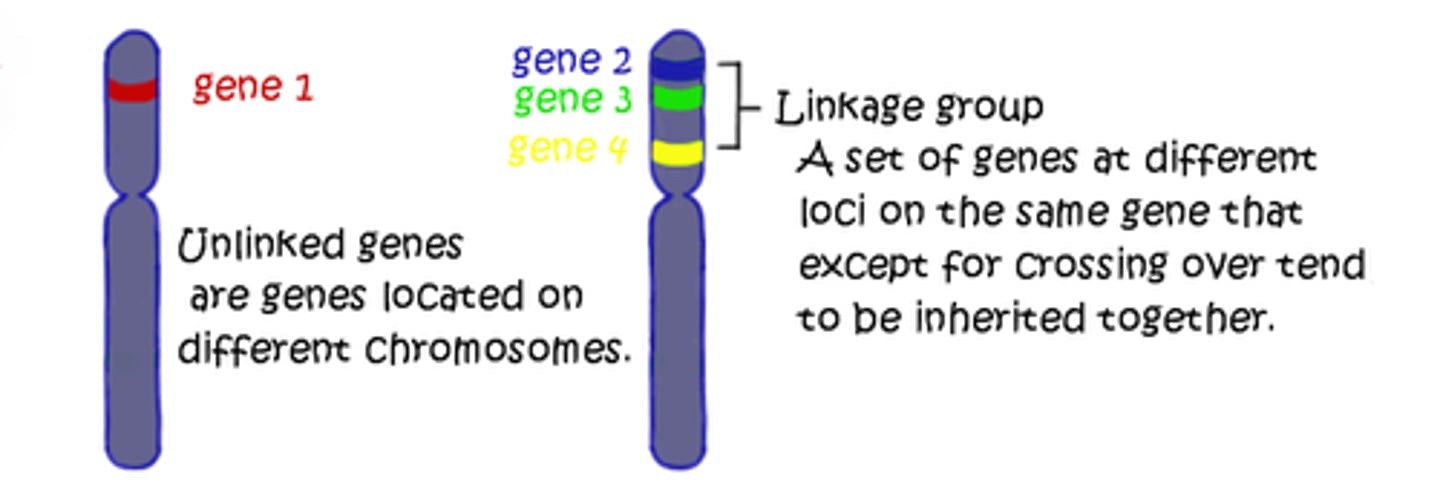
gene linkage
the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction
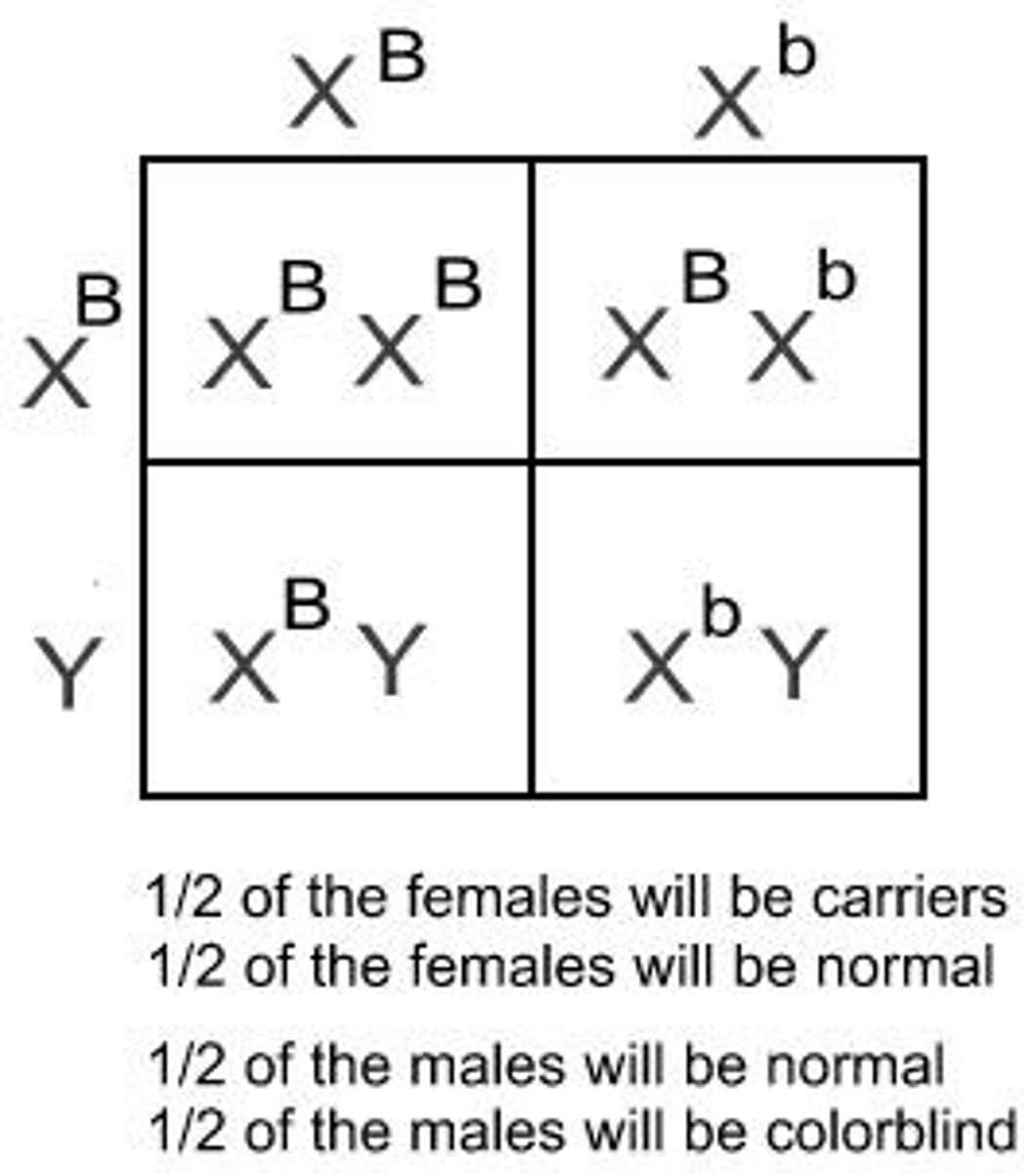
Sex Linked Traits
Traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes, color-blindness is an example in humans
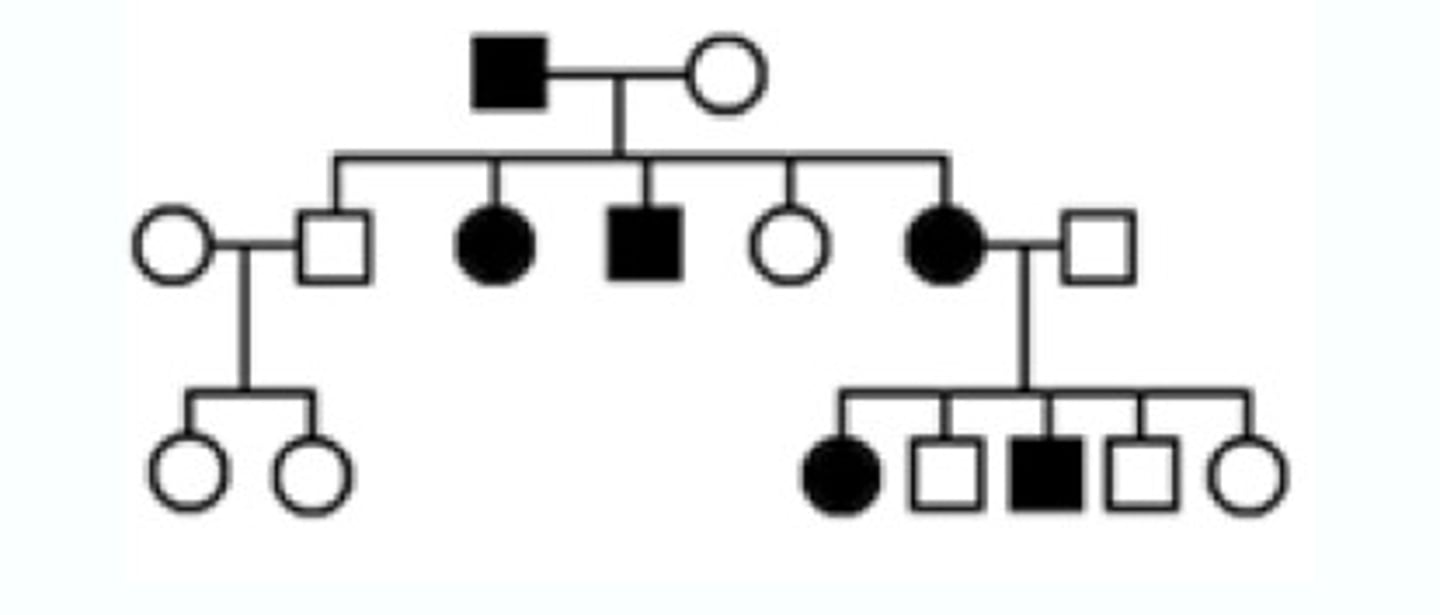
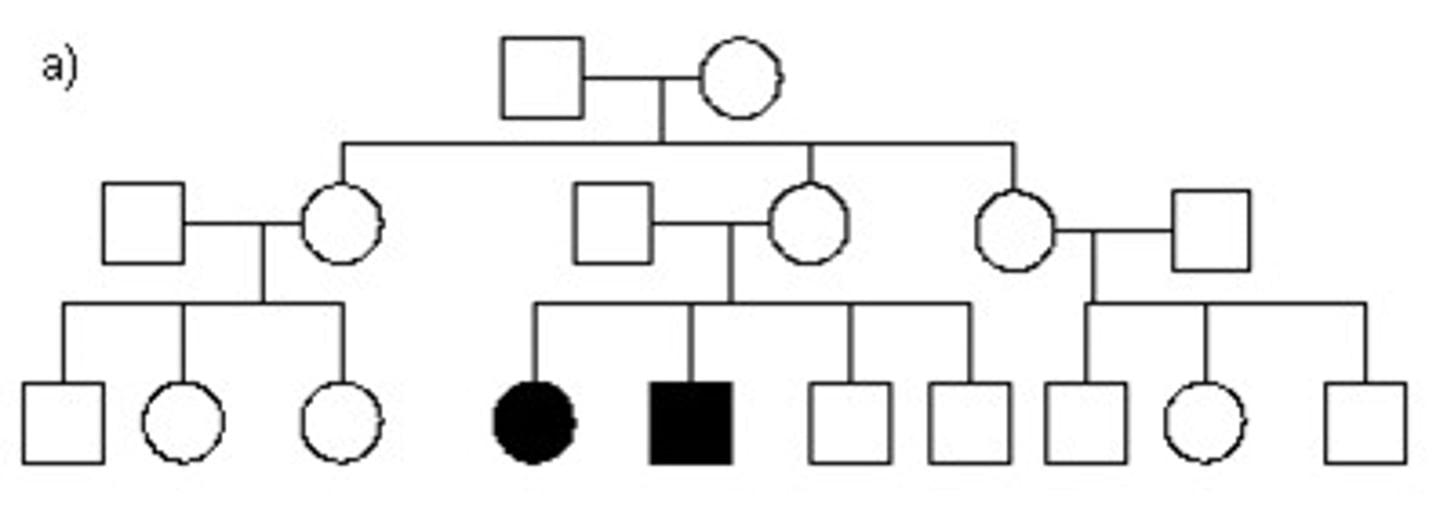
Autosomal Recessive Pedigree
May skip a generation. If the child has it, the parents have to have it or be carriers for the trait.
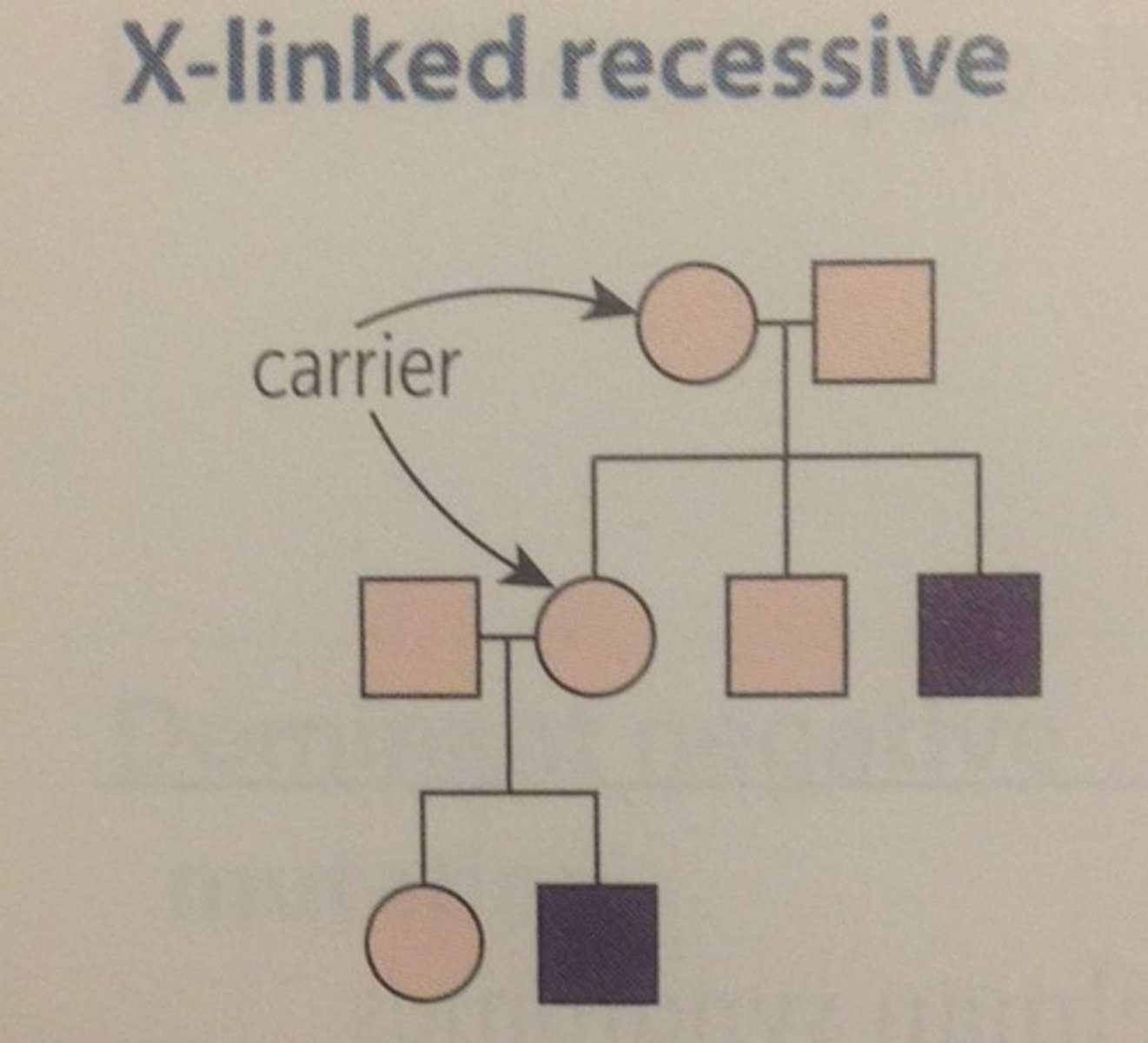
Pedigree: X-linked Recessive (sex-linked recessive)
Recessive gene is carried on the X chromosome
MORE MALES ARE AFFECTED
NO male-to-male transmission of trait
F: two copies of gene to express
M: one copy of gene to express
** CARRIERS -- Females w/only 1 copy of gene
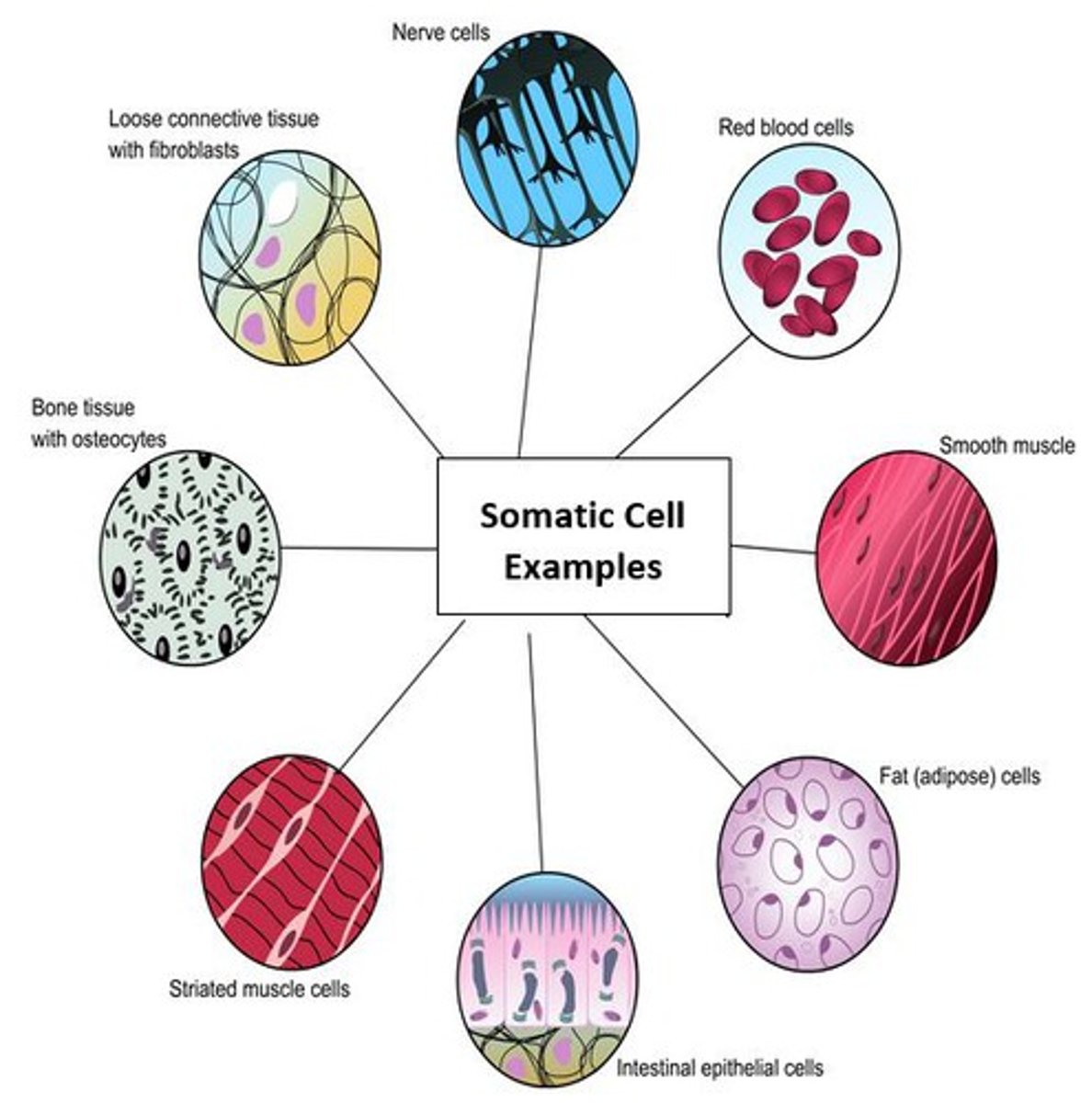
somatic cells
Any cells in the body other than reproductive cells, produced by mitosis
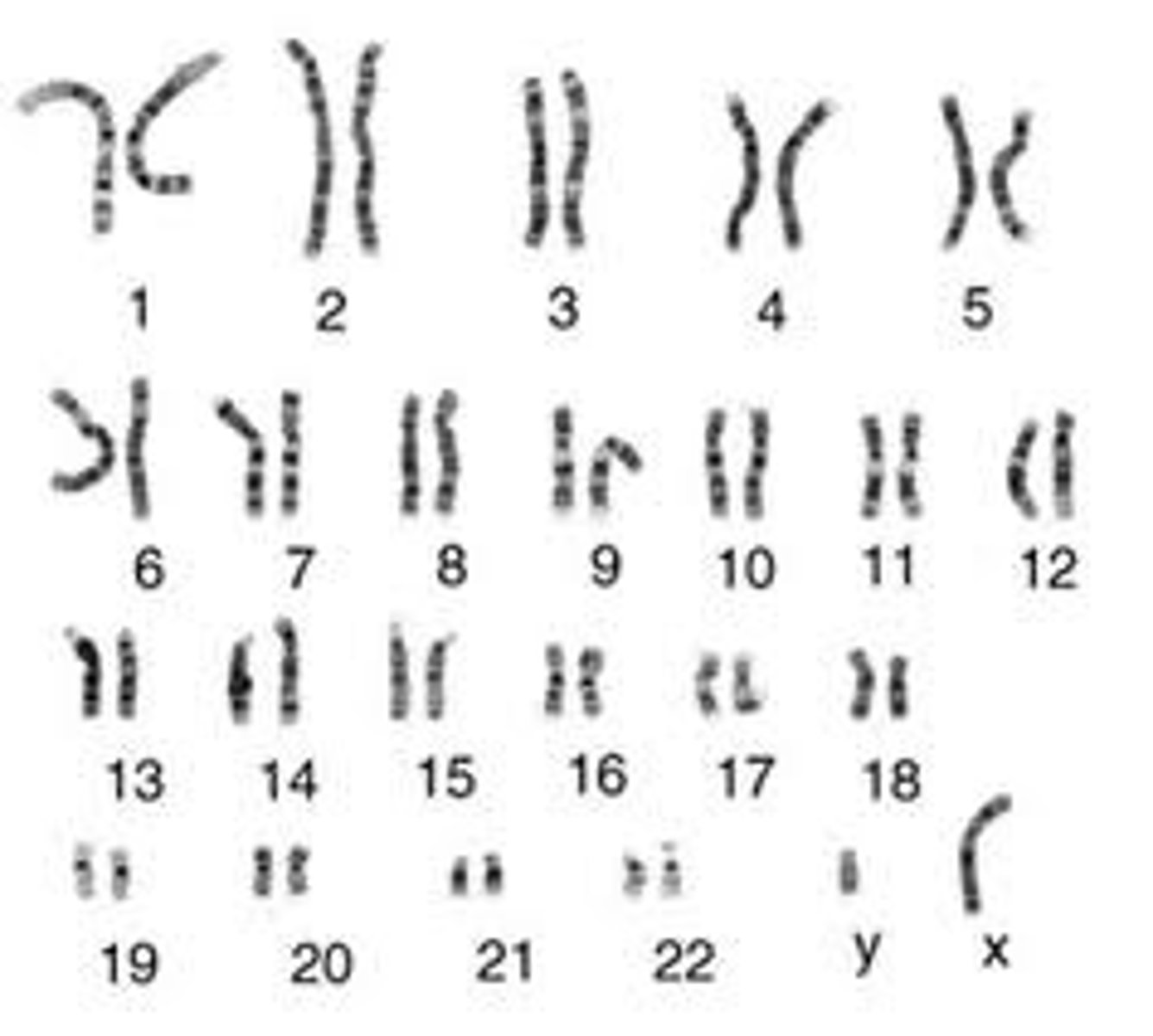
karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape. (XX = female XY= male)
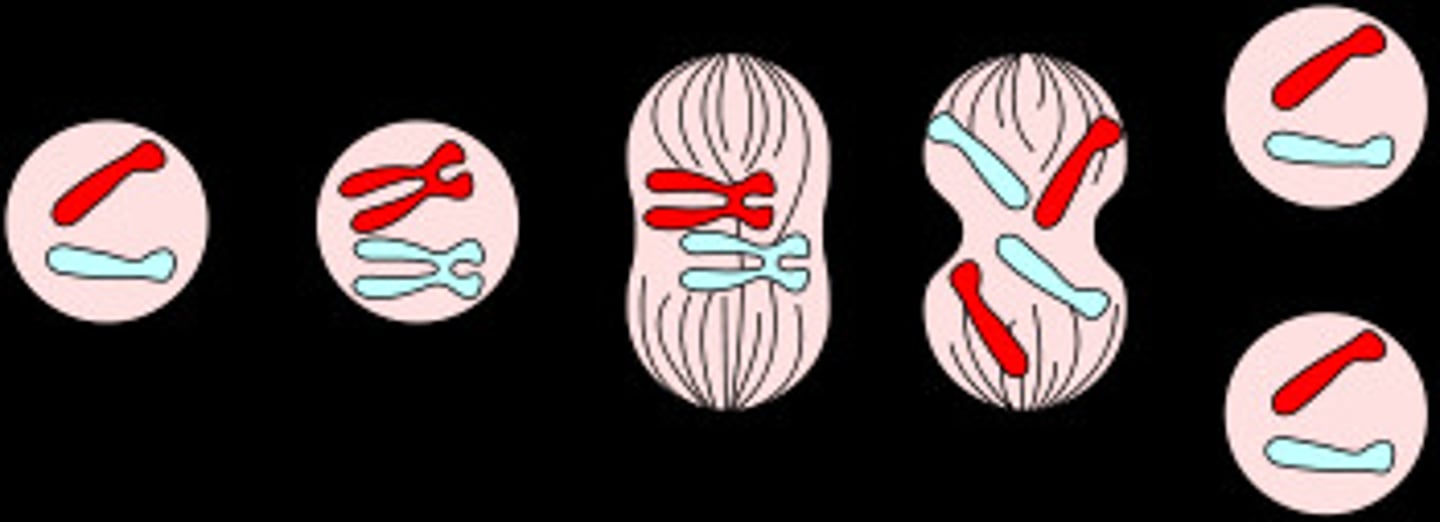
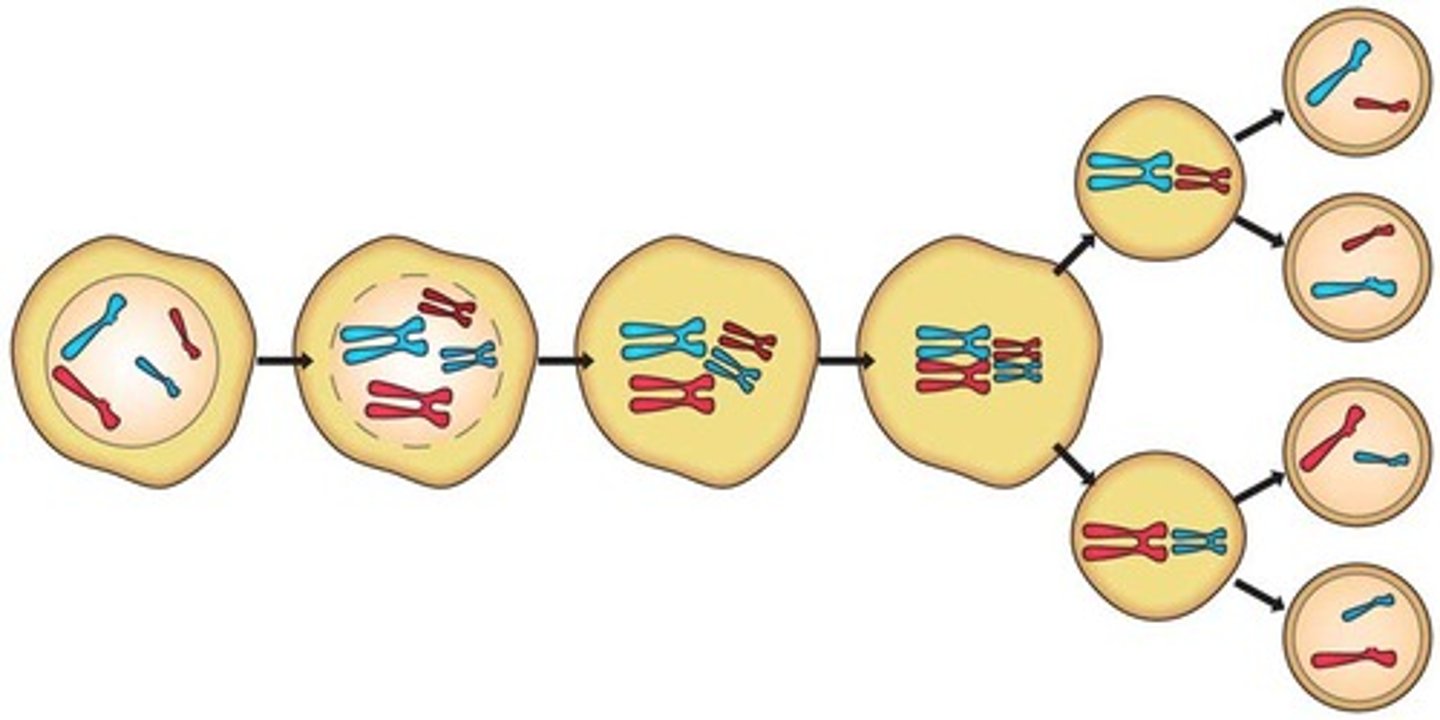
Meiosis
process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half to produce haploid gametes for sexual reproduction
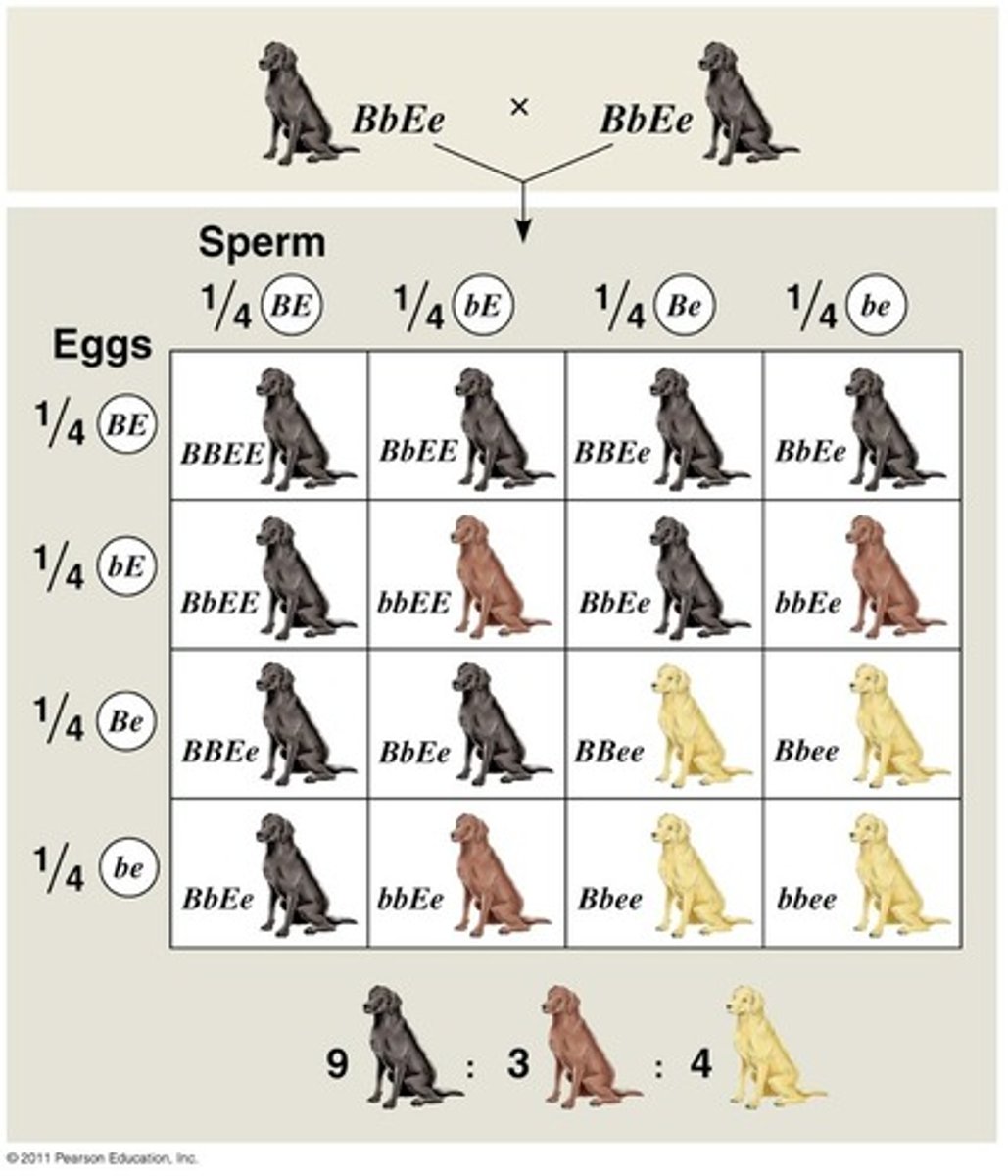
Hybrid
Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits

Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.
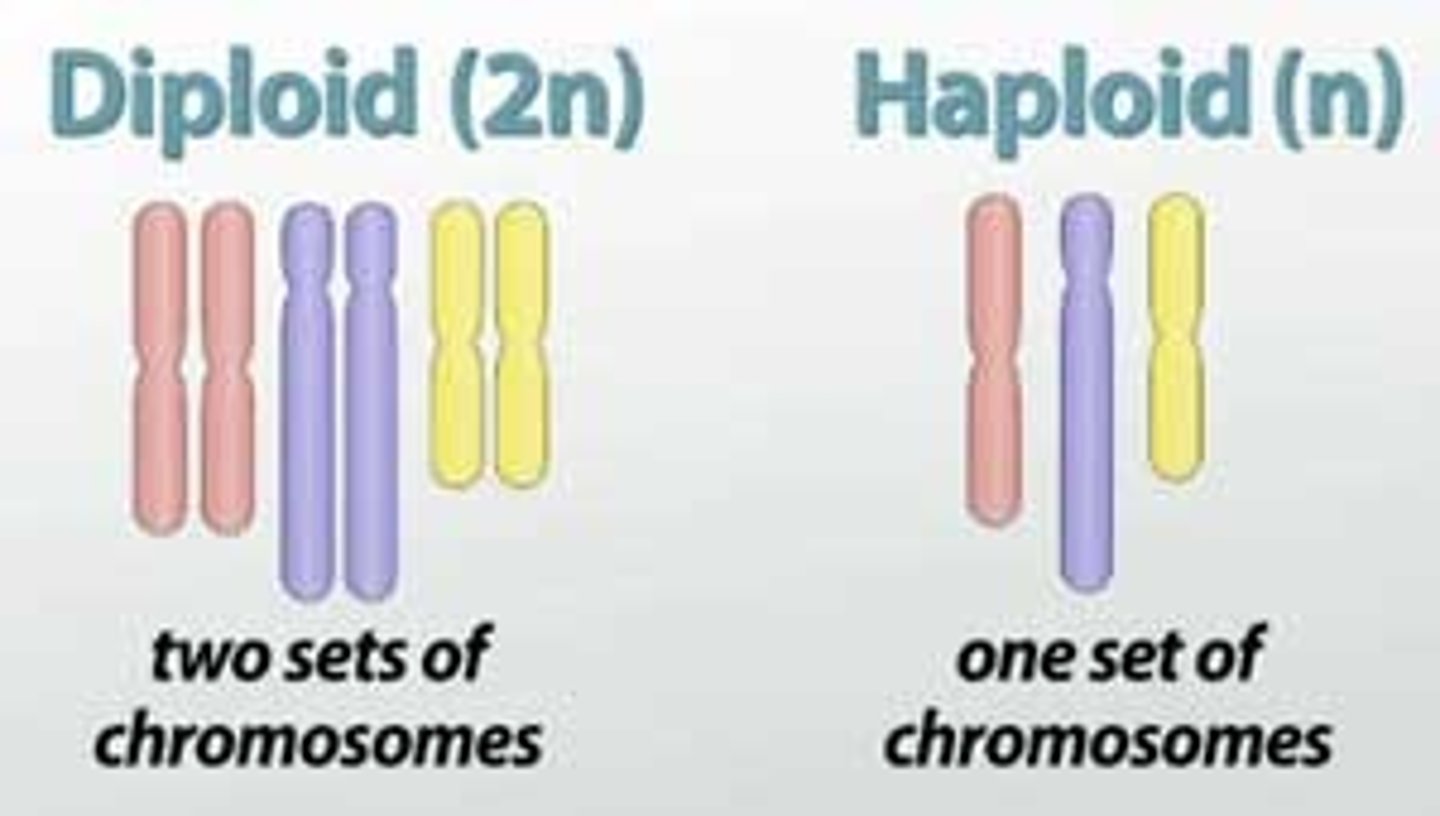
haploid (1n) cell
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes, gametes (sperm & egg)
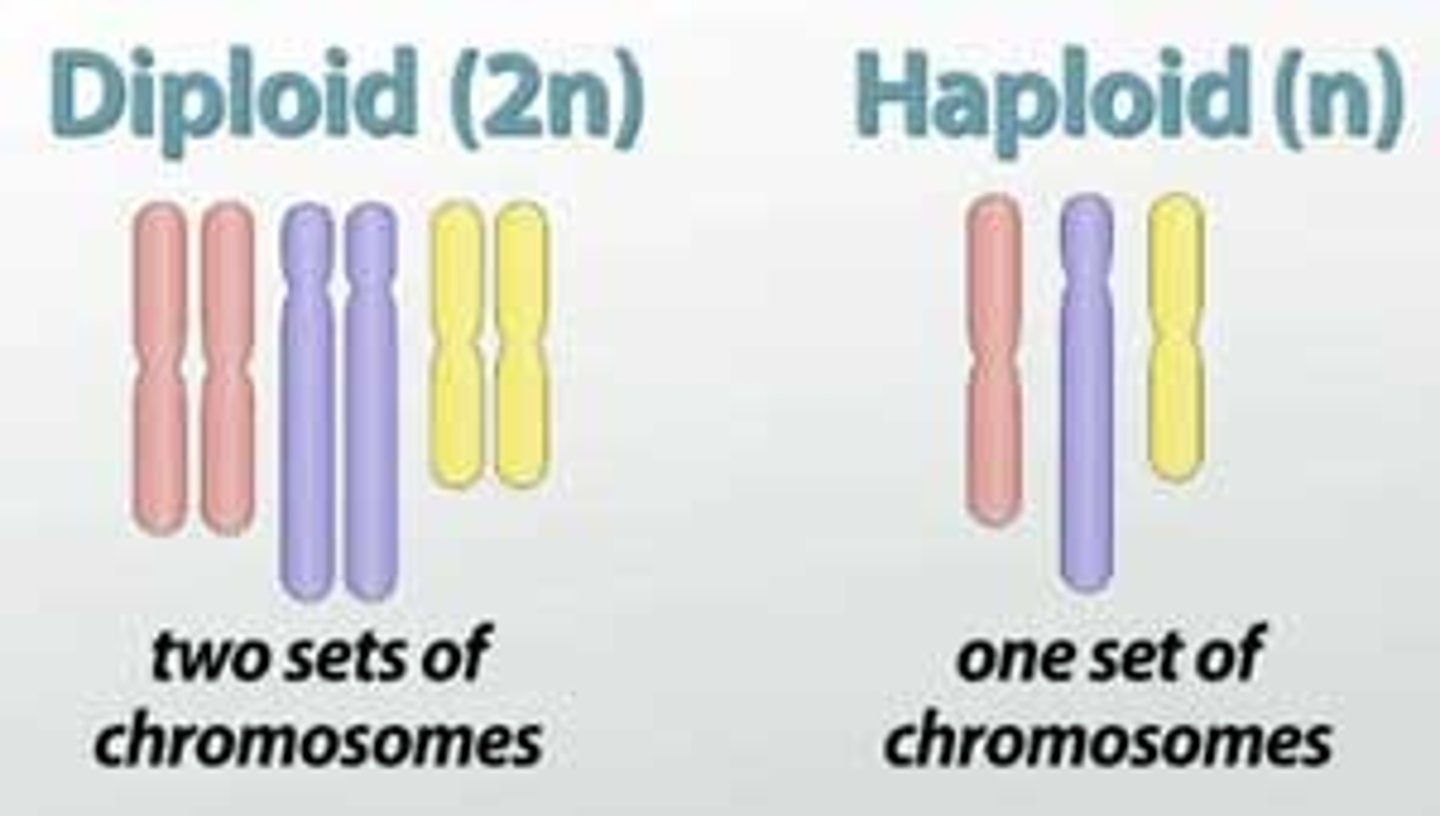
Diploid (2n)
two copies of each chromosome, # of chromosomes in body cells